Periods (phases) of the menstrual cycle
Every menstrual cycle, a woman's body prepares for pregnancy. The menstrual cycle can be divided into several periods (phases).
Most often, the duration of the menstrual cycle is 28 calendar days. However, for each woman it is strictly individual; it’s normal if it falls within the range of 21 to 35 days. The main factor is its constancy throughout the reproductive period; permissible deviations are no more than 3 days. An important indicator is also the amount of discharge and the woman’s well-being during this period. Any changes in the normal rhythm or signs of malaise are a reason to consult a doctor, as they may well become the first signs of a disease.
Bleeding intensity
The bleeding that we call "discharge" or "period" is not always the same in intensity. Various life circumstances - the birth of a child, diet, stress, different methods of contraception - can affect how long your period lasts and the intensity of discharge during this period. It is different for different women, and also sometimes differs for the same woman in different menstrual cycles - all this is not a deviation from the norm. Therefore, tampons are available in many formats and with varying degrees of absorbency. By choosing the right product, you will be protected and able to feel comfortable every day of the month - so that nothing gets in the way of enjoying life without compromise, even during menstruation. Use our tampon selector to find out which tampon is right for you. Talk to your doctor or gynecologist if you have questions about your period or problems with your menstrual cycle.
Follicular period of the cycle
This is followed by the follicular period, characterized by the cessation of discharge. At this time, increased synthesis of pituitary and hypothalamic hormones begins, affecting the ovaries. The main one is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which causes intensive growth and development of several follicles. The ovaries, in turn, produce the sex hormone estrogen; its significance is to stimulate endometrial renewal and prepare the uterus to receive an egg. This stage lasts about two weeks and ends due to the release of hormones into the blood that suppress FSH activity.
Rules of behavior and hygiene during menstruation
Relaxation can help relieve pain during menstruation. Activities that promote blood circulation will help reduce cramping. Take a walk, ride a bike, put a heating pad on your stomach, or take a warm bath.
Before your period, it is important to do things that bring you pleasure: communicate with friends, buy yourself your favorite treat, sleep more, in a word, do things that will help neutralize the effects of the negative symptoms of PMS (premenstrual syndrome).
Water will help cope with bloating and reduce fluid retention in the body before menstruation. It's hard to believe, but consuming it can actually reduce PMS symptoms. Eat vegetables and fruits with a high water content, drink warm herbal tea and juices. Add foods high in magnesium and vitamin E (dried apricots, bananas, avocados, etc.) to your diet. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of black and green tea, coffee, salt and sugar.
During menstruation, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene: use pads or tampons to absorb discharge, shower daily, wash your face 2-3 times a day. Experts recommend stopping sexual activity during menstruation.
Ovulation
The phase of ovulation begins, that is, the release of a mature egg from the follicle. As a rule, this is the largest of them. This is facilitated by a sharp increase in the level of luteinizing hormone (LH). The egg enters the lumen of the fallopian tube and begins its movement towards the uterus, at the same time awaiting fertilization. Its lifespan does not exceed two days, so to increase the likelihood of conception it is necessary that the sperm is already in the fallopian tube. At this time, the process of preparing the epithelial layer continues in the uterus.
Signs of the first menstruation
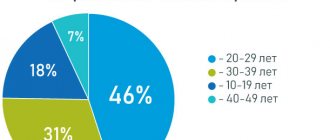
The first menstruation in teenage girls can begin at different ages and depends on when puberty began, when the body begins to mature and enter the phase when the girl becomes sexually mature, that is, she is able to become pregnant.
One of the first noticeable signs of the onset of puberty is the “swelling” of the breasts. This should not be confused with the growth of a real breast: this means that the nipple simply becomes more prominent. For other girls, the first sign may be the appearance of pubic hair. On average, after 4-4.5 years, periods usually begin, but a normal range is from one and a half to six years.
Often a sign of the age at which menarche occurs—the first menstruation in a girl's life—is the appearance of armpit hair and breast growth to the size of an adult bra (with A, B, C cups, etc.). From this point on, you can expect your period to start between 3 and 6 months, if it hasn't already started. A common sign of the onset of menstruation is a slowdown in growth.
Then, within six months, the girl may notice an increase in pubic hair growth or the appearance of pubic hair, and after another six months, the peak moment of growth occurs. After another year, the breasts grow to adult size and hair appears on the armpits. The first period usually occurs during or after 4 months after this.
Six months before the first menstruation, many girls notice an increase in the volume of vaginal discharge: this is normal
Important! If there is itching or a strong odor before the first menstruation, you should consult a gynecologist for advice: this may be a sign of infection.
Luteinizing period of the cycle
The final period of the menstrual cycle is the luteinizing period. Its duration, as a rule, does not exceed 16 days. At this time, in place of the follicle that the egg left, a special temporary gland is formed - the corpus luteum. It produces progesterone, which is designed to increase the sensitivity of the endometrium, in order to facilitate the implantation of a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus. If implantation does not occur, the corpus luteum regresses and progesterone levels drop sharply. This causes destruction and subsequent rejection of the epithelial layer, the cycle closes.
Your first period: what do you need to know?
The onset of menstruation (months) in teenage girls is an important stage of puberty.
This is one of many signs that a girl is entering puberty and can now become pregnant. Menstruation is a delicate topic that not every family’s parents can cover correctly and explain what is happening, give scientific information about what changes are now happening to her body and what will now change in her life. Many girls dread the day they get their period, and some look forward to the change. What you feel at this moment is normal.
Unfortunately, due to fragmented data and the absence of special classes on reproductive health in the school curriculum, many girls and most boys lack basic knowledge about the structure of the female reproductive system and what menstruation is and how it occurs, and the rules of safe hygiene and protection. This is very sad, because a simple lack of reliable information in this extremely important area can lead to unpleasant consequences for your health.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
| First phase (follicular, or egg development) Day 1-5. Menstruation: Menstruation usually lasts from 2 to 7 days, with an average of 5 days. During this phase, the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) is shed and menstruation begins. Contractions of the uterus at this moment may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. Some women have short periods (for example, 2 days), while others can last as long as 7 days. Bleeding may be profuse and spotting. In the first half of the menstrual cycle, a follicle grows in the ovary, where an egg develops and matures, which then leaves the ovary (ovulation). This phase lasts about 7-21 days, which depends on many factors. | Ovulation Day 14. Release of the egg. Ovulation usually occurs from the 7th to the 21st day of the cycle, often in the middle of the menstrual cycle (approximately on the 14th day in a 28-day cycle). After leaving the ovary, the mature egg moves to the uterus through the fallopian tubes. | Second phase (formation of the corpus luteum) Day 15-28. Thickening of the inner lining of the uterus. After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces the hormone progesterone. |
You can make an appointment with a doctor by phone in Moscow: +7 (495) 601–15–15 or here. you can see the doctor here.
| m. Krasnopresnenskaya |
| Konyushkovskaya st., 26 |
The structure of the female genital organs
A woman's external genitalia include the labia majora, labia minora and the clitoris. The labia minora border the opening of the urethra (urethra) and the vestibule of the vagina. The point of their connection is the clitoris, covered with a thin mucous membrane, the so-called mucosa. The clitoris, due to its sensitivity, plays a significant role in sexual arousal. Inside, the vagina is connected to the cervix, which is its lower part. Then the uterus expands, and it is into it that the egg enters, and the embryo and fetus develop during pregnancy.
Ovulation
When your body produces enough sex hormones, one egg matures in one of your ovaries approximately every 4 weeks. A mature egg leaves the ovary and moves to the fallopian tubes. This process is called "ovulation". During this period, you may experience more abundant and clear discharge.
Fallopian tubes
Over the next 4 days, the egg moves through the fallopian tubes to the uterus
Location of the egg
At the same time, the endometrium (the lining of the uterus) thickens to create the most comfortable place for the subsequent placement of the egg, strengthened by blood vessels and supplied with nutrients.
Menstruation
If the egg is not fertilized, it leaves the body along with menstrual flow. The place prepared for the development of a fertilized egg also becomes unnecessary. Approximately 2 weeks after ovulation, the upper layers of the endometrium are shed and excreted from the body in the form of menstruation. With the onset of menstrual flow, a new egg begins to mature and a new cycle begins.
How often do periods occur during pregnancy?
15–20% of pregnancies end in spontaneous abortion in the early stages.
However, it is important to understand that although bloody vaginal discharge against the background of a live intrauterine pregnancy is designated by doctors as a “threat of miscarriage,” in a large number of cases, despite the dire diagnosis, such a pregnancy is successfully carried to term. If an interruption does occur, in most cases (overwhelming) we are talking about genetic abnormalities of the fetus that are incompatible with life. Other reasons include infectious diseases in the early stages, hormonal imbalances, physical overload, and so on.
Increased progesterone in the luteal phase
The following signs may indicate increased levels of progesterone in the luteal phase:
- acne;
- memory problems;
- swelling of tissues;
- increased anxiety;
- difficulty concentrating;
- bloody spotting;
- frequent headaches;
- anxiety, depression.
Important! Hormone levels may increase during pregnancy. In other cases, exceeding the norm indicates the development of pathology of the urinary or reproductive system (renal failure and other kidney diseases, neoplasms, etc.), so patients are prescribed additional studies to determine the cause.
What can periods mean during pregnancy?
After the fertilization of the egg and the onset of pregnancy, menstruation does not occur throughout the entire process of gestation.
It should be remembered that the appearance of any bloody discharge from the vagina during a confirmed pregnancy (positive urinary pregnancy test, ultrasound data, hCG levels) indicates possible pathologies. For example, when there is a threat of miscarriage and termination of pregnancy (spontaneous abortion that has begun), placenta previa (low, marginal, complete).
Scanty spotting during the first days of pregnancy may represent nothing more than implantation bleeding. Implantation of a fertilized egg (blastocyst) into the endometrium occurs 7-10 days after conception, that is, essentially around the days when menstruation should come in case of late ovulation.
The penetration of the blastocyst is accompanied by the destruction of capillaries, and, consequently, a small amount of blood is released. But, unlike true menstrual bleeding, implantation bleeding does not last long: in most cases, a day, or even less.