Candidate of Medical Sciences, ENT surgeon Gaidukov Stanislav Sergeevich
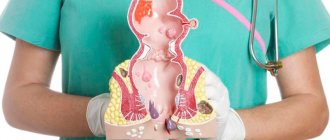
The palatine tonsils, together with the lingual and nasopharyngeal tonsils and other smaller accumulations of lymphoid tissue of the pharynx and nasopharynx, form the Pirogov-Waldeyer lymphoid ring, which is a protective barrier against infection in the lower respiratory tract.
But all of the above applies to healthy tonsils. If a chronic inflammatory process occurs in them, then the tonsils themselves become a source of infection, which gradually weakens the immune system. Inflamed tonsils can provoke serious diseases of other organs and systems: heart, kidneys, joints, liver. In addition, the course of many chronic diseases is aggravated, allergic reactions occur, and tonsillogenic intoxication may occur: a person becomes lethargic, quickly gets tired, and appetite decreases. It often happens that conservative treatment in this case is not enough, then removal of the source of chronic infection may be indicated, i.e. surgical intervention to remove the tonsils - tonsillectomy. This is one of the oldest surgical interventions, actively used by people over the past 2000 years. During this period of time, new techniques were formed (use of electric current, ultrasound, laser, etc.).
What is tonsillectomy?
Removal of palatine tonsils is one of the most common operations in the practice of an ENT doctor.
Many people think that it is performed only for children, but this is not so. Adults may also need it if chronic tonsillitis has become severe and is accompanied by purulent complications, and enlarged tonsils interfere with swallowing and even breathing, causing sleep apnea syndrome - a short-term cessation of breathing during sleep. The palatine tonsils sometimes become inflamed. Inflammation of the tonsils (tonsils) is referred to as tonsillitis. It, in turn, can be acute and chronic.
Inflammation of the tonsils. Photo: James Heilman, MD / (Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license)
Acute tonsillitis is called tonsillitis. With chronic tonsillitis, the inflammatory process lasts for years, with periodic exacerbations. An exacerbation is usually accompanied by fever, sore throat and sore throat, including when swallowing.
The tonsils become coated, bad breath appears, and the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged. If exacerbations recur one after another, and conservative treatment does not help, you have to resort to surgical treatment - removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy).
Indications for tonsillectomy
In addition to chronic tonsillitis, this operation is indicated for pathological enlargement of the tonsils (hypertrophy), which narrow the lumen of the pharynx.
Also, tonsillectomy surgery may be necessary for conditions such as rheumatism, pyelonephritis, endocarditis. If oncology of the palatine tonsils or papillomatosis of the palatine tonsils is suspected, in all cases, after tosillectomy, further histological examination of the tonsils is carried out.
Until about four years of age, complete removal should only be carried out in an emergency situation (for example, in the case of an abscess, encapsulated purulent inflammation, sleep apnea), since at this age the tonsils are quite important for the development of immunity.
Difference from tonsillotomy
Along with tonsillectomy, there is another operation with a similar name - tonsillotomy, in which enlarged tonsils are removed not entirely, but partially (usually in children). The indication for such an operation is the hypertrophy of these tonsils, when they occupy the entire space from the anterior palatine arch to the midline of the pharynx. With tonsillotomy, only the “excess” of enlarged tonsils is removed, returning them to normal size. Tonsillotomy is less traumatic than radical removal of the tonsils, and allows you to preserve their protective functions.
How to prepare properly
Before surgery, a number of tests are required:
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Blood test for HIV and syphilis;
- Coagulogram (blood test for clotting);
- Electrocardiogram;
- Fluorography;
- Bacterial culture from the tonsils to determine the type of pathogenic microflora;
- A conclusion from a general practitioner that the patient has no contraindications to this operation.
Additionally, other diagnostic procedures may be prescribed.
In addition, the patient must follow the following recommendations:
- A couple of days before surgery, you can take mild sedatives (in consultation with your doctor) to avoid feelings of anxiety or fear;
- The operation is carried out on an empty stomach, 7-8 hours before the procedure you are required to refuse food;
- You must tell your doctor what medications you take on an ongoing basis. Some medications that may affect blood thinning may need to be discontinued several days before surgery;
- It is recommended to stop smoking 3-4 hours before surgery;
- Alcoholic drinks must be eliminated at least 3 days in advance.
Why doesn't conservative treatment help?
Due to immunodeficiency (congenital or acquired) or concomitant diseases that contribute to prolonged inflammatory processes (diabetes mellitus, chronic infection), conservative treatment of tonsillitis may be ineffective.
Important! Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus can settle in the tonsils, which causes rheumatic damage to the heart, joints and kidneys. Removing the tonsils avoids these complications.
Other factors that complicate conservative treatment include smoking and alcohol abuse. For teachers, singers and actors, the risk factor is the need to talk long, loudly and a lot.
Acute tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis - tonsillitis - is most often caused by streptococci. It must be remembered that they are transmitted to others by coughing and sneezing, so a patient with a sore throat needs to be isolated - placed in a separate ventilated room, with separate dishes allocated for him.
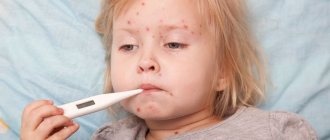
Sore throat is an infectious disease accompanied by high fever, general weakness, aching muscles, joints, etc., with local manifestations on the palatine tonsils in the form of swelling, redness, ulcers or plaque. This pus is an accumulation of dead cells that fight the causative agent of sore throat. Often, with a sore throat, an ichorous (putrid) unpleasant odor is felt at a distance from the patient. It is emitted by dead microbes, from which the toxin has been released, placed in the pharynx and absorbed into the body through the vessels, through breathing - into the lungs, through the digestive tract. There is a powerful bacteremia - the body is filled with toxic substances and bacteria.
The danger of sore throat is that the body, fighting the streptococcus that causes sore throat, destroys its own organs. Streptococcus contains a special protein similar to some proteins in the human body. Because of this similarity, the body’s protective antibodies against streptococcus begin to attack its own tissues in the heart, kidneys, and joints. This is a complication of angina.
If a sore throat is not treated correctly, complications may include heart defects, kidney disease - glomerulonephritis, and joint damage. It is believed that the huge number of heart defects in modern 70-80 year old people is due to the fact that in the 30s, when they were children, there were no drugs to combat such microbes. These drugs were invented only in the late 30s and early 40s.
Sore throats can be complicated by a paratonsillar abscess - suppuration of the soft tissue around the tonsil. This is a very serious disease that requires hospital treatment.
It is important to note that many people often mistake any sore throat for a sore throat. Typically, a sore throat, especially a very severe one, is a sign of acute or exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis, and not a sore throat. In any case, the diagnosis of angina should be made by a doctor, preferably an otolaryngologist.
At what age is surgery performed?
Surgical treatment may be recommended for adults and children over 8 years of age. By this time, the tonsils are fully formed. The palatine tonsils are an integral part of the pharyngeal ring - a group of tonsils (paired palatine and tubal, unpaired nasopharyngeal and lingual) - an important organ of local immunity of the nasopharynx and respiratory tract. Early removal of tonsils can contribute to the development of atopic diseases - allergic rhinitis or bronchial asthma. Such operations are usually not performed on children under three years of age, since they rarely have tonsillitis - the tonsils are too small.
Important! Tonsils can be removed no earlier than six months after polio vaccination.
Indications for tonsil removal at the First Surgery clinic
Surgical removal of the tonsils is prescribed to the patient after a comprehensive examination. The patient undergoes examination not only from an ENT specialist, but also from other doctors.
Tonsil removal is recommended for people with the following problems:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- complications after chronic tonsillitis;
- rheumatism;
- polyarthritis;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- kidney diseases;
- inflammation of the thyroid gland;
- purulent complications in the throat;
- lack of results from drug treatment of tonsillitis;
- snore;
- neoplasms on the tonsils.
Need a procedure? Make an appointment
Contraindications
They can be absolute (excluding the possibility of tonsillectomy) and relative, when everything is postponed until the reasons preventing the operation are eliminated.
Absolute contraindications:
- diseases with increased bleeding: hemophilia, hemorrhagic diathesis, Werlhof's disease, agranulocytosis, leukemia;
- heart failure grade 2–3;
- acute infectious diseases and exacerbation of chronic ones;
- active form of tuberculosis;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
Relative contraindications:
- caries (before sanitation - dental prophylaxis of the oral cavity);
- inflammation of the gums;
- pustular diseases of the mouth and skin;
- ARVI and influenza;
- exacerbation (decompensation) of chronic diseases;
- menstruation;
- pregnancy after the 26th week due to the risk of premature birth.
Why you should contact us
If you need tonsil removal or other ENT procedures, contact the RAMI clinic in St. Petersburg.
We carry out various types of surgical interventions, as well as laboratory tests. With us you will receive specialist consultations, diagnostics and support during the rehabilitation period to speed up recovery.
The price of tonsil removal depends on the technique, individual characteristics of the patient and other factors. The final cost is calculated by the doctor during consultation.
To make an appointment, call the clinic.
If you are really looking for your doctor...
Types of tonsil removal surgeries
Classical
The surgeon installs a mouth retractor and separates the tonsil tissue along with the capsule from the surrounding tissues in a “blunt” way using a raspator. The bleeding is stopped, the vessels are cauterized with an electrocoagulator or laser. The whole process takes from 15 to 40 minutes.
Electrocoagulation
Figure 1. Incision at the base of the tonsil during electrocoagulation.
Source: Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery / Open-i (Attribution 4.0 International) Instead of a scalpel, a high-frequency current electrode is used. The vessels are “sealed”, so blood loss is minimal. Recovery may take longer due to associated injuries to surrounding tissues.
Removed tonsils. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery / Open-i (Attribution 4.0 International)
Cryodestruction
Tonsils are frozen with liquid nitrogen. As a result, they become pale, flat and hard, and after a day they die and are gradually rejected. The method is recommended for patients with an increased risk of bleeding (thrombocytopenic purpura, hemophilia, etc.), severe heart failure and endocrine pathology.
Important! The cryosurgical method is used in a series of procedures lasting up to 1.5 months. During this time, a relapse of the disease is possible if not all of the tonsil tissue has been destroyed. Cryosurgery is used when classical surgery is not possible.
Ultrasonic destruction
High-frequency sound vibrations warm up the tissues to prevent bleeding. Unlike exposure to liquid nitrogen or electricity, surrounding tissue is almost not damaged. Ultrasound method is one of the least traumatic.
Radio wave destruction
A probe is installed inside the tonsils, which generates radio waves. They evaporate the water from here and cause scarring. Ablation can be repeated several times. Anesthesia is not needed here - only local anesthesia or light sedation. Recovery is quick, but radical tonsil removal is almost impossible. Therefore, radio wave therapy is used for their hypertrophy, but not for chronic tonsillitis, when radical intervention is required.
Cold plasma destruction
A relatively new method of removing tonsils. It is based on the property of cold plasma (radio frequency energy converted into ionic dissociation) to separate molecular bonds in tissues without releasing thermal energy. Plasma is called cold because it causes minimal heating of the tissue, which means that pain after surgery will be insignificant, recovery will be easy and quick. The method is low-traumatic and can be used for partial or complete removal of tonsils.
Laser removal
Laser tonsillectomy can be complete or partial (with cutting of the upper layers of the tonsils). Different types of laser are used - carbon, infrared, etc. Only pathological tissues are removed, and healthy ones are not affected. Other advantages include immediate separation of the tonsil from the underlying tissues with coagulation of blood vessels, which reduces the risk of bleeding and infection.
Operation options
Most often, a bilateral tonsillectomy is performed, that is, complete bilateral removal of the tonsils. How is tonsil removal done? There are several variations in how the operation is performed.
The classic type of operation is mechanical removal using a scalpel, a special loop and surgical scissors. This is a radical way to get rid of chronic tonsillitis. Recovery after surgery is long and quite painful. Another disadvantage of this operation is the high likelihood of bleeding.
Currently, classical surgery is being replaced by microinvasive tonsillectomy, which is much easier to tolerate by patients, avoids heavy blood loss and makes it easier to recover from surgery. There are several modern methods for removing tonsils.
- Laser tonsillectomy. How is laser tonsillectomy performed? Under the influence of laser radiation on the lymphoid tissue of the tonsil, liquid evaporates from it, and the vessels are coagulated (cauterized), which avoids bleeding. The patient does not experience pain. The wound at the site of the removed tonsil heals quickly enough, so the patient’s recovery is quick and easy. The downside of this operation is the heating of healthy tissue, which can lead to burns.
- Radio wave method. How is tonsillectomy performed using the radio wave method? Under the influence of a radio wave created by the Surgitron or Fotek surgical apparatus, the liquid from the tonsil tissue is evaporated. The operation is bloodless and does not damage healthy tissue. Swelling after surgery disappears quickly enough, and the patient recovers easily.
- Ultrasonic removal is carried out using an ultrasonic scalpel, which heats and destroys the affected tissue. This is a low-traumatic, safe method of removal. Thanks to the effects of ultrasound, tissue regeneration proceeds faster.
- Cryodestruction. During this procedure, the tonsils are exposed to low temperature, the source of which is liquid nitrogen. After this, the inflamed tissue is rejected. This is the most non-traumatic, bloodless method of removal. It does not require special postoperative care, is carried out quickly and is very easily tolerated by patients.
- Coblation is the effect of cold plasma on the tonsils. The operation is performed using a special device that converts electricity into plasma. The plasma flow does not burn healthy tissue. The recovery period after coblation is the shortest and most painless of all removal methods. The disadvantage of the operation is its price and low prevalence. Few medical institutions offer this service.
When deciding on an operation, the ENT doctor will definitely explain all the pros and cons of each type of surgical intervention and give recommendations on what is best to choose in a particular case.
Many patients before tonsillectomy ask the question: “What is the danger of removing tonsils?” Possible complications after surgery include the likelihood of relapse if tonsil tissue is not completely removed; the likelihood of bleeding in the first hours after surgery and infection of the wound (more often in patients with weak immunity).
Postoperative period
Figure 2. Appearance of the throat after tonsillectomy. Source: James Heilman MD, CC BY-SA 3.0.
Recovery usually takes 3–4 weeks, the first of which takes place in the hospital. This is necessary in order to respond in time to the most common complication of tonsillectomy – pharyngeal bleeding. To prevent it, hemostatic drugs are prescribed.
From the operating room the patient is transferred to a ward under the supervision of the attending physician. On the first day, it is forbidden to swallow, spit or expectorate saliva. You can only breathe through your mouth. In case of severe pain, the patient is prescribed painkillers.
A diet is recommended for all days of the postoperative period
- on the first day, adults should refrain from eating, and small children should not eat or drink for the next 6 hours;
- In the first week after surgery, it is recommended to eat liquid, smooth food;
- During the recovery period, food should be soft; it is not recommended to eat too hot, cold, sour, or spicy. This may irritate the mucous membranes of the throat and mouth.
- In the postoperative period, if necessary, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
Figure 3. Memo: what you can and cannot eat after surgery.
Source: verywellhealth.com Bed rest must be observed for 2 days. In most cases, the patient is discharged from the hospital within a week for outpatient observation and treatment.
Recovery period after removal of tonsils
Complete rehabilitation occurs 2–3 weeks after the operation. During this time, the child and his parents need to follow certain measures that will help prevent the development of a new infection and injury to the palate.
- In the first 6–8 hours after removal of the tonsils, you should not give your child food or drink.
- Subsequently, for 3–6 days, the child’s diet should consist of soft, pureed foods that are easy to chew and swallow.
- You should not give babies sour, very sweet, excessively hot and salty foods.
- Cold drinks, meals and ice cream can only be offered if children have been exposed to cold foods without any consequences before surgery.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor every day.
- Limit communication with other children, strangers and distant relatives during rehabilitation.
- Avoid visiting crowded places, swimming pools, baths, and ponds to reduce the risk of re-infection.
In the absence of complications and good health, children after tonsillectomy can lead a normal lifestyle. It is advisable to somewhat limit physical activity in the first week of rehabilitation and carefully monitor that children do not damage the palate with foreign objects.
Complications after removal of tonsils
The most common of them is bleeding, which can develop both on the first day after the intervention (primary bleeding, and 5-6 days after it. The incidence of postoperative pharyngeal bleeding ranges, according to various observations, from up to almost 60%. Minor bleeding after removal of the tonsils is stopped using a tampon, electrocoagulation, or the anterior and posterior palatine arches are sutured together to reduce the area of bleeding.
Also, as a side effect of the procedure, there is a risk of blood aspiration (blood entering the respiratory tract). Then the blood is urgently removed with an electric suction and bronchoscopy is performed.
After removal of the tonsils, swelling of the soft palate and larynx is possible. If signs of difficulty breathing appear, decongestant therapy is carried out.
If the wound becomes inflamed after removal of the tonsils, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
In most cases, the operation takes place without complications or side effects. If the patient experiences pain, the doctor will prescribe analgesics on the first day after removal of the tonsils, and then non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Sometimes the patient may experience voice changes, taste disturbances, and nasal sounds.
It is extremely rare to experience damage to the temporomandibular joint due to forceful opening of the mouth with a mouth opener during tonsil removal.
Possible consequences of surgery for children
The likelihood of adverse events after removal of the tonsils is minimal, especially if the operation was performed in a specialized clinic. In rare cases, complications after tonsillectomy include:
- discomfort when swallowing;
- minor bleeding;
- damage to surrounding tissues during thermal excision methods;
- pain in the first time after surgery.
For the most part, all these phenomena go away on their own as the tissue heals. If the wounds have healed and the discomfort and pain have not disappeared, additional diagnostics are carried out.
The most dangerous complication is bleeding.
- In case of minor bleeding from small vessels, it is enough to treat the surface with antiseptics.
- In more serious cases, the vessel that is the source of bleeding is identified, a clamp is applied, and the bleeding tissue is sutured.
- In case of massive bleeding, tamponade is used: a gauze swab is inserted into the oral cavity and pressed against the palate under strong pressure. After 3-5 seconds, the tissue is removed to see the source of the bleeding, and then it is eliminated using a clamp and stitching. The patient is additionally administered drugs that accelerate blood clotting.
To prevent infection, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed before and after surgery.
Sources
1. Palchun V.T.
Otorhinolaryngology: national guidelines. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2016. 2. Karpishchenko S.A., Svistushkin S.M. Chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis. Immunological and clinical aspects. St. Petersburg: Dialogue, 2017.
3. Lukan N.V., Sambulov V.I., Filatova E.V. Conservative treatment of various forms of chronic tonsillitis. Almanac of Clinical Medicine, 2010, 23: 37-41.
4. Belov, B.S., Shcherbakova M.Yu. A-streptococcal tonsillitis: modern aspects. Pediatrics. 2009, 88(5): 127-135.
5. Turovsky A.B, Kolbanova I.G. Chronic tonsillitis - modern concepts. Doctor.RU, 2009, 49(5): 16-21.
Chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the palatine tonsils, which participate in the formation of immunity and protect the body from infection.
If infectious attacks are prolonged, frequent, or a person’s immunity is weakened, the accumulation of bacteria on the tonsils leads to inflammation.
If tonsillitis is not treated in a timely manner, it can develop into a chronic form. Chronic tonsillitis can also be caused by:
- frequent respiratory diseases;
- chronic pathologies that reduce general immunity;
- immunodeficiency states;
- the presence of deviated nasal septum and other problems in the functioning of the ENT organs;
- long-term foci of inflammation, for example, caries, stomatitis, pharyngitis, enlarged adenoids, otitis media and others.
As a rule, chronic tonsillitis is caused by streptococci. Less common pathogens are staphylococcus, mycoplasma and chlamydia.
The development of chronic tonsillitis is facilitated by eating cold food, general hypothermia, alcohol abuse, smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, frequent stress and overwork, and poor nutrition.
Chronic tonsillitis is of two types: compensated and decompensated. In the first case, the functioning of the tonsils is practically not affected, local symptoms appear. The decompensated form is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication and complications.
We care about your health
Palatine tonsils or, as they are also called, tonsils , are located in the nasopharynx. They represent a concentration of lymphoid tissue and perform two important functions. The hematopoietic one is most important at an early age, and the protective one is responsible for immunity - general and local. The tonsils are the first to take the blow that viruses and bacteria inflict on the body. Frequent sore throats and viral infections, as well as decreased immunity, contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis - inflammation of the tonsils. This disease - tonsillitis, according to statistics, is diagnosed in every 10th adult and in 15% of children. At the initial stage, the pathology often responds to conservative therapy, including physical therapy. If there is no progress in the treatment of chronic tonsillitis, the doctor recommends removing the tonsils using surgery - tonsillectomy. The operation is performed in several ways, but the most effective and safest is the removal of tonsils (tonsils) using a laser.
Tonsillitis - what the disease looks like
What does a healthy throat look like?
What does tonsillitis look like - inflammation of the tonsils (glands)
Preparing for tonsillectomy surgery
Laser tonsillectomy is a highly precise, bloodless operation that uses a laser system. A source of directed laser radiation affects the inflamed tonsils, their tissue is excised. Radical laser tonsillectomy involves removing the entire tonsils to remove a chronic source of infection.
Benefits of tonsillectomy:
- There is no bleeding, compared to classical surgery, there is no need for electrocoagulation of blood vessels, as well as subsequent antibacterial therapy.
- A tonsillectomy does not require general anesthesia.
- Possibility of performing the intervention on an outpatient basis.
- Long-term recovery is not required, and the patient’s ability to work is not affected.
The procedure does not require special preparation. The patient is prescribed a set of standard tests - urine and blood tests, if necessary - ECG, conclusions of other specialists. The operation itself lasts no more than 30 minutes. Depending on the degree of damage to the tonsils, surgery can be performed using different types of laser:
- holmium;
- fiber optic;
- carbon;
- infrared.
Carrying out a tonsillectomy under anesthesia involves local anesthesia - an anesthetic drug is applied to the mucous membrane. The patient feels only numbness or slight tingling during the operation. The doctor then grasps the tonsil using forceps and uses a laser beam to excise the tissue. Removal occurs in 4 approaches - each on average 15 seconds. There is no bleeding, since under the influence of the laser tissue the vessels instantly coagulate.
Indications for laser tonsil removal
Removal of tonsils is carried out according to strict indications, although several decades ago this operation was prescribed for preventive purposes. But later experts proved that preserving the tonsils is very important for the immune system. Indications for intervention include:
- Frequent relapses of chronic tonsillitis (more than 4 times a year).
- Lack of effectiveness of antibacterial treatment.
- Complications on the kidneys, heart, joint damage (rheumatism).
- Significant proliferation of tonsil tissue, which causes breathing and swallowing problems.
If there is significant damage to both tonsils and taking into account the client’s wishes, the doctor may prescribe a tonsillectomy under general anesthesia. In the event that there are no contraindications to this.
Inflammation of the tonsils (glands) - photo
Chronic tonsillitis - enlarged tonsils interfere with swallowing
Tonsillitis - inflammation of the tonsils (glands), a chronic form of the disease
How is recovery going after surgery to remove tonsils?
The use of anesthesia during tonsillectomy allows the patient not to experience discomfort during the operation. But 2-3 hours after it, unpleasant sensations may appear in the throat - they are relieved with the help of painkillers. On days 2–3, the postoperative field is covered with a white-yellow film, which disappears after about a week.
The total duration of the rehabilitation period is two to three weeks. It ends when complete epithelization of the wound surface occurs. All this time, the patient must follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- On the day of the operation, you are allowed to drink a little water, but you cannot eat.
- Over the next few days, the diet should consist of pureed food at room temperature - purees, liquid porridge.
- For another 14–16 days, you should avoid sour, spicy and hot foods - they can cause irritation of the mucous membrane that has not completely healed.
- Heavy physical activity, hot baths, visiting a bathhouse or sauna are prohibited.
During the rehabilitation period, difficulty in nasal breathing may occur, caused by swelling of the nasopharynx. The condition will be alleviated by vasoconstrictor drops - they should only be prescribed by a doctor. We treat tonsillitis (remove tonsils/tonsils) with the Medkvadrat ENT clinic.
Tonsillectomy surgery in Moscow is performed in many medical institutions. But contacting the Medkvadrat network of family health clinics guarantees you the following benefits:
- You will be assisted by highly qualified doctors and extensive experience.
- Modern high-tech equipment facilitates accurate diagnosis and increases the efficiency and safety of treatment.
- An individual treatment regimen is selected for each patient, taking into account the severity of the pathology, the characteristics of the body, and the general state of health. Our specialists will select the most effective and safe method.
- You come for a consultation with a specialist who will accompany you from the beginning of treatment to its completion. This approach allows you to achieve maximum results, since the doctor is aware of each stage of therapy.
When prescribing a tonsillectomy, the price of the operation depends on the type of laser that will be used during the operation, the complexity of the manipulations, and the qualifications of the surgeon. The doctor will tell you the exact amount after clarifying the diagnosis and determining the scale of the surgical intervention. He will help you make your choice and carefully explain the importance of timely treatment.
Comparative characteristics of the two methods
Laser tonsil removal
Carbon dioxide laser is used (CO2 laser)
- the operation is almost bloodless
- lower risk of bleeding after surgery
- faster wound healing compared to traditional removal
- less pain in the postoperative period
- Minuses:
- heating of surrounding tissues, there may be burns to the edges of the wound.
Radio wave tonsil removal
Surgitron radiosurgical device is used
- the operation is also almost bloodless
- radio wave produces an antibacterial effect, reducing the likelihood of inflammation after surgery
- postoperative swelling in the wound is less pronounced, the wound heals much faster
- there are no burns or damage to healthy tissues, because the effect of the cut is carried out without physical pressure, the removal of the tonsil is carried out carefully
- early complete tissue healing without the formation of a rough scar
In some cases, to achieve maximum effectiveness, doctors can use a combined method: both laser and radio wave.