05 August 2020
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrine disease that is caused by a deficiency of insulin produced. The following types of this disease are distinguished: type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent), type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent).
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrine disease that is caused by a deficiency of insulin produced. The following types of this disease are distinguished: type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent), type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent). Type I occurs when there is insufficient production of insulin, and type II occurs when the body is unresponsive to insulin.
Type I diabetes occurs due to an absolute deficiency of insulin in the body against the background of a hereditary predisposition. Manifestation of the disease is possible after contact with certain viruses (rubella, mumps, hepatitis, mononucleosis), direct damage to pancreatic cells that produce insulin. This type of diabetes is often combined with other autoimmune diseases (glomerulonephritis, thyroiditis and others).
Type II diabetes develops as a result of a relative deficiency of insulin in the human body against the background of hereditary predisposition, poor nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, stress, long-term use of certain medications (diuretics, hormones, salicylates, cytostatics), and old age.
Diabetes mellitus in women: main signs and symptoms
In most cases, the causes of diabetes in women are the same as in men, but its occurrence and manifestation have a number of differences due to the physiological characteristics of the female body. The disease occurs due to disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system, which becomes more vulnerable during periods of childbirth, menopause and the postmenopausal stage of life 1.
Plus, the female body is more prone to obesity, which predisposes to metabolic problems and hormonal disorders that affect blood glucose levels. There are two types of diabetes mellitus – the first (DM1) and the second (DM2)1.
Yeast infections and gangrene
Diabetes weakens the immune system and a person becomes susceptible to all sorts of fungal diseases. Fungus and other microbes feed on glucose; this is a favorable environment for them to live and reproduce.
High sugar levels not only provoke inflammation in open wounds, but also interfere with rapid healing. Due to poor circulation, it is difficult for blood to reach the affected areas of the body and repair the damage. In addition, diabetes provokes the creation of a bacterial environment and rot, which can result in gangrene. The peripheral parts of the body are affected first, i.e. legs. Gangrene begins first with tingling and numbness in the big toe, and then spreads throughout the leg. The rotting of a living organism is one of the most unpleasant and terrible sensations. A person experiences it in two cases: with gangrene and cancer. In the end, in despair, the patient, exhausted by pain, decides to amputate the limb.
Naturally, maintaining a daily diet is an expensive and burdensome pleasure. In addition to the fact that a person must eat “tasteless” food, he must also carefully select and dose it, and this for the rest of his life. As a result, most people suffering from diabetes have a breakdown within the first year after the diagnosis is announced. Firstly, this is a huge shock for the patient, and secondly, the understanding that this disease is incurable and the medicine must be taken on an ongoing basis can cause denial of the disease itself.
Pathology of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2
In T1DM, the body stops producing or significantly reduces the production of the insulin gene due to the death of pancreatic beta cells. This happens because the immune system malfunctions and, instead of foreign microbes and bacteria, mistakenly begins to destroy the cells and structures of its own body.
This is called an autoimmune pathological process, the trigger for which can be:
- genetic predisposition;
- viral infections;
- some chemicals1.
In T2DM, insulin-dependent tissues of the body - fat, muscle and liver - cease to provide an adequate metabolic response to the insulin gene. The receptors interact poorly with insulin, making it difficult for it to penetrate tissues. To overcome the obstacle, the pancreas begins to produce more insulin 1.
This entails the depletion of beta cells responsible for gene production. Over time, there is not enough insulin to maintain blood glucose at normal levels. The insensitivity of insulin-dependent tissues to insulin is called insulin resistance. The main cause of diabetes in women is obesity. Others include genetics, family history, age 1.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in women
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is characterized by an early age of onset, although in a small percentage of cases (5%) it also occurs in older generations. It mainly affects girls, young women and young women under 25 years of age. In 50% of cases, the disease is diagnosed in children under 10 years of age 1.
Symptoms appear unexpectedly and quickly, which are easy to recognize:
- copious amounts of urine with frequent urination;
- an irresistible feeling of hunger and thirst (due to loss of fluid in the urine);
- sudden loss of body weight even with increased appetite;
- lethargy, apathy, drowsiness (due to the lack of insulin, the body lacks energy);
- temporary vision problems;
- pungent odor of acetone from the mouth;
- vomiting and nausea 1.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes in women
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is typical for people aged 40 to 60 years who are overweight 2. Insulin resistance develops in them due to the consumption of large amounts of carbohydrate foods. This type includes 80-90% of all cases of disease, and it is inherited in 90-95% of cases. 1. The symptoms of type 2 disease do not differ from the symptoms of type 1 diabetes, since they have the same cause - high blood glucose levels.
Other signs may include:
- skin itching;
- weakness;
- infectious skin lesions (boils, carbuncles, small ulcers);
Additional symptoms of diabetes in women with untimely identified type 2 disease manifest themselves in the form of cataracts, joint pain, and angina pectoris 1.
Features of the manifestation of the disease in women
The specific characteristics of the female body influence the manifestations of the disease. Since a woman is more dependent on fat metabolism in the body than a man, diabetes, regardless of age, can manifest itself as:
- rapid gain of excess weight, turning into obesity;
- sudden weight loss;
- excessive appetite 1.
Signs of type 2 disease are often itching and burning of the skin, dryness of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia 1. Unpleasant sensations in the genital area are the result of many reasons, including hormonal changes, which, for example, occur during menopause, pregnancy, and menstruation. Therefore, due to the uncertainty of their origin, a woman does not always consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Primary manifestations of diabetes mellitus in women also include:
- tingling and temporary loss of sensitivity in the skin of the hands, feet, and genital area;
- menstrual irregularities;
- vaginal and oral candidiasis;
- polycystic ovary syndrome, expressed in darkening of the skin on the elbows, neck, and armpits (with a predominance of male hormones over female ones)1
Diabetes mellitus during menopause
A woman is at maximum risk of the disease at the age of 50 years and older, while a man on average gets sick earlier - at 35-40 years 1. This is due to the onset of menopause. In the female body, the production of estrogens sharply decreases, which stimulate the secretion of the hormone insulin by the endocrine apparatus of the pancreas, thereby affecting blood sugar levels. During menopause, metabolism and fat distribution are disrupted, which in turn prevents the effective participation of insulin in maintaining glycemia at a stable level 2. Thus, menopause has a direct impact on the risk of the onset and development of the disease.
Loss of vision.
If your vision is not as clear as before, you should visit an ophthalmologist. However, if the doctor rules out abnormalities directly in the eyes, you should contact an endocrinologist and take a glucose test. Due to the displacement of the fluid, the lens inflates and changes shape, as a result the eye begins to perceive everything in a blurry and unclear form. At first, when the disease is just beginning to develop, with a correct and timely diagnosis, it is possible to prevent the further development of blindness by keeping blood sugar under control.
Diabetes and pregnancy
If signs of diabetes mellitus in women are detected during pregnancy, it receives the technical name “gestational”, indicating the period of time from conception (the day of the last menstruation) until the birth of the child 1. This type of disease is associated with the restructuring of the female body and changes in the volume of hormones produced. Some of them interfere with the action of insulin. The first signs of the disease appear, as a rule, at the 24th week of fetal development; it occurs as type 2 diabetes 1.
Risk factors for the disease during pregnancy include:
- family inheritance;
- obesity;
- age (from 25-30 years);
- previously observed elevated blood glucose levels;
- arterial hypertension;
- glucosuria;
- weight gain during pregnancy;
- undiagnosed prediabetes 1
It must be emphasized that with proper treatment, pregnant women give birth to completely normal children. The lack of competent treatment and supervision by medical staff, on the contrary, is dangerous for women’s health and the fetus.
Diagnostics
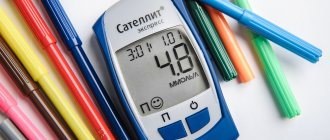
To make a diagnosis, a specialist will first need a blood and urine test, which will show glucose levels. In addition, additional tests may be prescribed. For example, an analysis for HBA1C (glycosylated hemoglobin) is a rather complex test that can only be carried out in well-equipped laboratories. The analysis will show how much glucose was in the body over the past 12 days, based on the amount of glycolyzed hemoglobin in red blood cells: hemoglobin has the property of combining with glucose, becoming glycosylated. In some cases (most often for pregnant women), the doctor may recommend a glucose tolerance test, i.e. insensitivity of body cells to insulin.
Thus, diagnosing diabetes does not seem difficult and is carried out in a short time. Therefore, it is extremely important for the patient to be attentive to his health and monitor the first symptoms of diabetes, avoiding serious complications by timely contacting a specialist.
Diagnosis of the disease
At the initial stage, diagnosis consists of laboratory tests. First of all, a general analysis of urine and blood is performed. A biochemical blood test is also performed, which determines the quantitative content of glucose, urea nitrogen, metabolic products - creatinine and electrolytes, gas composition is determined, etc. 3.
The composition of urine is tested for the presence of ketone bodies. If any are detected, their presence in the blood serum is determined.
Additional examination methods can be used to diagnose the disease:
- electrocardiography of cardiac muscle activity;
- chest x-ray;
- analysis of biological material of body fluids.
Dark spots on the curves of the body and itching.
Acanthosis nigricans is a condition where dark patches of skin with a velvety texture appear on the body. Usually their habitat is the bends and folds of the skin, such as the armpits, neck, groin, knee and elbow bends, etc. Experts believe that such symptoms are the first signs of diabetes. Darkening of the skin and itching, especially in the perineum, may be the “first signs”.
If these symptoms appear, first of all you need to visit an endocrinologist and venereologist. If sexually transmitted diseases are excluded, then the endocrinologist, based on the tests, can certainly diagnose diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes treatment
After confirming the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, treatment with insulin is prescribed, which compensates for the lack of production of the gene by the body’s own 3. The most important element in the treatment of type 2 disease is diet.
In the first case, a diet is also necessary, and the patient must carefully monitor the diet, evaluate and take into account the amount of carbohydrates in dishes and sugar in order to correctly calculate the dose of insulin.
In the second case, the main goal is to combat obesity. It is carried out not only with the help of diet, but also with physical activity, by giving up bad habits, etc. In case of morbid obesity, bariatric surgery is indicated - surgical reduction of the size of the stomach 1.
A mandatory condition for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in women is constant monitoring of blood sugar levels. For this purpose, special devices are used - glucometers, which can work with blood from a finger and other parts of the body.
Increased thirst and urination.
This is the most common sign of diabetes. Since insulin is not produced by the body, or is produced in insufficient quantities, sugar is in free flight. Once in the kidneys, sugar is excreted along with urine, simultaneously collecting fluid from other tissues, thus loading the kidneys and dehydrating the body. As a result, a person begins to drink more water, trips to the toilet increase, forming a kind of vicious circle. A person becomes constantly tired and irritable (who enjoys spending days involuntarily engaged in the “water cycle in nature”!), in addition to the kidneys, the heart is also in a stressed state, because Sugar safely “removes” fluid from the circulatory system, the blood becomes viscous and thick, and the heart has to push it to the peripheries with redoubled force, raising blood pressure.
Drug treatment
The current concept of treatment for type 1 diabetes involves injections of insulin, which is produced by the pharmaceutical industry in the form of pen syringes.
The injection regimen consists of two parts:
- injection of a long-acting hormone under the skin for 12–24 hours (administered 1–2 times a day), which covers the body’s need for insulin at night and between meals;
- introduction of “ultra-short” insulin or, as it is also called, insulin “for food”. It is used after meals or when signs of unwellness to reduce excessive glucose increases1
In the treatment of type 2 disease, insulin is rarely used, only if other approaches are ineffective. In both cases, patients take additional glucose-lowering drugs, as well as medications that prevent the development of possible complications 3.
Diet
The diabetes diet is aimed at reducing body weight mainly in diabetics with type 2 disease. It involves avoiding foods rich in carbohydrates. The main essence of the diet is to organize timely nutrition with high-quality products and maintain target blood glucose values.
The choice of food products, as well as the mode of their consumption, is determined by a qualified nutritionist or endocrinologist. When compiling a diet, the type of disease must be taken into account, i.e. whether insulin is produced by the body on its own or requires injection in a certain dose.
Prevention
Prevention of symptoms of incipient diabetes involves eliminating the toxic effect on the pancreas and reducing resistance to infectious processes. Preventive measures against type 2 are based on body weight control and nutritional correction, especially in individuals with a complicated hereditary history.
Patients with symptoms of the onset of diabetes mellitus need consultation with a general practitioner and an endocrinologist. For combined pathologies, consultations with specialized specialists are indicated: cardiologist, nephrologist, rheumatologist. The prognosis depends on the diseases of vital organs and systems aggravating the pathological process.
Disease prevention
The best methods for preventing diabetes in women are regular physical activity, proper nutrition and an overall healthy lifestyle. Physical activity in the form of walking and jogging, swimming, cycling, fitness accelerates metabolism, stabilizes hormone levels, smoothes out hormonal fluctuations, helps 4:
- to burn calories;
- control body weight;
- minimize the level of “bad” cholesterol;
- absorption of oxygen by the body;
- prevent the development of heart disease;
- improve sleep.
Healthy and proper nutrition does not necessarily require giving up traditional or national cuisine. The main thing in it is the balance of proteins, fats and, first of all, carbohydrates, for which it is enough to adhere to the general rules for eating foods.