Lymphocytes - what are they, what are they?
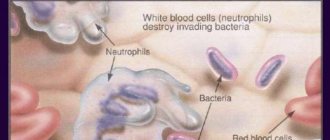
Lymphocytes are one of the components of white blood cells; a complete blood test for lymphocytes . They play an important role in the formation of immune responses. Their function is to recognize pathogens and mutated own cells. After identifying a foreign object, lymphocytes destroy it in one way or another: phagocytosis, production of special antigens. To destroy their own cells that have degenerated into cancer or have undergone other changes, lymphocytes send a special chemical signal that causes such a cell to start the process of self-destruction. In addition to a general blood test for lymphocytes, a biochemical blood test is performed at the MedArt Medical Center.
There are three types of these cells:
- T lymphocytes. They mature in the thymus. They play an important role in the fight against foreign bodies and infections. Some T-lymphocytes perform regulatory functions and are responsible for the duration and strength of the immune response. It is these cells that are affected when infected with HIV.
- B lymphocytes. Their main task is to produce antibodies against viruses and other infectious agents. In addition, they are able to retain information about past diseases, thereby creating permanent immunity.
- NK – cells. Their main function is to detect and eliminate body cells that have degenerated into malignant ones.
Lymphocytes are formed in the red bone marrow; their young, immature forms are called lymphoblasts. Maturation occurs in several stages, occurring not only in the bone marrow, but also in the lymphoid nodes and other organs of the lymphatic system.
The appearance of an increased number of lymphocytes can serve as a marker of bone marrow pathologies and the development of tumor processes in it. An increase in the level of lymphoblasts is also recorded during prolonged infectious processes. In this case, this serves as a sign of depletion of the body's defenses. The immune system does not have time to prepare a sufficient number of lymphocytes to fight the pathogen, and this becomes the reason for the appearance of a large number of lymphoblasts in the blood.
What is lymphocytosis?
The laboratory term reflects disturbances in the functioning of the body. He talks about activating defense forces to combat the invasion of alien agents:
- bacteria;
- viruses;
- protozoa;
- parasites.
Other prerequisites may be massive damage or cell death (extensive burns, necrosis), inflammatory processes, allergic reactions. Sometimes reactive immune processes are directed against the body itself (autoimmune diseases). The formation of tumors may be a prerequisite for lymphocytosis. In this case, the cells are produced, reach the pathogenic focus, but die as the destruction progresses.
Chronic lymphocytosis can be the result of diseases of the blood or hematopoietic organs, the lymphatic system. Protective bodies do not fully undergo the process of maturation and differentiation, which is why they do not cope with their functions. To restore balance, the bone marrow produces even more cells, but this is of little benefit.
Lymphocytes can accumulate in the blood if the process of their utilization in the spleen is disrupted.
What is important is not so much the fact of deviations in the analysis as its causes. The prerequisites for a shift in the leukocyte formula should be detected as quickly as possible. If the immune system malfunctions, the risk of developing chronic infectious diseases, autoimmune attacks, and the appearance and proliferation of atypical cells increases.
Indications for analysis
A general blood test for lymphocytes is prescribed if there is a suspicion of an increase or decrease in their number. The analysis can be prescribed for other reasons; it allows you to obtain a lot of valuable data about the state of the blood and the whole body. The main indications include:
- Detection of the immune response to the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.
- The state of human immunity.
- Physical and chemical composition of blood.
- Preventive analysis - to detect hidden changes in the blood formula that do not manifest themselves with specific symptoms.
Preparing for analysis
The analysis for lymphocytes is included in the general blood test, the rules for their conduct are the same. That is, such an examination does not require special preparation. There are only two conditions that must be met:
- Blood is taken in the morning.
- 8-12 hours before blood sampling you need to abstain from food.
You should also not smoke 2-3 hours before the procedure. Components of tobacco smoke can cause serious temporary changes in white blood cell levels. You should avoid drinking alcohol 2-3 days before taking the test, as alcohol can also affect the reliability of the results obtained.
If these requirements are not met, the accuracy of the examination may deteriorate, which will lead to the doctor receiving unreliable information and possible errors in diagnosis or re-prescribing the examination.
The role of lymphocytes in the body
Lymphocytes are round-shaped white blood cells (one of the groups of leukocytes) that our immune system produces to fight disease and infection.
Lymphocytes are divided into groups:
large and small components of a single protective barrier in the human body.
The first group is T and B cells, the second is NK lymphocytes or also called “zero” lymphocytes.
Types of lymphocytes
| Variety | Blood percentage | Functions |
| 1. B lymphocytes | 10-15% | The most important cells form the “memory” of the immune system. Every time B lymphocytes encounter pathogenic cells, they adapt to them and “record” this condition in “immune memory”. Thanks to them, vaccination becomes effective, and throughout life the body develops immunity and remains resistant to previous diseases. |
| 2. T lymphocytes | 80% | They are engaged in suppressing pathogenic viruses, bacteria, and fungi. |
| 3. NK lymphocytes | 5-10% | They are responsible for the destruction of their own cells, on the surface of which a marker of infection is detected. With their help, the body itself can overcome virus-infected and tumor cells. |
Research method
Material for analysis of lymphocytes is collected from a vein using a conventional syringe or a special vacuum system. The traditional technique of taking an analysis using a conventional syringe is currently outdated and can lead to the following difficulties:
- Blood clotting in a needle.
- Destruction of some blood cells.
- Long manipulation time.
- Contact of blood with the environment
- It is difficult to maintain the correct ratio of blood and reagents. In addition, the traditional technique does not exclude contact of medical personnel with the patient’s biomaterial, which can pose a health hazard. Therefore, many clinics use modern vacuum containers for blood collection.
Blood enters it due to the vacuum in the test tube; all parameters of the vacutainer are selected at the production stage in order to reduce the time for blood collection and ensure the correct ratio of the amount of reagent and blood.
Advantages of vacuum systems:
- A standardized blood collection process that takes minimal time.
- Contact of medical staff with the patient’s blood is completely excluded.
- Simple labeling and identification of samples, eliminating confusion with tubes.
- Almost painless procedure.
You can take blood for a general analysis from a finger, but at the moment this procedure is used much less frequently.
Norms
The normal level of lymphocytes in the blood depends on the age of the patient. In children, the number of lymphocytes is higher; over time, this figure gradually decreases. The number of these cells is influenced by the gender of the patient; in women the indicator is relatively higher. This is due to the greater activity and adaptive capacity of the lymphatic system of the female body.
| Person's age | Absolute content | Ratio in % |
| In a child under one year old | 2-12 | 45-71 |
| In a one-year-old child | 4-10 | 38-61 |
| 2-4 years | 3-9 | 34-50 |
| 4-10 years | 1,6-6,7 | 31-51 |
| 10-18 years | 1,3-5,3 | 31-43 |
| Over 18 years old, adults | 1-4,9 | 20-40 |
| Cancer risk for women: | 265 | 368 |
Lymphocytes are increased
The reason why lymphocytes are elevated is often a variety of viral infections. This increase is called lymphocytosis, and is most often recorded in diseases caused by viruses:
- Epstein-Barr.
- Adenovirus.
- Herpes.
- Childhood infections (rubella, measles, mumps).
The number of lymphocytes may increase with some bacterial infections, such as syphilis, whooping cough, or tuberculosis. Diseases caused by protozoa, such as malaria and toxoplasmosis, can lead to lymphocytosis. Often, an increase in lymphocytes is caused by helminthic infestations.
Lymphocytes may be elevated for reasons unrelated to infection. These include:
- Hypersensitivity reactions.
- Stress lymphocytosis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Disorders of the endocrine organs, especially the thyroid gland.
- Development of tumors and pretumor processes.
The most striking signs of an increase in the number of lymphocytes include:
- Enlarged liver, spleen, lymph nodes.
- General malaise, manifestations of respiratory infections, redness and swelling of the mucous membranes.
- A sharp increase or decrease in temperature, accompanied by chills.
- Dyspeptic symptoms - vomiting, stool disorders, nausea.
- Nervous system disorders due to elevated temperature.
It should be borne in mind that lymphocytosis does not always manifest itself through severe symptoms. Often, elevated levels of these cells are discovered by chance. Only a doctor can accurately determine the reason why a change in the blood formula occurred; this often requires additional tests.
To eliminate lymphocytosis, you need to cure the disease that led to an increased immune response. It is important to understand that the hematopoietic system responds to recovery with a certain delay. Even after complete recovery, lymphocytosis can persist for up to several months.
FAQ
The reasons why, most often, lymphocytes in women are slightly elevated
It should be understood that the norm of lymphocytes depends on the age of the woman, and a figure of about 40 is not a cause for alarm, since such indicators are the norm for adults.
Is there a relationship? When Lymphocytes are around 40-50 throughout the year and the temperature rises before menstruation.
Yes, it may be related. Such prolonged lymphocytosis may be associated with a chronic, active viral infection.
And on the eve of menstruation, the functioning of the immune system in women decreases, which can lead to the activation of chronic foci of inflammation with an increase in body temperature.
It is definitely advisable to conduct a more in-depth examination to clarify the cause of lymphocytosis and increased body temperature.
What does an increase in lymphocytes over 56 indicate?
A slight increase in the level of lymphocytes indicates that you have recently suffered a viral infection or that there is an allergic component to the allergen in the body.
It is advisable to repeat the blood test in a month. If lymphocytosis persists, take a blood test for Ig E
Reasons why for 6 months Neutrophils are reduced and Lymphocytes are increased.
Lymphocytosis is caused by the following infections: EBV, rubella, whooping cough, mumps, infectious hepatitis, cytomegalovirus, HIV, herpes simplex virus, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, brucellosis, syphilis.
It is recommended to be tested for IgM VCA antibodies to EBV and IgG to HIV 1.2.
Without other symptoms, an infectious disease specialist will not be able to recommend anything. If the tests are negative, then there is no need to worry further.
Reasons for increases in Lymphocyte and Basophil tests
Basophils are a type of white blood cells, or leukocytes. These cells are produced in our bone marrow and are part of the body's immune system.
Normally, the level of basophils is less than 1% of all leukocytes. A healthy range is 0 to 3 basophils per microliter of blood.
Basophilia is an abnormally high level of basophils in the blood. It is not a disease, but a condition that may indicate chronic inflammation in the body. Sometimes this condition means that too many white blood cells are being produced in the bone marrow due to a disease.
Reasons for increased lymphocytes and ESR
ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is an indicator that indirectly reflects the protein content in the blood plasma. An elevated ESR indicates possible inflammation in the body due to increased levels of inflammatory proteins in the blood. In addition, an increase in ESR occurs in anemia, malignant tumors, etc.
When platelets and lymphocytes are elevated
Platelets are responsible for blood clotting. If their level is low, the patient will not be taken for surgery - it will not be easy to stop the bleeding. At elevated levels, there is a high risk of thrombus formation—blood clots that block a vessel and cause a heart attack or stroke.
The level of platelets indicates the condition of blood vessels, and in combination with others helps to understand the nature of many diseases.
Why do Lymphocytes and Monocytes increase?
A monocyte is a representative of white blood cells. This is a fairly large cell, which has a large nucleus, slightly eccentrically displaced, and in our body it performs very important functions.
An increase in the level of monocytes is a normal reaction of the body during an infectious disease or inflammatory process. But often an excess of monocytes can also indicate pathology. To reliably establish the cause, it is necessary to carry out appropriate diagnostics.
Red blood cells and lymphocytes are increased, reasons
Erythrocytes are red blood cells, the most numerous blood cells. Formally, they are not cells, since during the process of maturation they lose many of the structures necessary for cells. For example, they lack nuclei and do not synthesize any protein molecules, unlike other cells in the body.
Red blood cells can be elevated due to many reasons, ranging from banal dehydration to erythremia - chronic leukemia.
Why does it happen that Lymphocytes are increased, and Leukocytes, on the contrary, are decreased?
Leukocytes are the most important cells of the immune system with a general name - white cells. White cells are produced by the bone marrow and are the body's main defender against various foreign microbes. Protection against microorganisms is not the only role of leukocytes; leukocytes also take part in metabolic processes and provide tissues with enzymes, hormones and other substances.
A low level of white blood cells in the blood is called leukopenia. This is not a disease, but a symptom that tells you: for some reason your immune system has weakened. This means you have become more vulnerable to diseases.
Lymphocytes are low
A decrease in lymphocytes is called lymphopenia. This condition is typical for the following diseases:
- AIDS.
- Long-term, severe infections.
- Bone marrow pathologies.
- Tumors of lymphatic tissues.
- Exposure to radiation.
- Taking certain groups of drugs, such as cytostatics.
- Pregnancy.
In most cases, a decrease in the level of lymphocytes indicates a depleted immune system, when the body, for various reasons, is unable to maintain the required level of these cells in the blood.
Lymphopenia rarely presents with characteristic symptoms. The most common signs of this condition include:
- Reduction or complete absence of tonsils and other peripheral lymph nodes.
- Skin diseases - eczema, pyoderma.
- Common signs of blood diseases are ulcers of the oral mucosa, petechiae, pallor, and jaundice.
- Enlarged liver and spleen.
As in the case of lymphocytosis, to normalize the level of these cells, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that led to the pathological condition. You need to see a doctor who can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
In the case of lymphopenia in pregnant women, with a moderate decrease in the level of lymphocytes, there is no need to take special measures. Enhanced monitoring of your health status and regular completion of all necessary examinations is sufficient. If there is a sharp drop in lymphocytes, you should seek medical help for additional diagnostics.
Oncology
With any cancer, the number of leukocytes in a person’s blood increases, most often due to young forms.
An increase in lymphocytes in the blood always indicates the presence of some kind of inflammatory process in the human body; an experienced specialist, based on the results of the analysis of everything, may suspect certain diseases and prescribe additional studies.
With the development of oncology in the body, a general blood test usually shows that the level of lymphocytes and leukocytes is increased, at the same time, hemoglobin is decreased, and the ESR is higher than normal.
Lymphoma in women
Lymphoma is a malignant tumor of immune cells. With it, lymphocytes increase significantly, divide uncontrollably and affect the lymphatic system:
- lymph nodes,
- Bone marrow,
- thymus gland.
Lymphoma differs from other oncological diseases by dissemination throughout the body: with the flow of lymph, degenerated malignant cells enter the internal organs and critically disrupt their functioning.
The disease is asymptomatic for a long time, and when it begins to manifest itself, the entire body is often already affected.
Most lymphomas are characterized by a progressive course and high malignancy with metastasis. However, if they are detected early, the favorable prognosis reaches ~90% .
If the disease manifests itself only as enlarged lymph nodes, doctors call this condition “small lymphocyte lymphoma.”
Causes of lymphomas
A single causative factor for the development of the disease has not been identified. At the moment, scientists believe that the pathological process is triggered by a complex of reasons.
These include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- regular contact with toxins and carcinogens;
- herpes virus, hepatitis, Helicobacter pylori and other infectious diseases;
- autoimmune and immunodeficiency conditions;
- recurring pneumonia;
- immunosuppressive therapy after kidney transplantation, stem cell transplantation, etc.;
- surgery to insert breast implants (presumably).
If the patient’s blood levels: increased leukocytes, decreased hemoglobin and platelets, then a diagnosis of “chronic lymphocytic leukemia” is made.
When a morphologist issues a conclusion based on the results of a study of a lymph node, the diagnosis is sometimes written with a slash, especially since the prognosis and treatment for these diseases are the same.
A more accurate diagnosis is made by the attending physician based on the completeness of the patient’s tests.
Symptoms of elevated lymphocytes
There are several symptoms that indicate elevated lymphocytes.
Among them:
- Enlarged lymph nodes, spleen and liver;
- External signs – nasal infections, hyperemia of the oral mucosa, relatively low level of general condition;
- Symptoms of respiratory tract disease;
- A sharp decrease or increase in body temperature, accompanied by chills and general exhaustion;
- Bowel dysfunction, nausea, constipation and diarrhea;
- In children - characteristic paroxysmal vomiting;
- General disorder of nervous activity, insomnia, severe enlargement of the tonsils against the background of a rise in temperature to 40 °C.