CPAP therapy, or continuous positive airway pressure, is a continuous supply of air into a special mask attached to the face. This air flow stabilizes the soft structures of the pharynx, preventing them from closing. This prevents breathing pauses during sleep - obstructive apnea. But sometimes a situation may arise that you not only inhale this air pumped by the apparatus, but also partially swallow it. As a result, it enters the respiratory tract, the esophagus, and then the stomach, causing an unpleasant side effect - aerophagia.
Reasons contributing to the appearance of aerophagia
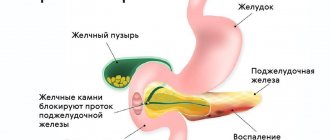
Aerophagia, which occurs after a large amount of food eaten at a fast pace, is usually called accidental and is considered a normal physiological phenomenon, since the swallowing of air and saliva is a natural process. But in other cases, it is most often a signal sent by the body that it has problems. These include: mental problems, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (irritable bowel syndrome, gastritis, ulcers, etc.), gall bladder, as well as changes associated with hormonal levels and pregnancy. Other reasons include:
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx;
- smoking abuse, excessive consumption of carbonated drinks and chewing gum;
- incorrectly selected dentures, diseases of the oral cavity and teeth.
These reasons are mainly associated with the ingestion of excess saliva and, accordingly, air.
Aerophagia in infants is a fairly common phenomenon that occurs as a result of swallowing air when crying and while eating. This can be caused by improper attachment to the breast, inappropriate nipple size, amount of milk and its flow to the breast in a nursing mother.
General information
Aerophagia is a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract without visible morphological changes, which manifests itself in the form of systematic repeated swallowing of large volumes of air during meals or outside meals, followed by regurgitation ( regurgitation ).
Aerophagia can be natural (physiological) - resulting from the involuntary ingestion of a mixture of gases from the surrounding atmospheric environment during drowning, poor swimming skills, during breastfeeding of small children, as well as pathological, caused by psychogenic disorders. They cause organ neurosis of the stomach . This is due to the fact that the functioning of the digestive system is closely related to the mental state of a person. One of the sections IV of the Rome Criteria, adopted in 2014 at a consensus conference in Rome entitled “Biopsychosocial model of functional digestive disorders,” demonstrated that there is a connection between the development of functional disorders and the influence of genetic factors, the environment, psychoneurological disorders and changes in physiology Gastrointestinal tract.
Aerophagia: symptoms
Number one is burping. It is usually odorless and can be present not only after meals, but also constantly (with a break during sleep). Other signs include: bloating and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, flatulence. A significant increase in the amount of air in the stomach contributes to pain in the chest and in the heart area, which is often confused with a heart attack. Manifestations of difficulty breathing and tachycardia are also possible.
In newborns, gastric aerophagia manifests itself with striking symptoms - they regurgitate after feeding, colic is observed, the stomach swells, to which babies react with loud crying, after the release of gases they calm down. These phenomena in an infant usually go away up to six months and are functional. If it has not ended by this time, you need to contact your pediatrician to prevent more serious illnesses.
Working pressure too high
Pressure for the treatment of obstructive apnea is selected strictly individually. The principle “the more the merrier” does not work here. The force of the air flow should be directed solely to maintaining the airways open. If the pressure is higher than necessary, the patient receives too much air, and the excess simply has nowhere to go except into the esophagus and then into the stomach. However, this is more likely to happen with a device that uses a fixed amount of air flow - non-automatic CPAP or BIPAP.
Solution.
If you feel that the machine is pumping air at too high a pressure for you, discuss the problem with your doctor. You cannot change the pressure up or down on your own. This may reduce the therapeutic effect.
It is also worth checking whether the device settings correspond to the doctor’s instructions. But even in this case, it is better not to act independently, but, for example, by enlisting the support of the supplier of your CPAP equipment.
Mouth breathing (using a nasal mask or nasal prongs)
Breathing through the mouth or sleeping with the mouth open are common causes of air leaks, which cause insufficient therapeutic pressure in the upper respiratory tract. As a result, not all episodes of apnea are eliminated; there is arousal from lack of air and too rapid convulsive inhalation, directing the air flow not only through the respiratory tract into the lungs, but also through the esophagus into the stomach.
Solution.
Make sure the mask fits you perfectly in both type and size. Proper sizing is important to minimize the risk of leaks. When purchasing a mask, ask a consultant to help with the choice, and also clarify how to properly adjust the tension straps for a correct and tight fit of the mask contour to the surface of the face. You can also additionally use special additional devices (for example, elastic bandages) to keep the mouth closed. If significant air leaks through the mouth still persist, then you should consider purchasing an oronasal mask model.
Nasal congestion
With a stuffy nose, we are forced to breathe through our mouths. An unusual breathing pattern coupled with the operation of the CPAP device can lead to swallowing air. Once again we are dealing not only with aerophagia and bloating, but also with oral leakage. This means that the therapeutic pressure is insufficient, and the effectiveness of therapy decreases.
Solution.
If your runny nose and nasal congestion are caused by a respiratory infection, use vasoconstrictor drops or sprays for several days before going to bed. If the cause of swelling of the nasal mucosa is allergies, then you should consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary antiallergic drugs. In addition, you can further adjust the humidifier settings so that the incoming air flow is more humid and warm.
Problems with overcoming air resistance when exhaling
Patients who are prescribed high therapeutic pressures usually experience a feeling of difficulty in exhaling. It is very easy for them to inhale, because the CPAP machine itself helps with this. But it can be difficult to breathe out. At the same time, pronounced resistance to air flow can even cause panic and a feeling of suffocation if you are unaccustomed to it. This disrupts the natural rhythm of breathing, which, among other things, provokes hyperventilation and rapid swallowing of air.
Solution.
If aerophagia develops due to resistance to airflow when exhaling, you may be able to help:
- expiratory pressure release function (most modern CPAP machines have this option);
- using an Auto-CPAP machine (however, the vast majority of devices presented on the domestic market are automatic by default);
- switching to a BIPAP machine (a last resort, which in this case is almost never required).
All the proposed options allow you to reduce the exhalation pressure and prevent the swallowing of air. However, in each case this happens differently and you may not be able to cope with this problem on your own.
Swallowing air complicates the treatment of sleep apnea. Therefore, if you are faced with aerophagia, do not put off visiting your doctor for too long. Perhaps the specialist will select a different mask for you, adjust the pressure level, or suggest switching to a two-level BPAP device. In addition, additional medications may be prescribed to relieve symptoms of impaired nasal breathing.
Diagnosis of the disease
Gases in a healthy person are usually expelled by belching, emitted through the rectum, diffusion into the blood, and released in the air that is exhaled. Therefore, first of all, the doctor studies and analyzes the medical history taking into account the patient’s complaints. Particular attention is paid to the characteristic features of belching - with aerophagia, the patient pulls his head forward, pressing his chin to his chest, while making empty swallowing movements. There may also be a high or medium pitch sound under the left rib when tapping, which indicates the presence of air accumulation there. But a more accurate picture is provided by an x-ray, with which you can see a gas bubble in the stomach, as well as a displacement of the contour of the diaphragm above its normal position. To determine the cause of aerophagia, other research methods are used:
- electrocardiogram;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- research within the competence of a psychiatrist or neurologist.
Epiphrenic diverticula
Epiphrenic diverticula, usually pulsational, are located along the posterior or right wall of the esophagus 2-11 cm above the diaphragm. Diverticula are spherical or mushroom-shaped. The leading factors in the formation of epiphrenic diverticula are the following factors: weakness of the muscular wall, increased intra-esophageal pressure and pressure of the food bolus on weak areas of the esophageal wall. Muscular weakness can be congenital or acquired. An increase in intra-esophageal pressure occurs due to uncoordinated peristalsis of the esophagus and its lower sphincter.
Treatment of aerophagia
To successfully treat a disease, it is necessary to start with eliminating the root causes that provoked it. If they are associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, then this is the responsibility of a gastroenterologist who will treat based on his protocols. In the case of a neurological origin of the disease, psychotherapy and sedatives are used. Treatment of a disease caused by poor nutrition involves following a diet and eliminating all bad habits.
But drugs for aerophagia are also used, which facilitate its course under any conditions. For example, it could be activated carbon, which alleviates the symptoms of the disease due to its adsorption properties. It helps remove excess air trapped with food and also has a moderate disinfectant effect. Probiotics will help restore the necessary microflora, which also promotes recovery. The doctor may also prescribe antacids, aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate, proton pump inhibitors, defoamers, anxiolytics and other medications used for aerophagia.
During treatment it is also recommended:
- thorough chewing of food and a calm atmosphere at the table;
- eating in a timely manner, eliminating spicy foods from the diet and reducing fatty foods;
- fractional meals;
- using sage, dill, rosemary, thyme as seasonings;
- instead of coffee and tea, use herbal infusions that improve digestion (chamomile, mint, anise, fennel);
- excluding stressful situations from life if possible.
Prevention and prognosis
You can avoid the development of the disorder with the help of simple preventive recommendations:
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- providing the baby with the correct position for feeding;
- avoiding the influence of stressful situations;
- compliance with the rules of food hygiene - leisurely consumption of food, thorough chewing of food, etc.;
- complete treatment of any disease;
- Regularly undergoing a complete preventive examination.
Symptoms and treatment of aerophagia affect the prognosis of the disease. In most situations, the outcome is favorable, but only with complex therapy. Complications develop extremely rarely.
Popular questions about aerophagia
Why is aerophagia dangerous?
The main danger is that as a result of aerophagia, the muscle (cardia), which is located between the esophagus and the stomach, can weaken, which in turn causes the development of reflux esophagitis. In infants, aerophagia can lead to weight loss and, consequently, abnormal development.
How long does it take to treat aerophagia?
Changing your eating habits can speed up the healing process. But the treatment time depends on the degree of neglect of the disease that caused aerophagia.
Which doctor treats aerophagia?
The treatment of this disease is mainly carried out by a gastroenterologist, but you may need the help of a psychiatrist if it arose from a nervous system.
Classification
Depending on the cause of occurrence, there are somatic, behavioral - caused by nutritional errors, and psychogenic forms of aerophagia - developed as a result of neurotic disorders.
Neurotic aerophagia
The pathology was assigned a code according to ICD-10 - F 45.3, it is designated as somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, a psychogenic form of aerophagia.
The neurotic form of aerophagia is one of the clinical manifestations of neuroses. These also include IV Rome criteria: anorexia , regurgitation , gastralgia , aerophagic tics , psychogenic nausea and vomiting , diarrhea , halitosis , dysgeusia , glossodynia , intestinal crises , etc. These syndromes are the main symptoms of “gastric neurosis”.