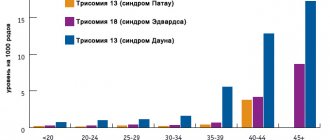
This hormone is produced by the corpus luteum in the ovaries every month after ovulation and is responsible for regulating the menstrual cycle. Progesterone also helps the body prepare for pregnancy if the egg is fertilized.
After ovulation, the hormone progesterone causes the uterus to thicken and prepare to fertilize an egg. If the fertilized egg implants, it is responsible for maintaining the lining of the uterus throughout pregnancy. However, if the egg is not fertilized, the level of progesterone in the body drops, and this leads to the fact that women begin to menstruate. Progesterone is also responsible for breast growth during pregnancy. It also prevents lactation until the baby is born. Men produce a small amount of it, which contributes to the development of sperm.
What to do if there are already problems
All of them can be solved with the help of aesthetic gynecology. This branch of medicine can completely restore orgasmic function in those 70% of women who cannot live a full life.
Hyaluronic acid
The injection of hyaluronic acid into the “G-spot” (clitoral legs) is very similar to the procedure for injecting fillers into the lips, which young girls love so much.
It is inserted into the legs of the clitoris to make them larger - in this case they will hang more into the vagina. As a result, during frictions the “G-spot” will finally be activated, due to which an orgasm will occur. Hyaluronic acid also helps when estrogens leave a woman. The mucous membrane immediately becomes dry, does not moisturize and does not produce natural lubrication. The procedure for intimate vaginal plastic surgery is carried out with a preparation that is not dense hyaluronic acid, which we inject into the lips, but, on the contrary, more liquid.
It literally pulls all the water onto itself, and if we insert it into the vagina, it will simply pull up all the moisture. In this case, there is no need for lubricants.
Kegel exercises
Regular Kegel exercises solve most problems - they prevent pelvic organ prolapse, strengthen muscles, and the vagina becomes more capacious.
As a result, the “G-spot” becomes easily accessible to the penis, which automatically eliminates anorgasmia. The same exercise is indicated if a woman has relaxed vaginal syndrome - muscle turgor improves, and the woman begins to feel something that she did not feel before.
Plasmolifting
During vaginal plasmolifting, we inject the woman with her own fibroblasts, which themselves are a source of their own hyaluronic acid.
The woman's blood is taken, passed through a centrifuge, and after some time we draw plasma into a syringe, which will remain on top of the tube. After this, we inject plasma into the vagina, and hyaluronic acid begins to do its job, that is, attract water to itself.
Often, after this procedure, women also no longer need artificial lubricants - we can renew the epithelium, moisturize it and “feed it with goodies.” Then both the clitoris and vagina will begin to please us again.
Laser treatment
The laser is a unique tool that can correct almost all problems.
Very often, patients who seek laser help have suffered from cancer. Often, due to the disease, women are forced to remove the uterus along with the ovaries, so estrogen ceases to be produced. Accordingly, the vaginal mucosa is very dry, and such women simply cannot be sexually active - when everything is removed, the vagina has nowhere to get hormones for its hydration. Due to dryness, the vagina becomes very thin - like the peel of an apple that should be juicy. New laser technologies turn a thin vagina into a thick one, because the better it is estragonized, the better - the vagina begins to moisturize again and produce its own hyaluronic acid.
The laser also combats vaginal relaxation syndrome - it is an ideal alternative to classical surgery. In fact, it does not affect the muscles in any way, but it can tighten the mucous membrane - it becomes elastic and contracts more strongly. Under the influence of a laser, the vagina narrows by 20%, and often this is enough for women.
At the top of the list of reasons why women end up in the gynecologist's office is vaginal discharge. They recur - patients are given treatment, and in the best case scenario we see them with the same problem six months later. Therefore, when we cannot cope with the problem with local treatment (suppositories, etc.), we move on to laser.
The vaginal tract as a whole, as well as the microbes in it, reflect the general condition of the body - we eat incomprehensibly what, we live in cities where only the name of ecology remains. All this is reflected in the vaginal tract. There are 10,000 germs in the vagina, and when this number increases, a woman begins to experience such problems. The laser renews the epithelium in the vagina - thanks to its effect, the vaginal walls begin to secrete glycogen, a nutrient material for lactobacilli.
They live only where they can eat, and leave the place where they cannot survive - then microbes take their place, which manifest themselves in secretions. The laser stimulates the layer of the vaginal walls and triggers the production of glycogen - lactobacilli begin to return, and the discharge goes away.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor, member of the Association of Gynecologists and member of the Russian Association of Endometriosis Inna Davidovna Dzhidzhoeva.
Treatment for low progesterone
You may not need treatment if you are not planning to have a child. However, you can do the following things to naturally increase your progesterone levels.
How to increase progesterone naturally
1. Taking vitamins.
Increasing your intake of vitamins B and C (which are responsible for producing progesterone) may help. Foods rich in vitamin B include whole grains (brown rice, barley and millet), meats (red meat, poultry and fish), eggs and dairy products (milk, cheese), legumes (beans, lentils) and dark leafy vegetables (broccoli , spinach). Foods rich in vitamin C include black currants, citrus fruits - oranges, limes and lemons, berries, kiwi, chili peppers, broccoli, sprouts.
2. Consumption of zinc-rich foods.
You can also boost your progesterone levels by eating more zinc-rich foods, such as meat, shellfish (these are low-calorie sources of zinc), legumes such as chickpeas, lentils and beans, seeds, nuts, dairy products, eggs and whole grains.
3. Stress management.
Excessive stress leads to the release of cortisol (the stress hormone), which in turn reduces progesterone production. You can reduce stress and emotional tension in general by exercising, meditating, yoga, taking deep breaths, and avoiding caffeine and nicotine.
Hormone therapy
The use of natural or synthetic hormones may be indicated to treat certain symptoms of low progesterone, such as menstrual irregularities and abnormal bleeding. If you experience severe symptoms, you may be given a combination of estrogen and progesterone. Hormone therapy is also advice for women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant sooner.
Pregnancy and hormone imbalance
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes enormous changes in terms of hormones.
In particular, during this period the following are developed:
- HCG. The appearance of this hormone in the blood is a signal from the body that pregnancy has occurred, and a restructuring of the entire metabolism is required. HCG levels double every 2 days, reaching their peak at 8-10 weeks. In the second half of pregnancy it remains approximately at the same level. The growth rate of hCG can be used to judge whether the pregnancy is developing normally. It maintains the corpus luteum in the ovaries, blocking the onset of the next menstruation.
- Estrogen. Its level increases 30 times. Estrogens affect the rate of cell division in the fetus. Under their influence, the mother's breasts prepare for the birth of the baby. High estrogen levels can cause pigmentation, headaches, and hair loss.
— Progesterone is a hormone that maintains pregnancy. It protects the fetus from the mother’s immune reaction to it as a foreign object, and relaxes the muscles of the uterus.
If a woman has a hormonal imbalance during this period, one may notice pathology in the maturation of follicles, a change in the thickness of the endometrium, the appearance of fibroids, a lack of progesterone, estrogen or excess testosterone.
Despite the protective powers of hormones, pregnant women are also at risk of developing various pathologies. For example, there is a high probability of iron deficiency and iodine deficiency. Endocrine system disorders are also common - hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function) and hyperthyroidism (increased thyroid function).
Symptoms of disorders
Hormones in a woman’s body are at their peak concentration at the age of 30-45 years. However, if there are disruptions in the endocrine, genitourinary or gastrointestinal tract, various unpleasant symptoms may appear.
For example, these:
- Constant fatigue. Excess progesterone causes drowsiness, and excess TSH depletes energy.
- Irregular menstruation. The norm at which the menstrual cycle should vary is from 21 to 35 days. A cycle is considered irregular if its duration fluctuates more than 7 days. If a woman is between 40 and 50 years old, inconsistent periods may be a sign of menopause. In other cases, this may indicate the presence of serious problems with the health of the reproductive system, for example, polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Problems with sleep. It is difficult to fall asleep quickly, sleep becomes short-lived and of poor quality.
- Changes in the shape and volume of the breast. A decrease in estrogen can make breast tissue less dense, and an increase in this hormone, on the contrary, makes the breasts more swollen. Lumps and even cysts may appear in it.
- Digestive problems. A lack or excess of thyroid hormones can negatively affect the digestion of food and cause diarrhea and constipation. A University of Texas study found that your gut microbiota is greatly affected by high levels of estrogen.
- Hair loss. Abnormal thyroid hormones, estradiol, progesterone, prolactin directly affect excessive hair loss. For example, the hormone dihydrotestosterone, under certain conditions, tries to destroy hair follicles.
- Weight gain. High levels of insulin, cortisol, serotonin and, conversely, low levels of testosterone and thyroid hormones slow down metabolism, lead to the accumulation of belly fat and increase cravings for sweets and starchy foods.
- Headache. They, like migraines, are closely related to the production of the hormone estrogen, which alleviates or aggravates pain. Therefore, during menstruation, when estrogen is on the decline, headaches may occur.
- Vaginal dryness. This is also facilitated by a decrease in estrogen.
- The appearance of rashes on the face, chest and back. Excess androgens cause the sebaceous glands to work harder, which leads to clogged pores and the appearance of rashes.
- Excessive sweating. Excessive sweating may indicate problems with the endocrine system caused by over- or underproduction of serotonin.
— Impaired memory and concentration, absent-mindedness indicate hormonal imbalance and problems with the thyroid gland.
- Mood swings. Dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin are responsible for this.
- Problems with conception. It’s not for nothing that progesterone is called the “motherhood hormone.” Due to its lack, a woman will either not be able to get pregnant, or the fertilized cell will remain in the uterus for no more than 2-3 days.
Norm and pathology
Hormones are guardians that protect our health.
They are responsible for:
— Coordination of the work of bodies;
— Humoral regulation (maintaining balance through body fluids: saliva, blood, lymph);
— Maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body, homeostasis (temperature, pressure, concentration of metabolites, etc.);
- Energy saving.
The most important hormones in the female body include:
· Estrogen. It stimulates the growth of subcutaneous fat, and during reproductive age it forms “estrogenic protection”: it preserves the beauty of the skin, hair, nails, affects the production of serotonin, protects blood vessels from atherosclerosis and heart attack, stimulates the growth and strengthening of bone tissue.
· Estradiol. The most important female sex hormone. It prepares the uterus for conception and ensures proper consolidation of the fetus.
· Progesterone. Prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg. Lack of progesterone can cause miscarriage.
· Prolactin. It is produced by the anterior pituitary gland. Prolactin starts and protects milk production. If the hormone is elevated, this may indicate possible diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, or liver failure.
· Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). They are synthesized in the pituitary gland and affect the maturation of the egg and its release into the fallopian tube in women, and also participate in the formation of secondary sexual characteristics (the structure and thickness of the skin, the volume of muscle mass, the distribution of areas of hair growth).
· Oxytocin. Increases the tone of the muscles of the uterus and ducts of the mammary glands. The main hormone during childbirth.
· Testosterone. This male steroid hormone is found in the female body in small quantities and is responsible for secondary sexual characteristics. Increased testosterone can lead to male pattern hair growth and problems with conception.
· Thyroid hormones. These include T3, T4, TSH. They are necessary for normal human growth and development, normalize the central nervous system, and improve cardiac function. Their excess or deficiency can cause problems with the reproductive system, including infertility.
· Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH). It allows you to assess the reproductive potential of a girl.
Diagnosis of hyperprogesteronemia
An increase in progesterone in women (symptoms listed above) should cause the patient to consult a doctor. He will order a blood test to determine the concentration of the hormone. If the results are elevated, additional testing is necessary to make a specific diagnosis, find out the cause, and prescribe adequate treatment.
How to prepare for the analysis?
Due to the dependence of the amount of the hormone on the phase of the menstrual cycle, you need to understand when it is better to donate blood. In most cases, the doctor prescribes testing on days 15-17 (the onset of ovulation in a 28-day cycle). If your periods are unstable, it is recommended to do the analysis 7, 14 and 20 days after the start of the previous menstruation.
If you are taking any medications, it is recommended to discontinue therapy 14 days before testing. If it is impossible to do this, the doctor must be informed about the name of the medicine and its dosage (indicated on the referral). Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach (you can drink water). The day before, it is better not to engage in sports, sex, eat spicy, fatty foods, or drink alcohol. Do not smoke an hour before.
Treatment of elevated progesterone is carried out depending on the reasons that caused it.