Simple medical procedures
Compress is an ancient healing procedure, first described by Hippocrates. They are medicinal multi-layer dressings that act as a distracting and absorbable agent. Based on the nature of the effect, this procedure is divided into several main types: cold (lotions), hot, warming and medicinal compresses.
Photo: Yandex.Pictures
If the procedure is painless, then you can love it and not cry! Compress is one of the most favorite therapeutic procedures for children!
The compress is a multi-layer medicinal bandage that acts as a distracting and absorbable agent. By the nature of the action it can be cold and warming.
Applying a cold compress
A cold compress is nothing more than a wet lotion.
As a result of the action of the lotion, local cooling occurs, and as a result, spasm of the blood vessels of the skin and internal organs adjacent to this area. The inflammatory process and traumatic swelling of tissues are limited, and bleeding is reduced.
Wet cold lotions are first aid in the first hours for bruises, nosebleeds, hemorrhoids and elevated body temperature.
The procedure is quite simple. You need to roll up a piece of soft natural fabric several times, moisten it with cold water and apply it to the appropriate area of the body: the bridge of the nose, forehead, bruised part of the body.
Photo: Yandex.Pictures
The only drawback of the cold lotion is that it quickly reaches body temperature. Therefore, cold lotions need to be changed very often, literally every two to three minutes.
Applying a warm compress
The heat generated by the warming therapeutic bandage causes local dilation of blood vessels. Due to this, blood circulation in the tissues increases and metabolism accelerates. During the inflammatory process in this area, the use of a warming bandage has an analgesic and absorbable effect.
Warming compresses are used to dissolve accumulations of blood and lymph in tissues, for example, after injections. This type of treatment is excellent for treating muscle and joint diseases.
Contraindications to the use of a warming compress are skin lesions, purulent skin diseases, and boils.
How to make a warm compress
A wet hot therapeutic bandage is used to resolve areas of local inflammation.
The warming compress consists of three layers. The bottom layer is gauze soaked in a hot medicinal solution, folded in several layers. You can also use any cotton fabric.
A piece of waterproof material (oilcloth, plastic film larger than the first layer) should be placed on the bottom layer.
The top layer is a thick layer of cotton wool or woolen fabric. This layer should be larger in size than the previous two layers.
If the compress is applied correctly, its inner layer remains moist all the time. If the dressing is not applied correctly, or when the second or third layer does not completely cover the wet layer, active evaporation occurs. Instead of warming, this bandage cools the body.
Stages of the procedure
✔ Moisten a fabric napkin made of natural material (you can use regular gauze or a bandage) in hot water, hot infusion of medicinal herbs. ✔ Wring out the napkin well. ✔ Apply a moistened napkin to the desired area of the body. ✔ Place oilcloth or cellophane film tightly over the fabric. ✔ Place cotton wool or warm woolen fabric (shawl, scarf) on top of the film.
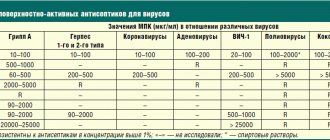
Topical therapy for skin diseases
N
It is impossible to imagine the treatment of dermatoses without the use of external agents. In some cases, they become of paramount importance, which is why it is so important to navigate the sea of medications that are constantly arriving on the market.
General principles for the use of external agents
Before carrying out external treatment, it is necessary to take into account the stage of the disease, the age of the patient (children, as a rule, are prescribed less irritating drugs in lower concentrations), and tolerability of the drug.
The effect of external treatment is more pronounced if the therapy is carried out comprehensively.
Powders
have a cooling effect on the skin, resulting in calming of burning and itching. During macerations from exposure to sweat, urine, and skin hyperemia, they also have a good effect. Powders are based on plant or mineral powders.
Aqueous solutions of medicinal substances are most often used in the form of lotions, wet-dry dressings and warm compresses
.
A piece of gauze folded in 4-5 layers and soaked in a cooled solution is applied to the affected area of skin. As it warms up, every 15-20 minutes, it is moistened again. This procedure lasts 1-1.5 hours, after which you should take a break for 1-2 hours. Due to the evaporation of water, the lotions
sharply cool the skin and cause a narrowing of blood vessels. This allows the use of lotions for acute inflammatory skin lesions, severely hyperemic, with swelling and weeping.
| Lotions reduce burning, itching and maceration phenomena |
A wet-drying dressing
is applied as follows: gauze folded in 4-5 layers, soaked in an appropriate solution, is applied to the affected area of the skin, covered with a thin layer of absorbent cotton wool and bandaged. The dressing is changed as it dries (usually after 3-4 hours), the slowly evaporating liquid cools the skin, like a lotion, only less actively, helps to subside the symptoms of acute inflammation, which is indicated in the treatment of subacute inflammatory processes accompanied by weeping. Depending on the medications included in the lotion, it has an astringent, disinfectant, drying effect, and in general an anti-inflammatory effect.
Warming compresses
act on the skin with moist heat and are used mainly in the treatment of chronic inflammatory processes. By causing active hyperemia, they increase metabolic processes in the affected area of the skin and help resolve the inflammatory infiltrate.
In addition, various antipruritic, antimicrobial and fungicidal solutions, which can be aqueous or alcoholic, are used externally. Alcohol solutions include solutions of boric and salicylic acids, resorcinol, lapis, iodine, aniline dyes, etc. Ethyl alcohol can cause skin irritation and have an astringent effect, which leads to drying, so its most desirable concentration is 70%.
Shaked suspensions, or “chatterers”
, are used for inflammatory and acute inflammatory (non-wetting) skin diseases (eczema, dermatitis, itchy dermatoses, etc.). Before use, they should be shaken to evenly mix all the ingredients - fine powdery substances that are suspended in water with oil or glycerin. The liquid part of the mash evaporates soon after lubricating the skin with it, and the powdery substances are deposited in a thin layer and are retained on it for a long time. In most cases, chatter is prescribed in equal parts - talc, zinc, glycerin and distilled water when a surface effect is needed. More liquid (up to 50-60%) is added to obtain a cooling effect and, conversely, 20-40% of liquid is taken to create a protective film on the skin. If the patient has dry skin or long-term exposure to the drug is required, it is recommended to prescribe oil suspensions. To speed up drying and enhance the effect, up to 10% alcohol or ichthyol, sulfur, menthol, anesthesin, tar, etc. are usually added to the “talkers”.
Pastes
used when there is a serous crust on the skin (in patients with eczema), for hyperemia (in patients with dermatitis), etc. The paste consists of equal parts of powder and fatty bases, has a dough-like consistency, and penetrates deeper into the skin than powders and mash. Depending on the composition (naftalan, sulfur, tar, lanolin, petroleum jelly), it acts as a cooling, softening and anti-inflammatory agent. The paste protects the skin well against abrasions after acute inflammatory phenomena have subsided.
Ointments
can be official (sulfuric, ichthyol, naphthalan, etc.) or prepared in a pharmacy according to a prescription. Animal and vegetable fats, oils, petroleum jelly, lanolin are usually used as a base, with the addition of various medicines. Ointments can be exfoliating, itching, epithelializing, softening, absorbing, etc.
In addition, medicinal varnishes and plasters
(for the treatment of condylomas, warts, calluses, onychomycosis), made on the basis of collodion, gelatin or lead plaster with the addition of the necessary medicinal substances.
Of course, all the previous well-known ointment products, including the so-called “complex” ones, manufactured to order, have not lost their relevance at all. However, the rhythm of life requires minimal time investment, and ready-made funds are of increasing interest.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
A review of local therapy can begin with drugs used in the treatment of allergic diseases. Allergic dermatoses require the use of different agents at different phases of the disease. In the presence of weeping lesions, lotions are recommended - boron, resorcinol, soda, with tannin - up to 3% - 5% of the active substance, as well as pastes from the above products, with the addition of naphthalan, tar, ichthyol, etc. After the acute weeping processes subside, sequence of ointment forms: flumethasone
(Lorinden), etc.
Among the monocomponent drugs for external use with anti-inflammatory effects, the following drugs have proven themselves well.
Hydrocortisone 17-butyrate
(locoid) - ointment, cream, lipocrem, lotion 0.1% - is an active synthetic non-halogenated glucocorticoid drug for topical use. Has a rapid anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, antipruritic effect. Used for superficial, non-infected skin diseases - eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis; Apply to affected skin 1-3 times a day. Ointment and lipocrem provide good occlusive and hydrating properties in combination with the cosmetic appeal of the cream. For weeping skin diseases, it is advisable to use dosage forms such as lotion and crelo. The latter, having the properties of cosmetic milk, is especially effective for application to extensive skin lesions, as well as to the scalp.
| Lotions are used for acute inflammatory skin lesions with swelling and weeping |
Elokom - 1 g of cream or ointment contains mometasone furoate
1 mg; in tubes of 15 g; 1 ml of lotion for external use - 1 mg in an aqueous-alcohol solution; in bottles of 20 ml. Has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic effect. Ointment and cream are used for psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, lotion - for lesions of the scalp, rubbing a few drops of lotion once a day.
Betamethasone valerate
(Celestoderm B) - ointment and cream, 15 g each in tubes. Has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic effects; eliminates swelling, hyperemia, itching at the site of application. Indicated for psoriasis, eczema, nodular prurigo, dermatitis, discoid lupus erythematosus, insect bites, generalized erythroderma. The effect of the drug can be enhanced by covering the treated surface with an occlusive dressing. The product is applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day until improvement, then used 1-2 times a day.
When the course of dermatoses is complicated by a secondary infection
I use products with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Of the ready-made drugs, aerosols Oxycort T (hydrocortisone + oxytetracycline), Polcortolone (triamicilone + tetracycline), Oxycyclosol (prednisolone + oxytetracycline) provide invaluable assistance for dermatoses complicated by secondary infection.
Diprogent
— 1 g of ointment or cream contains betamethasone dipropionate 0.5 mg (0.05%) and gentamicin sulfate 1 mg (0.1%) in tubes of 15 and 30 g. It has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiallergic, antibacterial effects. Inhibits the growth of gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, including staphylococci resistant to penicillin, Proteus, E. coli, salmonella, etc. Indicated for psoriasis, contact and atopic dermatitis, eczema (including microbial), dyshidrosis, itching of the anus and external genitalia organs.
Celestoderm B with garamycin
— 1 g of cream or ointment contains 1 mg of betamethasone valerate and 1 mg of gentamicin sulfate, in tubes of 15 and 30 mg. It has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiallergic, antibacterial effects. Used for infected inflammatory and allergic dermatoses: contact, seborrheic, intertriginous dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, neurodermatitis, anogenital and senile itching. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day, if necessary, longer use is possible.
In the treatment of chronic dermatoses characterized by severe infiltration and peeling (psoriasis, seborrhea, chronic eczema), agents that combine an anti-inflammatory (betamethasone) and keratolytic (salicylic acid) substance - ointments and lotions Diprosalik, Belosalik - are highly recommended.
In addition to the certainly positive effect of corticosteroid ointments, it is necessary to mention general contraindications for their use: viral skin infections, primary fungal and bacterial skin lesions, undesirability of long-term use due to the risk of skin atrophy.
In this regard, it is advisable to pay attention to effective products without corticosteroid components: a series of Skin-cap preparations based on zinc pyrithioneate
(aerosol, ointment, shampoo) and nizoral shampoo, which have a good effect in the treatment of psoriasis, seborrhea (especially the scalp).
To improve the processes of epithelization, gels and ointments Actovegin, solcoseryl, dexpanthenol (Bepanten), also not containing hormones, are indicated.
Antifungal drugs
Drugs with antifungal effects have been well known for a long time. In addition to the already known terbinafine
(Lamisil), the spray is very successful due to its convenient form of application.
Exoderil
- 1 g of cream or 1 ml of solution for external use contains naftifine hydrochloride 10 mg; cream in tubes of 15 and 30 g, solution in bottles of 10 ml. It has an antifungal (fungicidal effect against dermatophytes, mold fungi, causative agents of sporotrichosis), antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipruritic effect. Effective in the treatment of mycoses of the hairy areas of the body and skin with hyperkeratosis, indicated for dermatomycosis and onychomycosis. Apply to the affected surface and adjacent areas, cleaned and dry, 1 time per day for 2-8 weeks, for onychomycosis 1-2 times per day, course up to 6 months.
Lotrimin - 1 g of cream contains clotrimazole
10 mg, in tubes of 15 g. Has antifungal (broad-spectrum), fungicidal, antibacterial effects.
Indicated for athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (caused by Candida albicans
), pityriasis versicolor (caused by
Malasseria furfur
). The required amount of cream is applied with rubbing movements to the affected area and surrounding skin 2 times a day. The itching usually goes away within the first week. The course of treatment for dermatomycosis is 3-4 weeks, for erythrasma and pityriasis versicolor - 3 weeks.
Pimafucin - 1 g of cream contains 20 mg of natamycin
, in tubes of 30 g;
1 ml of suspension for topical use contains 25 mg of natamycin, in 20 ml bottles with a pipette. It has an antifungal, fungicidal effect, and is active against many pathogenic yeast fungi (especially Candida albicans
), dermatophytes. Indicated in the treatment of mycoses of the skin and mucous membranes, otomycosis, candidiasis of the skin and nails. The drug is applied once a day or more often.
In the treatment of combined skin pathologies, external agents that combine anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antimicrobial effects are used with great success.
Triderm
— 1 g of ointment or cream contains 0.5 mg of betamethasone dipropionate, 1 mg of gentamicin sulfate and 10 mg of clotrimazole, in tubes of 15 g. It has a local anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictor, antipruritic, antibacterial, antifungal effect. Used for various forms of bacterially infected eczema, as well as dermatomycosis, candidiasis, especially when lesions are localized in the groin area and large folds of the skin. A small amount of the drug is applied to the affected areas, lightly rubbing, 2 times a day; the duration of treatment is determined individually. The recommended duration of treatment for dermatomycosis of the feet is 2-4 weeks.
Pimafukort
- 1 g of cream or ointment contains natamycin 10 mg, neomycin 3.5 mg and hydrocortisone 10 mg; in tubes of 15 g; 1 g of lotion - natamycin 10 mg, neomycin 1.75 mg and hydrocortisone 5 mg; in dropper bottles of 20 ml. Action: local antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory. Used for superficial dermatoses complicated by bacterial or fungal infection, otomycosis. Apply to affected areas of the skin 2-4 times a day for 2-4 weeks.
Acne treatment products
The products used in the treatment of acne deserve special mention. For mildly expressed processes, sinerite
- erythromycin-zinc complex, has a bacteriostatic effect on microorganisms that cause acne;
skinoren
is an ointment based on azelaic acid, the therapeutic effect of which is due to its antimicrobial effect, as well as a decrease in the content of free fatty acids in skin lipids and the normalization of disrupted keratinization processes in the skin follicles.
In the case of poorly resolved inflammatory and infiltrated elements, drugs such as Retin-A gel, Airol ointments and lotions, and Lokacid are indicated to accelerate their maturation and resolution. These products are based on trans-retinoic acid.
, a natural metabolite of retinol. Enhances cell proliferation in the papillary layer of the skin, reduces the adhesion of cells involved in the formation of acne vulgaris. When treating closed acne, it promotes their transition to open acne, which then heals without scarring after removing the keratin plug.
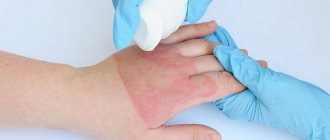
Warming alcohol compress
Alcohol compresses are used to resolve inflammatory infiltrates. They cause long-term and persistent dilation of superficial vessels. Blood circulation increases, resorption occurs in the source of inflammation and the underlying tissue. Pain sensations decrease.
The procedure for applying an alcohol dressing is almost identical to applying a wet hot dressing. A cloth or gauze should be moistened in vodka, salicylic or camphor alcohol. Or use any other medicinal alcohol infusion.
In exceptional cases, you can apply a compress with a weak vinegar solution.
To apply an alcohol dressing, the fabric must be moistened with the prepared solution and wrung out well. Apply to the sore spot, put cellophane and cotton wool on top. Remember that each subsequent layer must be larger than the previous one.
The area of the alcohol dressing should be carefully bandaged.
If the fabric of the first layer has dried before 6 hours, it should be removed. Before replacing a used bandage with a new one, the area where it was applied should be washed well with warm water. This will help avoid irritation.
Sometimes we get hurt. Sometimes we get hurt. The good news is that you can provide first aid for pain or injury using the means at hand - something cold or hot.
However, remember that cold and heat are opposite concepts, which means their effect is different. Proper use of a heating pad and ice will relieve pain. But improper use will greatly worsen the patient’s condition.
So how do you know when to use ice and when to use a heating pad?
Mechanical injuries (bruise, sprain, tendinosis, tendinitis)
“At first glance, ice seems uncomfortable and repulsive, while a heating pad seems pleasant and cozy,” says sports medicine doctor Anna Rex. “However, ice helps with acute pain, inflammation and swelling. The high temperature of the heating pad leads to the rapid development of inflammation.”
Sports health physical therapist Carol Fercovich adds that "using a heating pad with warm water helps relax injured muscles before using ice to relieve pain."
Headache
“You can relieve the throbbing pain of a migraine by applying a cold, damp towel to your forehead, temples, or eyes,” advises neurologist Jennifer Crigler. However, one of the causes of headaches is neck spasms. In this case, it is better to apply a heating pad with warm water to your neck for a while.
Arthritis and gout
A heating pad, as a pain relief, is suitable not only for arthritis, but also for injuries that do not go away within 6 weeks. “Patients with chronic arthritis usually benefit from using a heating pad with warm water. It relaxes tight muscles, promoting joint mobility,” says rheumatologist Linda Mileti. However, for acute pain, Linda Mileti recommends ice exclusively.
"Be careful in areas of decreased sensitivity if you have neuropathy (from diabetes or another condition) or Raynaud's syndrome," says Dr. Mack. "Temperatures that are too hot or cold can damage the skin."
KEY FINDINGS
Heat – relieves spasms, relaxes tense muscles, relieves “stiffness” of ligaments
Ice – soothes acute pain, reduces swelling or bruising, calms inflammation
Now you know in which cases to use ice and in which to use a heating pad, and you will be able to help with pain or injury to the person who needs it. Share this material or infographic with your friends and acquaintances so that they too know how they can help someone who has been injured and is in pain.
Let's help each other! And take care of each other!
Based on materials from health.clevelandclinic.org
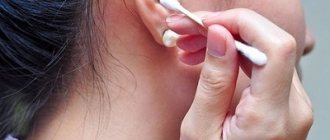
Compress on the ear
Photo: Yandex.Pictures
A warming bandage on the ear helps relieve pain from otitis media. Children are often given such dressings.
The procedure is not at all different from applying a regular compress, except that in the first and second layers of the future bandage it is necessary to make a slot for the auricle. The last layer must be pre-warmed.
Is the compress really effective?
Alcohol compresses are a treatment method that is often used not only by traditional healers, but also prescribed by doctors. It is quite simple to use, but there must be control. Its main task is to warm the ear in order to speed up metabolism and improve blood circulation. With its help, you can reduce pain and make it not as severe as it seems. By accelerating blood flow, toxins are quickly removed from the site of inflammation, as well as the effectiveness of the medications used increases.
All processes associated with healing are an order of magnitude faster. This compress is used most often for chronic non-purulent and acute otitis media. In addition, it can be used if discomfort is observed during the treatment of upper respiratory tract diseases.
compress on the ear, what to do
How long to keep the compress
Different types of procedures require a certain amount of time. The operating time of a water-based hot dressing is not long. It should be changed after 10–15 minutes.
The alcohol-based procedure takes the longest, but it should not exceed 12 hours. For any type, as soon as the first layer dries, the procedure can be considered complete.
It is recommended to keep alcohol dressings on for at least 6 hours, so it is preferable to do them at night. It is necessary to secure all the layers of the bandage well, then it will not fall off and its therapeutic effect of the layers will not be disrupted.
How to make a healing compress correctly. Types of compress.
Cold compresses.
A cold or cooling compress (lotion) is effective for bruises, bleeding, fractures and sprains. This is the safest of compresses. The only contraindication to its use is pneumonia. Such compresses are recommended for nosebleeds, migraines and functional pain in the heart area. They are often used to prevent high blood pressure in older people during thermal procedures (for example, baths).
The effect of such a compress is to narrow blood vessels and slow down trophic processes in the body. Due to its ability to reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings, it can also be used as a pain reliever.
A cold compress is applied topically to inhibit acute inflammatory processes, reduce swelling and reduce pain. It is also used for neurasthenia (with a gradual decrease in water temperature on the interscapular area and shin) and elevated body temperature.
To carry out this procedure, you will need a clean towel (a piece of gauze folded in several layers, or a large ball of cotton wool). It is moistened in cold water or a medicine (for example, a decoction of plants), squeezed out and applied to the sore spot. After heating the compress, it is again dipped in cold liquid and again placed on the inflamed area of the body. Usually the procedure is repeated every 2-4 minutes until relief occurs.
Instead of cold water, you can use ice (water frozen in a thick plastic bag) or clean snow. In this case, you need to take a break of 10–15 minutes between repeated procedures. Such compresses are not recommended for children.
healing compress
Hot compresses.
This compress is used as a resolving agent for local inflammation. The procedure is performed for renal, hepatic or intestinal colic, migraine with spasm of cerebral vessels, angina attacks, bronchial asthma, joint pain and muscle spasms of the lower extremities. Hot compresses are also effective for injuries, but in this case you should not start using them immediately, but only on the 2nd day.
This procedure activates metabolic processes, eliminates vascular spasm, increases local blood flow and relaxes muscles, which leads to a pronounced analgesic effect.
To carry out the procedure, you will need a gauze pad or other natural fabric that absorbs water well. It is moistened in water heated to 60–70° C, lightly squeezed and applied to the sore spot. To keep warm, put oilcloth or plastic film on top, then cotton wool, and on top of it a woolen cloth, blanket or heating pad. The compress must be changed every 10–15 minutes.
The effect of this procedure can be enhanced with the help of medications or natural remedies (decoctions, infusions, etc.).
Hot compresses are contraindicated for purulent skin diseases and bleeding. In addition, they cannot be performed at elevated body temperature and high blood pressure, as well as in the presence of inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity.
Types of compress.
Warming compresses.
These compresses lead to a prolonged expansion of the superficial and deep blood vessels, as well as a rush of blood to the site of inflammation, as a result of which it resolves and the pain disappears.
Warming compresses are used for certain inflammations, sore throat, colds, infiltrates after injections, myositis, cervical osteochondrosis, lumbar radiculitis, rheumatism, gout, arthrosis, arthritis, consequences of injuries to joints, ligaments and bones. These procedures are also useful in treating inflammation of the ear, pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi.
Since a warm compress has a strong therapeutic effect, you should always consult a doctor before using it. The fact is that in some cases such a procedure can lead to an exacerbation of the disease.
For this compress you will need gauze or other fabric (cotton, linen), folded in 3-5 layers. It is dipped in water or a healing solution at room temperature, lightly squeezed and applied to the sore spot. The compress should extend approximately 2 cm beyond the edges of the problem area.
Compress paper is placed on top, which should be 3–4 cm larger than the fabric, and a layer of cotton wool. Then this area of the body is covered with woolen cloth and secured with a bandage, scarf or warm scarf.
How to make a therapeutic compress correctly
The effect of a warming compress is to create an environment with high humidity and temperature under the compress paper (steam bath conditions). It is very important that each subsequent layer overlaps the previous one, in which case the moisture will not evaporate ahead of time.
If chills appear after the start of the procedure, it means that the warming compress was poorly made; it must be removed and applied correctly. When cotton wool or compress paper does not completely cover the moistened gauze or everything is loosely fixed, air begins to enter the space between the compress and the skin. In this case, the evaporation of moisture will cause cooling rather than warming.
A warming compress, unlike a heating pad, uses internal and not external heat, which accumulates in the body tissues during the procedure. Its effect is to improve blood supply to cells and accelerate metabolic processes.
As a result, the healing substance from the compress penetrates through the opened pores of the skin into deeper tissues. Swelling decreases, inflammation subsides, painfully contracted muscles relax.
It’s easy to check whether the compress is applied correctly: just put your finger under the bandage and determine the moisture content of the inner layer. The procedure was carried out well if after 2 hours the inner layer did not dry out, but remained wet. After removing the compress, the skin should be rinsed with warm water and blotted dry with a terry towel, and then wrapped.
You cannot use the same tissue for repeated procedures, as toxic substances released from the skin accumulate in it. Before making a new compress, the material must be washed.
If the compress is used to treat trophic ulcers or non-healing wounds, compress paper cannot be used in it. When dilating the veins of the lower extremities, compresses with decoctions of chamomile, sage and horsetail are used; for allergies - decoctions of viburnum, string and celandine.
healing compress
The duration of one procedure and the temperature of the compress depend on the medicinal substance used. Exposure can last from 2 to 8 hours (but not more than 12 hours). The compress can be applied overnight. The course of treatment is usually 5–20 procedures. If necessary, a warm compress can be applied 2 times a day, but in this case the break should be at least 2 hours to avoid skin irritation.
It is recommended to change therapeutic dressings in the morning and evening. If rashes appear on the skin after a warming compress, it should be lubricated with baby cream or treated with baby powder. Further procedures using the drug that caused the allergic reaction should be avoided.
If vodka (alcohol) is used for a warming compress, you need to keep in mind that it evaporates quickly. Because of this, the bandages need to be changed more often. You should not resort to such procedures often, as they irritate the skin.
A warming compress is contraindicated for dermatitis and pustular diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (boils, carbuncles, erysipelas). It should not be used for eczema, psoriasis, neurodermatitis, lichen, bleeding of any kind, skin damage, purulent otitis media, bronchitis, pleurisy and tumors.
A warming compress should also be avoided in case of elevated body temperature and allergic skin rashes. This procedure is not recommended for people suffering from cardiovascular diseases of the II–III degree with symptoms of heart failure, as well as for atherosclerosis with damage to cerebral vessels and fresh thrombosis (thrombophlebitis, varicose veins).
Medicinal compresses
Medicinal compresses.
A variety of ingredients can be used for medicinal compresses, including vodka, alcohol, cologne, a weak vinegar solution, oil extracts, herbal decoctions, juice and gruel from berries or vegetables (potatoes, cabbage, etc.).
For cervical radiculitis, rheumatism, osteochondrosis, gout and injuries, compresses with alcohol, which is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 3, or with vodka, diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 1, have a good effect. The fabric moistened with alcohol should not come into contact with the external environment so that evaporation does not occur from under the compress. Compress paper is placed on the alcohol pad and covered with a warm cloth on top.
Compresses with oil extracts are called activated. Natural vegetable oils are used for them, for example sea buckthorn, rose hips, juniper, peach, olive. Such compresses are good for joint diseases (radiculitis, gout) and the consequences of joint injuries. They can also be used for skin diseases (ulcers, burns, non-healing wounds, etc.).
A good therapeutic effect can be achieved by using medicinal plants (cherry or lingonberry leaves, raspberries, juniper) in compresses. Herbal decoctions and infusions are most often used for lotions.
Compresses on large joints of the upper and lower extremities A compress on large joints of the arms and legs is applied according to the following scheme. Prepare a piece of warm woolen fabric of such a size that you can wrap it around the joint twice. Spread the cloth on a stool or chair and put compress paper on top.
Moisten gauze or other cotton cloth with water or the prepared medicinal product, squeeze lightly and place on compress paper. Carefully wrap the sore joint with the prepared three-layer compress and leave for the required time.
How to make a therapeutic compress correctly
Compresses for small joints.
Such compresses are applied by bandaging. Then you need to put on warm socks on your feet, and woolen gloves on your hands. Compresses are also applied to the face and head using the bandaging method. Compresses for the back
This compress is used to relieve pain in the back and spine, and is also used for blood stagnation and feverish heat.
A piece of cotton fabric folded several times, length from the first cervical vertebra to the tailbone, is placed on a woolen blanket. You need to lie on it with your back, turning the edges of the material to the sides. Then you should cover yourself with a warm quilt so that air does not get on the compress. Keep the compress for 45 minutes. If necessary, the procedure can be repeated.
Medcare.ru
Warming and cooling compresses
Warming compress
A warm compress causes long-term dilation of blood vessels, which leads to an increase in blood flow not only to the skin, but also to deeper tissues. This achieves the absorbent and analgesic effect of the compress.
Remember! A warming compress cannot be used at high temperatures or when the integrity of the skin is damaged.
When applying a compress to the upper limb, you must:
- prepare: a bottle of 45-degree alcohol or an ampoule of 25 percent magnesium sulfate solution, gauze, compress paper, cotton wool, bandage, container;
- Wash the hands;
- roll up a gauze napkin into 6-8 layers;
- moisten the prepared gauze napkin in a container with 45-degree alcohol;
- apply a moistened napkin to the injection site;
- place a larger compress paper on top of the napkin (the paper should be 2 cm larger than the gauze napkin on all sides);
- put a layer of cotton wool on top of the compress paper, completely covering the two previous layers (the cotton wool should be 2 cm larger than the compress paper, so it will retain the heat generated under the compress);
- secure the compress with a bandage so that it fits snugly on the limb, but does not restrict movement;
- leave the compress for 6-8 hours (preferably overnight);
- Wash the hands;
- check the moisture level of the lower napkin 1.5-2 hours after application;
- Wash the hands;
- remove the compress after 6-8 hours;
- wipe the skin dry;
- apply a dry bandage;
- Wash the hands.
Note: medications used for compresses can cause irritation, therefore, before applying the compress, the skin must be lubricated with petroleum jelly.
Alcohol compresses dry out faster, so they need to be changed after 4-6 hours. You should not apply a compress to skin lubricated with iodine - this can cause deep burns.
Cold compress
A cold compress is used for severe pain, bleeding, and high fever (above 39°C). It causes cooling of the skin and constriction of blood vessels. When applying a cold compress, the caregiver should not leave the patient, as the wipes should be changed every 2-3 minutes. The duration of the procedure is from 5 to 60 minutes.
- Prepare: a container with cold water at a temperature of 14-16°C (cool in the refrigerator), 2 napkins:
- moisten a napkin in cold water;
- squeeze out water;
- fold the napkin in several layers;
- place a napkin on the surface of the skin;
- moisten the second napkin in a container of cold water;
- squeeze out water;
- fold the napkin in several layers;
- replace the first napkin (if it gets hot) with the second one.
Note: Wring out the napkin better so that it does not leak water onto the patient’s pillow or bed.
Ice pack
For a deeper effect on blood vessels, organs and tissues in case of pain and bleeding, use an ice pack. The effect of dry cold is due to the narrowing of blood vessels, as well as a decrease in the sensitivity of nerve receptors.
Prepare: an ice bubble, a container with ice, a container with water at a temperature of 14-16°C:
- place the ice pack on a smooth surface and screw on the lid;
- wrap the bubble in a napkin and place it on the patient’s body;
- drain the water from the bubble as it melts;
- add pieces of ice to the bubble.
Note: If you don't have an ice pack, you can make two plastic bags inside each other. Fill the bags with ice and place them on a flat surface. Press down the bag with your palm, release the air from it, tie it tightly, wrap it in a napkin and use it like an ice pack. Change bags as the ice melts. The ice pack is kept for a long time. Every 20-30 minutes you need to remove the bubble or ice pack for 10-15 minutes