On what day does ovulation occur?
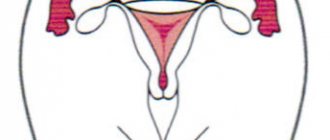
The menstrual cycle lasts on average 28–32 days. Without special research, it is impossible to accurately answer the question of when a girl ovulates. Ovulation usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle (days 12–15). For a more accurate calculation, it is necessary to plot your basal temperature over several months.
Another way to try to find out when ovulation occurs is with a calendar. To find out when ovulation occurs after menstruation, you need to count 14 days from the beginning of your last menstruation on a calendar. With an ideal 28-day cycle, there will also be 14 days left until the next period, that is, ovulation will occur exactly in the middle of the cycle. But does ovulation always occur on the 14th day?
Doctors say that the ideal classic version is not so common. For most women, ovulation occurs between the 11th and 21st days of the cycle, counting from the first day of the last menstrual period. There are 12 to 16 days left until the next menstruation. How long it takes for ovulation to occur depends on the hormonal background and the emotional and physical state of the woman, and in different cycles ovulation can occur on different days. Doctors also know of cases when during one menstrual cycle a woman had two ovulations at once.
Follicular phase
The follicular phase is a period of the menstrual cycle during which the growth and development of several follicles containing oocytes occurs, of which one (less often two) become dominant, and the rest undergo reverse development.
At the time of puberty, a woman's ovaries contain several hundred thousand very small primordial follicles containing an immature egg. Several of them (on average from 5 to 30) begin to actively grow, and from them preantral (primary) follicles are formed. Changes continue to occur inside each of them (an inner and outer membrane appears, granulosa cells are formed).
The antral (secondary) follicle already reaches approximately 500 µm in diameter, which is approximately 10 times the size of the primordial follicle. A cavity is formed inside it filled with follicular fluid.
Under the influence of LH, androgens are produced in the theca cells of the follicle, which are then converted into estrogens in granulosa cells under the influence of FSH. For normal development of follicles in the early stages, a high level of FSH and a fairly low level of LH are required, since a high concentration of luteinizing hormone causes increased production of androgens and provokes follicular atresia.
Of a fairly large number of antral follicles, only one or two (much less often) become dominant. Periovulatory (tertiary) follicles reach 18-20 mm in diameter. The concentration of estrogen in the follicular fluid increases significantly. Due to the increase in estradiol levels and the secretion of inhibin, FSH production begins to decrease.
The follicular phase normally lasts from seven to twenty-one days.
How many days does ovulation take place?
Ovulation is a short stage of the menstrual cycle, lasting only 48 hours. During this period of time, the egg, ready for fertilization, leaves the ovary, descends the fallopian tube and moves towards the uterus, where it will await fertilization. If fertilization occurs, the egg will attach to the wall of the uterus.
Favorable days for pregnancy are two to three days before ovulation and one day after, and on the day of ovulation the chances of conception are especially high. Therefore, to calculate favorable days, it is very important to keep an ovulation calendar and imagine how long ovulation occurs.
A mature egg is viable for only 24 hours, so within a day after ovulation the so-called safe days begin. The likelihood of fertilization after ovulation is extremely low.
How to correctly diagnose anovulation?
When a woman has not had her period for a long time or her cycle is very unstable and has large gaps, anovulation can be diagnosed very quickly. It is enough to undergo a short examination. The gynecologist will prescribe:
- progesterone test;
- gynecological ultrasound;
- folliculometry.
If the progesterone test does not give a clear result and the ultrasound does not show ovarian pathologies, additional studies are carried out:
- smear for a group of infections;
- comprehensive pelvic ultrasound;
- Ultrasound of the ovaries;
- Ultrasound of the corpus luteum;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, since it also produces hormones that can affect reproductive function;
- a set of hormone tests: sex hormones, thyroid hormones and pituitary hormones are examined.
How do you know if ovulation is happening?
Many women think about how to find out when ovulation occurs, because correctly determining this period will allow you to conceive a child faster. It is convenient to use the following methods at home without visiting a doctor.
- If you have regular periods, you can use the calendar method to calculate ovulation. According to it, ovulation should occur approximately in the middle of the cycle, but how can you understand whether ovulation occurred on the days you planned? Connect additional methods for determining ovulation!
- Measuring your basal temperature will also help determine that ovulation has occurred. An increase in temperature in the rectum indicates the release of an egg ready for fertilization. You can find out at what temperature ovulation occurs by charting your basal temperature every month. Typically, basal temperature during ovulation differs from pre-ovulatory values by approximately half a degree.
- An ovulation test is another way to determine whether ovulation is occurring. Ovulation strip tests are similar to pregnancy tests, only they show two strips not in case of successful fertilization, but when the egg is released from the ovary.
What is an anovulatory cycle?
As the name suggests, an anovulatory cycle is a period when a woman misses ovulation. For those who do not plan to have children, use contraception, or do not attach any importance to it, anovulation often occurs unnoticed. This is due to the peculiarity of menstrual bleeding - periods can occur as usual. In a normal menstrual cycle, the production of the hormone progesterone, which regulates bleeding during menstrual periods, is stimulated by the release of the egg. It is this hormone that helps a woman’s body maintain regular periods. During the anovulatory cycle, insufficient levels of progesterone can cause uterine bleeding of a different nature, which is mistaken for menstruation.
When does fertilization occur after ovulation?
After ovulation, the sperm has about a day to meet the egg and fertilize it.
If conception does not occur, the egg is destroyed in the fallopian tube within 24 hours, and after about 14 days the woman begins menstruation again - this is the release of an unfertilized egg.
If the meeting of the sperm and the egg was successful, the fertilized zygote descends into the uterus within 6–12 days, after which it is fixed there and pregnancy occurs. With the onset of pregnancy, the ovaries stop producing new eggs, so there is no fear that ovulation occurs during pregnancy - re-fertilization is impossible.
Signs that ovulation has not occurred
The main sign of anovulation is the absence of menstruation. The remaining symptoms are less noticeable, but they can be easily calculated if you know how the normal process proceeds.
Signs of normal ovulation, observed between 7-14 days after the last menstrual period:
- Changes in the nature and amount of vaginal discharge during the entire cycle - from liquid transparent to viscous, milky color.
- Soreness, tension of the mammary glands.
- Pulling sensations in the area of the ovaries, lower abdomen.
- Jumps in basal temperature.
- Increased libido.
More information about ways to determine ovulation is written in our article “What is ovulation.”
Ultrasound
Folliculometry is performed several times per cycle to track the growth of the dominant follicle, its rupture and the formation of the corpus luteum. You need to do an ultrasound for the first time on days 8-10 of the cycle, before ovulation begins. At this time, the dominant follicle should grow to 1.5 cm. When it grows to 2.5 cm, it will burst. After ovulation, the doctor should see the corpus luteum and fluid in the back of the uterine space.
This method allows you to find out the exact day of follicle rupture and identify abnormalities. You can talk about diseases of the ovaries or thyroid gland only if an ultrasound scan has confirmed the absence of ovulation for 3 cycles in a row.
Any woman can experience menstrual irregularities
Failures can be associated not only with diseases of the pelvic organs, but also with disorders in the endocrine, nervous, and immune systems. It should also be remembered that sometimes they signal the development of certain infectious diseases or pathological conditions:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- neoplasms in internal organs;
- malignant or benign neoplasm in the uterus or on its surface;
- STD;
- tuberculosis.
Some girls believe that tampons also provoke changes in the cyclicity of menstruation, but this opinion is incorrect. They are the same means of hygiene during menstruation as pads and menstrual cups.
Is it possible to get pregnant without ovulation?
If suddenly this problem comes to your home, then under no circumstances should you lose heart, but should go to the doctor. Perhaps here, in the absence of egg maturation, lies a serious pathology that needs to be urgently treated in order to observe how the tummy grows in the near future. Most likely, the doctor will talk about hormonal imbalance. To identify the reason for the lack of ovulation, it is recommended to first take the necessary tests and undergo an ultrasound examination. And this action will be the most correct, because the doctor, based on the medical results, will tell you in detail how to get pregnant without ovulation in your specific case.
And yet, what does modern medicine offer us? Is it possible to get pregnant without ovulation? If the cause of the pathological condition does not lie in serious anatomical disorders, then hormonal therapy is recommended, which will provoke the correct maturation of the egg. One of the treatment options is taking medications based on progesterone (for example, Duphaston).
So, if you are not sure whether it is possible to get pregnant without ovulation, then in this case it is best to set yourself up for a positive outcome. All that is required is to conscientiously carry out medical prescriptions. Remember: proper treatment helps achieve the goal of pregnancy and childbirth.
Diagnosis of a disrupted menstrual cycle
Many women who have problems with menstruation put off visiting the doctor because they are afraid of prescribing hormone therapy. In fact, hormones are indicated only in some cases, and careful diagnosis is necessary to select an adequate treatment regimen.
In addition to a gynecological examination, smear and general blood and urine tests, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and thyroid gland;
- hormone analysis;
- hysteroscopy;
- studies to identify chromosomal pathologies;
- PCR, etc.
The doctor decides exactly what tests are needed after a detailed questioning, in which he can find out the presence of a genetic predisposition, features of the patient’s lifestyle and other nuances that affect the frequency and intensity of menstruation. You may also need to consult doctors of other specialties (endocrinologist, therapist) and additional studies (computed tomography, skull radiography, etc.).
PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a complex of disorders in the body, which is characterized not only by gynecological symptoms, but also affects other organs. During the process of formation, the ovaries change their structure, which is why the girl’s entire menstrual cycle is disrupted. Most women with this syndrome are diagnosed with infertility.
The activity of the ovaries depends on the pituitary gland. It produces hormones that trigger the process of maturation and release of the egg. The ovaries themselves also produce hormones - estrogen and progesterone, which affect all organs. A woman with hormonal system disorders has the following abnormalities:
- Obesity;
- Male pattern hair growth;
- Irritability, insomnia, sudden mood swings;
- Lack of vaginal lubrication.
The main symptom of PCOS is rare, scanty menstruation, and an unstable cycle. This is a reason to contact a gynecologist. The sooner the girl comes to the doctor, the more successful the treatment will be. The diagnosis is made after a blood test and pelvic ultrasound.
Treatment of PCOS involves a complex effect on the endocrine system. First of all, doctors recommend bringing your weight back to normal and getting rid of obesity. Patients are prescribed vitamins and hormonal contraceptives that regulate hormone levels in the body. This allows you to restore a two-phase regular cycle and induce ovulation.
How to measure basal temperature
This method involves taking your temperature every day and creating a chart. A simple and free method requires a certain discipline, but it allows you to better understand your body. All you need is a mercury thermometer and a notebook or computer for keeping graphs.
Despite its simplicity, regular monitoring of temperature can reveal anovulatory cycles, hormonal problems, and inflammation. To do this, you need to record your daily temperature for 3 months. You can do the analysis yourself or bring the charts to the gynecologist.
Measurement Rules:
- During one cycle, you need to measure the temperature at the same time - optimally from 6 to 8 am;
- Measurements are taken rectally, orally or vaginally;
- Do not get out of bed before taking measurements.
2 days before the release of the egg, the temperature drops by several values, and then rises sharply and remains stably high. If, subject to all the rules, the graph remains single-phase, that is, there is no sharp increase in temperature in the second phase, then there is no ovulation.
Symptoms of menstrual irregularities
Too scanty or, conversely, abnormally heavy periods have their own characteristic symptoms. It is well known that any disturbances in the human body never go away without a trace, and a disruption in the menstrual cycle can be recognized by the following signs:
- disturbance in the regulation of bleeding;
- copious discharge with the presence of clots;
- significant delay;
- very scanty menstruation;
- painful attacks of various types;
- premenstrual syndrome.
In the case of normal menstruation, the woman does not feel any significant symptoms. In some cases, a nagging pain in the lower abdomen may appear, which does not particularly disturb the general rhythm of life. If the menstrual cycle is disrupted, the pain syndrome can become too severe, the pain can radiate to the hip and lower back.
The intensity of the syndrome is determined by the following indicators:
- loss of ability to work – it’s hard to sit, do usual work, there is a constant desire to lie down;
- number of painkillers taken;
- In adolescents, menstrual irregularities are often caused by excessive emotional stress that arises from the expectation of bleeding.
Treatment of menstruation disorders
Often the irregularity of the cycle is short-lived, but it is necessary to consult a doctor. He will conduct an examination, prescribe a list of tests and help determine the factor contributing to the development of this condition. A failure caused by hypothermia, stress, moving or overexertion does not require serious treatment or the use of medications.
During heavy workloads and sports, it is important to provide the body with rest, walk less, but also not lie down for several days in a row. When the climate changes, you can take vitamins; over time, the body will get used to the changes and will not react sharply to changes in temperature and humidity.
If the disturbances are caused by a diet, you must immediately stop it and start eating a balanced diet. Lack of nutrients provokes vitamin deficiency, the treatment of which begins with the use of vitamin and mineral complexes.
Male reproductive system
In fact, infertility occurs equally in both women and men. Male and female factors account for approximately two-thirds of all causes of infertility. The remaining third is either combined or unclear infertility. The following is information that may shed light on the working principle of these special male “swimmers” - sperm.
As in the female reproductive system, the normal anatomy of the male reproductive organs and balanced hormone production play an important role in pregnancy. The same hormones that regulate female reproductive functions also regulate sperm production in men. FSH stimulates sperm production, and LH stimulates the synthesis of testosterone, which helps maintain sperm production.
A sperm cell is a highly specialized cell that consists of a head, which stores chromosomes, and a tail, which allows for movement. Sperm are produced in the testicles, located in the scrotum. It maintains a lower temperature than the general body temperature, which ensures the normal development of sperm. The sperm then travel to the epididymis, an organ that stores and nourishes the sperm as they mature. During sexual intercourse, sperm from the epididymis together with fluid from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland form sperm. This fluid enters the woman's vagina. Sperm can live in the female reproductive tract for 48 to 72 hours, retaining the ability to fertilize an egg.
At the Center for Assisted Reproductive Technologies you can get tested for male infertility and get a spermogram analysis.
Reduced number of ovulations due to menopause
Lack of ovulation is also observed during menopause. The reduction in their number begins at about 30 years of age. For some women earlier, for others later. If girls have anovulatory cycles 1-2 times a year, then for older women - almost every month. And sometimes more often. It is for this reason that it becomes more difficult to get pregnant as you age, and why during this period, due to the lack of ovulation, you sometimes do not have regular periods.
Anovulation prevents pregnancy. To find out the cause, you need to undergo a full examination by a gynecologist. If no pathologies are found in the reproductive organs, the endocrine system and other possible causes of anovulation should be checked.
Change of scenery
If a woman does not ovulate, this may be due to travel or moving to a new place of residence. This reason is one of the most common factors that provoke lack of ovulation. The body can regard the emotional outburst experienced as stress. This is caused by a sharp change in climate and habitual rhythm of life. Disruption of the body's biological clock does not go away without leaving a trace. It takes time to adapt. This is especially pronounced when there is a sharp change in time or climate zone.
But this doesn't happen to everyone. Sometimes, with a sudden change of situation, for example, while on a business trip, there are no special disturbances, but when returning home, malaise appears; a cold may appear even in the summer, an exacerbation of chronic diseases and the absence or delay of menstruation.
Women whose profession involves constant travel - flight attendants, conductors - also experience such pathological conditions. The body can adapt over time and the menstrual cycle will improve. But sometimes adaptive abilities are reduced and in order not to harm your health you have to change your specialty. In such cases, most often a woman’s monthly cycle lengthens due to delayed ovulation. During such a period, menstruation and ovulation may be absent altogether.