Home » Hemorrhoids » Hemorrhoids in women - symptoms, treatment, prevention
Sign up for a consultation with a proctologist for the treatment of hemorrhoids for 3,500 rubles and receive a treatment prescription within 30 minutes for 1 appointment
Find out what day you need to make an appointment to get a consultation without a queue.
Experience 44 years 73 operations per month 876 operations per year 171 reviews Author of 73 scientific papers Has 9 patents 6,818 requests per month
Call
According to statistics, hemorrhoids are more common among females. Women are predisposed to the development of proctological diseases, so every third woman suffers from the appearance of hemorrhoids. The size of varicose veins increases, and inflammation of the rectal mucosa is observed.
Hemorrhoids form in the anus, the size of which rapidly increases if left untreated. Why do hemorrhoids develop in women? What are the signs of the disease?
Hemorrhoids: what are they?
Hemorrhoids are a severe and painful manifestation of hemorrhoids.
Depending on the location where the venous protrusion has formed, the hemorrhoidal node may be:
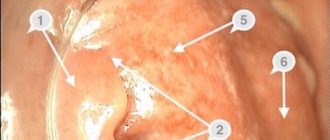
- Internal. In this case, the wall of a blood vessel grows in one of the high-lying sections of the rectum. The node enlarges, causing pain in the lower abdomen and constipation. When defecating, blood is noticeable, the anus swells and itches.
If at this stage the patient engages in heavy physical labor or lifts a load, the internal hemorrhoid may descend into the rectal (close to the anus) area or even fall out.
- Outer. The node grows outside, in the lower parts of the rectum. As a rule, the patient unmistakably feels the external hemorrhoidal node. During an examination, the doctor identifies it without difficulty. This type of growth bleeds profusely and also causes constipation, hard stools, and discomfort.
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids
An examination by a coloproctologist involves complex procedures, among which it is worth noting an examination of the rectum. Upon examination, external hemorrhoids can be identified, and by carefully spreading the edges of the external anal sphincter, internal nodes can be identified. Using a digital rectal examination, which should be carried out in all cases, except those when there is an exacerbation of the process, it is possible to establish the presence of compacted hemorrhoids, the tone of the anal sphincter, and identify concomitant diseases of the rectum. To establish that hemorrhoids have come out, the patient is asked to strain. The doctor must also perform a sigmoidoscopy. A thorough examination of the patient allows us to exclude anal fissure, paraproctitis, polyps and rectal cancer.
Reasons why hemorrhoids form
Hemorrhoids are a very common disease. Its manifestations can be found in every second person of middle and older age. However, there are special risk groups here too.
The main reasons why hemorrhoids form:
- weakening of the muscles and ligaments that keep the hemorrhoidal veins stable;
- tissue destruction as a result of vascular pathology;
- venous congestion. They are a consequence of sedentary work and a sedentary lifestyle, when intra-abdominal pressure and on the rectal area increases;
- work involving heavy physical activity. In this case, generalized varicose veins occur and blood vessels expand literally throughout the body. But the veins in the legs and rectal area are especially affected;
- frequent constipation and intense diarrhea. In both cases, the walls of the intestinal blood vessels become tense. And when you strain, intra-abdominal pressure increases. As a result of unstable stool, old hemorrhoidal cones may become inflamed and even fall out and new ones may form;
- anal sex, frequent enemas, douching and excessive anal hygiene. All this irritates the intestinal mucosa and forms nodes;
- unbalanced diet. Eating excesses disrupts stool cycles, creates an imbalance in the body and irritates the intestines. Provocative foods in this case are sweets, salty, spicy and heavy foods;
- smoking and alcoholism. Nicotine and alcohol cause a sharp narrowing of the blood vessels of the pelvis. As soon as the blood rushes to the spasmodic areas, it overflows and stretches them, forming nodes on the blood vessels;
- pregnancy and childbirth. An increase in intra-abdominal pressure provokes the fetus forming in the mother’s womb;
- heredity. This concerns the characteristics of metabolism, the structure of the circulatory system and blood vessels.
Causes of hemorrhoids in women
The causes of hemorrhoids in women can be different. The development of pathology is influenced by factors such as:
| Pregnancy and childbirth | 1. During pregnancy, the fetus develops rapidly, putting pressure on the woman’s internal organs. The body cannot function normally and weakens, which leads to the appearance of hemorrhoidal cones. 2. When pushing, pathology also often forms. This is due to the fact that the woman pushes, the soft tissues of the anus become irritated, and hemorrhage opens. Anal fissures appear, causing discomfort to the patient. |
| Poor nutrition | 1. With a poor diet, the risk of developing hemorrhoids is extremely high. Fast food, sweets, fried and smoked foods negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Products that promote fermentation of the body also negatively affect the condition of the abdominal organs. We are talking about cabbage, beans and other legumes. 2. If complaints arise, you should exclude these products from your diet and include plenty of fluids, vegetables and fruits, cereals, and broths. |
| Alcohol addiction and smoking | 1. Bad habits negatively affect all organs of the human body. Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages affects the mucous membrane of the rectum, leading to duodenal ulcers and chronic gastritis. Hemorrhoidal cones form inside and outside. |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 1. Diarrhea, frequent flatulence, constipation lead to the appearance of anal fissures and hemorrhoids. Intra-abdominal pressure increases, the integrity of soft tissues is impaired. 2. With constipation, feces stagnate in the body and become hard. In this regard, the woman experiences cramping pain in the intestines. Hemorrhoidal veins become inflamed. 3. With diarrhea, the patient is bothered by a frequent urge to defecate. The walls of the rectum become tense and their tone is lost. Injury to nodes is observed |
| Obesity | 1. People who are overweight are predisposed to developing proctological diseases. Their intestinal and stomach functionality is impaired. Unpleasant sensations constantly appear, which intensify after eating. Subcutaneous fat is deposited inside the body, making venous outflow in the rectum difficult. 2. Blood stagnates in the hemorrhoidal plexuses, which causes thrombosis and inflammatory processes. The elasticity of soft tissues deteriorates and they become thinner. The work of the sphincter and muscle tone is weakened. |
| Increased physical activity | 1. Lifting weights and physical work affect intra-abdominal pressure. The risk group includes gymnasts, athletes, salespeople, and builders. 2. Intense blood flow is observed, which affects the thinning of blood vessels and their wear and tear. |
| Passive lifestyle | 1. As a rule, office workers and drivers lead an inactive lifestyle. In such people, the functioning of the sphincter is disrupted, intra-abdominal pressure increases, which leads to loss of muscle tone. 2. Anal fissures form, which bleed before and after defecation. |
| Problems with the endocrine system | 1. Problems with the thyroid gland are often accompanied by hemorrhoids. Hormonal levels change, the body weakens. 2. Blood clots form. |
| Adolescence | 1. During puberty, many changes occur in a girl’s body. Chronic constipation or diarrhea and gynecological problems may develop. 2. Most females experience heavy bleeding during menstruation. Diets and sudden changes in diet negatively affect the condition of the esophagus. |
| Anal sex | 1. Regular sexual activity injures the mucous membrane and promotes necrosis of soft tissues. Attempts during sex lead to an inflammatory process and damage to the walls. 2. The abdominal muscles tense, the flow of blood into the pelvic organs increases. As a result, venous expansion is formed in the anus. |
| Spinal cord problems | 1. All internal organs in the human body are interconnected. If a woman has injuries associated with the spinal cord, then problems arise during bowel movements, muscle tone weakens, hemorrhoids rapidly enlarge and fall out of the anus. |
| Age-related changes | 1. In old age, the functioning of internal organs is disrupted. The connective tissues become weak and thinned, and varicose veins of the anus are observed. |
| Reduced immunity | 1. Proctological diseases often develop in people with reduced immunity. |
Psychosomatics in women can also affect the development of hemorrhoids. A person who is depressed or emotionally exhausted is more predisposed to the occurrence of proctological diseases than others. There is pressure in the abdominal organs, psychological trauma leads to constipation.
Degree of development of hemorrhoids
At the initial stage, the patient feels slight discomfort during bowel movements. Blood sometimes appears in the stool. At this time, it is enough to simply adjust your diet and devote time to light physical training. The initial stage is the best time to start treating hemorrhoids.
Further, the hemorrhoids enlarge and, in the case of external hemorrhoids, may fall out of the anus. This can happen with heavy lifting, bowel movements and physical activity. Since the size of the node is still small, after the end of the traumatic action it can be reduced on its own. Itching and burning increase, constipation and mucous discharge appear. The situation can still be corrected with conservative treatment.
At stage 3, hemorrhoids fall out even without physical exertion. Bleeding from the anus appears, the nodes become inflamed and acute pain occurs in the anus.
At the 4th stage of development of hemorrhoids, their size reaches 5 cm, they can fall out when moving, coughing, or passing gas. Bleeding is frequent and massive. Possible pinching and inflammation of the nodes.
Causes
The main reason for the development of internal forms of hemorrhoids is a violation of the inflow and outflow of blood in the cavernous (cavernous) bodies. In a healthy person, these corpuscles fill with blood when the intestines are filled with feces, which causes them to increase and makes it easier to control the urge to defecate. After successful bowel movement, blood flows out and the cavernous bodies shrink.
If the regulation of outflow is disrupted and the cavernous bodies are constantly in an increased size, then over time this leads to varicose veins and thinning of the venous vessels. The main causes of blood outflow disorders traditionally include the following factors:
Symptoms of the disease
If you suspect hemorrhoids, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Feeling that the intestines are not completely emptied. During defecation, internal hemorrhoids descend into the lumen of the rectum and are felt as a kind of obstacle and create a feeling of heaviness;
- Burning sensation in the anus. Inconvenience is not always associated with going to the toilet. Large hemorrhoids swell due to increased blood flow, which, in turn, provokes active secretion of mucus. Mucus accumulates, irritates the mucous membrane of the rectum and anus;
- Pain and bleeding during bowel movements. Feces injure the inflamed venous node, causing short-term pain. If the patient is prone to constipation, hard feces provoke pronounced discomfort. Over time, the hemorrhoid begins to bleed on its own, regardless of when the patient visited the toilet.
- As the disease progresses, hemorrhoids fall out or become pinched. Severe pain in the anal area occurs when moving or trying to sit down.
Internal hemorrhoids symptoms
In acute cases, the development of hemorrhoids is usually characterized by sharp pain that intensifies during the act of defecation. Also, the pain may intensify during long walking, when laughing, coughing and other tension in the abdominal muscles.
symptoms of internal hemorrhoids
Also, during defecation, you can detect an admixture of scarlet blood in the stool.
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis: photo
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node occurs if the disease is not treated and if you do not try to alleviate the course of the disease with symptomatic medications or diet.
With thrombosis, a blood clot forms in the vessels of the rectum. It partially blocks the blood flow, the node swells and increases in size. The patient constantly, regardless of the act of defecation, feels acute pain.
Symptoms of developing thrombosis:
- skin redness;
- increased body temperature above 38 degrees;
- pain of the node and greater density on palpation;
- increasing swelling, itching and burning in the anal area.
If the resulting thrombosis is not treated, the nodal structure is infringed. Necrosis of the node develops, the adjacent layers of the intestine and subcutaneous tissue begin to die. From this moment on, medical assistance must be provided urgently.
Is it necessary to treat stage 1 hemorrhoids?
To treat or not to treat hemorrhoids at stage 1 depends on the symptoms. If there is severe discomfort, itching, and blood appears during bowel movements, then it is necessary to treat. As a rule, treatment begins with the regulation of nutrition. To avoid constipation, you need to follow a diet: eat more fiber (fruits, vegetables, legumes, cereals) and maintain water balance; it is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day. Next, conservative treatment of hemorrhoids may be prescribed - topical medications, physiotherapy. If conservative treatment has no effect, minimally invasive non-surgical methods are used.
If you were diagnosed with stage 1 hemorrhoids during a routine examination, or the symptoms are so minor that they do not cause discomfort, there is no bleeding, and you feel well, then there is no need for treatment. After all, as we wrote above, the treatment of stage 1 hemorrhoids is symptomatic. It is necessary to adjust the diet so as not to provoke constipation, and maintain physical activity.
The main problem is that, having discovered such symptoms as blood, pain, discomfort in the rectum, people themselves diagnose themselves with hemorrhoids and begin to self-medicate. This is absolutely not worth doing! Besides hemorrhoids, there are many other diseases with similar symptoms. Because of the fear of visiting a proctologist, you can even reach the fourth stage of hemorrhoids, not to mention more serious diseases. Only a doctor at an appointment can make a correct diagnosis. Believe me, in fact, a proctological examination in modern clinics is absolutely not a problem that you need to worry about. In medical diagnostics, diagnostics are carried out absolutely painlessly, using local anesthesia, in the most comfortable conditions for the patient. As for the treatment itself, several painless procedures may be required.
Take care of yourself, do not advance the disease, because treating hemorrhoids in the early stages is always easier and faster.
Treatment of hemorrhoids
The initial stage of the disease can be easily cured with the help of rectal suppositories and anti-inflammatory ointments. In consultation with your doctor, you can practice folk remedies and sitz baths.
At the second stage, the doctor prescribes vasoconstrictors, phlebotropic and painkillers. It is permissible to make lotions from medicinal herbs and microenemas. For bleeding, minimally invasive treatments are prescribed: installation of latex rings on hemorrhoids, photocoagulation and cryotherapy.
In the third stage, in addition to drug therapy, surgical intervention may be necessary: ligation or removal of nodes, the use of sclerosing techniques. Treatment will necessarily be comprehensive, including a special diet, strengthening of the pelvic muscles, normalization of physical activity and vascular tone. According to indications and subject to monitoring the blood condition, the patient is prescribed antiplatelet agents and thrombolytics, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal and hormonal drugs.
If there is an associated infection, antibiotic therapy is necessary.
The fourth stage of the disease involves long-term treatment. Most often we are talking about removing inflamed nodes or laser coagulation. Among the methods of surgical intervention:
- hemorrhoidectomy using the Milligan-Morgan method;
- thrombectomy;
- Longo's operation.
Reliable remission is possible only when the patient begins to lead a healthy lifestyle, provides himself with sufficient physical activity and revises his diet in favor of healthy, minimally processed foods.
Features of therapy
Treatment of the pathological process requires a thorough approach:
- begin at the first appearance of symptoms;
- be comprehensive;
- include both medications and changes in the patient’s usual lifestyle.
Only fulfilling all the conditions will help you recover and forget about the problem.
Diet food
Hemorrhoids are caused by poor circulation and weakening of blood vessels. The disease requires exclusion from the daily menu:
- acute;
- smoked;
- fried food;
- alcoholic drinks.
The patient should reduce the amount of salt consumed. The menu should contain coarse fibers and plant fiber supplied from vegetables, fruits, and cereals.
Pills
Complex therapy involves the use of drugs that strengthen the vascular walls, helping to stabilize local blood circulation and facilitate lymph outflow. Popular means include:
- Detralex - reduces the distensibility of venous vessels, increases their tone, strengthens the walls, prevents fragility, use 2 tablets. per day, in the acute phase - up to 6 units per day;
- Glivenol is an angioprotector and microcirculation corrector;
- Rutoside - affects capillaries, suppresses swelling, strengthens blood vessels.
The attending physician is responsible for selecting the appropriate medication.
Candles
They are used for local effects on pathology, treatment is carried out with Relief, Ultra-Proct, Aurobin, etc. The active components of the drugs stop the inflammatory process, relieve obsessive itching and tissue swelling. Due to the drugs, damaged tissues are restored, they have a local hemostatic spectrum of action.
During pregnancy and the development of hemorrhoids, taking any medications should be justified. Medicines must meet safety criteria; preference is given to options with a natural base:
- with sea buckthorn - the element effectively reduces inflammation, relieves redness, swelling, pain, has an antibacterial spectrum of action, and at the same time increases immunity;
- with propolis - the ingredient helps improve local blood circulation, suppresses itching, soreness, and affects areas of inflammation.
Both products are considered harmless, but require prior consultation with a proctologist and permission to use them. During pregnancy, the most harmless medications can cause unusual reactions.
Disease prevention
Heredity in our case is not a decisive factor. And even if you do heavy physical work, or are planning a pregnancy, the risks of hemorrhoids can be minimized.
For this:
- improve bowel function. Bowel movements should be regular, preferably twice a day;
- ensure active blood circulation. The best tool for this is physical activity. Don’t sit too long and don’t stagnate, choose active walking, running and simple physical therapy exercises;
- Maintain hygiene of the perineum and anus.
How to treat external hemorrhoids in men
To treat external hemorrhoids in men, conservative treatment methods are used in most cases. Medications can relieve the patient from painful syndromes and complications. Medicines help normalize blood circulation, increase the firmness and elasticity of veins.
External hemorrhoids are removed in critical cases. We are talking about the third and fourth stages of proctological disease. Held:
- laser coagulation,
- latex ligation of hemorrhoids,
- sclerotherapy using special drugs that are injected into the anus.
Each patient is assigned individual treatment. The duration of rehabilitation and treatment depends on the patient’s condition and the size of the hemorrhoids.
A popular method of treating hemorrhoids in men is called cryodestruction. The affected area is treated with liquid nitrogen. Ultra-low temperatures allow you to painlessly remove hemorrhoids in a short time. The tumors die and fall out on their own after a few hours. The advantage of this therapy is that it is bloodless and effective. Relapses occur extremely rarely.
Conservative method - medications for external hemorrhoids
The conservative or medicinal method is used mainly in the stage of exacerbation of external hemorrhoids, and is a set of measures designed to reduce symptoms, relieve inflammation and prevent the formation of blood clots. A number of dosage forms are used:
- tablets for oral administration with antithrombotic (phlebotropic), analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- external and local agents in the form of creams and ointments with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- rectal suppositories (used mainly in the presence of anal fissures).
All medications for external hemorrhoids are prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the existing symptoms and taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body. The most effective are gels and ointments with heparin, antibiotics, anesthetics and glucocorticosteroids - Proctosedyl, Posterisan, Aurobin and Hepatrombin. Applications with Heparin ointment and Vishnevsky ointment are also used.
Oral drugs with venoprotective and venotonic properties have also proven themselves: Detralex, Phlebodia 600, Venarus, Ginkor Forte, Axlezan A and Pilex. In case of exacerbation of hemorrhoids, it is possible to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin.