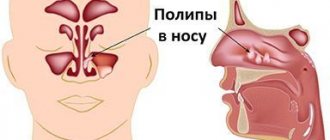
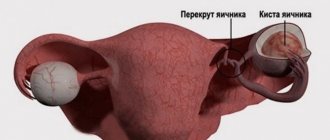
Polyps are benign and develop from the basal layer of endometrial cells. Their size can be several millimeters or centimeters. Typically, neoplasms are localized in the uterine cavity, but sometimes they grow into the vagina. The age group of patients is different, so they are often detected even in young girls.
The structure of neoplasms includes endometrial glands, stroma, and the central vascular canal. They can be subject to infection, metaplasia, ulcers, and necrosis. There are 4 types of neoplasms:
- formed by the glandular endometrium, usually appear in girls;
- glandular-fibrous - in addition to the glandular layer, they include connective tissue, most often develop in middle-aged patients;
- fibrous, formed by connective tissue, women over 40 are susceptible to them;
- they are formed by glandular epithelium, have signs of proliferation, and may precede uterine cancer.
Placental polyps that arise due to complications after childbirth, abortion, miscarriage, or frozen pregnancy are also identified.
Do I need to remove polyps in the uterus?
The opinion of experts is clear - remove them, since they are often the cause of infertility and can lead to various complications. In some cases, the final decision is made by the patient, who is informed of the possible consequences of refusing surgery. If the following indications are present, surgical intervention is mandatory:
- age after 40, premenopausal period, when hormonal changes occur in the body, provoking the active growth of tumors;
- if the size of the polyps is more than 10 mm, they interfere with conception, cause bleeding, and can develop into oncology;
- in the treatment of infertility - overgrown formations impair the movement of sperm through the tubes, and even in the case of fertilization lead to termination of pregnancy in the early stages;
- lack of effect from hormone therapy, which relieves the symptoms of the disease - bleeding, menstrual irregularities, pain, discharge mixed with pus;
- the presence of adenomatous forms.
The decision is made by the doctor after diagnosis. If the neoplasms are single, their size does not reach 10 mm, conservative treatment with the use of hormonal drugs is possible.
Causes
The reasons for the appearance of polypous growths are still being studied, but an important role in etiopathogenesis is played by:
- hormonal imbalance;
- injuries, including medical procedures (curettage);
- infectious, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives, etc.
Diagnosis of polyps is difficult; often they do not manifest themselves at all, and the disease is asymptomatic. Reasons for examination include excessive discharge (leucorrhoea) and intermenstrual bleeding. The diagnosis is made by ultrasound examination of the uterus. Hysteroscopy is used to identify small polypous growths. If a polyp is detected, treatment is required. Sometimes reverse development of the tumor is observed after conservative therapy. Removal is resorted to if there is no result.
Hysteroscopy is usually used for diagnostic examination and resection of a mass in the uterus. It can also be removed with a laser, but the prices for such a service are higher due to the high cost of the equipment.
There are several theories for the development of cervical and uterine polyps. Most often, a polyp in the uterus appears as a result of hormonal imbalance - this is the most common version of the causes of the pathology. Under the influence of high levels of estrogen, the endometrium of the uterus (inner layer) grows. The endometrium can grow evenly, then hyperplasia appears. In case of uneven growth of the endometrial layer, polyps form in the uterus and cervix. Progesterone deficiency ensures the active growth of benign formations.
The following factors contribute to the appearance and growth of polyps in the cervix and uterus:
- Fibroids and myomas.
- Ovarian dysfunction.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Endometrial hyperplasia.
- Chronic infection in the genitourinary organs, including sexually transmitted infections and human papillomavirus. During inflammation, there is a sharp increase in the number of leukocytes (immune cells), which, along with the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms, promotes the growth of cells of the inner uterine layer.
- Cervical polyps most often appear after unsuccessful curettage.
- Chronic stress leads to an increase or decrease in hormone levels.
- Vascular obstruction - epithelium grows around a blocked vessel.
- Hereditary factor - polyps of the uterus and cervix are more often formed in those patients whose relatives suffered from polyposis. This category of women should be especially attentive to their health and undergo regular preventive examinations.
- An inactive lifestyle contributes to the appearance of congestion in the pelvic organs, as a result of which the uterus and appendages experience a lack of oxygen, which leads to hormonal imbalance and cell proliferation.
- The drug Tamoxifen is used in the treatment of cancer; it causes hormonal disorders. In some patients, a polyp may form in the cervical canal of the cervix or in the uterus.
Diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, obesity) contribute to the development of polyposis. The endocrine glands function in close connection, so disturbances in one gland lead to a malfunction of the other, in particular in the ovaries, which begin to produce sex hormones at an accelerated pace. In diabetes mellitus, microcirculation is disrupted, cell hypoxia occurs, which contributes to their proliferation and atypical changes. With excess weight, adipose tissue produces estrogens, which provoke an increase in cervical polyps. When ovarian function is disrupted, a large amount of estrogen is synthesized, which is released into the blood constantly (normally, the hormone is produced in the first 14 days of the cycle).
As a result, during menstruation, individual fragments of the endometrium remain in the uterine cavity, rather than exfoliating and coming out. Gradually, connective fibers and vessels grow into these areas. This is how a uterine polyp appears.
Surgery to remove endometrial polyp
Polyps are removed in several ways, the most used of which are hysteroscopy and curettage. Regardless of the technology of surgical manipulation, a tissue sample must be sent for histological examination for oncology. Other methods are also used:
- scraping;
- cryodestruction (carried out with liquid nitrogen);
- polypectomy;
- laser coagulation;
- diathermocoagulation.
Before determining the optimal technique, the doctor conducts a thorough diagnosis - examination, ultrasound, tests. The patient’s age, individual characteristics of the body, and areas of localization of tumors are also taken into account. The order of the procedure and the timing depend on the method of intervention.
Preoperative diagnosis
The proctologist diagnoses formations located near the anus during a digital examination. However, the main method for diagnosing rectal polyps is a hardware examination using sigmoidoscopy, which will provide a volume of information sufficient to select a treatment method: • localization, size and morphological appearance of growths; • presence of complications (bleeding, suppuration); • histological type of tumor (tissue sampling is carried out according to indications); • condition of the rectum.
If the doctor decides to undergo surgery, it will be necessary to undergo a standard preoperative examination, which includes: • a general blood and urine test; • blood chemistry; • determination of blood group and Rh factor; • coagulogram + determination of blood sugar levels; • tests to detect blood-borne infections (hepatitis B and C, HIV, syphilis); • ECG; • fluorography; • consultation with a therapist, and for women – consultation with a gynecologist.
Additionally, you may need: • gastroscopy (EGD); • colonoscopy; • CT scan of the abdominal cavity; • Doppler ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities; • ECHO-KG.
Removal of endometrial polyp - hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopic removal is considered the most gentle, since it is carried out without violating the integrity of the tissue. Dilators are inserted into the vagina, allowing the surgeon access to the affected areas. Then, using a hysteroscope equipped with a light source and a video camera, an enlarged image of the polyp is displayed on the monitor. Guided by the video material, the doctor removes the tumors and cauterizes the areas where they were located.
The procedure lasts 20-40 minutes and is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the number of polyps.
A week before hysteroscopy, the patient should not douche, use suppositories, take medications (except those prescribed by the gynecologist), and sexual intercourse should be avoided for the last 3 days. The operation is scheduled for the 10-15th day of the menstrual cycle. The recovery period lasts 1-2 months. You can plan a pregnancy in six months.
Removal of endometrial polyp with laser
Laser therapy is an effective technique that involves the use of laser beams of varying intensities. So, for small tumors, weaker rays are used. For large ones, over 10 mm, high-intensity rays are used. During the procedure, a hysteroscope with an LED and a mini camera is inserted into the vagina. Then the surgeon, guided by the image on the monitor, directs a laser at the affected area and burns out the polyp. The beam removes the tumor layer by layer without damaging other tissues, eliminating infection and completely removing the stem. There are no scars left after the procedure.
Appearance
The appearance of polyps is varied: most grow on a thin stalk, hanging into the intestinal lumen. Less common are neoplasms with a wide base, and even less common are tumor-like forms that slightly rise above the surface of the rectal mucosa. The size of a typical polyp is from 0.5 to 2 cm, but there are also giant forms that can block the intestinal lumen. As the size of the formation increases, the risk of transformation into a malignant tumor increases. Small formations (up to 0.5 cm) are represented predominantly by hyperplastic polyps , the cells of which differ little from normal epithelial cells and are characterized by a minimal risk of cancer transformation.
Large pathological elements (more than 2 cm) often have a villous surface, which is easily injured and bleeds. Such neoplasms are especially dangerous in terms of transformation into rectal cancer .
Endometrial polyp curettage
Curettage or curettage is a popular technique that involves removing the top layer of endometrial cells. To do this, an inert gas or a special liquid is pumped into the uterus to improve visibility of the operated area. Then a hysteroscope equipped with a camera and illumination is inserted into the cavity vaginally, through which an enlarged image of the area affected by polyposis is displayed on the monitor screen. Having obtained a clear image, the surgeon scrapes off the endometrial mucosa with a curette. The procedure takes 20-40 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia. If no complications arise, the patient is discharged the next day. Contraindication to curettage is inflammatory processes in the uterus.
Watch the video
Preparation
The procedure is usually carried out on days 6-10 of the cycle. This is the most favorable period, since it is at this time that the endometrium is thin. This approach greatly simplifies the process of removing polyps. If surgery is needed urgently, the doctor can prescribe it on any day of the cycle. The main condition is the absence of severe bleeding.
In preparation for the procedure, the woman is examined by a gynecologist, anesthesiologist, and therapist. Additional studies may be required as directed by your doctor to identify concomitant diseases. The vagina is carefully examined. A repeat ultrasound is performed. Laboratory tests are also being carried out and test results are awaited.
A day before the operation, the woman should begin preparation. Do not eat heavy foods that can lead to gas formation. In the evening, you should refuse to eat, but continue to drink still water as needed. An enema is given at night. On the morning of the operation, smoking is prohibited and you should refuse food and liquid. The enema is also repeated. After or before the procedure, in order to avoid the development of inflammatory processes, the patient may be prescribed a course of antibacterial drugs.
Recovery
After using minimally invasive polypectomy techniques, the recovery period is 2-3 months, which depends on the patient’s age, body condition, the nature of the tumors, their size, and quantity. To consolidate the effect and prevent relapses, the following types of therapy are practiced:
- Medication. For the first three days, No-Shpa (Drotaverine) is prescribed to eliminate pain and also prevent the accumulation of blood clots in the uterus. If necessary, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and/or antibiotics if there is a pathogenic microflora.
- Herbal medicine, taking vitamins, dietary supplements, diet, promoting a speedy recovery.
- Hormone therapy. Indicated if the occurrence of polyps is due to hormonal imbalance. The selection of drugs is carried out individually.
One of the treatment methods or all in combination can be used. Also, after the operation, you cannot have sex, lift weights (no more than 3 kg), play sports, go to the sauna, or take baths.
Complications
• Large polyps can block the intestinal lumen and cause a fatal condition - acute intestinal obstruction. • Bleeding from villous growths contributes to the development of anemia. • Secretion of mucus by adenomatous tumors leads to dehydration and symptoms of hypokalemia : ___• increased fatigue; ___• muscle weakness up to the development of paralysis; ___• heart rhythm disturbances. • The inflammatory process associated with fibrous formations depletes the body and can be complicated by purulent inflammation of the perirectal tissue and sepsis. • Adenomatous and villous polyps inevitably develop into rectal cancer 5-15 years after their occurrence. Treatment for rectal cancer often involves “life with a colostomy bag” and painful courses of chemotherapy. High mortality is associated with early liver metastases, in such cases the prognosis becomes hopeless.
Pregnancy after endometrial polyp removal
Usually you can plan a pregnancy after six months. This depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the severity of the disease, but you should not delay it, as relapses are possible. After removal surgery, the likelihood of becoming pregnant increases several times.
In medical practice, there are cases when a neoplasm appears during pregnancy. There is no need to panic if after childbirth, due to changes in hormonal levels, the polyp does not resolve, it will be removed. Such procedures are not performed during pregnancy.
Symptoms
Rectal polyps are characterized by an asymptomatic course. In typical cases, formations are discovered accidentally during examinations that were prescribed for preventive purposes or for the diagnosis of another disease. Symptoms appear with significant growth sizes, as well as with multiple polyposis. • Formations consisting of fibrous tissue are prone to inflammatory reactions, which are manifested by signs of proctitis: frequent painful urge to defecate, loose stools, mucus and pus on the surface of the stool. • Adenomatous (glandular) polyps secrete a lot of mucus into the intestinal lumen, which can cause loose stools. • Villous formations often bleed, so blood may be released in the stool. • growing on a long stalk can “fall out” from the anus, attracting the attention of patients.
Consequences of polyp removal
Since polypectomy is considered a minimally invasive, gentle operation, complications are rare. Usually after it there is bleeding that lasts up to 10 days, brown discharge, and leucorrhoea mixed with blood. If the discharge has an unpleasant odor or contains pus, you should immediately consult your doctor. After removal, the first few days the temperature may rise to 38 degrees, pain in the lower abdomen. There is also a change in the menstrual cycle. The first couple of months the cycle is not regular. Then it is restored. If menstruation has not returned, has become painful and lasts more than 7-8 days, this is a reason to consult your doctor.
Polypectomy is usually well tolerated and proceeds without complications in 90% of cases.