Pleurisy is an inflammation of the serous membranes that cover the outside of the lungs. Most often it becomes a complication of various pulmonary, cardiovascular, and oncological diseases. It practically never occurs as an independent pathology. Statistically, it is more common in men, since they do not like to go to doctors, they often abuse alcohol, smoke, and suffer from tuberculosis. Women turn to specialists more willingly, and therefore their prognosis is more favorable. Pleurisy in older people is usually caused by chronic heart disease, post-infarction syndrome, and cancer metastases. They are characterized by a severe course, a rapid increase in respiratory and heart failure, severe complications, and long-term treatment.
Types of pleurisy
There is no generally accepted classification. In Russia they use the Gembitsky and Bryusov gradation from 1991.
According to the etiological characteristics, pleurisy can be:
- Infectious. Depending on the pathogen - pneumococcal, echinococcal, staphylococcal, tuberculosis, etc.
- Non-infectious types of pleurisy. Depending on the primary pathology - lung cancer, rheumatism, chest injury, etc.
- Idiopathic. The reasons for the development are unknown.
According to the presence and nature of exudate (effusion):
- Exudative - pleurisy with serous, serous-fibrinous, purulent, putrefactive, hemorrhagic, mixed effusion, etc.
- Fibrinous - dry, that is, without exudate.
With the flow:
- spicy;
- subacute;
- chronic.
According to the localization of effusion and the extent of the process:
- diffuse or free;
- limited or encysted.
According to the location of the source of inflammation:
- unilateral, more often with pneumonia;
- double sided
Prevention
Preventive measures can prevent the development of both the disease itself and possible undesirable consequences and complications. A few general recommendations:
- timely and adequate treatment of colds and viral infections;
- to give up smoking;
- climate change with regular infectious diseases of the respiratory system;
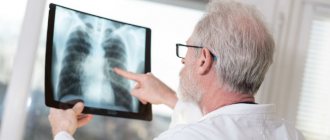
- chest x-ray at the first suspicion of pneumonia;
- strengthening the immune system;
- performing breathing exercises.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Symptoms of pleurisy
Even if a person is diagnosed with pleurisy, the symptoms vary from person to person. This is determined by the etiology, localization of inflammation, and its form.
However, some clinical signs are basic or common:
- stabbing pain in the chest, causing the patient to lie on the affected side (Rubinstein's symptom);
- shallow breathing;
- increased pain when coughing, sneezing and sudden movements;
- subsidence of pain during the transition of dry pleurisy to exudative.
- reflex dry cough.
As the disease progresses, shortness of breath and symptoms of acute cardiovascular failure increase, signs of intoxication, weakness and nocturnal hyperhidrosis appear. The functional capacity of the lungs decreases, the affected side bulges slightly and the intercostal spaces smooth out, there are signs of mediastinal displacement. On the affected side, breathing is weakened, a specific pleural friction noise is heard, and over the source of inflammation there is a dullness of the percussion sound.
If pleurisy is diagnosed due to coronavirus, fever, headache, myalgia and general malaise are added to the general symptoms.
In children, the clinical picture is more pronounced. Left-sided inflammation of the pleura of a rheumatic nature is more common.
Our doctors
Orlova Tatyana Vladimirovna
Doctor - allergist-immunologist, pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 37 years
Make an appointment
Glushko Raisa Alexandrovna
General practitioner, pulmonologist, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
60 years of experience
Make an appointment
Complications of pleurisy
The outcome largely depends on the etiology, as well as the timeliness of diagnosis, adequacy of treatment and compliance with medical prescriptions. If dry pleurisy has acquired a long course, it becomes exudative, and there is a risk of complications.
Complications of pleurisy:
- adhesions in the pleural cavity;
- complete fusion of the pleural cavity or interlobar fissures;
- calcification of the serous membrane;
- the formation of massive moorings - the formation of an intrapleural substrate in the form of adhesive strands, fibrous threads, adhesions;
- thickening of the pleural layers due to pleurosclerosis;
- increasing respiratory failure;
- limited mobility of the lung and dome of the diaphragm on the affected side;
- pleural empyema and the possibility of pus breaking into the bronchial cavity.
Prevention comes down to timely consultation with a doctor and the adequacy of the prescribed treatment.
Causes of pleural effusion
| Transudate | Exudate |
| Congestive heart failure Nephrotic syndrome Liver cirrhosis Pericardial diseases Myxedema | Tuberculosis Viral infections Fungal infections Rheumatoid arthritis Parasitic infections SLE Meigs syndrome Chylothorax Hemothorax Pleural mesothelioma Dressler's syndrome Metastatic lesions of the pleura Actinomycosis |
In most cases, pleurisy is a complication of an underlying disease, for example, congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, liver cirrhosis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, viral, fungal infections, rheumatoid arthritis and many other various nosologies. The most important aspect of differential diagnosis is the division of pleural effusion into exudate or transudate, taking into account the concentration of protein, LDH and cellular components.
The Light criteria are considered generally accepted in the diagnosis of exudative pleurisy: 1) The ratio of protein in pleural effusion to protein in blood plasma is >0.5. 2) The ratio of LDH in pleural effusion to plasma LDH is >0.6. 3) LDH in the pleural effusion >2/3 of the upper limit of normal for plasma LDH.
Treatment of pleurisy
Drug treatment can be etiological and symptomatic. Pleurisy cannot be tolerated “on your feet.”
Indications for the treatment of infectious pleurisy are broad-spectrum antibiotics, penicillins in combination with clavulanic acid or beta-lactamase inhibitors, fluoroquinolones, 2nd and 3rd generation cephalosporins.
The principle of treatment for tuberculous pleurisy is anti-tuberculosis drugs for several months. For purulent pleurisy, the pleural cavity is washed with antiseptics and antibiotics are administered intrapleurally.
Symptomatic treatment in adults - analgesics to reduce fever, diuretics; in the elderly - cardiovascular drugs, and after resorption of the effusion, physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
If dry pleurisy is detected, treatment is also symptomatic. To reduce pain, warming alcohol compresses, electrophoresis with calcium chloride, mustard plasters, and the method of tightly bandaging the chest with an elastic bandage are recommended.
In case of exudative inflammation of the pleura, physiotherapy is carried out only after the acute period has subsided. Electrophoresis with calcium chloride, heparin, paraffin and magnetic therapy, and vibration chest massage are indicated.
A recommendation for pleurodesis is the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the pleura. To seal the cavity and reduce the fluid in it, chemotherapy drugs or talc are injected into the pleural cavity.
For chronic purulent pleurisy, surgical intervention is indicated - pleurectomy. This is an operation to remove the visceral and parietal pleura, which forms the walls of the purulent cavity.
Classification of the disease
Pleurisy of the lungs can occur in different forms. First of all, doctors use classification according to the nature of the disease. There are several types of it: • infectious – if the causative agent is a viral, bacterial or fungal infection; • non-infectious – when the inflammatory process occurs for other reasons, for example, against the background of oncology; • idiopathic – has an unclear etiology.
Based on the nature of the course, pulmonary pleurisy is divided into two large categories: • exudative – characterized by the accumulation of mucus between the layers of the pleura. It may have a purulent form, which is much more difficult to treat; • fibrous – characterized by the accumulation of protein deposits on the surface of the mucosa. Pulmonary pleurisy is also divided into subacute, acute and chronic. Such a detailed classification allows doctors to make the diagnosis as detailed as possible and prescribe effective treatment.
Preventive actions
Determining preventive measures, knowing the causes of the disease, turns out to be quite easy. They consist of the following points: • strengthening the immune system, increasing the body's resistance. This is mainly achieved by an active lifestyle, proper nutrition, proper rest and the elimination of bad habits; • reducing the risk of infection. You should try to spend less time in places where the likelihood of infection is high. Be sure to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene; • timely treat emerging diseases of a viral, fungal and bacterial nature. It is important to understand that inflammation of the pleura often does not develop immediately after pathogenic microorganisms enter the body, but during their prolonged existence here. Accordingly, timely disposal of the primary disease becomes an effective way to protect against complications. Such simple preventive measures will help to significantly reduce the risks of developing the disease and the need for treatment for pleurisy. The main thing is to pay due attention to your health and not neglect qualified medical care. If suddenly some problems appear in the body, you should not leave everything to chance or try to solve them with folk remedies. You need to see an experienced doctor as soon as possible.
Examination methods
First of all, the doctor examines the patient, collects anamnesis, and studies the clinical picture. Then he will be able to draw up a diagnostic program to clarify the diagnosis. Typically the examination includes: • laboratory tests of blood and urine; • X-ray of the lungs; • Ultrasound of the chest; • pleural puncture and cytological and bacteriological examination of the obtained material; • thoracoscopy with pleural biopsy.
Diagnostics turns out to be quite informative, allowing the doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment for pleurisy. The patient must strictly follow the recommendations received in order to speed up recovery.
Illness due to oncology
If treatment is required for pleurisy, which has developed against the background of a malignant formation in the body, first of all, doctors administer chemotherapy. It turns out to be effective both in relation to the tumor itself and the inflammatory process in the pleura. Usually, after several procedures, the patient’s condition normalizes and the symptoms become less obvious. During therapy, doctors use modern antitumor drugs. These are new generation developments that are characterized by high efficiency with the highest possible safety for the patient’s body. After courses of chemotherapy, there are much fewer side effects than after using older analogues. With regard to the dosage of medications, the number of procedures and the duration of treatment, the attending physician decides all these issues individually for each patient, taking into account his state of health and symptoms.
When treatment methods using antitumor drugs are ineffective, the patient is prescribed surgery - pleurodesis. The goal is to artificially create adhesions between the layers of the pleura to eliminate existing cavities. Thus, doctors get a situation where the exudate simply has nowhere to accumulate. Accordingly, the patient’s well-being after surgery returns to normal. There are other methods of treating pleurisy caused by oncology. Therefore, doctors draw up an exact treatment regimen individually, taking into account the health status of a particular patient. We looked at the most common ways to get rid of the problem, which are used in practice in the vast majority of situations.