A separate disease called “ lack of air”
" does not exist. A feeling of shortness of breath is a symptom, a sign of a painful condition.
As stated above, there are two groups of reasons for this symptom:
1. Internal diseases: pathology of the heart, lungs, blood diseases, obesity, oncology, infections, injuries, etc.
2. Nervous and mental disorders:
- consequences of stress,
- prolonged or intense overload,
- neuroses,
- neurasthenia,
- panic attacks and other anxiety disorders,
- depression,
- consequences of organic damage to the nervous system,
- psychosomatic and somatoform diseases.
Statistics say that the vast majority of cases of feeling short of air when inhaling is a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
The mechanism for triggering this symptom is associated with the development of anxiety, overexcitation of the midline structures of the brain, excessive activation of autonomic centers, and the predominance of excitation processes over inhibition processes in neurons.
The feeling of shortness of breath may be accompanied by other symptoms:
- feeling of heartbeat,
- dry mouth or excessive sweating,
- feeling of heaviness in the chest or stomach,
- discomfort in the head and neck,
- internal trembling
- insomnia,
- loss of appetite,
- gastrointestinal disorders (diarrhea, constipation),
- fear of death.
Previously, doctors called such conditions VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia), but in our time this term has ceased to be used.
Types of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
During significant physical exertion, the body does not have enough oxygen, so usually in such cases the breathing rate increases. This is the so-called physiological shortness of breath
. However, if shortness of breath occurs with light exertion or at rest (for example, in a lying position), then its nature is pathological.
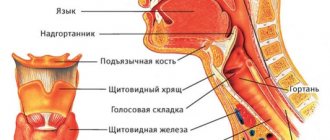
It is of great importance which stage of breathing causes difficulty - inhalation or exhalation. Shortness of breath that occurs during inspiration is called inspiratory dyspnea
, on exhalation -
expiratory shortness of breath
. Mixed shortness of breath is also common, in which both inhalation and exhalation are difficult.
Causes of central sleep apnea
With central sleep apnea syndrome, disturbances leading to respiratory arrests do not occur at the level of the respiratory tract, but in the respiratory center of the brain. It is his disorders that cause pauses in breathing in patients during sleep.
There are many reasons for SCAS. Respiratory arrest can occur in people taking opioid drugs (morphine, heroin, methadone), and apnea is also detected in people with severe forms of kidney and heart failure. Similar problems can occur in healthy people who find themselves in high altitudes. Very rarely, central apnea occurs in patients receiving CPAP therapy for obstructive sleep apnea. It is not known what causes the development of apnea in such patients, but it has been established that this phenomenon in people on CPAP therapy is temporary.
Causes of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is caused by various reasons. The most common causes of shortness of breath are:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system
. Cardiovascular pathologies lead to insufficient blood circulation. The organs do not receive the required amount of oxygen, and carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood. The body reacts to this condition by breathing faster - more air is pumped through the lungs per unit of time. Shortness of breath due to cardiac pathology occurs or worsens after physical exertion or while lying down. In a sitting or semi-sitting position, shortness of breath goes away. This type of shortness of breath is characterized by difficulty breathing; - pathologies of the respiratory system
. Shortness of breath may be caused by obstructions to the passage of air through the respiratory tract, for example, by narrowing of the lumens of the bronchi. Therefore, shortness of breath is a typical symptom of bronchial asthma. In this case, exhalation is difficult. Shortness of breath can also be caused by a decrease in the respiratory surface of the lung tissue. As a result of such a decrease, in order to maintain the required amount of oxygen entering the blood, more intensive work of the lungs is required, that is, more frequent inhalation. The list of diseases of the respiratory system in which shortness of breath may occur is extensive and includes such dangerous pathologies as tumors, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and others; - anemia
. A lack of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and hemoglobin leads to the fact that even with normal functioning of the heart and lungs, the blood is not able to provide the organs with the necessary amount of oxygen, and the body tries to compensate for this by increasing the breathing rate; - neuroses and panic attacks
. In this case, a clinical examination does not reveal pathologies of the heart and lungs, but subjectively the patient experiences a lack of air, and psycho-emotional changes lead to increased breathing. - Obesity and diabetes also often lead to shortness of breath.
Lack of air with VSD
One of the common manifestations of VSD is a feeling of lack of air or hyperventilation of the lungs. At the same time, you may feel a “lump in your throat,” increased breathing, and you experience a feeling of lack of oxygen. It is actually a condition in which there is not enough carbon dioxide in the blood. The body begins to give a command to slow down your breathing, and if you are prone to anxiety, you instinctively begin to breathe more often.
Along with the lack of air, accompanying symptoms may appear - rapid heartbeat, ringing in the ears, tingling in the limbs.
Attacks are especially active during stressful conditions.
Treatment of shortness of breath
Treatment of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is not an independent disease, but a symptom indicating a malfunction of certain organs. To make it easier to diagnose the disease, before visiting a doctor, try to answer the following questions:
- When did you notice that shortness of breath appeared?
- Does shortness of breath always occur after physical exertion, or does it bother you even at rest?
- What is more difficult - inhaling or exhaling?
- In what position does it become easier to breathe?
- What other symptoms bother you? This may include chest pain, swelling, weakness, dizziness, cough, and fever.
Other diseases affecting breathing
Shortness of breath can occur as a result of any violation of the integrity of the chest, which occurs, in particular, as a result of injury. Very often, patients experience difficulty breathing after a rib fracture. The pain that occurs as a result of the injury does not allow a person to breathe fully, causing him to feel short of air. Shortness of breath can also occur due to contact with allergens, or when a person has a disease such as diabetes.
Even if a person knows about his illness, if shortness of breath occurs, he needs to consult a doctor who will conduct a full examination and draw up a series of procedures to alleviate the patient’s condition.
What to do if it becomes difficult to breathe
Shortness of breath in people of different age categories
Shortness of breath can occur in people of all ages, from infants to the elderly.
In children, shortness of breath can be both physiological and pathological. The appearance of physiological shortness of breath is caused by physical exertion or high anxiety, which is considered normal. When the respiratory system is immature, pathological shortness of breath occurs in the infant. How to determine the type of shortness of breath and its causes is decided by the pediatrician, selecting the necessary diagnostic methods.
In old age, people's tolerance to physical activity decreases and the efficiency of the respiratory system decreases. Due to age-related changes, the physical strength of the respiratory muscles decreases, as a result of which gas exchange worsens and normal breathing becomes difficult. In addition, older people tend to have diseases of the cardiovascular system and lungs, which lead to shortness of breath. Most often, they do not pay attention to this symptom for a long time, so the diseases that accompany it are diagnosed at advanced stages. As a result, treatment becomes more difficult, the quality of life and its duration are significantly reduced. So it is better to immediately seek medical help if shortness of breath occurs in older people, without waiting for the condition to worsen.
The best pulmonologists in Moscow - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Alexander Vyacheslavovich Averyanov, Candidate of Medical Sciences Alexander Evgenievich Shuganov are receiving appointments at the therapy center of the Yusupov Hospital. Klina is equipped with innovative high-tech equipment for conducting the most modern diagnostic studies. Thanks to an integrated approach involving specialized specialists in various fields, our doctors identify the exact cause of shortness of breath and select an effective treatment regimen, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
What is shortness of breath in humans: symptoms
The occurrence of shortness of breath in the initial stages of damage to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is associated with physical exertion (for example, when the patient climbs up the stairs). As the pathology progresses, shortness of breath and fatigue appear even with a slight load (walking on a flat surface, tying shoelaces, etc.), as well as at rest.
Patients perceive shortness of breath quite subjectively. It may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing (inhalation/exhalation);
- compression in the chest;
- feeling of congestion in the chest area;
- tightness in the chest;
- feeling of lack of air;
- inability to take a deep breath or exhale completely;
- suffocation.
Unable to take a full breath - causes, treatment
Respiratory disorders (dissatisfaction with breathing, deep breaths, lack of air) can be of a psychogenic nature, for example, they arise against the background of a disturbance in the emotional state, anxiety, severe stress, depression, and sometimes against the background of childhood negative impressions. In this case, there is no serious organic disease, but there is a mental nature of the disorders. To solve the problem, of course, it is better to contact a specialist. First, see a pulmonologist to find out the nature of incomplete inspiration, and then a consultation with a psychologist and neurologist would not hurt. In the case of a psychogenic nature, the following set of measures will help solve the problem - breathing exercises, self-hypnosis, hypnosis, treatment of neurosis by a neurologist. When symptoms suddenly appear, fresh (street air) helps a lot. In medicine, attacks of inhalation dissatisfaction that appear as a result of stress or nervous disorders are also considered the equivalent of a panic attack.
Now let's look at other reasons and diseases that make it impossible to take a full breath.
1) One of the most common causes of this symptom is vegetative-vascular dystonia. In this case, it is recommended to get rid of a bad habit - smoking, walk more in the fresh air, try to avoid stress, and then the manifestation of incomplete inspiration can be minimized.
2) Malignant formation in the lungs (cancer). Every year, all Russians are required to undergo a fluorographic examination of the lungs; this is necessary in order to detect lung cancer and tuberculosis in the early stages. Therefore, you should not neglect passing this important examination.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Long-term sleep disturbance in the form of insomnia and effective methods of treatment
3) Problem with the spine. The whole point may be excessive muscle tension in the cervicothoracic region. In this case, a consultation with a neurologist and a massage course are necessary.
In any case, a doctor will help you correctly understand the problem; first consult a therapist, and then, if necessary, he will refer you to a specialist.
Sleep apnea in a child
Apnea is especially dangerous in children under one year of age, which is due to the imperfection of their respiratory system. If a child suffocates during sleep, this may be due to the following reasons:
- insufficient formation of respiratory centers (in premature infants);
- birth injuries;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- infections;
- anomalies in the structure of ENT organs;
- adenoids or chronic tonsillitis;
- allergic reactions to microorganisms living in pillows and bedding (the most common cause in adolescents);
- asthma;
- bronchospasm;
- runny nose;
- dry air in the room.
Shortness of breath: diagnosis
Diagnosis of the underlying pathology that provoked shortness of breath is carried out using the following research methods:
- general examination (general medical examination, counting the frequency of respiratory movements of the chest, listening to the lungs with a phonendoscope);
- general blood test;
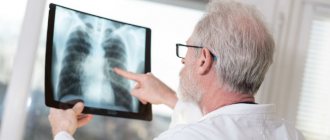
- chest radiography;
- computed tomography of the chest;
- spirometry (spirography) – to assess air flow through the respiratory tract and the ability of the lungs to expand;
- tests using a bronchodilator - spirometry is performed before and after inhalation with a bronchodilator drug. This study allows us to evaluate the reversibility of bronchial narrowing;
- bronchoprovocation test - spirometry is performed before and after inhalation of histamine and methacholine. It is carried out to detect increased sensitivity of the bronchi, which causes bronchospasms;
- studies of the gas composition of the blood (the level of tension in the blood of carbon dioxide, oxygen is determined, the saturation of the blood with oxygen is assessed);
- body plethysmography – allows you to evaluate the function of external respiration. It is used to assess all volumes and capacities of the lungs, incl. those that spirography cannot determine;
- electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart, echocardiography) - allows you to assess the functional state of the heart and pressure in the pulmonary artery system;
- fiberoptic bronchoscopy is a study that is used to examine the mucous membrane of the bronchi from the inside and study its cellular composition with a special preparation. The use of this method is advisable for patients with an unclear diagnosis. Allows you to exclude other possible diseases with similar symptoms;
- angiopulmonography – during the procedure the blood vessels of the lungs are examined;
- lung biopsy;
- consultations with a pulmonologist, cardiologist.