Endocrinologist, nutritionist, nutritionist
Evdokimova
Elena Viktorovna
13 years of experience
Endocrinologist, nutritionist, nutritionist, member of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists. Member of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)
Make an appointment
Author of the article: Elena Viktorovna Evdokimova, endocrinologist, nutritionist, nutritionist, member of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists. Member of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)
Diabetes mellitus is a pathological condition characterized by constantly elevated levels of glucose in the blood and metabolic disorders.
Symptoms and signs of diabetes
Patients with diabetes complain of the following symptoms:
- dry mucous membranes, thirst;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- sudden weight loss or, conversely, obesity;
- blurred vision;
- dizziness;
- the appearance of ulcers on the skin;
- deterioration in performance, frequent infectious diseases;
- insomnia, frequent fatigue, increased appetite.
If such symptoms appear (all or part of them), you must immediately visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
Causes
Causes of diabetes:
- deterioration of immunity;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- genetic predisposition;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- use of corticosteroids;
- disruption of the adrenal glands;
- pancreatic diseases;
- obesity.
The essence of diabetes mellitus is that the functioning of the pancreas is disrupted and the functioning of the cells that produce insulin is not regulated. It is he who delivers glucose through the blood to the tissues.
Are you experiencing symptoms of diabetes?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Risk group
Diabetes can be congenital or acquired, occur in a latent form, or manifest during periods of high hormonal activity (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, etc.). If a congenital metabolic disorder in children is facilitated by a burdened heredity or a teratogenic effect on the fetus during a woman’s pregnancy, then an acquired one can occur against the background of the following diseases or conditions:
- obesity, physical inactivity;
- long-term uncontrolled use of certain medications (cytostatics, hormones, adrenaline, anticoagulants, diuretics, antihypertensive drugs);
- mental disorders, psycho-emotional instability;
- renal failure, adrenal dysfunction;
- cardiovascular failure;
- dysfunction of the liver and organs of the hepatobiliary system.
Any disease in which metabolism is disrupted, as well as emergency conditions: acute poisoning, dehydration, severe infection, viruses, can affect the development of diabetes.
Complications
If a person has diabetes, this can lead to serious consequences. First of all, the immune system deteriorates greatly. Because of this, for various diseases, recovery lasts much longer, and chronic pathologies appear.
Wounds heal much worse. Blood vessels and nerve tissues are also affected. Atherosclerosis gradually develops. Possible damage to the kidneys and eyes.
Another complication is diabetic foot syndrome. This area of the limb is considered the most vulnerable place for diabetes. Pathological changes can lead to inflammation, ulcers, and necrosis. In advanced cases, the leg may be amputated.
Medicines for type 2 diabetes in older people
In the modern world, there are a huge number of medications to combat diabetes. Drugs to stimulate insulin production, to reduce insulin resistance, to increase the excretion of glucose in the urine, to slow down the absorption of glucose in the intestines. Important! Only a doctor, based on the test results, will be able to prescribe therapy and prescribe the necessary medications. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or change medications without permission during treatment!
A special feature of therapy for older people is that, as a rule, in addition to diabetes itself, they also have a number of chronic diseases. In this case, many medications are prescribed, and the patient’s task is to strictly follow the regimen for taking them. It is important here that the drug use regimen is simple for a diabetic, and, if possible, relatives or close people can be involved in helping to control this process.
In addition, in old age, with diabetes mellitus, there is a violation of the recognition of hypoglycemic conditions, and an important goal of treatment is the prevention of these manifestations through strict adherence to diet and daily routine.
When to see a doctor
An endocrinologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. At JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg), which is located at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya per. 10, you can find first-class specialists. As soon as the first signs of diabetes mellitus appear in women or men, it is necessary to go to the hospital.
Symptoms of diabetes mellitus in men and women are usually expressed in strong and frequent thirst, frequent urination (especially at night), sudden weight loss, and increased appetite.
Professional care for older people with type 2 diabetes
Guardianship helps its wards regularly follow all the “diabetes rules”. If you need help caring for an elderly relative diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, you can always get it by contacting us. One of the options would be the service of a professional nurse who will look after the patient at home - control the intake of medications, ensure timely intake of proper food, exercise the patient and much more. Another option may be to accommodate an elderly person with complicated type 2 diabetes in any of our boarding houses. This guarantees round-the-clock care, care, attention and company for communication in the person of staff and other guests.
Preparing to visit the doctor
If you suspect diabetes, you should consult a doctor. Before visiting an endocrinologist’s office, you need to pay attention to:
- arterial pressure. It needs to be checked periodically (preferably twice a day), and then the data must be recorded. The same applies to the pulse;
- ambient temperature that a person feels comfortable;
- calculate the number of hours for sleep and how effective it is;
- weight changes recently (within the last 3 months or even a year);
- regularity of the menstrual cycle, since diabetes mellitus can also appear during pregnancy.
When visiting a doctor, you need to describe in detail all the sensations you have had recently, as these may be symptoms of diabetes. Also, in the future, this will help determine what type of diabetes the person has. You also need to write down your daily routine in detail, especially pay attention to your diet and diet, and also mention the amount of fluid you consume. Moreover, it is important to indicate in what form the body receives it: pure water, coffee or tea, any drinks.
If you suspect diabetes mellitus, no special preparations are required before going to the endocrinologist. The studies that the doctor prescribes for diagnosis also do not require such preliminary measures. The patient’s task when diabetes is suspected is to correctly assess his condition and describe everything to the doctor as accurately as possible.
Living with diabetes. Rules for the life of an elderly person with diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is still considered an incurable disease in the world, but by no means a death sentence! It is possible to live a quality and long life even with such a serious disease. It is rightly said that any problem should be looked at from a different angle. So let's look at diabetes from the point of view of changes in ourselves and our lives. An illness can and should serve as a reason to develop new healthy habits, become friends with sports and begin to pay due attention to yourself and your health.
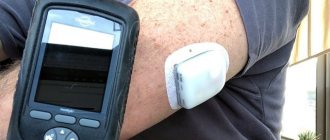
Old age is not at all a hindrance to changing your lifestyle and starting to renew yourself. An elderly person with type 2 diabetes can live fully and minimize the risk of complications by following simple rules. We talked about them in our article, but now we’ll just repeat them - proper nutrition and diet, losing excess weight, reasonable physical activity, quitting smoking and alcohol, regular visits to the doctor, monitoring glucose levels in the body, following a daily routine, getting adequate sleep.
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
To get diagnosed with diabetes, you need to make an appointment with an endocrinologist. Doctors of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg), which is located at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane 10 near the Mayakovskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Chekhovskaya, Tverskaya, Belorusskaya metro stations, will study the patient’s complaints, collect anamnesis, determine risk factors, and then prescribe examinations :
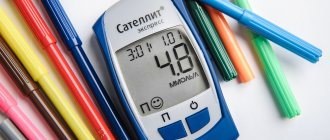
- fasting blood test. Before the tests, you should not eat anything in the morning or evening. During the procedure, blood is drawn;
- blood test at any time. This is necessary to confirm the types of diabetes and its presence in general;
- Analysis of urine. Patients with any type of diabetes have high levels of glucose in their urine.
All of the above tests can be done directly at the clinic of JSC “Medicine” in the Central Administrative District of Moscow.
Treatment
Treatment of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 is prescribed by an endocrinologist only after diagnosis. The main goal of therapy is to reduce blood glucose levels, prevent the development of complications and remove unpleasant symptoms. First of all, the 9th table and diet for diabetes mellitus help with this. This will help control your blood sugar. And for this purpose, they consume only fruits and foods that are acceptable for diabetes, and strictly at certain hours and in prescribed quantities. After all the diagnosis and confirmation of the presence of the disease, the doctor will tell you what to eat if you have diabetes and give recommendations. This will help improve your quality of life and avoid unpleasant consequences.
In addition, drug therapy is carried out. Only a doctor can prescribe medications. These are medications that lower blood glucose levels. Insulin can also be given through injections if necessary.
Main classification
Clinically significant classification consists of two main types of disease:
- symptomatic or secondary - a consequence of pathologies of the pancreas or thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, chronic renal failure;
- primary or true.
True pathology is classified into the following types:
- Type I is insulin-dependent - your own insulin is not produced at all or is synthesized in an insignificant amount.
- Type II or insulin-independent - body tissues are not sensitive to insulin at any concentration in the blood.
A separate group consists of pathology in pregnant women. What is important is the severity of diabetes – I, II, III – and the stage of compensation for carbohydrate metabolism disorders: compensated (well-controlled course of the disease), decompensated (complete lack of effect from treatment) or subcompensated (treatment is carried out, but it is not enough).
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of diabetes
What are they wrong about when they talk about diabetes:
- it develops due to excessive consumption of sugar and sweets;
- the disease is transmitted by heredity;
- Diabetes mellitus in a woman during pregnancy can be transmitted to the child;
- honey is allowed for this disease;
- With this disease, it is necessary to limit the consumption of carbohydrates as much as possible.
All these facts turned out to be wrong, so you shouldn't rely on them.
Prevention
To prevent the development of diabetes, you must:
- normalize body weight;
- constantly practice moderate physical activity, play sports, walk in the fresh air;
- switch to a healthy diet, which involves eating plenty of fruits and vegetables;
- promptly treat pancreatic diseases.
People with obesity, frequent stress, and poor diet need to be especially careful. Diabetes mellitus is also possible during pregnancy.
How to treat type 2 diabetes in older people
The essence of treating diabetes for people of all ages is to ensure that blood sugar levels are always normal, and the risks of complications associated with this disease are minimized. Proper nutrition, exercise and taking medications will help you achieve your goals.
The nutritional recommendations are quite simple and easy to follow. We exclude from the diet foods containing fast carbohydrates. Sugar, packaged juices, baked goods, sweets – we remove them. We minimize salt consumption - no more than 4 grams per day. If possible, we refuse animal fats - remove butter, fatty meats, and cheese. We refuse alcohol as a product that increases appetite and contains a large number of calories.
In food we give preference to proteins, complex carbohydrates - vegetables, fiber, not very sweet fruits, we eat cereals, dairy products, seafood. We take food in small portions with short breaks throughout the day.