From Greek thorax - chest By the way, in 2021, the ProfGid career guidance center developed an accurate test for career guidance. He himself will tell you which professions are suitable for you, and give an opinion about your personality type and intelligence.
A thoracic surgeon is a specialist in the surgical (through operations) treatment of the chest * and mediastinal organs * .
Features of the profession
Thoracic (also known as thoracic) surgery deals with the surgical treatment of the lungs and pleura, mediastinum and other organs of the chest.
The work of a thoracic surgeon is often associated with pulmonology and phthisiology. It is no coincidence that thoracic surgeons work in tuberculosis dispensaries. But even from the definition it is clear that this profession is somewhat broader.
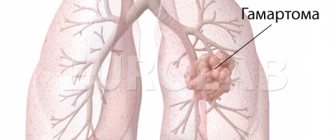
A thoracic surgeon can treat injuries (including penetrating ones) of the chest and hidden organs (including the heart), inflammation of the sternum and ribs, tumors of the lungs, chest, thyroid gland, etc., ruptures of the lung, esophagus, diaphragm, etc. P.
At different times, thoracic surgery included surgery of the heart, esophagus, and breast surgery. Then they separated from her. But recently there has been a reverse movement: narrow specialties have begun to move closer together again. This can be seen both in domestic clinics and abroad.
The reason is new technical capabilities. For example, many operations can now be done using a thoracoscope (endoscope for the chest cavity). Its illuminated optical system allows operations without large incisions. The surgeon sees his own actions on the monitor. Even the tumor can be removed through 3-4 cm incisions.
In this way you can operate on the lungs, esophagus, mediastinum, chest and even the heart. This makes the surgeon’s work easier and speeds up recovery.
And yet, usually the surgeon does not specialize in the entire vast field of thoracic surgery, but focuses on part of it. For example, it can treat pulmonary emphysema, tumors of the lung and mediastinum, and pleurisy. Or devote yourself to the treatment of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the extremities. (Arteries, as you know, originate from the heart.)
What does a thoracic surgeon treat?
A thoracic surgeon provides assistance to patients suffering from various diseases of the thorax and its main organs. These may be conditions caused by injuries - hemothorax, pneumothorax and chylothorax (accumulation of blood, air and lymph in the pleural cavity), treatment of tumors of the chest organs, bronchial diseases, pneumonia, pathologies of the pleura or pericardium (tissue lining of the heart). A specialist in the field of thoracic surgery diagnoses and treats patients with the following diagnoses:
- pleurisy;
- lung abscess;
- pulmonary artery blockage;
- tracheal stenosis;
- accumulation of pus (empyema) in the pleural cavity;
- pulmonary atelectasis;
- inflammation of the costal bone tissue;
- bronchiectasis;
- pathologies of the esophagus, thyroid and thymus glands.
Thyroid and thymus gland
The thyroid gland is responsible for the production of the main hormones that regulate metabolic processes. It is susceptible to open and closed mechanical damage, inflammatory diseases (thyroiditis), and can become a site for the development of a malignant tumor. A thoracic surgeon makes an accurate diagnosis and treatment (surgery) for cancer, cystic formations, nodular or toxic goiter of the gland.
The thymus gland or thymus, located in the center of the sternum, produces cells of the immune system, carries out lymphopoietic, endocrine and immunoregulatory functions. The state of the entire immune system of an adult and the development of all organ systems in a child depend on it. With an increase in size, hypofunction or hyperfunction of the gland and its other pathologies, autoimmune diseases develop, so timely examination by a doctor or surgeon specializing in diseases of the thorax is important.
Chest injuries
The following chest injuries are distinguished, in which victims are taken to the thoracic surgery department for emergency care:
- penetrating wound (gunshots, puncture wounds);
- industrial, road traffic injuries of a blunt nature;
- damage to the chest wall - fractures, bruises of the ribs;
- damage to mediastinal organs
The surgeon conducts a visual examination, percussion and auscultation of respiratory sounds, a complete examination of the body, and prescribes the necessary general and special laboratory tests. First aid includes ensuring free breathing (if foreign bodies get into the wound, they are removed as soon as possible to free the entire airway), relieving shock, and reducing pneumothorax tension. Further therapy is carried out according to the nature of the injury and the patient’s general medical history.
- Meatballs in the oven with gravy: recipes
- How to find a lost phone by satellite if it is turned off. Finding a phone if lost via satellite and IMEI
- Appendicitis: where is the appendix located in humans?
Respiratory diseases
A surgeon who deals with diseases of the lungs and other respiratory organs is a specialist highly qualified in this area of medicine. The subject of its activity is inflammatory processes, damage, congenital or acquired pathologies of the bronchi, trachea, and respiratory tract. If necessary, performs surgical intervention for tuberculosis or cancer of these organs.
Surgical treatment of esophageal pathologies
Surgery on the esophagus is necessary for such pathologies as diverticulosis (deformation of the wall of the esophagus with the formation of cavities in its wall, leading to the accumulation of food debris in them), the formation of malignant and benign tumors, chemical or thermal burns. It can be performed by a surgeon specializing in the treatment of thorax organs, a professional in the field of thoracic surgery.
Types of treatment
The most important method today remains thoracotomy - an operation in which the chest is opened. Along with proven techniques, priority is given to less traumatic interventions. One of them is thoracoscopy. Professionals figuratively call it the “keyhole” method. In this case, all surgical procedures are performed through minor skin incisions.
Modern surgeons have the opportunity to perform complex operations using an endoscopic device. A thoracoscope allows you to look inside the chest cavity and operate without significant incisions. In this case, the surgeon observes and evaluates his actions on the monitor screen.
Videothoracoscopy is widely used - a minimally invasive technique that radically changes the concept of traditional surgery. Surgeries on damaged nerve fibers, recognized as dangerous due to increased morbidity, have been revived. Diagnostic capabilities have expanded by taking tissue sections for histology.
Lengthy operations with large volumes of blood loss are becoming a thing of the past. Complex surgery for combined pathologies of the heart and lungs has become possible. The achievements of thoracic surgery are eloquently demonstrated by the growing success rates of treatment.
When is a consultation with a thoracic surgeon necessary?
Other specialists - therapists, pulmonologists, gastroenterologists, oncologists - often refer you for consultation to a surgeon involved in the surgical treatment of thorax organs. Self-referral to this highly specialized specialist is possible if you have symptoms such as difficulty breathing, impaired swallowing, persistent cough with purulent expectoration, traces of blood in the vomit, chest pain of a focal or general nature. Whether or not to admit you to a hospital for a comprehensive examination will be decided by the doctor conducting the initial consultation.
Professional qualities and skills
A thoracic surgeon must have a high level of knowledge in the field of fundamental medicine, as well as thoracic surgery. This specialist must have:
- self-organization;
- responsibility;
- confidence;
- high intelligence;
- good hand motor skills;
- concentration;
- finger mobility;
- sequence.
In addition, the thoracic surgeon is required to treat patients with special care, attention and understanding.
What symptoms should you contact a thoracic surgeon for?
You should immediately visit a doctor if you experience:
- chest pain (increasing with exercise, while walking);
- exhausting cough (especially interspersed with blood or pus in the sputum, unpleasant odor of breath);
- hemoptysis;
- frequent heartburn, feeling of a lump in the chest, belching;
- shortness of breath (with minor exertion);
- feelings of suffocation;
- difficulty swallowing (dysphagia);
- difficulties and pain when food passes through the esophagus.
Often the disease develops asymptomatically in the initial stages, so it is recommended to undergo regular fluorography and preventive examinations.
to contents ^
Thoracic surgery in Moscow
The establishment of thoracic departments in hospitals and clinics has recently become a normal practice in healthcare. Thoracic surgery of the lungs and other organs of the thorax is a specialization of the surgical departments of the following clinics in Moscow:
- RNHC named after. Academician B. Petrovsky;
- Clinic of Thoracic Surgery and Oncology;
- Center for Respiratory Medicine Integramedservice;
- National Medical and Surgical Center named after. N.I. Pirogov;
- Filatov Children's Hospital;
- Institute of Surgery named after. A.V. Vishnevsky.
Content
- General information
- What organs does a thoracic surgeon treat?
- What diseases does a thoracic surgeon treat?
- Breast diseases
- Chest wall diseases
- Lung diseases
- Pleural diseases
- Pericardial diseases
- Mediastinal diseases
- Diseases of the esophagus
- Diaphragm diseases
- Complications of postoperative treatment
- When to contact a thoracic surgeon
- How to prepare for your appointment
- Consultation stages
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Diagnostics that must be completed before surgery
Before prescribing surgical treatment, it is necessary to undergo some examinations prescribed by the doctor.
First of all, a general blood and urine test is taken, tests are carried out for plasma coagulability, sputum microscopy, the presence of tuberculosis bacteria, and blood electrolytes.
The main instrumental diagnostics include:
- lung scintigraphy;
- radiography;
- thoracoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- bronchoscopy;
- CT, MRI;
- spirography;
- esophagogastrography.
In emergency cases, diagnostics must be carried out quickly and as informatively as possible in order to quickly identify the cause of the problem and carry out timely surgery, which can sometimes save the patient’s life.
Prices:
| Code | Name of service | Prices |
| 1 | Initial appointment | 1200 |
| 2 | Repeated appointment | 900 |
| 3 | Calling a surgeon to your home | 3500 |
| 4 | Abdominal ultrasound | 2200 |
| 5 | Ultrasound of veins and vessels | 2400 |
| 6 | Doppler 2-3 trimester | 1200 |
| 7 | Rectoscopy | 1500 |
What does he do?
The competencies of a surgeon dealing with diseases of the thorax include making a diagnosis using modern diagnostic methods (ultrasound, MRI, tomography, x-ray examination), deciding on the need for surgical intervention, performing an operation, and managing the patient in the postoperative period. Thoracic surgery requires high qualifications, so most renowned medical institutes have departments that train these specialists.
Methods for diagnosing chest diseases
Thoracic surgeons have access to a variety of cutting-edge or traditional diagnostic methods, which increases the accuracy of diagnosis and determines the effectiveness of subsequent treatment. Diagnostics are used using the following tools and methods:
- ultrasonography;
- X-ray;
- CT scan of the chest;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- bronchoscopy;
- spirography;
- thoracoscopy;
- pleural puncture;
- biopsy;
- angiography (to determine the condition of blood vessels).
What is important for a thoracic surgeon in diagnosing diseases in patients?
Here are the three main pillars that a thoracic surgeon relies on to establish indications for surgical treatment.
The surgeon is interested in:
- General picture of the chest. To do this, the following is performed: X-ray examination (x-ray, multispiral computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging).
- Condition of the bronchial tree. — A fiberoptic bronchoscopy is performed.
- Functional capabilities of the patient's respiratory system. — Spirography is being done.
If, according to these examinations, there are no contraindications to surgery, then in the second stage the thoracic surgeon determines the scope of surgical treatment, taking into account the main diagnosis, concomitant pathology, risk factors, etc., and sometimes the patient’s age.
About the department
The work of the department is supervised by the chief thoracic surgeon of the Krasnodar region, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation (1998), Person of the Year in Oncology and Thoracic Surgery (1998-1999), Knight of the Order of Honor (2000), laureate of the Vocation Award (2002), chief thoracic surgeon of the Krasnodar region, head of the department of oncology with a course of thoracic surgery, member of the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons, member of the European Cardiothoracic Society, member of the European Respiratory Society, member of the International Anti-Cancer Union, member of the problem commission “Thoracic Surgery” of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Medicine Sciences, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences Vladimir Alekseevich Porkhanov.
He has gold medals: “For outstanding services in the development of Kuban”, 1st degree (2000), “Hero of Labor of Kuban” (2003). Awarded the title of Honorary Resident of Krasnodar. The department of thoracic surgery No. 1 is headed by a doctor of the highest category, Valery Borisovich Kononenko. Thoracic Surgical Department No. 1 was created in 1989, on the basis of the KMLDO (GB No. 2), and since 2003 it has been part of the Center for Thoracic Surgery, which dynamically merged with the Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1 in 2005.
Surgeons of the department:
|
Origin of the profession
Thoracic surgery has its origins in general surgery and was originally a field that dealt with the treatment of the mammary glands, heart, esophagus and lungs. In the 20th century, this area became an independent discipline, and such medical areas as pulmonology, vascular and cardiac surgery also departed from it. Currently, these areas are in close cooperation.
Thanks to the development of the specialty "thoracic surgeon", new possibilities have emerged for the surgical treatment of diseases of the lungs, heart and mediastinum. Diagnostic capabilities have expanded significantly and new methods of histological examination have appeared, and operations are no longer hours-long and of increased complexity.
Surgeries for malformations of the anterior chest wall
- Thoracoplasty for pectus excavatum with resection of costal cartilages and stabilization of the sternocostal complex with a metal plate (according to Paltia);
- Thoracoplasty for pectus excavatum deformity without resection of the costal cartilages and stabilization of the sternocostal complex with a metal plate (according to Nuss);
- Thoracoplasty for keeled chest deformity, combined deformities;
- Autochondroperichondroplasty with or without free autorib transplantation for congenital costomuscular defects;
- Muscle plastic surgery with a displaced thoracodorsal myofascial flap for congenital hypo- and aplasia of the pectoral muscles (together with microsurgeons);
- Thoracomioplasty for congenital cleft sternum according to Sabiston and in our modification.
Diagnostics
When planning an operation in a hospital, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out. In addition to the above tests, instrumental studies are carried out (they are prescribed by the surgeon, taking into account the condition of the particular patient):
- spiral CT;
- positron emission tomography;
- Ultrasound;
- angiography (to determine the condition of blood vessels);
- thoracoscopy of the pleura;
- MRI;
- puncture;
- biopsy;
- autofluorescence bronchoscopy (to search for possible tumors);
- spirography (determination of lung volume).
to contents ^