Urologist
Mkrtchyan
Karen Gagikovich
13 years of experience
Candidate of Medical Sciences, member of the European Association of Urology and the Russian Society of Oncourologists
Make an appointment
Author of the article: Mkrtchyan Karen Gagikovich, Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, member of the European Association of Urology and the Russian Society of Oncourologists
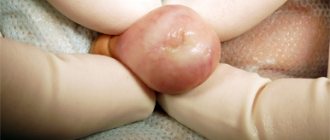
Balanoposthitis occurs only in the male population. The disease is quite widespread. According to statistics, this disease is diagnosed in 11% of the entire world population. The peculiarity of balanoposthitis is that the disease combines 2 diseases at once. With this ailment, the head of the penis and its foreskin are simultaneously affected. There is also separate balanitis, when the head of the penis itself becomes inflamed, and fasting, if only the foreskin of the organ becomes inflamed. However, if the nature of the disease is infectious, then the damage will quickly spread to both areas, since they are located next door.
Symptoms and signs of balanoposthitis
Symptoms are varied, but most often there are several phenomena that indicate the presence of pathology. So, balanoposthitis in men has the following symptoms:
- feeling of discomfort, itching and burning in the penis area;
- the foreskin is swollen and red;
- atypical discharge from the penis appears, which smells unpleasant and looks like pus;
- erosive processes on the surface of the genital organ;
- lymph nodes have increased in size;
- apathy, lethargy, chronic fatigue;
- frequent, recurrent headaches;
- increased body temperature;
- the head of the penis stopped opening due to swelling of the organ.
Balanoposthitis also has the following symptoms:
- blood rushes to the head of the penis;
- red-scarlet spots with clearly defined edges appeared;
- unpleasant discomfort when emptying the bladder and during intimacy, other manifestations of pathology.
Do you have symptoms of balanoposthitis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Diagnostics
The final diagnosis is made based on an external examination by a urologist, as well as the following laboratory tests:
In doubtful cases, additional consultation with an endocrinologist and dermatologist-venereologist may be required.
Causes of balanoposthitis
It has been established that balanoposthitis has the following causes:
- injury to the penis;
- the foreskin was washed with one or another remedy;
- the salt content in urea has increased;
- the patient uncontrollably took all kinds of medications, which resulted in irritation of the surface of the head of the genital organ;
- there was an infectious pathogen in the human genitourinary system.
The reasons that served as a prerequisite for the development of the pathology determine how its further development will proceed. If you see a photo of balanoposthitis, then in detailed photographs there are different manifestations of symptoms. This is either irritation of the surface of the genital organ, or the presence of erosion of the skin of the penis.
Causes
Since the foreskin is removed during circumcision, balanoposthitis only affects “uncircumcised” men. It can appear at any age.
The disease has many causes, but the most actively contributing to its development are:
- poor hygiene,
- narrowed, thickened foreskin.
A number of factors can increase your risk of developing the disease. In people with balanoposthitis, one of several causes is often identified:
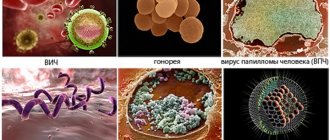
Infections
one of the most common causes of balanoposthitis. Although balanoposthitis itself is not a sexually transmitted pathology, some sexually transmitted microorganisms can contribute to its occurrence:
- yeast fungi
- chlamydia
- gonorrhea (pathogen: gonococcus)
- herpes simplex
- human papillomavirus (HPV)
- primary or secondary syphilis
- Trichomonas.
Yeasts
another common cause of balanoposthitis. Candida is a type of fungus that is usually found in small quantities in the human body.
Non-infectious processes
may also increase the risk of balanoposthitis. Some of these conditions include:
- chronic balanitis (constant inflammation of the foreskin)
- eczema
- injuries and accidents
- irritation caused by rubbing or scratching
- irritation from exposure to chemicals
- diabetes mellitus (due to constant irritation of the foreskin by high-glucose urine)
- taking antibiotics (causes an imbalance of microflora, promotes the emergence of fungi - candida to the fore in the area of the preputial sac)
- local allergic reactions, including those caused by antibiotics
- psoriasis
- reactive arthritis
- narrowed, thickened foreskin.
Household irritants can also lead to balanoposthitis. For example, exposure to chlorine in a swimming pool can cause irritation to the penis.
In other cases, balanoposthitis appears a few days after sexual intercourse and may be the result of friction or the use of latex condoms.
Routes of infection
Depending on what exactly triggered the disease, chronic balanoposthitis comes in different types. This:
- candidal balanoposthitis;
- allergic;
- circinar;
- anaerobic;
- ulcerative
Accordingly, candidal balanoposthitis in men is provoked by fungi of the genus Candida. The circinar type of pathology is caused by chlamydia. The anaerobic type of disease is caused by gram-negative microorganisms. Ulcerative pathology is caused by fungi, staphylococci, etc.
What can balanoposthitis be confused with?
Differential diagnosis should be carried out with the following diseases:
- lichen sclerosus
- psoriasis (skin disease)
- penile cancer
- paraphimosis (strangulation of the penis by a narrowed foreskin)
- Penile cavernitis (inflammation of the internal structures of the penis)
- Reiter's disease (rheumatic disease combined with a ring-shaped lesion of the head of the penis)
- Zoon's disease (redness of the head of the penis with the formation of pink shiny spots and a “weeping” surface that occurs in older men)
- erythroplasia of Queyrat
- boil, abscess (inflammatory purulent cavity) of the cavernous body and penis
- cellulite of the corpus cavernosum and penis.
Phimosis, balanitis and balanoposthitis
When talking about balanoposthitis, it is often confused with two similar diseases: phimosis and balanitis. All three pathologies, one way or another, affect the penis. However, each pathological condition affects a different part of it.
- Phimosis (N 47 according to ICD-10) is a condition that makes it difficult to remove the head of the penis as a result of narrowing of the foreskin.
- Balanitis (N 48.6 according to ICD-10) is an inflammation of the glans penis.
- Balanoposthitis (N 48.1 ICD -10) is inflammation of both the glans penis and the foreskin.
Phimosis can occur along with balanitis or balanoposthitis. In many cases, it is both a symptom and a cause. For example, the presence of phimosis provokes irritation of the head of the penis and foreskin. Once this irritation occurs, pain and swelling can make it difficult for the head to emerge from the foreskin.
Treatment
Treatment of balanoposthitis is carried out using different methods:
- conservative methods;
- operation;
- treatment using alternative (traditional) medicine methods.
Clinics use the first 2 treatment methods. An individual treatment plan is drawn up for each patient.
Various medications are also prescribed by a specialist. Medicines are selected depending on the type of pathology and what infections it is caused by. For different types of balanoposthitis, treatment with tablets or ointments will be different. It happens that with balanoposthitis, an ointment for treatment is prescribed in conjunction with taking antibiotics.
Sometimes corticosteroids are prescribed, sometimes anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, zinc ointment treats balanoposthitis better than all other remedies. Therefore, it is important not to self-medicate, but to consult a specialist.
Causes of redness and itching of the head in men
Symptoms of inflammation are caused by:
- Fungal infection - occurs in 20% of cases, the spots are characterized by the presence of a specific white lumpy coating, the smell of sauerkraut or fish.
- Sexual infections - chlamydia, ureaplasma, gonococci and other microbes can cause plaque on the head in men, redness and swelling of the tissues; Discharge from the urethra does not always occur.
- Dysbacteriosis is a violation of the bacterial microflora, when bacteria that are usually not characteristic of it, for example from the intestines, settle on the scalp.
- Allergies to shower gel, lubricants, synthetic underwear - can only appear on the scalp, without affecting other parts of the body; characterized by red pimples and peeling, the spots are very itchy.
Redness, swelling and other manifestations of inflammation intensify after sexual intercourse and ejaculation.
To identify fungi or bacteria that cause redness of the glans in men, 2 tests are done: PCR and culture of smears from the urethra and the skin of the penis.
When the presence of microbes is not detected, basic immunological tests are performed. If they are rejected, a consultation with an allergist is prescribed.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of balanoposthitis
Some people believe that this disease is harmless and may go away on its own over time. There are also opinions that this pathology can be cured at home using folk remedies without any problems. However, both of these myths are dangerous for patients with balanoposthitis. The pathology not only does not go away on its own, but can also provoke a number of unpleasant complications. The longer a visit to a urologist is postponed, the more difficult and time-consuming it will be to treat the disease. Treatment with traditional methods cannot eliminate the root cause of the pathology. At best, it provides temporary minor relief. However, without contacting a specialist, the disease will progress and the patient’s condition will worsen.
Why does the penis itch?
Physiological reasons
The symptom develops briefly in connection with certain external influences. The manifestations do not reach a level requiring contact with a specialist and quickly disappear when the provoking factor is eliminated. Penis itching can occur in the following situations:
- Failure to maintain intimate hygiene.
Infrequent hygiene procedures and irregular changes of linen lead to the accumulation of dirt and irritation of the skin. Unpleasant sensations are especially disturbing after sexual intercourse, since seminal fluid remains on the penis. - Irrational choice of linen.
Underwear made from synthetic fabrics or too thick impedes heat transfer in the intimate area, causes discomfort and increased sweating, followed by itching and burning. - Mechanical impact.
Sexual intercourse with insufficient lubrication from the partner can lead to poor penile glide, excessive friction and skin irritation. Along with itching, quickly disappearing local hyperemia is often observed. - Stressful situations.
Psychogenic itching does not have an organic basis, occurs during nervous tension and intense experiences, and is not accompanied by external changes.
Inflammatory processes
The most common cause of itching in the penis area is considered to be balanitis and balanoposthitis of various etiologies. The pathology is nonspecific or is provoked by specific pathogens. May be observed with the following STIs:
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- chlamydia.
In addition, fungi and viruses act as sexually transmitted infectious agents. Balanitis is manifested by itching, pain, swelling and redness of the head, the appearance of plaque, plaques and ulcerations, problems with urination and erectile function. With balanoposthitis, swelling and accumulation of secretions in the preputial sac are added to the listed symptoms. The clinical picture depends on the nature of the pathogen and the characteristics of the process:
- Catarrhal form.
More often observed with nonspecific inflammation, occurs with STIs. The most favorable variant of the disease, accompanied by the most vivid subjective manifestations. Patients complain of intense pain, excruciating itching, and a burning sensation during urination. - Urogenital candidiasis.
Patients are bothered by burning and itching in the head area. The coronary groove, head and inner layer of the foreskin are swollen, inflamed, hyperemic, covered with whitish films. Possible erosion. The discharge is whitish, with the smell of kefir. Urination is normal. - Genital herpes.
Transparent bubbles appear in the affected area. After some time, the rashes become cloudy, open, and brownish crusts form in their place. General hyperthermia, regional lymphadenitis, and quite severe pain are possible.
Along with infectious lesions, inflammation and itching of the head can be non-infectious in nature and develop with diabetes mellitus, urological diseases and some other pathologies. A special form is xerotic balanitis obliterans, which often occurs in older people. Itching is moderate. Areas of atrophy, blisters and spots form on the inner leaf and head, which subsequently transform into sclerotic plaques.
Itching of the penis
Dermatitis
Itching of the penis is accompanied by dermatitis of the corresponding localization:
- Atopic dermatitis.
It most often occurs in childhood, but can also manifest itself in old age. Pale pink lesions with increased dryness and roughening of the skin, cracks, papules, and peeling appear on the face, neck, in the folds of the skin, on the flexor surfaces of the joints and in the groin area. The penis is not a typical location, but it can be affected. The pathology is often complicated by secondary infection with the formation of balanitis. - Simple contact dermatitis.
Develops under the direct action of irritating substances (cosmetics, powder residues on linen). Itching and pain are not intense. The skin is dry, sometimes with cracks. It is possible to form bullae with their subsequent opening and formation of erosions. With constant contact with the irritant and the occurrence of chronic dermatitis, the symptoms are smoothed out, there is little or no itching. - Allergic contact dermatitis.
It is observed in case of an allergic reaction to washing powders, care products, synthetics, and clothing dyes. In the acute form, the affected area has clear boundaries and corresponds to skin contact with the allergen. Against the background of severe itching, swelling and hyperemia, papules appear, which quickly transform into blisters, open and heal with the formation of crusts. With chronicity, changes spread beyond the contact area. Scratching occurs due to constant itching. - Orthogenic contact eczema.
It is detected in men who abuse hygiene procedures and use irritating care products. Itching and discomfort in the projection of the penis are complemented by erythema and the formation of scabs. With prolonged exposure, lichenification and hyperkeratosis may develop.
Scabies
Typical localizations of itching and rashes due to scabies are the abdomen, the anterior inner thighs, interdigital folds, and the lateral surfaces of the fingers. In men, the scrotum and penis may be involved in the pathological process. Upon examination, traces of scratching and scabies are found in the form of lines 5-7 mm long with a vesicle or papule at the end.
Other dermatological pathologies
In the listed diseases, damage to the skin of the penis is not a specific symptom, but one of the possible (and often not the most common) localizations:
- Psoriasis.
A single lesion in the penis area is found extremely rarely; changes in several zones are more common. Small psoriatic plaques and papules are detected on the skin of the penis, accompanied by mild itching. Bright red plaques are often detected in the groin, axillary areas, and other places. - Lichen planus.
Characterized by intense itching and possible burning. The skin changes appear as small, smooth, purple bumps that often spread from the periphery to the center. The rash may also appear on the ankles and wrists. After resolution, areas of hyperpigmentation remain. - Lichen scleroderma.
A rare disease. Uncircumcised men of mature age are more often affected. As a rule, the head is involved in the process, often with a transition to the foreskin. Flat white papules transform over time into sclerotic and atrophic plaques. Itching, burning, and difficulty urinating are noted. Bleeding is possible.
Consultation with a urologist
How to treat balanoposthitis: therapeutic methods
The treatment regimen for the disease is determined by a urologist after a preliminary examination and a series of clinical tests. With well-chosen therapeutic tactics, inflammation of the prepuce can be treated quite successfully. After completion of treatment, most patients experience reproductive dysfunction. These are temporary disturbances that return to normal over time.
Treatment of balanoposthitis involves the use of systemic medications and local agents. With timely treatment (in the early stages of pathology), it is possible to get rid of inflammation with the help of ointments and creams. The main criteria that are taken into account when choosing the most suitable drug are the cause of the inflammatory process and the presence of systemic pathologies.
- Treatment of the mycotic form of balanoposthitis involves the use of antifungal drugs and the use of local antimycotics.
- Viral inflammation involves taking antiviral drugs.
- Getting rid of the viral form of the disease is quite difficult. As a rule, it becomes chronic, alternating with periods of remission and exacerbations.
- For the treatment of bacterial balanoposthitis, antibiotics and local procedures are prescribed to disinfect the area of inflammation.
- For the allergic form of the disease, the use of antihistamines is indicated.
- Purulent inflammation requires surgical intervention. In severe cases, partial or complete removal of the genital organ is performed.
- Balanoposthitis due to diabetes is also treated with antibacterial drugs. At the same time, medications are prescribed to normalize the concentration of glucose in the blood and urine. An integrated approach will help avoid relapse of the pathology.
Uncomplicated inflammation does not require hospitalization. The patient can take the medications at home. Inpatient therapy is carried out in cases where balanoposthitis occurs together with pyelonephritis, cystitis and other pathologies of the genitourinary organs. Hospitalization is also indicated for gangrene and purulent inflammation.
To achieve quick and maximum therapeutic results during the course of treatment, you must adhere to a number of recommendations:
- use contraceptives (condoms) during sexual intercourse;
- regular, thorough hygiene of intimate areas (washing with soap, treating affected areas with antiseptic drugs);
- wearing high-quality, natural underwear.
It is not recommended to change sexual partners during therapy. He also needs to be tested for sexually transmitted infections.
Actions for redness of the glans in men: how to treat
The most dangerous tactic is to try to use any ointments or other medications yourself before consulting a doctor. In 90% of cases, this does not help, distorts test results, and makes them false negative. Until the causes are clarified and cured, you need to stop having sex.
When inflammation on the head of the penis does not go away after careful hygiene, changing linen or detergents, contact our clinic. At the Clinic Dr. AkNer you will receive all the necessary tests and expert advice.
Urologist, andrologist Akopyan Nerses Grigorievich.
Back to list of articles
Diagnosis of balanoposthitis
A doctor can determine balanoposthitis very quickly. In this case, the patient will not need to undergo any specific tests. The examination procedure is also painless. Most often, balanoposthitis occurs due to poor hygiene, but it can also be caused by bacteria. Therefore, the doctor may prescribe a microbiological test to determine what causes the disease. Additionally, the patient may be recommended to take tests for sugar and syphilis. After all, for proper treatment and recovery of the patient, an accurate diagnosis is needed, which means the doctor needs to see the whole picture of the disease.
Prognosis for balanoposthitis
Most often, with this disease, the prognosis is favorable for men. However, in the acute course of the disease, balanoposthitis can become chronic. Therefore, it is so important to start treatment in a timely manner.