Why do my hands swell?
Physiological reasons
Unilateral swelling can occur when the lymphatic and blood vessels of the arm are pressed by the body or clothing during sleep.
Small symmetrical swelling of the fingers and distal parts of the hands, especially noticeable when wearing a wedding ring, is observed after drinking alcohol, consuming salty foods and large amounts of liquid in the evening. In women, swelling of the hands, caused by hormonal changes, is often expressed during gestation. As pregnancy progresses, the symptom increases from mild pastiness to a significant increase in volume. Some patients note morning swelling of the fingers before the onset of menstruation, especially against the background of premenstrual syndrome.
Traumatic injuries
Local swelling while maintaining limb function is characteristic of bruises. Accompanied by minor or moderate pain, hyperemia, and sometimes abrasions and bruises. With hematomas, the symptom is more pronounced, and fluctuation can be detected. With sprains, tears, and ruptures of ligaments, swelling is usually more noticeable than with bruises. The pain intensifies when attempting to move or deviate the arm in the direction opposite to the injured ligament. With a complete rupture, some of the functions of the limb are lost.
Fractures are manifested by rapidly increasing swelling, deformation, loss or significant limitation of function, pathological mobility, and severe pain. In case of injuries without displacement of fragments, epiphysiolysis in children, pathological fractures, some of the listed symptoms are absent or weakly expressed, the swelling is insignificant. Dislocations are characterized by clearly visible, rapidly progressing swelling, which is complemented by severe deformation in the joint area, pain, and springy resistance when trying to move.
With frostbite, swelling affects the fingers and spreads to the hands. It can reach a significant volume, which is why the hands resemble pillows. Against the background of increasing swelling, a tingling sensation occurs, turning into a burning pain. The formation of blisters and areas of necrosis is possible, and in severe cases, some of the fingers are torn away. In patients with burns, swelling is combined with sharp pain, redness, and blistering.
Local infectious processes
Swelling, rapidly increasing twitching pain, cyanosis, hyperemia are the main symptoms of all forms of panaritium. In patients with superficial forms of the disease, swelling of the finger is local, minor or moderate. In deep forms of felon, the swelling is significant and extends beyond the finger to the hand. A more rare lesion of the fingers is chinga, a disease that occurs in people who cut up the carcasses of marine animals. Most often the proximal joint of the finger swells.
Boils and carbuncles appear on the shoulder, forearm, and less often on the back of the hand - where there are hair follicles. The swelling in these pathologies is limited; a dense bluish-purple formation with one or several yellowish areas in the follicle zone is detected. With abscesses, the purulent focus is larger in size, and the edema covers a significant part of the segment. Cellulitis does not have clear boundaries; following pus, swelling spreads along the limb.
With infected wounds, the edges and nearby tissues swell, serous and then purulent discharge appears. Erysipelas is characterized by pronounced swelling and the presence of a clearly defined red spot, reminiscent of a geographical map. The appearance of swelling and other symptoms is preceded by fever; in severe cases, disturbances of consciousness and delirium are possible.
Severe swelling is accompanied by purulent lesions of bones and joints - purulent arthritis, osteomyelitis. Pathologies are characterized by intense twisting, tearing, twitching pain, local hyperemia and hyperthermia, and a sharp limitation of movements. Fever and severe intoxication are noted.
Swelling of the hand
Joint diseases
Local swelling is observed in all forms of arthritis. The severity of edema, as a rule, correlates with the severity of the process and intensifies during periods of exacerbation.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
There is symmetrical damage to the joints of the fingers and hands. The swelling is combined with transient or permanent stiffness, redness, and limitation of movement. - Gouty arthritis.
Manifestation of the disease with symptoms of polyarthritis in the fingers is more common in women. In young people, damage to the elbow, wrist, and shoulder joints is possible. The rheumatoid-like form occurs as oligo- or monoarthritis of the fingers. Typically a rapid increase in edema, sharp pain, dysfunction, general hyperthermia. - Psoriatic arthritis.
The shoulder joints, small joints of the hands and fingers suffer. The onset may be acute or gradual. Patients complain of swelling and pain in the affected joints. The pain syndrome intensifies at rest, at night, weakens with movement, throughout the day. Local swelling and purple-bluish skin color are visually determined. - Infectious arthritis.
It is provoked by viral and bacterial infections. With a viral infection, volatile arthralgia and transient edema are observed. Gonorrheal arthritis typically involves the elbow joint and hands. In the syphilitic form of the disease, the fingers are affected. - Occupational arthritis
. Pain and swelling are detected in the most loaded joints; the location of the lesion depends on the profession. Typists, pianists, and office workers experience swelling in their finger joints. Builders and loaders are often concerned about pain, swelling, and limited movement in the shoulder joint.
Deforming arthrosis is chronic. Swelling of the hand occurs some time after a decrease in resistance to stress, discomfort and pain. In the post-traumatic form of the disease, a connection with a previous injury (dislocation, fracture-dislocation, periarticular fracture) is revealed. In idiopathic arthrosis, there are no obvious causes; a history of joint overload is possible.
Vascular lesions
Swelling of the arm due to thrombosis of the vessels of the upper limb occurs below the location of the thrombus. Accompanied by a feeling of fullness and painful heaviness, intensifying with palpation and lowering the hand. Upon examination, tissue compaction and a purplish-bluish tint of the skin are revealed. Numbness, crawling, and decreased sensitivity are possible.
Lymphatic edema of the arm can be detected in patients who have undergone a mastectomy with removal of regional lymph nodes. Sometimes swelling develops against the background of defects of the lymphatic system, scars after burns, postthrombophlebitic syndrome, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis. At the initial stage, swelling appears in the evening and disappears on its own during the night. Then the swelling becomes permanent, combined with tissue compaction. A distinctive feature of edema due to lymphedema is a dimple that does not disappear for a long time after pressure.
Other reasons
Other conditions that cause swelling of the hands include:
- Erythromelalgia.
Attacks occur suddenly, are provoked by compression or overheating of the limb, and are accompanied by severe pain, swelling, intense hyperemia, and an increase in the local temperature of the fingers and toes. All symptoms disappear within a few minutes, sometimes several hours. - Heart failure.
At first, the swelling is hidden and manifests itself as an increase in body weight. In the final stages, swelling of the legs, arms, and face is observed in combination with ascites, hydropericardium, and hydrothorax. - Kidney diseases.
Swelling is observed in the morning, with prolonged hanging of the arms downwards. At first they are hardly noticeable, identified by the difficulties when trying to remove the wedding ring from the finger. Subsequently they become more obvious. They are distinguished by their softness, wateriness, combined with a yellowish coloration of the skin.
Types of hygroma
There are different types of hand hygromas:
Mucous cysts - hygromas occur against the background of deforming arthrosis of the joints. Most often they form at the distal interphalangeal joint - in this case, hygroma occurs in the area of the nail phalanx, at the base of the nail. Hygroma on the finger develops when osteophytes, present in deforming arthrosis, begin to irritate the skin, underlying tissues and capsular ligamentous apparatus. Because of this, a hygroma occurs - a formation that is hollow inside, in a transparent capsule, with transparent, jelly-like contents.
When a hygroma appears on the nail phalanx, it begins to put pressure on the growth zone of the nail and deform it.
Treatment of hand hygroma
Treatment boils down to excision of the cyst. Due to the fact that with mucosal cysts the skin over the lump on the hand becomes weak, the formation is excised along with the changed skin. After the operation, plastic surgery is performed - both with free skin grafts and with complex skin reconstructions.
A tendon ganglion is a cyst that is formed from the tendon sheaths and the walls of the tendon sheaths. Such hygroma of the hand can cause not only pain, but also limitation of motor functions.
Treatment of a tendon ganglion involves removing the formation - this does not pose any technical difficulty. After operations there are practically no relapses or side effects.
Synovial cysts in the area of the wrist joint (hand hygroma) are the most common type of hygroma.
Diagnostics
Orthopedic traumatologists are often involved in determining the cause of hand swelling. If indicated, patients are referred to surgeons, rheumatologists, vascular surgeons, and other specialists. The diagnosis is made based on the results of the following procedures:
- Questioning, physical examination
. The specialist determines the circumstances and time of swelling, identifies other symptoms, and monitors the dynamics of the disease. Evaluates the localization, prevalence, severity of edema, range of motion in joints, color, density, tissue temperature. - Radiography
. Prescribed for injuries, joint diseases, and some purulent processes. Allows you to confirm the presence of fragments or displacement of the articular ends of the bone, inflammatory and degenerative changes. - Ultrasonography.
It is carried out to confirm thrombosis, determine the condition of venous and lymphatic vessels, and assess the prevalence of purulent processes. - Other imaging techniques
. In doubtful cases, MRI is performed for a detailed study of soft tissues, and for the study of hard structures. - Laboratory research
. Tests help detect signs of inflammation, markers of rheumatic diseases, and renal dysfunction.
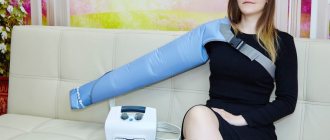
Pressotherapy of hands
Edema during pregnancy
Pregnancy is often accompanied by swelling. This can be explained by physiological reasons: the growing fetus puts pressure on the organs, which disrupts the outflow of blood and causes disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys.
It is more difficult to remove fluid from the body during pregnancy. This phenomenon is especially typical for the first trimester.
But cases of abnormalities in the functioning of the heart and kidneys cannot be ruled out. Therefore, the expectant mother, when swelling of the extremities is first detected, should consult with her doctor. Treatment can only be started after consultation with the doctor, otherwise dealing with swollen hands on your own can have a negative impact on the child.
The doctor prescribes dietary nutrition, medication or herbal diuretic teas. A win-win option is proper nutrition and exclusion of smoked, fried and salted foods from the diet.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
General recommendations include placing the limb in an elevated position. In case of traumatic injuries, the arm should be fixed with a splint or bandage, cold should be applied, and the victim should be given an anesthetic. For joint diseases, local medications with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects can be used. The presence of rapidly growing swelling and intense pain is grounds for immediate contact with a specialist.
Conservative therapy
In case of injuries, the injury site is anesthetized, the arm is straightened or reduced, and a plaster cast is applied. For burns and frostbite, dressings are performed. The treatment regimen for diseases accompanied by hand swelling may include the following methods:
- Protective mode
. The patient is advised to limit the load on the arm. Orthopedic devices are used according to indications. - NSAIDs
. They are used for joint diseases in the form of topical agents, tablets or injections. Reduce the severity of pain. Eliminate inflammation and, as a result, swelling of the hands. - Glucocorticoids
. Blockades with hormonal drugs are performed for joint damage. Indications are intense pain, active inflammatory process, which is not relieved by other medications. - Vascular agents
. Angioprotectors, phlebotonics and antispasmodics are recommended for diseases of the veins and lymphatic vessels. - Physiotherapy
. To reduce pain, relieve inflammation, and improve blood circulation, medicinal electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, UHF, mud therapy, and lymphatic drainage massage are prescribed. - Physiotherapy
. Special exercise therapy complexes are used during the rehabilitation period after injuries, and for diseases of blood vessels and joints. Therapeutic exercise is supplemented with massage and manual therapy.
Surgery
Taking into account the characteristics of the pathology that causes swelling of the hands, the following surgical interventions can be performed:
- Injuries
: osteosynthesis of the humerus or forearm bones, open reduction of dislocations of the shoulder and elbow joint, opening of hematomas, excision of areas of necrosis during frostbite, plastic surgery for burns. - Infectious processes
: opening of felon, boil, carbuncle, abscess or phlegmon, arthrotomy, sequestrectomy. - Joint diseases
: arthroplasty, arthrodesis, endoprosthetics. - Vascular pathologies
: regional thrombolysis for venous thrombosis, tunneling for lymphedema, lymphovenous shunting.
After operations, painkillers are prescribed, antibiotic therapy is carried out, and rehabilitation measures are carried out using physiotherapeutic techniques.
Hygroma of the wrist joint
Most often, wrist hygroma occurs on the dorsum of the joint and looks like an ordinary lump on the hand - round and tumor-like. Hygroma is inactive, painless, dense, elastic consistency, with unchanged skin. According to statistics, almost 70% of hygromas are formed on the back of the wrist.
If the hygroma occurs on the dorsum of the hand, then it is clearly visible when the joint is flexed.
Much less commonly, wrist hygroma develops on the palmar surface of the wrist joint, in the area of the radial artery (in the place where the pulse is usually checked). This arrangement makes the surgical procedure very difficult.
Treatment of hygroma on the wrist
Treatment of such a hygroma is very difficult, since you have to very carefully isolate the cyst in the area of the radial artery, trying not to damage it. Carelessness during surgery can result in serious injury to the artery, which can disrupt the blood supply to the hand. Hygroma on the wrist requires the most professional and careful treatment, so only an experienced surgeon can perform a correct and effective operation.
Folk remedies and doctors' recommendations
If your hand swells for no serious reason, express measures to quickly relieve swelling are:
- compresses - a towel soaked in cold water is applied to the problem area; ice cubes or frozen foods are suitable as an alternative;
- cloth soaked in herbal decoction (chamomile, mint, string, juniper);
- tincture of birch leaves: 3 tbsp. l. pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and keep in a water bath for 10 minutes, then leave in a dark place to infuse for 8–10 hours. Strain through cheesecloth, take 100 g three times a day.
To quickly get rid of puffiness in the morning, you need to raise your arms up for 3-5 minutes to reduce the flow of fluid. Squeeze and straighten your fingers, you can massage your hands and fingers. To prevent your fingers from swelling, it is important to follow preventive measures:
- select jewelry according to size and remove it at night;
- do not wear handbags on the bend of the elbow, because this compresses the blood vessels and causes blood stagnation;
- before going to bed, refrain from consuming foods containing salt and any fast food, reduce daily fluid intake to 1 liter;
- regularly ventilate the room and avoid stuffy spaces;
- add moderate physical activity to your daily routine that will keep your body in good shape: walking, jogging, cycling;
- a contrast shower accelerates blood circulation, and this reduces the risk of swelling;
- baths with the addition of sea salt and herbs will prevent the appearance of edema;
- Monitor blood and urine counts with regular testing.
If you notice morning swelling, you shouldn’t run as fast as you can to the nearest pharmacy for a “miracle drug.” First you need to establish the exact cause of this phenomenon, and only then begin to fight it. Otherwise, self-medication can cause damage to your health. And in order to never experience swelling, it is enough to adhere to simple and accessible preventive measures.
First aid at home
Swollen fingers can be treated with herbs, brew: horsetail, fox birch, St. John's wort. You can buy compression gloves at the pharmacy - they are especially convenient.
First aid should begin with improving blood flow in the fingers:
- Take off everything unnecessary : rings, bracelets, watches; Treat the open wound with an antiseptic and apply a bandage.
- Wrap some ice in a clean cloth and apply it to your swollen fingers. You can also make an iodine grid after some time.
- Massage will also relieve swelling; simple manipulations will increase blood circulation and the outflow of excess fluid.
- For inflammatory diseases you can take : Diclofenac, Nimesil, Ibuprofen.
- In case of allergic reactions , it is necessary to stop any contact with the allergen. Take any antihistamine: Larotadine, Suprastin, Fenistil.
Suprastin
Fenistil
Larotadine