What are neutrophils
Blood Basics neutrophils are one of the types of leukocytes, white blood cells, thanks to which the body fights all kinds of infections. Moreover, this type of blood cells is the most numerous.
Up to 70% of the Blood Basics of all leukocytes in the human body are neutrophils.
Doctors call them immediate response cells. Having discovered a virus or bacteria, neutrophils rush to attack with lightning speed. Even if it means leaving the bloodstream and going into the tissues of the body.
The more clearly the immune system perceives a threat, the more neutrophils are produced in the bone marrow and the higher their level in the blood.
Normal in blood
Neutrophils are the most numerous cells of all types of leukocytes: their share is from 50% to 70% of all white blood cells.
If you look at the test form, you can see their different designations due to the fact that when counting, neutrophils are divided into band (not fully mature) and segmented (fully mature). The norm of segmented leukocytes in the blood of women is the same as that of men, and is 1500 – 8000 units/mm3. The determination of low segmented neutrophils in the blood of a child differs from the norm in an adult. The lower norm for children aged 2 weeks to 1 year is 1000 units/mm3. But after a year, this norm becomes like that of an adult.
It should be noted that the count of leukocytes strongly depends on the type of equipment (ie hematology automatic analyzers) on which the count is carried out. Therefore, segmented neutrophils, the norm of which is measured on different equipment and in different laboratories, should always be compared only with those values that are printed on tests in the laboratory.
Why are neutrophils elevated?
The most common Neutrophilic Leukocytosis and the most obvious cause of neutrophilia is infection. The number of neutrophils increases more noticeably and most often with bacterial What are the causes of neutrophilia in leukocytosis? diseases.
However, other reasons can also lead to an increase in the level of neutrophils in a blood test. What are neutrophils and what do they do? :
- Serious injuries. For example, fractures, burns, complex surgical operations.
- Inflammatory diseases. These include colitis and other intestinal inflammations, vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), hepatitis (inflammation of the liver).
- Taking medications. For example, based on corticosteroids.
- Pregnancy.
- Obesity.
- Emotional or physical (related to overexertion) stress.
- Some types of cancer. For example, leukemia. It affects the bone marrow, which produces blood cells. And may increase neutrophil production.
Normal indicators
There is a leukocyte formula that allows you to assess the condition of the blood and the body as a whole.
The table shows the indicators of a healthy person:
| Index | Normal values |
| % | x10 9 /l | |
| Band neutrophils | 42887 | 0,04-0,3 |
| Segmented neutrophils | 45-72 | 2-5,5 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5-5 | 0,02-0,3 |
| Basophils | 0-1 | 0-0,065 |
| Monocytes | 43042 | 0,09-0,6 |
| Lymphocytes | 19-37 | 1,2-3 |
What are segmented neutrophils responsible for? For the immune response during a bacterial infection.
Of the total number of neutrophils in the blood, 45-72% are cells with segments in the nucleus. This is an indicator of the norm.
It varies depending on several factors:
- Segmented neutrophils are reduced
- The age of the person. In newborns, the indicator may be at its maximum level. During the first month of life, a decrease occurs down to a minimum percentage of immature cells. When a child reaches 6-7 years of age, the number of segmented neutrophils stabilizes. The immune system is strengthened. After 7 years, the norm of mature elements in a child coincides with the indicators of an adult.
- Absolute indicator. In some cases, a value is taken into account, which is calculated by the number of mature cells per microliter of blood. The norm for an adult is 1800-6500 neutrophils.
- Temporary factors. Mostly, deviations occur in children. A decrease and increase occurs after vaccination, during teething.
In other cases, deviations from the norm are a sign of an inflammatory process.
Primary sources of increase in indicator
High levels of elements indicate the presence of injuries and many diseases. Sometimes the source of changes is a bacterial infectious process of a focal or generalized subspecies.
The root causes of increased indicators are presented:
- infectious lesions of the upper respiratory system in the form of pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis;
- pneumonia, kidney pathologies;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- abscesses, boils, other purulent-inflammatory foci at the local level;
- measles, chicken pox, mumps, rubella, and other viral diseases;
- oncological processes;
- hormonal therapy;
- infections with bacterial etiology, including tuberculosis, dysentery, anthrax, cholera;
- toxic poisoning;
- tissue necrosis - with gangrene, burn disease, myocardial infarction;
- organ injuries, fractures, damage to the dermis in the form of abrasions, cuts;
- gout, septic lesion.
Increased cell content can be provoked by regular consumption of canned food. The problem is associated with products that do not contain living bacteria, but contain toxic residues of their vital activity.
Functions of neutrophils
The doctrine of immunity is constantly evolving and becoming more complex. The role of each type of leukocyte cell is clarified. Some are “scouts”, others retain the memory of the attack by a foreign agent and “train” young cells.
Segmented cells, together with lymphocytes, are responsible for the direct organization of the “attack” and participate in the “fight” with pathological organisms both in the blood and in tissues.
Beginning of the attack: the neutrophil draws in an unclear object
What is important is their ability not only to “swim” along the bloodstream, but also to release their own “legs” and move towards the lesion with amoeba-like movements (flowing from one part to another).
The neutrophil, approaching the source of infection, envelops the bacteria and destroys them. In this case, it dies itself, releasing a substance into the blood that attracts help from other cells to the focus. Millions of leukocytes die in a purulent wound. Dead cells are found in the discharge.
- Band neutrophils: normal in the blood, reasons for increase and decrease
Neutrophils have a special preference for bacteria, but they practically do not touch viruses. Therefore, in a blood test for any acute bacterial infection, an increased number of segmented cells is detected.
By the number and percentage of neutrophils, viral and bacterial infections can be distinguished. Any deviations from the norm indicate important disorders in the immune system.
Sources of reduced performance
A drop in the level of cells in the blood is called neutropenia; its main sources include various diseases or drug therapy using certain drugs. The root causes of low neutrophil levels are:
- hepatitis of viral etiology, influenza, mononucleosis, typhus;
- pathologies of the autoimmune type - systemic vasculitis, Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis;
- radiation damage, leukemia, anemic conditions of various origins.
Neutropenia is provoked by medications, a wide group of drugs is represented by:
- NVPS;
- antibacterial, thyreostatic;
- antimalarial, antiviral drugs;
- means to lower blood sugar levels;
- sulfonamides, cytostatics.
When treating with these medications, regular monitoring of the blood picture is necessary. Laboratory tests are prescribed by the local physician.
If segmented neutrophils are reduced
Segmented neutrophils are low in a condition called neutropenia. Detection of a level in the leukocyte formula below normal (47% or less) requires counting the absolute number of cells.
The usual norm is from 1500 to 7000 cells per mm3 of blood plasma (1.5 - 7.0 x 103 cells/mm3). The decline occurs:
- for diseases of the blood and hematopoietic organs;
- the use of chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with cancer;
- treatment with antiviral drugs;
- long-term exposure to viral infection;
- severe allergic reactions;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- as a result of genetic mutations.
Neutropenia can be temporary, manifesting itself in low numbers in the first 3 to 4 days when suffering from influenza or adenoviral infections. A reduced level of segmented neutrophils is found in 95% of patients undergoing treatment with the well-known antiviral drugs Interferon and Ribavirin.
It is important to promptly identify severe neutropenia and diagnose its cause.
- A decrease in granular neutrophils to 500–1000 cells per 1 mm3 is considered moderate.
- If the number of cells is below 500, then the form of the disease is severe, it is accompanied by a breakdown of all protective reactions.
“Over the counter” does not mean safety, quite the contrary.
Clinically, it manifests itself as pneumonia, severe ulcerative stomatitis, inflammatory diseases of the ears, and a septic condition as a complication of a common infection.
Various scientists have identified 20 to 30% of the adult population who have persistent neutropenia without other blood changes. These people do not have any symptoms of disease. This is usually reflected in the outpatient card. Patients should be aware of their peculiarities and warn the doctor.
Another normal variant is cyclic neutropenia. It is found in human blood repeatedly with intervals from several weeks to two months. At the same time, the level of monocytes and eosinophils increases. Changes return to normal on their own.
Structure
Leukocytes are divided according to their structure into granulocytes, which have pinpoint granules in the plasma, and agranulocytes, without additional inclusions. Unlike red blood cells and platelets, these cells are endowed with a nucleus and are able to exit blood vessels and move towards inflamed tissues.
There are two neutrophils in the center, their nuclei are divided into parts (segments)
Granulocytes differ in relation to staining using the Romanowsky method for basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils.
The group of neutrophils is also not homogeneous: according to the shape of the nucleus, they are divided into segmented (the nucleus is divided into parts by constrictions) and rod-nuclear (the nucleus has the shape of an elongated ball).
In the normal blood composition of an adult, the level of segmented neutrophils is 47–75%, and band neutrophils are only 1–6%. “Rods” are considered the precursors of nuclear division; their small number is normally explained by the rapid process of transformation into a segmental, more mature form.
If you are interested in the norms of this indicator in children and the reasons for their deviation, we recommend reading this article.
General information
Neutrophils are the main type of white blood cells found in the bloodstream. They account for approximately 48-73% of all leukocyte units. A small percentage consists of functionally immature, young leukocytes that do not have a nucleus characteristic of mature cellular structures - a band type of neutrophil.
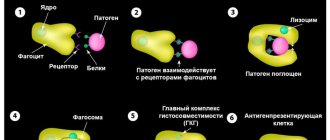
Cells are able to actively move, go beyond the bloodstream, and travel to areas susceptible to inflammation or damage. Neutrophils are macrophages designed to capture and digest small solid particles. After completion of the procedure, the elements die, resulting in the release of biologically active substances, which subsequently infect fungal and bacterial pathogens.
The structure of the cells contains a special enzyme that leads to the formation of an antibacterial agent. Dead neutrophils, together with other elements and individual microorganisms, degenerate into a purulent mass.
Leukocyte units are of great importance for protecting the body from fungus and bacteria. They play a lesser role in the fight against viral agents. They are powerless against helminths and the development of tumors.