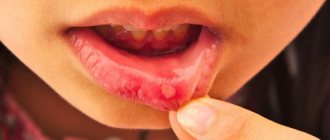
Statistics say that every second woman has suffered from thrush at least once in her life. This is not surprising, since the causative agent of the disease, a fungus from the genus Candida, is always present on the mucous membranes of the vaginal area. The disease (candidiasis) develops when optimal conditions are created for the life of the fungus, and its population rapidly increases.
Candidiasis is a common disease
Classification
The Candida family includes about one and a half hundred species of fungi. Of these, 20 species are capable of living in the human body. In 90% of cases, the disease is caused by fungi of the Candida albicans variety.
Candida is transmitted:
- during primary infection - during childbirth or during the first year of life;
- in case of secondary infection - during intimacy (almost 100% probability), through contact and household contact (underwear, household items, food).
If the word “Candida” appears in your test results, do not rush to the pharmacy. The main thing is not the presence of the fungus, but its concentration and the presence of signs of disease. Thrush manifests itself:
- in women - in the form of vulvovaginitis (colpitis);
- in men - in the form of balanoposthitis.
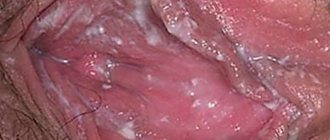
The main signs of thrush in women:
- itching, burning, irritation, swelling, redness of the mucous membranes;
- curdled discharge from the genitals, the smell of the discharge is sour milk;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- burning when urinating.
If the disease is diagnosed in one “half,” everyone needs treatment. Therapy “one at a time” does not make sense - all the fungi will come back after the first intimacy.
You should not have sex until the thrush is completely cured. If the disease is diagnosed in your sexual partner, and the symptoms do not bother you, you will still have to be treated.
The main signs of infection with Candida fungus in men:
- itching, burning sensation;
- redness, swelling of the head, foreskin, whitish coating;
- pain during intercourse.
Candida is diagnosed in women and men
Candidiasis is diagnosed by:
- external signs;
- results of bacterial culture of smears from the vagina and urethra;
- PCR.
How to cure thrush in a woman?
Candida loves warm, moist places with minimal air access, so the fungus is more than comfortable on the vaginal mucosa. To get rid of an unpleasant neighborhood, you need to use the following drugs:
- local action: vaginal suppositories, tablets, creams with econazole, clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole (Clotrimazole, Pimafucort);
- systemic action: tablets, capsules with fluconazole, itraconazole (Nystatin, Fluconazole, Difluzol, Diflucan);
- drugs to strengthen the immune system, probiotics, symbiotics (Wobenzym, Lactovit, Dactiale, Derma-Pro, Vagilak, Viferon).
Untreated disease spreads quickly
On average, the course of treatment takes from 3 to 6 days. Fungal spores mature within 20 days, so a second course of treatment may be necessary. Some medications (such as Betadine) can be used during menstruation.
In 20% of cases, the treatment prescribed by the doctor does not help. If thrush continues to bother you after a week:
- This is not candidiasis. You will have to retake tests and undergo additional examinations.
- the disease is not caused by Candida albicans, but by another type of fungus that is more difficult to destroy;
- this is a relapse that is possible with diabetes, during antibiotic therapy, or reduced immunity.
If relapses of candidiasis occur more than 4 times a year, the doctor will prescribe preventative treatment.
Chronic and recurrent candidiasis requires lifestyle changes
Topical medications can cause inconvenience - leaking and staining clothes. So that they are evenly distributed over the surface of the vaginal mucosa and do not cause discomfort, it is best to use them before bed. Suppositories and tablets should be placed approximately in the middle of the vagina. Medicines placed too close will leak out, and if placed too far away they can injure the delicate cervix.
If you have thrush, douching and other methods of “washing there” are prohibited, as this causes an imbalance of the microflora.
VK Clinic
Clinical symptoms of VK are nonspecific and may be associated with other vaginal diseases, including bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. A distinctive feature of the symptoms is itching and burning. In some cases, dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse) and dysuria may develop.
In vivo studies have shown that imidazole antifungals (miconazole and clotrimazole) are less effective in treating non-albicans Candida species. Thus, C. tropicalis and C. glabrata are 10 times less sensitive to miconazole than C. albicans.
How to cure thrush in a man?
Help to overcome candidiasis:
- locally - creams with clotrimazole;
- systemically – fluconazole (drugs Fluconazole, Diflazon, Forkan, Medoflucon, Mikosist).
The duration of the average course of treatment is 5 days.
During treatment, underwear and towels should be changed daily. Hygienic procedures are carried out using products without fragrances or additives. Despite the fact that most drugs are used topically, alcohol should not be consumed during treatment.
Men are prescribed drugs of local and systemic action
How to avoid relapse of candidiasis?
Candida is an opportunistic microorganism that is usually present in the microflora of intimate areas. In order not to provoke its excessive reproduction again:
- strengthen your immune system;
- do not wear tight synthetic underwear;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- take enough vitamins, reduce the amount of fast carbohydrates;
- reduce the amount of foods and drinks that contain mold and yeast;
- use contraception;
- avoid stress.
During treatment for thrush, you will have to adjust your diet
Regardless of lifestyle, thrush can develop:
- when hormonal levels change (pregnancy, taking birth control pills, endocrine diseases);
- after operations;
- as a result of antibiotic therapy;
- during serious illnesses;
- with vaginal dysbiosis;
- after hypothermia.
Side effects
Diflucan 150 mg® has a favorable safety profile, possible adverse reactions:
- headache;
- fainting or seizures;
- changes in taste sensations;
- nausea, abdominal pain and flatulence;
- skin rashes;
- liver damage;
- allergic reactions;
- blood composition disorders.
Therefore, if you discover characteristic signs of the disease, do not rush to prescribe Diflucan 150 mg® against thrush without consulting a specialist! The dosage, frequency of administration and duration should be determined by the doctor after studying all objective data.
The effectiveness and safety of Diflucan 150 mg® have been well studied, and the possibility of using the drug for treatment in children and the elderly has been confirmed (4).
What happens if thrush is not treated?
Untreated thrush can lead to serious problems.
The diagnosed disease must be treated. Despite the fact that Candida fungus is an opportunistic microorganism, the body needs help to cope with overgrown colonies and neutralize the consequences of their vital activity. Untreated disease:
among women:
- will reduce immunity, resulting in the development of secondary sexually transmitted infections;
- will provoke erosion of the mucous membrane;
- disrupts the menstrual cycle;
- will cause inflammation of the cervix.
for men:
- will lead to prostatitis, vesiculitis, which can cause infertility.
Causes
Factors that can trigger the development of candidiasis are conventionally divided into three categories:
- Exogenous factors - the environment facilitates the penetration of harmful
- microorganisms:
- increased levels of fungi in the air under production conditions;
- temperature conditions that cause excessive sweating;
- improperly observed hygiene regime.
- Endogenous factors – a decrease in the body’s resistance due to the occurrence of:
- vitamin deficiency;
- metabolic diseases such as obesity, dysproteinemia, ulcerative colitis, diabetes mellitus, dysbacteriosis;
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- infectious chronic processes;
- vegetative dystonia with increased sweating;
- neoplasms;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- diseases of the blood system, etc.
How to cure thrush during pregnancy?
Statistics say that Candida fungi are detected in 80% of expectant mothers. Before giving birth, you must say goodbye to them. If this event is postponed until later, the baby will become infected during childbirth. Transmission of the fungus is also possible after - during feeding or hygiene procedures. This is fraught with thrush in the mouth, in girls - on the genitals, and a series of subsequent problems with the baby’s health.
To treat expectant mothers, gynecologists prefer to use topical medications - suppositories, tablets, creams. Suppositories Pimafucin and Primafungin can be used in any trimester of pregnancy, Terzhinan tablets - in the second. Systemic drugs are prescribed if the disease cannot be cured locally. Only the doctor prescribes medications and outlines the treatment regimen, depending on the clinical picture; amateur activity is unacceptable here.
Self-medication of candidiasis is unacceptable
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of vaginal candidiasis is carried out as follows:
- Microscopy of a smear test for thrush: a scraping is taken from the vaginal walls with a special swab onto a glass slide for further examination under a microscope. If there is an infection, Candida fungi will be present in the smear.
- Sowing - growing a culture of fungus from a smear scraping for analysis for thrush. Candidiasis is only diagnosed when fungal colonies grow to 10,000 CFU/ml, since in most women they are always present in the vagina.
- Determination of the type of Candida fungi and their sensitivity to medications.
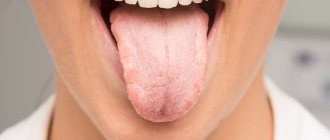
How to cure oral thrush?
Since Candida fungi live on all mucous membranes, they can cause diseases in the oral cavity. Characteristic features:
- redness of the mucous membrane, swollen palate, gums, throat;
- “geographical” language - the surface is covered with whitish dots, later - with spots shaped like a circle or oval;
- painful swallowing;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth, which quickly become covered with a cheesy coating. The redness increases in size;
- temperature increase;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Untreated candidiasis moves from the tongue to the cheeks, then to the lips and throat. When you try to scrape off the plaque, blood appears.
Candidiasis of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is diagnosed visually (at advanced stages), based on the results of bacterial culture and laryngoscopy. When treating children, drugs are selected taking into account their age category.
Candida fungi can even live in the mouth
Thrush in the mouth is especially dangerous for infants. Discomfort in the oral cavity causes them to refuse to suck, which is why dehydration and exhaustion quickly develop. A fungal infection can spread to other vital organs - the intestines, lungs, etc. Girls develop vaginal candidiasis, which provokes inflammation and the development of synechiae.
Advanced thrush threatens the baby's life
To overcome the disease at the initial stage, it is enough to treat the oral cavity and affected areas with an antiseptic solution (for example, Miramistin, Hexoral, Maxicold) and an antifungal drug (for example, Candide, Nystatin). You can rinse your mouth with a soda solution. At more severe stages, systemic drugs are used - Fluconazole, Mikosist, Fucis, Diflucan. Lips and skin can be treated with antihistamines (Fenistil). Avoid contact with mucous membranes (eyes, nose, mouth).
Untreated fungus colonizes the palate, esophagus, lungs, and other organs
During the treatment period, reduce your consumption of sweets, avoid smoked foods, spicy, salty foods, foods containing yeast, and mold.
Do not under any circumstances lubricate the affected areas of the mucous membranes and skin with rose jam. This promotes the growth of fungal colonies.
Treatment of all types of thrush should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Strengthen your immune system, follow the recommendations of nutritionists, use contraceptives, and most likely you will not face an unpleasant neighborhood. Be healthy!
Sources
- Bogomolova, N.S. Candidiasis in the surgical clinic: species composition of pathogens, sensitivity to antibiotics, preventive therapy / N.S. Bogomolova [and others] // Anesthesiology and resuscitation. - 2011. - No. 5. - pp. 43-48;
- Voznesensky, A.G. Clinical pharmacology of antifungal drugs / A.G. Voznesensky // Gedeon Richter in the CIS. - 2001. - No. 2(6). - pp. 50-53;
- Volosach, O.S. Method of combined immunotherapy for patients with chronic inflammatory diseases complicated by candidiasis: instructions for use No. 084-0909: approved. 09.17.2009 / Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus; comp. O.S. Volosach, V.M. Tsirkunov, S.B. Poznyak, S.M. Deshko.
How to treat thrush (gynecologist L. Shupenyuk answers)
How to cure thrush in women and men. Simple tips. Effective means
Contraindications
You should not take Diflucan 150 mg® if you have thrush:
- if there is increased sensitivity to the components of the drug;
- simultaneously with taking certain medications to regulate heart rate;
- pregnant and lactating women.
There are also a number of other contraindications. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will decide on the advisability of taking the drug.
Bibliography:
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis: clinical picture, diagnosis, principles of therapy. V.N. Prilepskaya, G.R. Bayramova, M.: Geotar-Media, 2010, p. 80; https://www.rmj.ru/articles/ginekologiya/Vulyvovaginalynyy_kandidoz_sovremennyy_vzglyad_na_problemu/
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015(June 5);64(RR-03):1-137. available on June 29, 2017 at https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/candidiasis.html
- Sobel, Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet 2007, 369: 1961-1971.
- Instructions for medical use of the drug Diflucan® P NO 13546\02
- Source of the article: https://www.diflucan.ru/molochnitsa/lechenie