Biliary dyskinesia: what is hidden behind this diagnosis?
Abdominal pain, nausea, constipation are the most common symptoms of biliary dyskinesia. We asked Yulia Anatolyevna Saltymakova, a gastroenterologist at the Expert Clinic Tula, to tell us why this disorder occurs and how it can be overcome.
— Yulia Anatolyevna, what is biliary dyskinesia?
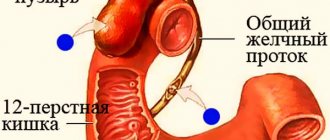
— This is a disruption of the functioning of the entire biliary system, and especially the gallbladder. This refers to both hypermotor disorders, i.e. excessive contraction of the gallbladder, and hypomotor disorders - insufficient (weak) contractility of the organ. This disease occurs in both adults and children.
— What are the causes of biliary dyskinesia?
- There are many reasons. The most common is, of course, a nutritional disorder. If we talk about small children (I mean up to three years old), then it can be difficult to feed them. Therefore, quite often parents and grandparents begin to act on the principle: let him eat at least something. And this, as a rule, is something sweet and tasty, that is, fast carbohydrates: juices, buns, sweets, pancakes or sausages. Children love these foods; they are easy to feed. But, unfortunately, this almost always leads to very unfavorable consequences.
If you take older children, their diet often changes when school, sections, and clubs appear. Between extracurricular activities and school, the child may have a quick dry snack and comes home late. And it turns out that he can eat a full meal only after 7 pm. Naturally, his hunger increases during the day, and heavy late meals have a very negative impact, primarily on the functioning of the gallbladder.
It's the same for adults. They say: “We are so busy that we can’t eat properly, so we eat twice a day – at lunch and then at night.” This is where the problems begin.
In addition, the nervous system is closely related to the digestive system. Increased emotional overload, some stressful situations in the family, school - all this negatively affects the functioning of the entire digestive system, and the gallbladder is most susceptible to such factors.
Its functioning is also strongly influenced by the functioning of the intestines. Sometimes constipation and infrequent bowel movements (once every two to three days) can affect the functioning of the gallbladder and cause biliary dyskinesia.
In children, almost all gallbladder diseases (in 99% of cases) are secondary. That is, they are associated, for example, with inflammation in the small intestine, more often in the duodenum. Reactive changes in the pancreas always affect the functioning of the gallbladder, due to the anatomical proximity of their ducts. Therefore, the doctor always strives to get to the bottom of the true cause of the dysfunction of the biliary tract.
The diagnosis of “biliary dyskinesia” may hide diseases of other organs, not just the gallbladder. Therefore, the diagnosis of abdominal pain often requires an extensive examination, which does not always cause understanding on the part of parents.
Read materials on the topic:
Is there a stress vaccine? Congestion again! What to do if your child is constipated? Constipation in adults: looking for causes and getting rid of it Pancreas: the one and only. How to keep her healthy?
— How does biliary dyskinesia manifest in children and adults?
— The main symptom in both children and adults is abdominal pain. Preschool children, if you ask them where it hurts, most often point to the navel, i.e., the peri-umbilical area. But a further examination of the child is required to determine whether the pain is really in the umbilical area or somewhere else. Because sometimes kidney diseases can manifest themselves as abdominal pain. It is better to contact a specialist, for example, a gastroenterologist.
In 80% of children, gallbladder dyskinesia occurs of the hypomotor type. Clinically, it is possible to distinguish between types of dyskinesias. Spastic, stabbing pain is more characteristic of hypertonicity of the gallbladder or sphincter of Oddi (a muscular valve located in the duodenal papilla of the duodenum). Aching, almost constant pain that occurs an hour after eating is characteristic of hypotension of the biliary tract.
In addition to pain, there is often nausea, irregular or loose stools, and changes in appetite (there may be either increased or decreased appetite).
Read materials on the topic:
Mom, my stomach hurts! What is hidden behind a child’s abdominal pain? An insidious pain-mask. Does abdominal pain always indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract?
— What could be the consequences if you ignore the symptoms of the disease?
— Let’s say the patient has insufficient (weak) contractility of the gallbladder. Accordingly, the separation of bile from the biliary tract will be impaired. That is, a certain stagnation of bile will form. When performing an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, we see that sediment or sometimes even sand appears in the gallbladder. This can lead to the development of chronic inflammation in the gallbladder itself or even the formation of stones. Sand, dense sediment is already the primary stage of cholelithiasis.
90% of chronic diseases in adults begin in childhood. The gallbladder is a “silent” organ, and in children it hurts extremely rarely. Ignoring any changes in the ultrasound of the abdominal organs means providing the child with chronic diseases of the digestive system in the future.
— What studies are prescribed to diagnose “biliary dyskinesia”?
— First of all, ultrasound of the abdominal organs. The function of the gallbladder can only be checked by cholecystography. The most affordable option is an ultrasound of the gallbladder with a test breakfast. In this case, an ultrasound of the gallbladder is done three times, and only then can one judge the types of dysfunction of the organ (hyper- or hypodysfunction). Changes in the volume of the gallbladder, its size, deformation (constrictions, kinks) and even sand, sludge syndrome (sediment in the gallbladder formed due to stagnation of bile) appear when there is a violation of the outflow of bile or liver diseases.
A general blood and urine test and coprogram are also prescribed. A coprogram is a stool analysis that can be used to judge which organ of the digestive system is most affected: the gallbladder, stomach or pancreas, and whether there are inflammatory changes in the large intestine.
— Yulia Anatolyevna, how is biliary dyskinesia treated?
— Treatment of biliary dyskinesia consists primarily of normalizing the diet. At the appointment, we discuss the diet with the patient in great detail: how often and at what time to eat, what foods are best excluded from the diet. Treatment of dyskinesia begins with the simplest drug therapy. It could be mineral waters or some kind of herbal infusion. Well, and, as a rule, choleretic drugs and enzymes that improve the functioning of the gallbladder, its contractility, and sometimes even improve appetite in children who are difficult to feed.
Of course, the treatment plan is always developed individually, taking into account all the nuances of the disease and contraindications. For example, choleretic drugs cannot be used for acute inflammatory changes in the biliary system (including cholecystitis), reactive hepatitis, ulcerative and erosive diseases of the upper digestive tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum). Therefore, any treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, preferably a gastroenterologist.
— How should you eat if you have biliary dyskinesia?
— The biggest impact on the functioning of the gallbladder is the excess of carbohydrate foods, preservatives, and dyes in our food products. Therefore, we always emphasize that the more natural the food, the better. Chocolate, sweets, juices, and baked goods, which are loved by both small children and teenagers, should be limited. There must be parental control.
You can always find an opportunity to normalize nutrition – both yours and your child’s. If, for example, the children are very busy, you can collect some small plastic containers for school, or take them with you when you take your child to classes or clubs. Everything can be adjusted and the problem can be gradually dealt with.
— How to prevent the development of biliary dyskinesia? Have measures to prevent this pathology been developed?
- Yes. I would like to say that first of all, this is, of course, proper nutrition, but proper sleep and rest are no less important. In some families, depending on the work schedule of their parents, school-aged children start studying late, go to bed late, and get up early for school. And the child’s body does not have time to fully recover. This results in overwork, which also affects the functioning of the digestive system.
Another important point is that you need to move more. Unfortunately, physical inactivity is now a scourge that affects not only adults, but also children. Due to the obsession with cell phones and similar gadgets, there is a lack of movement. Physical inactivity in children entails the appearance of excess weight and, accordingly, disruption of digestion. It is very important to prevent these problems, since some chronic pathologies can develop due to overweight or obesity. Changing eating behavior, for example, in a child aged 12–13 years, when it has already formed, is very difficult. Therefore, it is important to think about such things as early as possible.
Read materials on the topic:
Childhood is for movement! What does physical inactivity lead to? How to make a child become obese?
You can make an appointment with a gastroenterologist here You can make an appointment with a pediatric gastroenterologist here
ATTENTION: services are not available in all cities
Interviewed by Marina Volovik
The editors recommend:
Not always gastroscopy. Examination for abdominal pain Remove or leave? What to do if gallstones are found? Not only a colonoscopy: what will a stool test tell you? How to protect your stomach from ulcers? When your gut rebels: what is irritable bowel syndrome?
For reference:
Saltymakova Yulia Anatolyevna
In 2003 she graduated from the Tver State Medical Academy.
2004 – internship in pediatrics.
2006 – primary specialization in gastroenterology at the Research Institute of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Nizhny Novgorod.
Currently, he is a gastroenterologist at the Expert Clinic in Tula. Receives at the address: st. Boldina, 74.
Symptoms and manifestations
A common symptom for all dyskinesias is pain in the right side. But its nature depends on the type of disease. The hyperkinetic form is characterized by severe paroxysmal pain, intensifying at night and after eating. Pain can radiate to the scapula, collarbone, and shoulder. The attack lasts no more than 20-30 minutes.
In the hypokinetic form, the pain is dull, aching, accompanied by heaviness and distension in the right hypochondrium. The pain lasts longer, and bloating may occur. After eating, the discomfort subsides.
Stagnation of bile, or cholestasis, which complicates hypokinetic dyskinesia, has other symptoms: darkening of urine and light-colored feces, changes in skin tone (yellowing) and sclera, itching.
The following symptoms may be common to both forms of the disease:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea;
- belching;
- stool disorders;
- decreased appetite;
- frequent urination;
- prostration;
- coating on the tongue;
- halitosis
It is important to tell your doctor about your symptoms and describe in detail the nature of the pain so that he can quickly make the correct diagnosis.
Classification
Dyskinesia is classified according to the etiological mechanism into primary and secondary forms, the causative factors of which were mentioned above.
Based on the type of tone disturbance and motor reflexes, hyperkinetic and hypokinetic dyskinesia are distinguished. The first, which is also called spastic, occurs when the influence of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system prevails. In this case, bile enters the intestines too quickly and in insufficient concentration, which negatively affects the digestive processes. This type of dyskinesia is more often characteristic of young people.
The hypokinetic or atonic form of the disease indicates the predominance of sympathetic innervation and is characterized by the slow movement of bile through the ducts. This leads to the fact that bile stagnates and a high concentration of it is released into the intestine, which subsequently is fraught with the development of an inflammatory process (duodenitis) and cholelithiasis. The atonic form of dyskinesia is more common among middle-aged and elderly people, as well as among people with unstable mental health.
Whatever form of the disease develops, the lack of optimal rate of bile secretion leads to disruption of digestive functions. The difference is observed only in clinical manifestations.