Haemorrhoids - the most common vascular disease in proctology, in which the cavernous (cavernous) bodies in the terminal part of the rectum expand. Many people do not attach importance to its symptoms, thus leading the process to complications.
According to statistics, every 7 out of 10 people on our planet experience symptoms of hemorrhoids. Lack of timely adequate treatment can lead to serious complications. Among them are bleeding from hemorrhoids, their inflammation, thrombosis and necrosis, anemia, paraproctitis and anal fissure. MedicCity proctologists recommend undergoing regular examinations by a specialist to prevent unpleasant consequences of the disease. In the early stages, hemorrhoids are treated using the most gentle methods possible!
Hemorrhoids in women usually occur during pregnancy and childbirth. Hemorrhoids during pregnancy are quite difficult to treat, since most medications can adversely affect the development of the fetus. Therefore, women are recommended to visit a proctologist at the stage of pregnancy planning.
1 Consultation with a proctologist in MedicCity
2 Consultation with a proctologist in MedicCity
3 Consultation with a proctologist in MedicCity
Hemorrhoids in men are no less common. The disease appears as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work (for example, hemorrhoids are an “occupational” disease of drivers), digestive disorders, constipation, alcohol abuse, and smoking. The cause of the disease can also be increased physical activity and hereditary predisposition.
It is customary to distinguish the following types of hemorrhoids: external (external) hemorrhoids and internal hemorrhoids.
This video talks about the main causes of hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are a chronic disease that, without timely treatment, progresses and often leads to serious complications.
Symptoms
At stages 1-2, internal hemorrhoids rarely cause any trouble and in most situations proceed hidden. In some cases, patients are disturbed by a feeling of discomfort in the anus, which intensifies after a long stay in a sitting position, as well as a feeling of incomplete bowel movement after defecation in the actual absence of constipation.
As the disease progresses to stages 3-4, more striking symptoms appear:
- itching, burning or constant discomfort in the anus;
- painful bowel movements, with pain persisting for 10-30 minutes after defecation;
- bleeding from the anus (less often - mucous discharge);
- prolapse of hemorrhoids from the anus to the outside.
- anoscopy - to assess the size of hemorrhoids;
- rectoscopy - to detect concomitant diseases;
- colonoscopy - to examine the general condition of the rectum.
Diagnostics
Internal hemorrhoids are easily detected during a digital examination of the anus by a proctologist or surgeon. In some cases, special instrumental research may be required:
Haemorrhoids
4348 28 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Hemorrhoids: causes, classification, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
In world statistics of proctological diseases, hemorrhoids rank first as the most common pathology (up to 41% of cases): more than 75% of people aged 45-65 years are diagnosed with varicose veins of the rectum.
Reasons for the development of hemorrhoids
- The development of varicose veins of the rectum due to compression from the outside (tumors of the pelvic organs or intestines) with impaired outflow through the intestinal veins.
- Impaired outflow of venous blood from the rectum due to pathologies not related to the pelvic and intestinal organs (liver disease).
- Dystrophy of the anatomical structures responsible for the elasticity of the venous wall.
Provoking factors for the development of hemorrhoids include:
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Connective tissue dysplasia.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Physical inactivity, predominantly sedentary lifestyle.
- Impaired intestinal motility with a predominance of constipation.
- Frequent or constant use of laxatives, regular mechanical irritation of the rectal mucosa.
- Activities associated with excessive muscle tension (weightlifting, physically demanding work).
- The predominance of spicy and spicy foods in the diet.
- Diseases of the pelvic organs, leading to compression of the pelvic veins.
- Pathology of the valve apparatus of the intestinal veins (in particular, the rectal plexus).
- Liver pathology (for example, cirrhosis) with the development of portal hypertension.
Classification of the disease By localization:
- interior;
- outer;
- combined.
With the flow:
- Spicy
- without inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- with inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- with the involvement of surrounding tissues in the inflammatory process.
- Chronic
- with bleeding without prolapse of hemorrhoids;
- with bleeding, but the prolapsed nodes are reduced spontaneously;
- reduction of nodes is possible only manually (with or without bleeding);
- the nodes are irreducible (with or without bleeding) or fall out immediately after reduction.
According to etiology, hemorrhoids are divided into:
- congenital (hereditary);
- acquired;
- symptomatic.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids
Acute hemorrhoids, due to the vivid clinical picture, immediately forces you to seek help. In this case, timely treatment prevents the process from becoming chronic.
In acute hemorrhoids, discomfort, itching and pain in the anus are noted, especially aggravated by defecation. Blood appears in the stool, and it covers the feces without mixing with them.
Chronic hemorrhoids are characterized by the same symptoms, but there are periods when the symptoms disappear, appearing again under the influence of provoking factors. With exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids, its symptoms are similar to those of acute disease.
During the period of remission of chronic hemorrhoids, there are no complaints of specific discomfort.
The clinical picture of hemorrhoids depends on the stage of the disease.
The first stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by minimal manifestations; discomfort during bowel movements and pain in the hemorrhoids are possible. When examined by a specialist, dilation of the capillaries of the rectal mucosa is recorded, which indicates venous stagnation, the appearance of nodes and local inflammation of the mucous membrane. Sometimes blood is released during bowel movements.
The second stage is characterized by prolapse of hemorrhoids during and after defecation with the possibility of their spontaneous reduction. In this case, bleeding and mucus discharge from the rectum occur more often, and itching and discomfort in the anal area are bothersome.
At the third stage, hemorrhoids fall out not only during defecation, but also during straining, coughing and other actions leading to increased intra-abdominal pressure (lifting heavy objects), and do not spontaneously reduce.
At the fourth stage, repositioning of the nodes is impossible either spontaneously or manually. This stage is the most dangerous in terms of the development of complications: prolonged heavy bleeding is possible, threatening the development of anemia (a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells that carry oxygen to all tissues, which, accordingly, will affect all organs), and thrombosis of hemorrhoids. Internal hemorrhoids in the early stages are asymptomatic; there may be a sensation of a foreign body in the rectum or a feeling of empty bowel. The discharge of blood and mucus at this stage is so scanty that it goes unnoticed. Hemorrhoids do not protrude into the lumen of the rectum.
As hemorrhoids enlarge, the intestinal lumen narrows, and therefore the process of fecal excretion is disrupted. Defecation is accompanied by pain and microtrauma of the mucous membrane, which leads to inflammation and aggravation of the symptoms of the disease. At a later stage, the entire symptom complex appears (bleeding, pain, discharge of blood and mucus from the rectum, prolapse of nodes, discomfort in the anal area), the likelihood of complications increases - anemia, thrombosis or the addition of a secondary infection with the development of paraproctitis (inflammatory - often purulent - tissue disease surrounding the rectum).
External hemorrhoids are characterized by the appearance of pain in the anus after exposure to provoking factors (coughing, prolonged sitting, heavy lifting, straining, defecation). With this form of the disease, bleeding occurs much less frequently than with internal hemorrhoids. Blood is visible not on feces, but on linen, toilet paper and personal hygiene products. Upon examination and palpation of the affected area, painful nodes are detected.
If persistent pain occurs in the perineum, not related to the act of defecation, or an increase in the size of the hemorrhoids, the development of thrombosis of the hemorrhoids is most likely, which, if left untreated, can lead to complications and the need for surgical intervention.
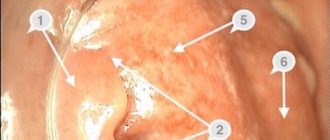
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids Diagnosis of hemorrhoids begins with an examination (external and internal) or by a proctologist. With internal hemorrhoids, the nodes are dark cherry in color, have a soft elastic consistency, are painful on palpation, and protrude into the lumen of the rectum. With external hemorrhoids, nodes of a similar type are visible around the anus. Instrumental diagnostic methods are used - anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy.
Causes
The main reason for the development of internal forms of hemorrhoids is a violation of the inflow and outflow of blood in the cavernous (cavernous) bodies. In a healthy person, these corpuscles fill with blood when the intestines are filled with feces, which causes them to increase and makes it easier to control the urge to defecate. After successful bowel movement, blood flows out and the cavernous bodies shrink.
If the regulation of outflow is disrupted and the cavernous bodies are constantly in an increased size, then over time this leads to varicose veins and thinning of the venous vessels. The main causes of blood outflow disorders traditionally include the following factors:
External (external) hemorrhoids
The external manifestation of hemorrhoids is the presence of varicose veins (hemorrhoids), which are located outside the anus. External hemorrhoids appear near the anus.
Enlargement and inflammation of hemorrhoids occurs due to stagnation of blood in the pelvis and in particular in the cavernous bodies of the anal canal.
When a blood clot appears in the external hemorrhoid, swelling develops and the person begins to feel pain. The sufferer may feel hemorrhoids as a large, firm “bump” covered with thin, sensitive skin.
With poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, heavy physical activity and stagnation of venous blood in the rectum, a complication in the form of acute thrombosis (the so-called “hemorrhoidal thrombosis”) may occur.
Blood in external (external) hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidal thrombosis) appears when the skin over the hemorrhoid becomes thinner and the blood clot breaks out in the form of a clot, then scarlet blood may appear.
1 Hemorrhoidectomy in MedicCity
2 Hemorrhoidectomy in MedicCity
3 Hemorrhoidectomy in MedicCity
Symptoms of external hemorrhoids
With this type of disease, the following symptoms of hemorrhoids can be distinguished:
- pineal-shaped protrusion around the anus;
- hemorrhoids, varying in size and location, which are easily palpable by the patient and increase with strain during bowel movements;
- pain and blood during bowel movements;
- unpleasant burning and itching in the anus;
- piercing pain at rest, after stool, when walking, coughing and sneezing (with the development of hemorrhoidal thrombosis);
- severe pain when touching hemorrhoids (hemorrhoids increase in size, swell, turn blue).
Treatment options
Internal hemorrhoids can be treated conservatively, but only if the disease was detected in the early, almost always asymptomatic, stages. In this case, the patient is prescribed regulation of motor activity, prevention of constipation (diet table No. 3), taking phlebotonic drugs and a course of therapy with rectal antihemorrhoidal suppositories.
If the favorable moment has been missed, only surgical methods will help to cope with the disease:
- 1. Sclerotherapy
: a sclerosing drug is injected into the hemorrhoidal node, causing “gluing” of the walls of the venous vessel and its gradual resorption. Effective for the treatment of stage 1-2 hemorrhoids. At stages 3-4 of the disease, the procedure helps reduce the size of the nodes.
2. Laser vaporization
: The hemorrhoid is removed using heat from a laser beam. Effective for the treatment of stage 1-3 hemorrhoids. At stage 4, vaporization is practically useless.
3. Hemorrhoidectomy
: direct removal of hemorrhoids using a scalpel or electric knife. It is used at the 4th stage when hemorrhoids prolapse outward.
4. Removal using the Surgitron device
: The hemorrhoid is removed with a narrow beam of high-frequency radio waves. Like hemorrhoidectomy, it is indicated for prolapsed nodes.
Latex ligation for the treatment of internal hemorrhoids, as a rule, is not used due to the low effectiveness of this method in combating advanced forms of the disease - that is, when the internal node falls out.
Hemorrhoids in men and women
There is no difference between the clinical manifestations of hemorrhoids in men and women. Differences may lie in the causes of the disease. Pregnancy and childbirth increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids in women. During pregnancy, the uterus increases in size, puts pressure on the pelvic veins, and the tone of the vein walls decreases, leading to blood stagnation. The vessels in the rectum begin to dilate and this leads to the formation of hemorrhoids.
During the birth itself, intra-abdominal pressure increases, as a result of which the veins of the rectum become filled with blood and swell, and hemorrhoids may fall out.
Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, women are recommended to undergo a proctological examination in order to exclude or identify hemorrhoids at the initial stage and undergo a course of treatment. This will allow you to avoid unpleasant manifestations of the disease during such a wonderful period of life for any woman.
Men have their own risk factors for developing hemorrhoids. Men are more likely than women to engage in strength sports, and their work more often involves lifting weights. Loads significantly increase intra-abdominal pressure, and if the walls of the vessels of the rectal veins are weak, hemorrhoids may develop. Also, drinking strong alcoholic drinks provokes the development of hemorrhoidal disease.
If we talk about the differences between hemorrhoids in men and women, we can note that men are less likely to visit a proctologist in the initial stages and see a doctor when the disease is already advanced. This may be due to embarrassment, or because the man does not want to change his lifestyle, profession, or hobbies.
Clinical prognosis
The overall clinical prognosis is always favorable. Modern proctological methods make it possible to successfully treat internal hemorrhoids even at the most advanced stages.
The disease can pose a threat to life only if the hemorrhoids become necrotized with the addition of blood poisoning, but this is only possible in the case of a long, persistent and conscious refusal of the patient to receive medical care.
Surgeon-coloproctologist, surgeon of the highest category. Rakhmatullin Andrey Albertovich
Treatment Options for Internal Hemorrhoids
There are many ways to combat the disease. What will be optimal in a particular case can only be said by a doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient. In the initial stages, conservative treatment also helps - painkillers, rectal suppositories, gels, ointments, creams, etc.
When the nodes are finally formed, minimally invasive methods of solving the problem are much more effective:
- Sclerotherapy. A sclerosing agent is injected into the affected node, gluing its walls.
- Laser vaporization, in which the nodes are “evaporated” under the thermal influence of the laser.
- Ligation. Using a vacuum ligator, a latex ring is placed on the hemorrhoidal node, which compresses the affected vessel, simultaneously depriving it of recharge.
- Disarterization. The problematic artery (and in some cases also a node) is sutured with a special thread.
- Milligan-Morgan operation. The hemorrhoid is removed and cut off using a laser, after which the affected area is sutured using a special thread.
In the final stages of internal hemorrhoids, surgical intervention is no longer necessary. In this case, doctors use hemorrhoidectomy and other options for excision of hemorrhoids.
Regardless of which treatment option is chosen, the patient is advised to follow a diet that helps normalize the functioning of the digestive tract.
To avoid all these unpleasant manipulations, it is necessary to regularly see a proctologist. Medical specialists are experts in their field. Make an appointment, and they will not only detect your illness in a timely manner, but will also select the optimal treatment option.
Treatment of hemorrhoids
In general, hemorrhoids are treated by a specialist called a proctologist.
Therefore, if you urgently go to the clinic, you need to look for it. This doctor treats hemorrhoids comprehensively, according to a specially developed individual scheme. It is impossible to say exactly how much treatment for hemorrhoids costs, since each type has its own prices for treatment to remove hemorrhoids. A professional proctologist first identifies the cause of the disease. If the problem is constipation, then he tries to improve the functioning of the stomach using a set of treatment methods. If the reason is a sedentary lifestyle, then the doctor will use physical therapy methods and eradicate this cause and give his testimony. If hemorrhoids started due to stress, then the proctologist will think about how to treat the psyche, whether any of the methods are effective, and will give a list of contraindications. There are different methods of treating hemorrhoids, as they come from the causes, the doctors of the clinic offer modern treatment for any hemorrhoids and innovative methods of treatment. Now they offer to use special equipment, a developed treatment regimen for hemorrhoids, methods for removing hemorrhoids, and drug treatment if surgery is not possible. Each hemorrhoid treatment regimen is developed individually and this is the task of the clinic’s proctologist.
Types of hemorrhoids
Based on the existing prerequisites for the development of the disease, primary and secondary hemorrhoids are currently distinguished. Primary hemorrhoids are the result of congenital predisposition and heredity. Secondary hemorrhoids occur as a reaction to an unhealthy lifestyle and other negative factors that lead to disruption of the outflow of blood from the venous plexuses of the rectum.
Depending on the nature and location of the disease, internal and external hemorrhoids are distinguished. With internal hemorrhoids, the veins of the rectal plexus, which is located under the mucous membrane of the lowermost part of the rectum, dilate, i.e. inside the intestines. External hemorrhoids are characterized by the appearance of external hemorrhoids that form around the anus and are often visible to the naked eye.