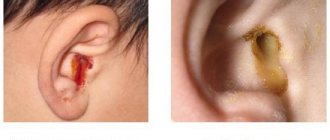
Important! If you are often bothered by otitis media, write down a recipe for an effective remedy for ear diseases...
Ear swelling is not a diagnosis, but only a sign of diseases of various origins. When in contact with the external environment, the human ear is susceptible to many adverse factors.
Swelling often causes discomfort or pain inside the affected ear.
Ignoring this symptom can lead to hearing loss. In advanced cases, there is a risk of infection entering the meninges with subsequent inflammation.
Why does the hearing organ swell?
Since ear swelling is quite common, it would be useful for every person to know the reasons for its occurrence. The ear swells as a result of the action of infectious, allergic and traumatic agents. Let's look at the reasons for this condition in more detail.
Swelling is often caused by viruses. It occurs in acute respiratory diseases, when simultaneous damage to the nose and throat occurs.
These organs are located near the auditory analyzer, so the infection can spread to the ears and cause inflammation. At first, the hearing organ only hurts inside, and after a while other inflammatory symptoms appear - redness, swelling, increased local temperature, decreased hearing. The disease most often occurs in people with weakened immune systems, chronic pathologies, and also with a lack of vitamins and microelements.
The hearing organ may swell internally due to radiation or other types of exposure. This is observed in people who work or live near sources of harmful radiation. In addition, swelling in the ear often occurs when there is a malignant tumor in the body, which is treated with radiation. Chronic inflammation of the auditory analyzer, manifested by its swelling, can develop with frequent radiological examination of the body (radiography, CT).
The next reason is allergic reactions. They are caused by various medications, food allergens, cosmetics, and also a substance released by insects when they bite. Swelling is observed not only in the ear canal, but also outside. The ear does not hurt, but only swells and itches. The swelling can be either slight or severe, up to complete blocking of the ear canal and hearing loss. As swelling increases, angioedema occurs, requiring immediate treatment.
Mechanical damage is a common cause of swelling in the ear. You can injure the ear canal when cleaning your ears with a cotton swab. Swelling also occurs when there is a blow to the head or ear.
Swelling of the auditory analyzer is often observed in swimmers as a result of barotrauma. In addition, frequent entry of water into the ear canal helps to wash out the natural lubrication of the ear. The protective barrier is broken, the skin becomes dry and begins to peel. There are microbes in the water, so when it gets into the ear canal, an inflammatory process develops. Otitis externa occurs. Redness of the skin near the auricle and in the ear canal is observed. The damaged ear swells and hurts inside.
For the treatment and prevention of acute and chronic otitis and other ear diseases in children and adults, Elena Malysheva recommends a proven, reliable remedy based on only natural ingredients, no chemicals! After talking with people who have experienced this method, we decided to publish a link to it.
Swelling in the ear canal also appears when foreign particles enter it. A pea, seed, bead, or insect can get into your ears. The most dangerous is being hit by an insect. Crawling inside, it causes irritation and pain.
Rare causes of swelling are a tumor of the auricle or external auditory canal, burns, chronic inflammation of the middle ear, the presence of polyps. The earlobe may swell with erysipelas, hemangioma, atheroma, or after a puncture under earrings.
Treatment of ear swelling
The choice of treatment method depends on the cause of the pathology. To relieve ear swelling in an adult, both traditional medicines and traditional medicine are used.
If the ear is swollen and red due to infectious diseases, local and general antibiotics are used. Local treatment consists of instilling ear drops into the ear canal, such as:
- Otipax.
If there are symptoms of intoxication (fever, general weakness) and ear pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. As the inflammation subsides, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed (UHF therapy, quartz treatment, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy). They are completely safe and can be performed even during pregnancy.
In case of severe swelling, when ear drops do not help, catheterization or blowing of the auditory tube should be done. Catheterization is the insertion of a special tube into the nose through which vasoconstrictor drops are instilled to relieve swelling.
Blowing is done using a special apparatus. This normalizes the pressure between the nasal cavity and the middle ear. The same procedures are carried out if the cause of swelling is barotrauma.
If swelling in the ear is caused by allergens, antihistamines and hormonal drugs (Claritin, Suprastin, Tavegil) are used. Desensitizing drops (Polydex, Dexamethasone) are instilled into the ear canal. If the ear turns red on the outside, use antiallergic ointments (Advantan, Beloderm). Quincke's edema requires immediate intensive care and can only be treated in hospital.
If there is a foreign object inside the ear canal, you need to tilt your head towards the blocked ear and shake it slightly. The item should fly out. Otherwise, you should contact an ENT specialist. It is forbidden to try to remove a foreign particle with a cotton swab. This can push it further and damage the drum membrane.
To remove the insect, you need to drip vegetable oil into the ear canal and wait a little, then rinse it with water from a syringe without a needle.
Alternative treatment involves the use of:
- Kitchen salt;
- Cabbage and bay leaves;
- Plantain.
The salt is heated in a frying pan, poured into a fabric bag and applied near the sore spot. The ears warm up and the inflammation subsides. You can also use a special heating pad for this purpose.
A cabbage or plantain leaf should be applied to the site of swelling and secured with a bandage. After 2-3 hours it is removed. The procedure should be done 3-4 times a day for 7-8 days.
Bay leaf helps relieve inflammation in the ear. To prepare the infusion, grind it, pour hot water and leave for 1-2 hours. Then a bandage roller is dipped into the resulting liquid and placed in the damaged ear canal for 3-4 hours. Repeat every day until recovery.
Feedback from our reader - Irina Korotkova
I recently read an article that talks about the natural remedy Immunity. With the help of this drug, you can get rid of otitis media in 1 course of use, without poisoning your body with antibiotics.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered one package. I noticed improvements after the first use. After several days of treatment, the acute pain in the ear and congestion disappeared, and the temperature subsided. I began to sleep better, the noise in my head disappeared. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
Swelling in the ear is a common symptom that affects many people. This is not as harmless a phenomenon as it seems at first glance.
Ear swelling can be complicated by life-threatening diseases. Therefore, when it appears, the cause should be determined as quickly as possible and appropriate treatment should be carried out.
Do you still think that it is impossible to get rid of discomfort and pain in your ears?
Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, you know firsthand what it is:
- excruciating pain in the ears...
- acute headache, pain radiating to the jaw...
- stuffiness and discomfort in the ear...
- constant noises and crackling...
- copious discharge of sulfur, formation of plugs, purulent discharge...
How much effort, time and health have you already spent on ineffective treatment? After all, sooner or later the SITUATION WILL GET WORSE and everything can end very BADLY, up to complete LOSS OF HEARING...
It's time to take your health seriously! That is why we decided to publish Elena Malysheva’s exclusive method for treating otitis media and other ear diseases at home...
Redness of the ear occurs in a child at any age from birth. This phenomenon may be a sign of normality or disease. Don't panic: assess the baby's condition and try to find the cause of the redness. Take a closer look to see if the upper eyelid is swollen, if the ear is colored on the outside or inside, or if there is swelling. In some cases, the source of the color change is common and does not require urgent action. If you have additional symptoms, take your child to the doctor.
Fine
Normally, the ears turn red when:
- baby's exploration of his own body. The body for young children is something new and unknown. Therefore, babies explore all its parts, touch them, pull them, drag them into their mouths. The subject of research will sooner or later be ears that turn red from prolonged exposure;
- overheating The body dilates blood vessels to quickly release heat to the environment. If you have a baby, then red ears are one of the first signs of overheating. Provide cooling: leave the warm room, remove outer clothing, wipe exposed areas of the body with cool water;
- experiences. Children experiencing fear or shame have red ears. This is due to the production of the stress hormone adrenaline. The work of the brain is also stimulated. The blood rushes to the head, the blood vessels dilate, and we see red ears;
- cooling The body protects parts of the body that are left without clothing (face, ears, hands) from cold by increasing blood flow to those areas;
- wearing a hat or tight-fitting headphones for a long time. The vessels are compressed, and blood flows in smaller volumes than usual. When removing a tight hat or headphones, the body strives to compensate for the lack of blood circulation. A large amount of blood enters and the ears become bright red;
- teething. In this case, the pain spreads to the cheeks and ears, causing the baby to constantly fiddle with them. Give the baby a special rubber ring to make the process easier ().
Before suspecting a disease, rule out natural, non-health-threatening causes of redness and swelling in your child’s ears.
For diseases and injuries
In a normal state, redness of the ears is not accompanied by the child’s moodiness, irritability, lethargy and other symptoms. The presence of such signs indicates illness or injury:
- skin (eczema). Skin diseases manifest as red rashes mainly on the face, limbs and abdomen. The skin peels and itches;
- . When an allergen enters the body, swelling and redness of the skin behind the ears appears, which spread to the upper eyelid. It is necessary to identify the substance that causes the allergy and prevent the child from coming into contact with it. In severe cases, antihistamines are given. With diathesis, the cheeks turn red and peel, and red spots are observed behind the ears;
- fungus With fungus, the skin in the ear area turns red, peels, itches, blisters and discharge from the ear canal appear. In some cases, hearing decreases;
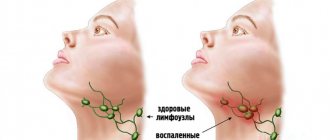
- infections (mumps). If your baby gets mumps, redness and swelling appear in the back of the ears. The disease affects one side, and after 2 - 3 days the second side is also affected. The child becomes lethargic and complains of pain near the ear and throat, which worsens when chewing. Body temperature rises. Over time, the swelling descends to the neck area;
- cyst or lipoma. When cysts or lipomas appear, the ear becomes red and swollen. A hard formation is felt, which moves when pressed;
- injury or foreign body. Young children often injure their ears by falling or sticking various objects there. Take a flashlight or lamp and carefully examine the outer ear and ear canal. If there is a wound, treat it with an antiseptic. Remove the object that is stuck in your ear. However, it is better to entrust such manipulations to a doctor;
- otitis Inflammation can affect the outer, middle and inner ear. Most often, redness is observed outside and inside the auditory organ, the baby complains of pain in the ear and head. Discharge appears from the ear canal. Body temperature rises. In some cases, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea develop. The child becomes lethargic and irritable (read -).
If you suspect that your child's ear is red and swollen due to illness, consult a doctor! Delay may cost your baby's hearing.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of inflammatory diseases of the external ear ranges from 17 to 30% among all otiatric pathologies. The growth of this pathology is facilitated by deteriorating environmental conditions, an increase in the level of resistance of the flora, an increase in the number of people with metabolic disorders, immune status, including allergopathology, irrational treatment of acute inflammatory pathology, untimely contact with an otorhinolaryngologist (ENT doctor) and a number of others moments.
Otitis externa is a fairly common disease, but the epidemiology has not yet been sufficiently studied, including due to the different designations of the same type of pathological process. Inflammatory diseases of the outer ear occur in all countries and regions of the globe, but are most often observed in hot and humid climatic regions; an increase in incidence is noted in the warm season. On average, every 10th person experiences this disease at least once during their lifetime, and 3–5% of the population suffers from a chronic form of otitis externa. On average, 0.4% of the population suffers from acute external otitis every year. The disease is most common among people exposed to high humidity for a long time.
Otitis externa occurs in all age groups, the highest prevalence is observed in older children and young adults, then increases slightly after 65 years. The incidence of inflammatory diseases of the outer and middle ear in men and women is approximately the same. No racial differences have been identified in the epidemiology of otitis externa.
Other causes of redness
A child's red ears may be a sign of some unpleasant processes:
- contamination of the ear canal. In this case, the child often scratches his ear. Remember: it is necessary to clean the ear canal weekly with a special cotton swab;
- ear piercing. The earlobes become swollen and red after the piercing. Treat them with disinfectants (hydrogen peroxide). If the inflammation does not go away within 2 - 3 days, purulent discharge appears from the holes, consult a doctor;
- water getting into your ears. When water gets into the ear canal, redness and swelling appear behind the ears, and hearing decreases. Remove the water and the symptoms will go away;
- insect bites. A small child scratches mosquito, lice or flea bites. The affected area swells and turns red;
- increases in blood pressure of various nature.
Redness and swelling in the child's ear area may occur due to natural causes or due to illness. In the first case, the skin quickly restores its normal color, the swelling subsides, and there are no other symptoms. When sick or injured, the child is lethargic, irritable, and complains of pain or itching in the ear. Hearing is often reduced. In such a situation, immediately take your baby to the doctor. The sooner you contact a specialist, the greater the chance of restoring your hearing.
We recommend reading: .
The consequence of diseases of the ENT organs can be swelling of the ear. Inflammatory processes are caused by the close proximity of neighboring organs, through which the infection can penetrate into the area of the hearing aid.
In order to prevent the spread of the inflammatory process in the child’s ear and nose, it is necessary to remove the swelling in time using known methods. If the internal tissue already hurts, then this is a clear sign of the onset of swelling.
This condition does not go away without a trace; a decrease in hearing levels, pain in the head and throat, nervous excitability, and decreased body tone may be observed.
Our doctors
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
19 years of experience
Make an appointment
Why should you pay close attention to tumors?
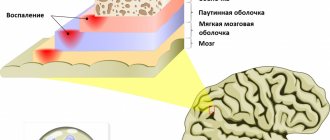
The difficulty in treating swelling in the ear lies in the proximity of brain tissue. As the area of inflammation increases, the head regions may be affected. The pain may appear in other places and cause great distress to the child.
Problems in the nose also deserve serious attention. The resulting abscesses, bursting, can penetrate the ears. When a child has an earache, it may be evidence of inflammation in the sinuses.
Self-treatment or inexperience of medical personnel will lead to a breakthrough of thin walls.
At the moment of tissue rupture, the child’s entire problematic part of the head hurts. There are also problems with breathing through the nose, discomfort in the functioning of the visual organ and will cause acute pain in the ear. A serious condition will require urgent intervention. The swelling must be quickly removed before it spreads to the brain area.
Causes of hearing aid tumors
Known causes of ear problems include:
- infections: viruses, bacteria;
- consequences of an allergic reaction;
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- mechanical rupture of the eardrums due to high noise levels or a sharp change in atmospheric pressure, these situations more often occur in people involved in professional sports: climbers, scuba divers and parachutists;
- Head trauma can contribute to the development of swelling in the ears.
Swelling affecting the ears can affect the child's other vital systems. So, next to the hearing departments there is an organ of balance. Severe swelling affects the ability to walk steadily and perform complex movements.
Hearing problems are caused by chemicals in the air around you. Poisoning of the body is accompanied by a headache in the child.
Outdoor recreation among plants will result in the acquisition of a tick that will crawl into a sleepy person’s ear. Having secured itself there with its paws, it will cause pain and swelling, you should not hesitate. The infectious disease specialist must carefully remove the insect without disturbing the membranes.
Ears are sensitive to temperature changes. More often, swelling is the result of walking in the cold after taking a bath or bath, when drops of liquid remain in the ear. A heated body will react with negative actions to a stressful situation.
Ear pain can cause angioedema. Allergic reactions contribute to a sudden accumulation of fluid.
A dangerous situation arises suddenly and develops at lightning speed. Sources of swelling can be food, pollen, water and even sunlight. The swelling must be removed quickly; if the tissues of the nasopharynx become very swollen, the child may suffocate.
The following factors complicate the course of the disease in the ear:
- formation of oncological inflammations;
- malnutrition: the body lacks important minerals. The main elements include vitamins A and C;
- acquisition of chronic diseases can provoke swelling and pain in the ear;
- ear problems may begin among those who like to use a cotton swab or other object to remove wax; the use of special drops has less harm to internal tissues;
- In people older than middle age, blockages of the ear canal occur; otitis media can be prevented by simple measures.
A swollen ear does not always cause pain. The main symptom of edema is decreased hearing. The tissue around the ear becomes swollen to the touch. During a conversation, you may feel like there is an echo in your head.
In allergic reactions, redness of the skin may occur. The child’s general well-being decreases; dizziness and fever may often occur.
Advanced stages of the disease are accompanied by the release of purulent substance from the ear canal. This occurs after the eardrum is perforated. Temporarily after the breakup there is an improvement in well-being.
The patient experiences problems in perceiving sounds that he previously heard without difficulty.
The external tissues may swell due to the formation of a boil. Ear pain occurs when eating, when the jaw muscles work. The skin is under pressure. However, there is no decrease in hearing levels.
Not only the ear itself hurts, but the surrounding tissues: neck, throat, nose. Body heat periodically develops, the patient complains of tinnitus, nausea and dizziness.
Treatment of hearing aid swelling
In a child, swelling in the ear can cause serious diseases of the brain and nasopharynx. Inflammation must be eliminated. Doctors who deal with swelling problems are: otolaryngologist, allergist, neurologist.
It is recommended to visit an ENT specialist first. He will determine the source of the swelling, conduct an appropriate examination of the level of hearing, prescribe tests for a microbial cause and refer to another specialist if necessary.
You can treat the ear using medical methods and folk remedies. Consultation with a doctor to choose a method is mandatory to exclude an incorrect diagnosis. If there is an infectious source, you need to fight the pathogen, then relieve the swelling.
At home, before visiting a doctor, you can reduce swelling in the ear using heated salt. A small amount is wrapped in cloth and applied to the site of inflammation. Cabbage leaves or plantain are also used.
As prescribed by a doctor, medications are used in the form of drops in the ear or nose. Among the well-known anti-inflammatory drugs used are: otipax, otrivin, boric acid, anauran. Divided by purpose:
- antimicrobial action;
- single drugs;
- containing glucocorticoids.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, the following types of therapy are prescribed: exposure to high-frequency electromagnetic fields on the hearing organs, warming with alcohol compresses. Electrophoresis procedures are often performed.
To reduce pressure in the ear, the method of blowing the auditory tube is used. When an insect gets inside, you need to use the following sequence: first immobilize it so that it does not damage the eardrum. To do this, use drops of boric acid or oil.
Then you will need to mechanically remove the trapped foreign body by rinsing with a syringe. This procedure is best performed in a clinic setting. All actions should be carried out based on the experience of traditional medicine. A swollen ear will quickly go away with the right technique.
The ear is considered one of the vulnerable and fragile human organs; it is the one that is susceptible to various inflammations, diseases and the formation of edema. Ear diseases are considered the most difficult; tumors can arise inside the ear for any reason and there are various reasons. Ear swelling can easily be classified as one of the most dangerous diseases, sometimes leading to partial hearing loss, and incorrectly prescribed treatment can aggravate the current situation.
Ear pain of non-infectious origin
Ear tumors
Neoplasms are most often localized in the outer and middle sections; tumors of the labyrinth are an extremely rare phenomenon. Malignant formations of the outer ear are accompanied by severe pain: the pain is burning and radiates to the temple. Possible bleeding; When the ear canal is obstructed, conductive hearing loss develops. If the middle section is affected, the symptoms are similar to otitis media; a high degree of hearing loss and intense pain, increasing in the evening, should alert you. When the process spreads, symptoms of damage to neighboring structures arise: loss of orientation in space, paresis of the facial nerve, trigeminal neuralgia.
Ear injuries
- Mechanical injuries. The auricle most often suffers with the formation of lacerations and damage to cartilage. Blunt trauma to the ear usually results in a hematoma. As a result of trauma to the ear canal, the ear hurts greatly, there is a feeling of stuffiness, and bleeding is possible. Such symptoms are an indication to consult a doctor, since rupture of the eardrum and fractures of the skull bones are possible.
- Barotrauma is caused by a difference in pressure in the external environment and the cavity of the middle ear, for example, during a sharp loud sound (explosion), take-off/landing of an airplane, deep-sea immersion (diving), climbing a mountain. As a result, the eardrum is pulled inward, which is accompanied by pain, noise or ringing, and congestion in the ears. The opposite situation is also possible, when a decrease in atmospheric pressure causes the membrane to bulge outward. As a rule, unpleasant sensations go away on their own, however, if sharp pain is noted, it makes sense to check the integrity of the tympanic membrane when examined by a doctor.
- Entry of a foreign body in the form of small objects or insects causes swelling of the skin of the ear canal, itching, pain, and sometimes hearing loss. Attempting to remove a foreign object yourself can damage the eardrum.
- With burns and frostbite of the ears, **pain // of varying intensity is observed, depending on the degree of damage.
- Conventionally, ear injuries include the formation of wax plugs, which irritate the skin of the ear canal, causing discomfort and tinnitus. Removal should be carried out by an otolaryngologist.
Causes of swelling
Tumors in the ear can occur for many reasons, including inflammatory processes with infections, radiation exposure and allergic reactions.
— The causes are most often attributed to inflammatory diseases that can form in the nasopharynx, but spread to the auditory tube. All pathogenic microbes and viruses penetrate the hearing organs and inflammation develops there, leading to hearing loss. This type of inflammation can occur due to weak immunity, lack of vitamin C and A, hypothermia, etc.
It is easy to get an ear infection when playing sports in winter, mainly from running, but it is also possible in summer, this applies to extreme sports enthusiasts and diving into deep water, this is primarily due to high blood pressure. Inflammation can occur due to bruises, blows to the ear and other mechanical damage. This often happens to children.
— Swelling caused by exposure to radioactive substances
. Provoking factors are ultraviolet irradiation, exposure to radioactive elements, chronic inflammation and ear diseases, as well as various types of injuries or, rarely malignant, more often benign formations.
— Allergic edema can occur in both children and adults, but mainly in women; it most often affects people over 25 years of age, and less often the elderly. This disease is commonly known as Quincke's edema. This allergic disease is less common than, for example, laryngeal edema or accounts for only 5-7% of allergic inflammations. In most cases, an allergic disease does not cause any particular harm to health, but if the patient’s condition does not improve, then it is worth seeking professional help.
The reasons can be varied, but usually there is pain in the ear, sometimes spreading to the neck, fluid in the form of pus may be released from the ear, the temperature rises, discomfort is felt, and the formation itself can be felt.
You should not ignore the pain and symptoms that appear; you need to start self-treatment
, but if it does not bring improvement in a few days, then you are powerless and cannot do without medical intervention.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis and treatment of pathologies associated with this symptom is carried out by an ENT doctor (otorhinolaryngologist) or an audiologist (a narrower specialty in otorhinolaryngology). During the appointment, the specialist talks with the patient, examines him, conducts the necessary examination, and establishes a diagnosis.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced, highly qualified otolaryngologists. Rich clinical experience helps them make the correct diagnosis in the most difficult cases.
How to treat swelling in the ear
So, the reasons for the appearance of edema have been established, and if a person is really sure why a tumor has formed in his ear, then you can try to use unconventional methods to eliminate this problem. But only if the problem has appeared recently, it can be neutralized at the initial stage, otherwise you should not wait for complications, but it is better to go to the hospital immediately
. Doctors will conduct a full examination of the hearing organs, determine the causes and prescribe conservative and correct treatment.
Swelling that can be relieved at home
You can get rid of the disease at the initial stage of its formation. There are also old grandmother’s methods for treating swelling and relieving inflammation.
- Salt heated in a frying pan is poured into a sock or any other fabric and while it is hot, applied to the sore spot. This will warm the ear and relieve inflammation. This method is effective only when the disease appears. The procedure must be repeated 5-6 times a day and the salt must be warmed well before applying. Today, special ear warmers are widely used.
- When a person first encountered the problem of swelling in the ear, such medicine and various drugs did not yet exist, so it was believed that you could simply apply a cabbage leaf or plantain to your ear, fix it with a rag and leave it for 2 hours, and then apply a new one. According to many, cabbage and plantain have medicinal properties and can relieve inflammation of any size.
Traditional treatment
At the first manifestations of edema, it so happens that people run to pharmacies for miraculous ear drops. Whether treatment will be effective in this case depends on the degree of the disease.
For inflammatory diseases, doctors prescribe vasodilating drops into the nose, from where the medicinal substances enter the auditory tube. Antibacterial drugs must be used; if the form of edema proceeds without complications, then they are used in the form of tablets, sometimes in injections. To relieve pain, the patient will be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. Depending on the degree of the disease, general therapy, UHF, physiotherapy, alcohol compresses, etc. are also used.
H7239xJg3YE
Tumors formed due to radioactive substances are removed through surgery or eliminated with a laser or radio wave. These swellings cannot be treated at home.
Ear swelling is not a separate diagnosis.
As a rule, this is a symptom of otitis media. Quite often, swelling of the ear is accompanied by otitis externa (changes in the inflammatory nature of the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the external auditory canal). But otitis media and internal otitis are also no exception.
How is barotrauma treated?
If, despite bleeding from the ear, there are no obvious tears or tears, the doctor will recommend physical therapy and further monitoring. Is the integrity of the eardrum compromised? It is important to prevent the development of infectious diseases - average or chronic purulent otitis.
Most often, it is enough to clean the ear, apply a sterile bandage and carry out symptomatic therapy - antibiotics, painkillers. Sometimes a special substance is applied to the membrane, which accelerates its regeneration. If the damage is large-scale, independent healing is impossible. To avoid the need for children's hearing aids in the future, surgical intervention is necessary.
In most cases, mechanical ear injuries do not pose a threat to the health of children. When parents act correctly, they have no consequences. If the young patient is not provided with timely assistance, severe complications may develop over time, including hearing loss. Protect your child from injury and be vigilant: when it comes to health, it is better to be overly attentive than underlooked.
Symptoms
Otitis externa, in addition to swelling of the external auditory canal, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- movement of the auricle causes severe pain, as does pressure on the tragus - the part of the cartilage of the auricle immediately in front of the auditory opening;
- persistent pain in the ear itself or in the parotid area;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the ear area;
- hearing impairment;
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- Possible purulent discharge from the ear.
The swollen ear is painful and reacts to touch. If you compare it with a healthy ear, they differ in size. Due to swelling of the walls of the ear canal, hearing is impaired. The body t can be raised, but this is not necessary.
Otitis media
The middle ear communicates with the nasopharynx through the Eustachian tube, through which infection can penetrate from the upper respiratory tract due to acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, sore throat, rhinitis, sinusitis and other diseases. Children are especially often affected because their Eustachian tube is short and wide, which makes it easier for infection to enter. The process can be one- or two-way.
Symptoms of acute otitis media:
- pain in the ear from moderate to severe, pulsating in nature (pain does not depend on pulling the lobe or pressing on the ear canal);
- increased body temperature;
- possible noise in the ear, dizziness, decreased hearing acuity;
- the presence of discharge (mucous, purulent, bloody) indicates a perforation of the eardrum.
With an aggressive course of the inflammatory process and the absence of adequate therapy, otitis media is fraught with such serious complications as meningitis, sepsis, intracranial abscess formation, and deafness.
Causes
Ear swelling most often occurs in people who frequently come into contact with water, who are professionally involved in sports characterized by increased injuries (professional swimmers, professional boxers, etc.). A sports injury, an unfortunate fall, a blow to the ear - all this can cause swelling of the ear, because it is a rather fragile organ. Constant contact with water, particularly immersion in water, can cause damage to the protective ear film that covers the skin in the auricle. Due to the fact that this lubricant barrier is washed away, dryness, irritation, and peeling occur. This, in turn, compromises the integrity of the protective tissue of the ear canal. And then the bacteria and fungi contained in the water freely enter the ear tissue, causing pain and inflammation. Mechanical damage, for example, when cleaning the ear with a cotton swab, etc. objects can also provoke the occurrence of external otitis, accompanied by swelling of the ear. Swelling of the ear, in particular the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity, can also be a sign of allergies.
Prevention
To prevent ear swelling, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Try to avoid getting water into your ear frequently. After completing the water procedures, the ears should be dried with a towel (and not with a finger or any other objects);
- do not swim in polluted waters;
- use special headphones to prevent water from getting into your ears;
- do not clean your ears with hairpins, sticks, paper, etc. - they can damage the delicate skin of the ear canal, thereby causing the development of infection in it;
- Protect your ears from irritation and from getting paint or hairspray into them, for example.
As for treatment, to reduce swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of the pharyngeal opening, vasoconstrictor nasal drops are used (sanorin, tizin, otrivin, nazivin, naphthyzin, xymelin-spray, etc.). Swelling is also relieved by antihistamines, such as Claritin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Telfast, etc. Antibiotics with cortisone instilled into the ear destroy bacteria and help reduce swelling. A very important condition during treatment is to keep the external auditory canal dry. It is necessary to avoid getting shampoo, soapy water, and other liquids into it until complete recovery occurs.