Frequent urination at night (nocturia) is a disorder of the urinary system. This is a condition in which a sleeping person experiences multiple urges to urinate. Doctors consider as a deviation from the norm the number of urges to go to the toilet more than once or twice a night without obvious reasons, for example, an increased amount of alcohol consumed at night, or taking diuretics.
This is not only an unpleasant problem that interferes with sleep and restoration of strength, but also an important symptom indicating a serious pathology of the body. The difficulty of treatment and full recovery lies in the fact that most people do not think about complications, they simply get used to it, adapting to nocturia. Although at the initial stage, almost any disease responds well to treatment.
Causes of frequent urination at night
In a healthy body, all processes slow down as soon as a person goes to sleep. This is due to the need to restore strength and stock up on energy.
The safest causes of frequent night urination are taking diuretics, antispasmodics, drinking alcohol, caffeine and other similar substances. In this case, nocturia is temporary and stops immediately after the cause is eliminated.
Doctors consider the following to be more dangerous development factors:
- Infections and other diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Injuries, surgery (adhesions) on the pelvic organs;
- Congenital and acquired anomalies of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system;
- Heart failure;
- Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine disorders;
- Slow blood circulation, blood microcirculation in the pelvic area;
- Obstructive apnea;
- Neurological, psychological and mental disorders.
In late pregnancy, women also experience frequent urges to urinate at night. This is due to the pressure of the growing fetus on the bladder. However, gynecologists advise not to neglect the symptom. Perhaps nocturia is caused by other pathologies, and pregnancy only provoked their development.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT WITH A UROLOGIST
Klokov Andrey Nikolaevich
Urologist-andrologist, doctor of the highest category
Make an appointment
The impact of sleep disturbance on physical health: increased risk of somatic diseases
It has been reliably established that the normal cycle of wakefulness and sleep ensures the stability of the homeostatic regulation of the autonomic, neuroendocrine and immune systems [24]. There are metabolic and endocrine changes in sleep-deprived healthy volunteers that are similar to those observed during normal aging. Accordingly, it has been suggested that chronic sleep loss may exacerbate the severity of age-related pathologies such as diabetes and hypertension [25]. Sleep also plays a role in regulating the immune system, as sleep deprivation has been noted to have a suppressive effect on the immune system. Loss of sleep also contributes to cardiovascular discomfort. Nocturnal complications can become factors of myocardial ischemia.
Types of nocturia
Urologists classify nocturia based on the cause of its occurrence.
Experts also identify the type of development: primary (due to pathologies of the genitourinary system) and secondary (due to problems with other internal systems).
In addition, urologists distinguish types of problems according to duration and course: temporary or permanent. Permanent is further subdivided into uncomplicated and complicated by other diseases.
Prevention
To prevent the development of polyuria, dysuria and other urological problems, it is recommended:
- observe drinking regime;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid hypothermia;
- establish a certain urination regime;
- use compression stockings on the lower extremities (at the first signs of venous congestion);
- perform exercises that strengthen the muscles of the perineum;
- promptly diagnose and treat inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- minimize the impact of stress and nervous tension - normalize work and rest schedules, do yoga or meditative practices, relax in nature and lead a quiet social life.
Ways to prevent nocturia
Consequences and complications
The safest consequence for a person suffering from frequent urination at night is lack of sleep and decreased concentration at work due to fatigue. In most cases, it is not possible to fall asleep quickly after going to the restroom, so a person is “robbed” of at least an hour in total from his total sleep time.
Due to urinary disorders, patients experience swelling of the face and limbs. In addition to an aesthetic defect, this brings problems with metabolic processes in the skin.
At night, it is difficult to fully maintain intimate hygiene, especially if the urge to urinate is frequent. Therefore, nocturia sometimes causes the development of urinary tract infections.
Due to problems in the body, the psyche suffers first of all: a person understands that a problem has arisen, but out of delicacy refuses to go to the doctor. For this reason, he becomes nervous, sometimes even aggressive, and depression develops. Insomnia often occurs against the background of nocturia, which further aggravates the problem. The sick person develops chronic fatigue and decreased immunity. There is a risk of developing endocrine disorders and cardiovascular problems.
Pathogenesis
Normally, an adult empties the bladder 4-6 times a day, and the volume of fluid can vary significantly from 100 to 400 ml, but most often it is 200-300 ml. In a healthy person, the ratio of daytime to nighttime diuresis is 4-3:1 and is no more than 30-40%, because during sleep the body’s blood pressure and all metabolic processes are significantly reduced.
Nocturnal polyuria can occur due to an increase in the volume of urine synthesis and the urge to urinate, increased renal filtration processes and bladder overactivity. People with heart failure experience stagnation of venous blood in the extremities and fluids in various tissues during the day, which is compensated by resting in more favorable conditions for the functioning of the cardiovascular system and the passage of fluids into the vascular bed to activate diuresis.
Disorders of urinary reflexes can be based on both neuropsychic disorders and somatic diseases, for example: latent form of diabetes , urinary tract obstruction, multiple sclerosis , parkinsonism , dementia , cirrhosis of the liver , metabolic disorders, etc. However, they are usually provoked by a disorder work and inflammatory diseases in the urinary system - chronic glomerulonephritis, nephrosclerosis , pyelonephritis, cystitis , etc.
Diagnostics
In modern urology, it is common to measure nocturia by its effect on the patient’s quality of sleep and life. For this purpose, international programs have been developed, including questionnaires. The sick person reads the statements presented and gives a rating from 0 to 5 next to each one - a criterion for the impact on his life.
For example, the patient must determine the following criteria:
- The need to sleep during the day;
- Degree of concentration during working hours and during active rest;
- Work process efficiency;
- Fear of worsening symptoms;
- Fear that they will find out about the problem.
Next, the urologist proceeds to examine the patient. He evaluates its appearance, then proceeds to visual diagnosis of the urethra and genital organs. Already at this stage, a urinary tract infection can be suspected.
Next, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests: urine, blood, and other biological fluids of the patient. During a urological or gynecological examination, smears are taken for microflora, bacterial culture and cytology.
However, a full picture of the state of health can be revealed only after instrumental diagnostics and functional tests:
- HUS (Hours of Uninterrupted Sleep) . The patient, connected to the equipment, falls asleep in the diagnostic room. The equipment determines the interval between the time a person falls asleep and the time he wakes up to urinate.
- Polysomnography . Experts determine the quality of sleep: assess muscle, cardiac and brain activity, and blood oxygen levels. The study is expensive, so it is rarely used. However, its indicators are informative.
- Actiography . Laboratory assistants put a special device on the patient’s hand, reminiscent of a modern smart watch. It records the position and movement of a person, determines the depth of sleep before waking up to go to the toilet.
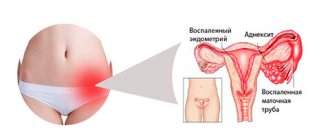
- Ultrasound of the pelvis . The study reveals possible abnormalities in the structure of the genitourinary system: enlarged prostate gland, proliferation of the endometrium, for example.
- MRI or CT . Indicates the exact localization of the pathological process.
- X-ray with contrast agent . Detects patency of the urinary tract.
Warnings
- Taking desmopressin acetate may be accompanied by hyponatremia. It should be noted that severe hyponatremia can be life-threatening and be accompanied by convulsions, coma, and respiratory arrest. In this regard, before starting therapy, it is necessary to determine the sodium level and then monitor the indicator during the first week and approximately a month after the start of treatment. Then monitor sodium levels periodically.
- In patients at high risk of developing severe hyponatremia (for example, patients with kidney disease, people taking loop diuretics or glucocorticosteroids) Noctiva should not be prescribed. Also, the drug should not be used in patients with congestive heart failure and uncontrolled hypertension, as fluid retention will lead to deterioration of well-being.
- Considering that the drug is available in the form of a nasal spray, in patients with allergic rhinitis or rhinorrhea, it should not be used until symptoms resolve.
- The most common side effects of therapy are: nasal discomfort, nasopharyngitis, nasal congestion, sneezing, increased blood pressure, back pain, nosebleeds, bronchitis and dizziness.
Source:
FDA News Release. March 2021.
Treatment of nocturia
Getting rid of the pathology and its consequences is possible immediately after eliminating the cause. Sometimes the patient adjusts the drinking regime and establishes proper nutrition, and the pathology disappears without a trace.
In more complex situations, urologists work in teams with other highly specialized specialists: cardiologists, endocrinologists, neurologists and psychologists. Doctors prescribe:
- Conservative therapy . With the help of medications and physiotherapeutic techniques, doctors eliminate urinary tract infections and normalize the functioning of the heart and pancreas.
- Radical treatment . It is required if the pathologies that cause frequent night urination do not respond to medications and other methods. For example, when the endometrium or prostate gland grows, the surgeon excises excess tissue and the pressure on the bladder stops. Using the same principle, severely affected tissues of the urinary system are eliminated.
After the treatment, you should definitely undergo a course of psychotherapy, as well as strengthen the body with the help of vitamin complexes and physical therapy. Exercises restore blood circulation in the pelvic organs, so the risk factors for developing nocturia disappear.
General information
Nocturia is a functional disorder of the urinary system, expressed in the need to wake up during the night, caused by the desire to urinate. Usually caused by an increase in nocturnal diuresis and its transfer from daytime to nighttime wakefulness, as well as a possible increase in hyperactivity and a decrease in the size of the bladder. It is also called nocturnal polyuria and is listed under the ICD-10 code: R35.
Interruption of sleep in order to empty the bladder can happen 2 or more times a night, then they talk about the phenomenon of nocturia . If the main sleep phase falls during the daytime and a person has to interrupt it due to little need, then such a deviation is also considered a manifestation of nocturia.
Nocturnal polyuria is a common urological problem. The excess of night diuresis (from 18:00 to 6:00) over daytime (from 6:00 to 18:00, respectively) is physiological and is usually observed up to 1-2 years, but most often this phenomenon is pathological in nature and is caused by the initial stage of cardiac decompensation, renal failure, urethritis, cystitis or cystopyelitis .
Depending on the stage of the disease, we choose one or more treatment methods:
Osteopathy
Soft technique of working with the spine, joints, muscles, ligaments, internal organs. Eliminates pain and starts the self-healing process.
Therapeutic massage, osteopathy, manual therapy
Helps bones and joints take the correct physiological position, relieves pain and spasms, relaxes muscles.
Acupuncture
Work on biologically active points. It affects the affected area and the body as a whole. Eliminates the cause of the disease and removes the symptoms.
In addition, according to indications, the following are used: taping, pharmacopuncture, FormTotix insoles, exercise therapy with an instructor and other methods. The choice of procedures depends on the current condition; taken together, they act faster and give a more lasting result.