Despite the fact that this disease is considered typically childhood, candidal stomatitis can often be found in adults, especially in old age. It is a fungal infection of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, which causes inflammation. The disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida albicans, and due to the characteristic whitish coating on the mucous membranes, it is often called simply thrush.
Causes of candidal stomatitis
Normally, the yeast-like organism Candida is in the body of every person and does not harm him in any way. When certain conditions arise, fungi begin to actively multiply, which leads to inflammation of the oral mucosa. Such factors include:
- metabolic failures;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hypovitaminosis;
- chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- pregnancy;
- use of birth control pills;
- bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking), etc.
In addition to the mentioned endogenous (internal) causes of candidiasis, there are exogenous (external) causes. These are chemical and mechanical conditions that lead to disruption of the integrity of the skin and oral mucosa. These include: plaque and tartar, sharpened edges of teeth, uncomfortable dentures, chemical contamination, etc.
Causes of oral candidiasis
A healthy person is still a carrier of fungi of the genus Candida, since they are part of the microflora and calmly coexist with other microorganisms without causing harm. But any change in the balance in the body can lead to rapid proliferation of bacteria and the development of disease. A weakened state of immunity plays a key role in the etiology of oral candidiasis, but any of these reasons can be the starting point for the onset of the disease:
- pregnancy;
- immunodeficiency states;
- infectious processes;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics or improper use of medications;
- injuries and damage to the oral mucosa;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- contact with an already sick person.
Signs of the disease
Symptoms of fungal stomatitis vary depending on the degree of inflammation, the characteristics of the patient’s body and his age.
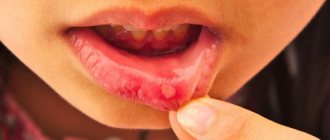
Signs of candidal stomatitis in young children are presented in the form of white cheesy plaques in the mouth. Parents often confuse them with leftover dairy foods. When plaque is removed, ulcers and erosions appear on the child’s mucous membrane and tongue. As the disease progresses, additional signs appear:
- the mucous membrane swells - it is difficult for the child to swallow;
- eating causes pain and discomfort;
- the patient loses appetite;
- When the infection penetrates the intestines, abdominal pain and digestive problems appear.
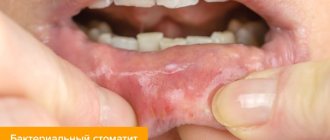
Symptoms of oral thrush in adults begin with a burning sensation in the larynx. Then a yellowish film appears on the mucous membrane and tongue, and when removed independently, blood is released. The patient complains of loss of taste, metallic taste. With chronic inflammation, the patient has a dry mouth and pain when swallowing.
Externally, fungal stomatitis in adults and children can manifest itself as glossitis (infection of the tongue) or as candidiasis.
Symptoms
A number of symptoms are characteristic of candidal stomatitis:
- The appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tongue, cheeks or palate. When trying to eliminate it, bleeding wounds may appear on the mucous membrane.
- Constant metallic taste.
- Feeling of heartburn on the tongue.
- Painful sensations from touching plaque.
- Later, as plaque spreads, difficulty swallowing occurs.
- Deterioration of tongue sensitivity and poor taste perception.
Types and forms of pathology
In practice, acute and chronic oral candidiasis occurs. The first develops rapidly, the second is characterized by a sluggish course and vague symptoms, periodic relapses and inflammation.
Acute fungal candidal stomatitis can be pseudomembranous (white plaque is easily removed and reveals reddened areas) and atrophic (there is no plaque, the mucosal surface dries, turns red and becomes painful).
Chronic thrush can be hyperplastic (white or grayish cheesy plaques form on the soft tissues) and atrophic (the oral mucosa dries out, becomes thinner, the patient complains of pain and discomfort).
What is oral candidiasis?
Oral candidiasis (also called oral thrush) is an infection of the mouth caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida. These microorganisms are part of a healthy microflora, but under certain circumstances their reproduction disrupts the favorable environment and becomes a source of disease processes. Inflammation and plaque on the tongue, ulcers on the mucous membrane and discomfort in the mouth - this disease is called oral candidiasis.
Infants are most susceptible to this disease, but at this age it is treated faster and is tolerated almost painlessly. Oral thrush is often observed in adults after 50 years of age, when the immune system is already weakened. Oral candidiasis is less common in men than in women. Recently, the percentage of cases has increased significantly, which is associated with uncontrolled use of medications: weakening of cellular immunity increases the risk of oral candidiasis after antibiotics, or rather their improper use. Microbiology, the science of microorganisms, studies the essence of oral candidiasis. And she successfully copes with her task, at the moment this disease has been studied in detail, and doctors know all the methods of treating and preventing infection.
How to treat fungal stomatitis?
In order not only to reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane, but also to prevent relapses, treatment of candidal (fungal) stomatitis in adults and children is carried out only in a comprehensive manner. Therapy involves taking several drugs at once:
- antimycotics – antifungal drugs for topical use;
- local antiseptic solutions for rinsing and irrigation (to prevent additional infection);
- antihistamines (recommended for the development of allergies to fungal activity);
- vitamin complexes (to eliminate deficiency of substances in the body).
To speed up recovery, the patient will have to follow a special diet. It is necessary to restore the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and pharynx.
Often sick patients are interested in how to treat candidal stomatitis at home, putting off going to the dentist. But it is impossible to cure candidiasis at home. Probably, it will only be possible to relieve the acute symptoms of the pathology, which will manifest itself again after a while. To prevent inflammation from becoming chronic, you should consult a doctor as soon as you notice the first symptoms of the disease.
Fungi of the genus Candida can infect the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, urogenital tract; in advanced situations, dissemination of the pathogen throughout the body can occur, affecting internal organs. The oral cavity is affected by the mycotic process quite often, especially in children and adults with a weakened immune system. Mucosal candidiasis can occur as a secondary infection in cases of severe somatic diseases. Opportunistic flora, which includes fungi of the genus Candida, can accompany diseases such as ulcers of a tuberculous or syphilitic nature, HIV infection, leukoplakia (precancer) and cancerous ulcers. Therefore, patients with signs of candidiasis should consult a doctor in all cases.
Oral candidiasis is considered a fairly common disease, especially in young children. In this case, predisposing factors for the development of this infectious disease are improper care of an infant (neglect of hygiene), trauma to the epithelium of the oral cavity, excess carbohydrate foods in the child’s diet, improper oral hygiene, and other inflammatory processes in the mouth that form a breeding ground for mushroom reproduction. Adults suffer from fungal infections most often when their immunity is weakened; candidiasis is a kind of indicator of a decline in human health. The most well-known conditions leading to immunodeficiency include HIV infection. In this situation, even deep tissues are affected by candidiasis - the pharynx, esophagus, and other internal organs. Exhaustion of the body and a decrease in immune defense can be observed with anemia of various origins, diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases of the ENT organs, allergic diseases, severe somatic diseases (heart and respiratory failure, tumors, generalized infections and other conditions).
Widespread dental caries, inflammatory diseases of soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity, violations of hygiene rules and severe dysbiosis of the oral flora, as well as the use of metal dental structures affect the development of candidal stomatitis in both children and adults.
There are acute and chronic forms of the disease. Depending on the visible inflammatory changes, candidiasis can occur in the form of atrophic (areas of redness with a smooth surface), erosive-ulcerative (cracks and ulcers of the epithelium), pseudomembranous (formation of film deposits that separate from the mucosa) and hypertrophic (additional growths on the mucosa).
Symptoms of fungal infection of the mouth, the etiological factor of which is Candida albicans, are characteristic “curdled” plaques. Depending on the type of inflammation, the plaque may be white or yellowish in color, easily removed from the affected area, or tightly adhered to the epithelium. In mild cases, all manifestations may be limited to visible changes. If the process takes on a moderate or severe degree, then other symptoms are added: pain and burning during meals, bleeding areas after the films are rejected, an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels, and regional lymph nodes may enlarge. If you do not consult a doctor in time, fungi may spread into deeper tissues and vessels, and the process may generalize, involving other organs of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
This is how acute forms of inflammation proceed; the duration of uncomplicated forms on average does not exceed two weeks. If the disease recurs, exists for a long time, or occurs against the background of other inflammatory or dystrophic changes, then a comprehensive examination of the whole organism is required.
The diagnosis and treatment of this disease is carried out by both a general dentist and a therapist. Additional consultation with a dermatovenerologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist or allergist may be required.
Candidal stomatitis can be diagnosed using a correctly collected history and complaints, examination of the oral cavity and microscopy of scrapings from the affected areas of the oral mucosa. Additionally, all patients who seek help from a doctor are prescribed tests for HIV infection and blood sugar determination. Differential diagnosis is carried out with ulcers of other etiologies, leukoplakia (precancerous changes in the epithelium), cancer and other serious diseases. It is possible that candidiasis joins them as a result of secondary infection.
Treatment is aimed primarily at eradication (destruction, removal from the body) of the pathogen. For this purpose, antifungicidal drugs of various groups are used: Pimafucin, Ketaconazole, Fluconazole, Flucytazine and others. Depending on the properties of the drug, forms of local and systemic action are used. For rinsing, you can use chlorhexidine (0.1-0.2 percent), herbal infusions (calendula, walnut, thyme). If a somatic pathology is identified that has led to a decrease in the body’s protective functions, the doctor carries out the necessary treatment and prevention of relapses of stomatitis.
Diagnosis of oral candidiasis
Candidiasis (thrush) of the oral cavity can be detected during an examination by a dentist if the patient has characteristic complaints. The doctor examines the condition of the oral mucosa, examines scrapings, and carefully examines the hair and skin. If you have oral candidiasis, you also need a blood test to check your glucose levels and rule out diabetes. The sooner you detect the presence of this infection, the easier it will be to get rid of it, so you should not delay diagnosis just because the symptoms do not cause you discomfort.