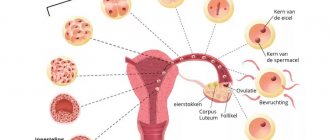
If a woman has problems conceiving, then after examination by a gynecologist and finding out the cause of infertility, treatment with hormonal drugs may be prescribed. They are needed to stimulate ovulation when follicles do not mature in the ovaries for some reason.
The selection of hormonal drugs and their dosage occurs strictly individually. The purpose of stimulating ovulation is the formation in a woman’s body of one or more eggs capable of fertilization. The use of drugs such as Clostilbegit and Proginova for this purpose has become the most common method of treating the causes of infertility.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Clostilbegit
Clomiphene (2-[4-(2-chloro,-1, 2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy]-N, N-Diethylamine dihydrogen citrate (mixture of E- and Z-isomer)). The active ingredient of the drug is a non-steroidal anti-estrogen that stimulates ovulation. The mechanism of action is explained by the ability to specifically bind to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus and ovaries. The drug in low doses enhances the secretion of gonadotropic hormones (prolactin, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones) and stimulates ovulation. Clostilbegit in high doses inhibits the secretion of gonadotropins. Does not reveal gestagenic and androgenic activity. After use, it is completely absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. Metabolized in the liver. It is excreted mainly with bile, subject to enterohepatic recirculation, and excreted from the body in feces. The half-life is 5–7 days.
Clostilbegit: negative reactions
Clostilbegit is a non-steroidal drug that can cause various adverse reactions from different body systems. Most often, it leads to the development of dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, weakness, changes in stool, flatulence, and others), but can contribute to the appearance of pain in the abdominal area. Some patients complain of dizziness, headaches, depression, irritability and insomnia, and allergic reactions. Visual dysfunction cannot be ruled out: double vision, photophobia, disturbances in light perception, so you should not drive vehicles or work with precise and dangerous machinery after taking the drug.
Clostilbegit can also negatively affect the state of the hormonal system, causing disruption of the menstrual cycle, uterine bleeding, enlarged ovaries, and pain in the mammary glands.
In addition, it contributes to the development of endometriosis, the progression of uterine fibroids and increases the likelihood of multiple or ectopic pregnancy.
The literature describes cases of clostilbegit overdose, so patients are not recommended to change the treatment regimen on their own, so as not to cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, lower back discomfort, visual disturbances and ovarian hyperstimulation (excessive enlargement). There is no specific therapy for such conditions; specialists take measures to eliminate unfavorable symptoms and promote rapid elimination of the drug.
Use of the drug Clostilbegit
In case of regular cyclic bleeding, it is recommended to start treatment on the 5th day of the cycle. Regimen I: daily dose of 50 mg (1 tablet) daily for 5 days, under control of the ovarian response through clinical and laboratory studies. Ovulation mostly occurs between the 11th and 15th day of the cycle. Regimen II: This regimen should be used in case of failure of treatment with regimen I. Daily doses of 100 mg (2 tablets) should be taken for 5 days, starting from the 5th day of the next cycle. If therapy does not lead to ovulation, a repeat course (100 mg) can be prescribed. If there is no ovulation, and in this case, after a 3-month break, you can try another 3-cycle course of treatment. If ovulation does not occur after this, repeating treatment is not recommended. The total dose during the cycle should not exceed 750 mg. In case of absence of menstruation after using contraceptives, it is recommended to take 50 mg (1 tablet) per day for 5 days. Regarding infertility in men, oligospermia is treated with a daily dose of 50 mg (1 tablet) for 6 weeks. It is important not to exceed the indicated doses.
Clostilbegit for infertility
Clostilbegit in the treatment of infertility is an inexpensive, highly effective first-line drug for the treatment of normogonadotropic anovulation. An important positive aspect of its use is the possibility of oral administration. However, the use of this drug is associated with a certain risk of complications and should be carried out only by a doctor, if possible, using ultrasound monitoring of folliculogenesis and endometrial development. In the vast majority of cases, the negative anti-estrogenic effect of Clostilbegit on endometrial thickness can be corrected by the use of estrogen drugs after the end of taking Clostilbegit in the planned fertile cycle.
Side effects of the drug Clostilbegit
Side effects that occur mainly only when the drug is used in high doses include headache, dizziness, nausea, sometimes vomiting, depression, fatigue, anxiety, insomnia, weight gain, abdominal pain, and hot flashes. Symptoms such as blurred vision disappear after stopping treatment. In some women, ovarian enlargement is possible, sometimes the ovaries can increase to 4–8 cm, so it is necessary to monitor the basal temperature and if a biphasic temperature curve appears, treatment should be stopped. With prolonged administration of the drug, hair loss may occur. In some cases, skin rashes accompanied by itching, allergic dermatitis, chest pain, painful menstruation, and difficulty urinating are noted. The likelihood of multiple pregnancies increases.
Risks and complications during ovulation stimulation
Any intervention in the human body, especially in the functioning of the human endocrine system, can cause complications and side effects. The most common complications are:
- multiple pregnancy,
- hyperstimulation,
- ovarian depletion,
- hormonal imbalances.
Hormonal drugs for stimulating ovulation “Klostilbegit” and “Proginova” should be taken only as prescribed by a gynecologist after an examination.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Clostilbegit
Before starting to use the tablets, it is necessary to determine liver function, hormonal status and the level of gonadotropin during renal excretion. A thorough gynecological examination is also necessary. Liver function and ovarian size should also be monitored over time. The drug can only be taken under the supervision of a gynecologist, who can reduce the dose of the drug or prescribe it only for a short time. After successful completion of the course of therapy with Clostilbegit, progesterone treatment may be prescribed. At the beginning of treatment with Clostilbegit, a temporary deterioration in vision is possible. In this case, driving vehicles and working with other mechanisms are contraindicated. Each tablet of Clostilbegit contains 100 mg of lactose, which should be taken into account when prescribing the drug to patients with diabetes.
Clostilbegit: indications and contraindications
The main purpose of taking clostilbegit is to stimulate ovulation, which is carried out in the following situations:
- Anovulatory cycles;
- Amenorrhea of various origins or oligomenorrhea;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS);
- Pituitary tumors causing galactorrhea;
- Prolonged postpartum amenorrhea and galactorrhea caused by various pathological processes, for example, Chiari-Frommel syndrome;
- Androgen deficiency.
Clostilbegit is prescribed not only to women, but also to men, since this drug has a positive effect on sperm quality, especially with oligospermia (reduced number of sperm in the ejaculate).
But this medication can cause adverse reactions from other organs and systems, so it is contraindicated in cases of renal and liver failure, neoplasms of the reproductive system and pituitary gland, ovarian cysts, kidney and liver failure. It should not be used in cases of changes in the functionality of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland, hypofunction of the pituitary gland, uterine bleeding of unknown etiology, visual and metabolic disorders. It is also not recommended to use clostilbegit during pregnancy and lactation, in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Clostilbegit: features of administration
Before you start taking clostilbegit, you should undergo a full medical examination and find out the etiology of infertility. Therapy with the drug is possible with normal test results, calm ovaries during palpation, adequate functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland, and sufficient concentrations of gonadotropin in the blood and urine.
While taking clostilbegit, the ovaries may become enlarged (up to 8 cm) and cysts may appear in them. In this case, the drug is discontinued until the body is completely restored, and then its dosage is reduced and the duration of the course is reduced. But sometimes clostilbegit is replaced with analogues when such complications occur.
Throughout the entire period of treatment, the doctor monitors the condition of the vagina, the reaction of the ovaries, checks their functionality, he can detect the phenomenon of the “pupil” - an increase in the amount of cervical mucus before ovulation.
In some patients, it is difficult to determine ovulation even after stimulation with clostilbegit, and the possibility of the formation of an inferior corpus luteum cannot be ruled out. Therefore, after the desired pregnancy occurs, women are recommended to use progesterone preparations.
Clostilbegit is a popular remedy that is prescribed in many specialized institutions, including the IVF Center clinic in Smolensk. This is due to the rapid positive effect of taking it immediately after the first course of therapy.
Compound
| Pills | 1 table |
| active substance: clomiphene citrate | 50 mg |
| excipients: gelatin - 2 mg; magnesium stearate - 2 mg; stearic acid - 2 mg; talc - 5 mg; potato starch - 39 mg; lactose monohydrate - 100 mg |
- Full trade name of the drug: Clostilbegit, international nonproprietary name: clomiphene.
- Dispensed by prescription.
- Release form: tablets 50 mg No. 10 in a blister of aluminum foil or a dark glass bottle. Each package contains instructions for use.
- Manufacturer: ZAT Pharmaceutical Plant EGIS.
- Active ingredient: clomiphene citrate.
Clostilbegit 50 mg No. 10 tablet.
Instructions for medical use of the drug KLOSTILBEGIT® Trade name Klostilbegit ® International nonproprietary name Clomiphene Dosage form Tablets 50 mg Composition One tablet contains the active substance - clomiphene citrate 50 mg, excipients: lactose monohydrate, potato starch, talc E-553b, gelatin, magnesium stearate E-572, stearic acid E-570. Description Round, flat, beveled tablets, debossed with “CLO” on one side, white, off-white, or off-white in color; odorless or almost odorless Pharmacotherapeutic group Sex hormones and modulators of the reproductive system. Gonadotropins and other ovulation stimulants. Synthetic ovulation stimulants. Clomiphene Code ATX G03G B02 Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics After oral administration, it is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Clomiphene is metabolized in the liver. The half-life is 5-7 days. Within 5 days, 50% of the oral dose is excreted, mainly through the intestines (42%) and urine (8%). Clomiphene is detectable in stool for 6 weeks. The average % of the excreted dose on the 31st - 35th day after administration of the drug labeled with the 14C isotope averaged 0.73%, and on the 42nd - 45th day - 0.45%. Fecal and urine samples were collected from 6 subjects between days 14 and 53 of the study. The parent/metabolite that is not excreted is slowly eliminated through the enterohepatic circulation. Long-term use of clomiphene may change the rate of cholesterol synthesis. With long-term treatment with clomiphene, patients may experience increased serum cholesterol levels. Clomiphene citrate is a racemic mixture of cis-(zuclomiphene) and trans-(enclomiphene) isomers. The cis-isomer is more active, the content of which in the drug is at least 30-50%. The half-life of zuclomiphene is longer than that of the trans isomer. Zuclomiphene is detected in healthy volunteers one month after administration. This fact indicates enterohepatic recirculation of the drug, which is stereospecific. Clomiphene can be detected early in pregnancy in women taking it to induce ovulation. Pharmacodynamics Clostilbegit is an antiestrogenic drug with a non-steroidal structure. The mechanism of action is explained by the ability to specifically bind to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, inhibiting the binding of estradiol to the receptors. According to the principle of positive feedback, the production of gonadotropin increases and, thus, ovulation is simulated. Indications for use: stimulation of ovulation in women with an anovulatory cycle in order to achieve pregnancy. Clostilbegit tablets can only be used by patients with proven ovulatory cycle disorders. Before prescribing the drug Clostilbegit, other causes of impaired fertility should be excluded or adequately treated. Method of administration and dosage The drug is used strictly as prescribed by the doctor! 1st course of treatment: the recommended dose is 50 mg (1 tablet) per day for 5 days. In the absence of recent uterine bleeding, treatment can begin any day. If induction of bleeding with a progestin is planned, or in the presence of spontaneous cyclic bleeding, it is recommended to begin treatment on the 5th day of the cycle. If ovulation occurs when using a dose of 50 mg, then further increasing the dose in subsequent cycles has no benefit. 2nd course of treatment: this regimen should be used if the 1st course of treatment is ineffective. If ovulation has not occurred after the 1st course of treatment, 100 mg of the drug should be prescribed daily (two 50 mg tablets as a single daily dose) for 5 days, starting from the 5th day of the next cycle, that is, 30 days after the previous cycle . Do not exceed the dose or duration of treatment (more than 100 mg/day for 5 days). Most patients who are able to respond to treatment respond to the first course of treatment. Three courses of treatment can usually be considered an adequate therapeutic measure. In the absence of ovulation bleeding, the diagnosis should be clarified. In patients without signs of ovulation, further treatment is not advisable. Long-term treatment Not recommended Special groups of patients In patients with hypersensitivity to pituitary gonadotropin (for example, with polycystic ovary syndrome), special care should be taken and, if possible, the drug should be prescribed in lower doses and for a shorter period of time. Side effects Very often (1/10) - vasomotor hot flashes - ovarian enlargement Often (1/100 - <1/10) - headache - nausea, vomiting, flatulence - blurred vision (blurred spots or flashes in the form of spots, sensation vibrating light in the eyes - so-called scintillating scotomas, afterimage) - discomfort and tenderness of the mammary glands - acyclic uterine bleeding, menorrhagia Uncommon (1/1000 - <1/100) - depression - dizziness - vertigo (sensation of rotation) - nervous tension, fatigue Rarely (1/10,000 - <1/1000) - cataracts, optic neuritis - seizures Frequency unknown (cannot be determined from available data) - hormone-dependent or hormone-related neoplasms/tumors - allergic reactions - hypertriglyceridemia - paranoid psychosis - syncope, acute cerebrovascular accidents, cerebral vascular thrombosis - nervous system dysfunction, disorientation, speech disorders - pancreatitis - liver dysfunction (changes in bromsulfalein test results, jaundice) - urticaria, rash, hair loss (alopecia) - erythema multiforme, ecchymosis, angioedema - multiple pregnancy - combination of ectopic and uterine pregnancy - ectopic pregnancy - endometriosis, worsening of endometriosis, decrease in endometrial thickness, significant enlargement of the ovaries. Studies indicate that adverse reactions develop more often with prolonged use of the drug and with using higher doses. When using the drug in recommended doses, adverse reactions are insignificant and only in rare cases become an obstacle to treatment. Enlargement of the ovaries When using the drug in recommended doses, an increase in the ovaries to pathological sizes is rarely observed, although in comparison with the usual cyclic changes in its size, the increase may be more pronounced. Likewise, cyclic ovarian tenderness may be more severe. When using higher doses or prolonging the treatment period, ovarian enlargement and cyst formation are observed more often, in addition, the luteal phase of the ovulatory cycle may lengthen. In rare cases, marked ovarian enlargement has been reported. Such a case was described in a patient with polycystic ovary syndrome taking Clostilbegit at a dose of 100 mg/day for 14 days. Abnormal ovarian enlargement usually resolves spontaneously. Most patients with this condition can be treated conservatively. Visual disturbances As the total dose increases, the incidence of symptoms known as blurred vision and spots or flashes (atrial fibrillation) increases. An after-image has also been reported. It is characteristic that the first appearance or intensification of these symptoms on the part of the organ of vision is mainly observed in bright lighting. There are reports of ophthalmologically confirmed scotomas, phosphenes and deterioration of visual acuity. In rare cases, cataracts and optic neuritis have been reported. These visual disturbances are usually reversible, although there have been reports of prolonged visual disturbances after clomiphene treatment has ended. In some cases, visual impairment may be irreversible, especially when clomiphene is used in high doses or when it is prescribed for a long period of time. Liver and biliary tract disorders The bromsulfalein test (BSF) determines the amount of BSF removed from the blood after intravenous administration of a known amount of BSF. 45 minutes after intravenous administration of 5 mg/kg BSF, only 5% of the dose remains in the blood. This test is an effective method for identifying diseases accompanied by damage to liver cells and the detoxifying function of the liver; however, this method is not applicable for the diagnosis of extrahepatic diseases or for the detection of intrahepatic obstructive jaundice. In 32 of 141 patients who underwent a BSF test, the BSF delay exceeded 5%. Of the 43 patients in this group, 5 were taking clomiphene at the currently recommended dose of 50 mg. Retention of BSF was usually minimal, except in patients taking clomiphene chronically for a long time or in cases of liver disease unrelated to the drug. Results of other liver function tests were usually normal. In a study in which patients received either placebo or clomiphene 50 mg tablets (3 days per month at a dose of 50 mg or 100 mg/day) during a 6-month course of BSF treatment, the test was performed on 94 patients. Results indicating a delay in ESF greater than 5% were obtained in 11 patients, 6 of whom took clomiphene and 5 of whom took placebo. Another study reported that one patient taking clomiphene tablets at a dose of 50 mg/day developed jaundice on day 19 of treatment. Liver biopsy revealed cholestasis without evidence of hepatitis. Metabolic disorders Hypertriglyceridemia (in some cases with pancreatitis) has been observed in patients who have or have a family history of hypertriglyceridemia and/or who took clomiphene for a period of time or in doses higher than recommended. Contraindications - hypersensitivity to the active or excipient of the drug - liver dysfunction or a history of it - ovarian cyst (with the exception of polycystic ovary syndrome) - metrorrhagia of unknown etiology - hormone-dependent tumors - endometriosis - ovarian dysgenesis, menopause or any condition with which is not expected to respond to treatment - pregnancy - children and adolescents under 18 years of age Drug interactions There are no data on drug interactions with Clostilbegit. Special instructions It is recommended to regularly monitor liver function. Before starting treatment, a thorough gynecological examination of the patient is necessary. The use of the drug should be under the constant supervision of a gynecologist. Adequate levels of endogenous estrogen (determined by vaginal smears, endometrial biopsies, urinary estrogen levels, or endometrial bleeding in response to progesterone) are required for ovulation in response to treatment with Clostilbegit. Reduced estrogen levels—although clinically less favorable—do not preclude treatment effectiveness. Treatment with Clostilbegit is not effective for primary pituitary or ovarian failure. Treatment with Clostilbegit does not replace special treatment for ovarian failure caused by other reasons, for example, diseases of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands. Hyperprolactinemia can also be treated with other methods. For infertility associated with low body weight, Clostilbegit is not the first choice drug, in addition, this drug does not affect the increased levels of FSH observed during early menopause. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) There are reports of the development of OHSS when clomiphene is prescribed to induce ovulation. With cyclic use of clomiphene, OHSS has occurred in some cases when clomiphene was combined with gonadotropin. Symptoms of this syndrome observed with the use of clomiphene are: pericardial effusion, anasarca, hydrothorax, acute abdomen, renal failure, pulmonary edema, hemorrhage into ovarian tissue, deep vein thrombosis, ovarian torsion and acute respiratory failure. Upon conception, rapid progression of a severe form of the syndrome may begin. In order to prevent the danger of possible enlargement of the ovaries during treatment with Clostilbegit, the lowest doses sufficient to achieve good treatment results should be used. Patients should be warned that if they develop pain in the abdomen or pelvic organs, if they gain weight, feel unwell or have flatulence after taking Clostilbegit tablets, they should inform their doctor. A few days after discontinuation of Clostilbegit, further enlargement of the ovaries does not occur. Patients with polycystic ovaries with increased sensitivity to gonadotropin may also have an increased response to usually recommended doses of Clostilbegit. Patients who complain of pain in the abdomen or pelvic organs, weight gain, poor health or flatulence after taking Clostilbegit tablets should be examined for possible ovarian cysts or other pathological changes. Due to the increased vulnerability of pathologically enlarged ovaries, examination of the abdomen and pelvis should be carried out with extreme caution. In case of pathological enlargement of the ovaries, Clostilbegit cannot be prescribed until the size of the ovaries reaches the original size (those before treatment). Ovarian enlargement and cysts during treatment with clomiphene usually spontaneously normalize a few days or weeks after discontinuation of the drug. Most patients can be treated conservatively. In the next treatment cycle, the dose or cycle duration should be reduced. Changes in the organ of vision Patients should be warned about the possible development of blurred vision or visual impairment such as pinpoint or ciliary scotoma. These disorders may develop during or shortly after treatment with Clostilbegit. Typically, these changes are reversible, although there have been reports of long-term visual impairment after stopping treatment with clomiphene. Visual impairment may also be irreversible, especially when clomiphene is used in high doses or when it is prescribed for a long period of time. The mechanism of such visual impairment is not known. If you complain of any visual impairment, treatment should be discontinued immediately and consult an ophthalmologist. Patients should be warned that, due to possible visual impairment, there may be danger when driving vehicles and working with machinery, especially under different lighting conditions. Hypertriglyceridemia In the post-registration period, cases of hypertriglyceridemia have been reported in patients taking clomiphene. The risk of developing hypertriglyceridemia increases in patients who suffer from or have a family history of hypertriglyceridemia and/or who take clomiphene for a longer period of time or in doses higher than recommended. In such patients, it is recommended to regularly determine the level of triglycerides in the blood plasma. Multiple pregnancy When conceiving while being treated with clomiphene, the likelihood of multiple pregnancy increases. Patients should be warned about possible complications and risks associated with multiple pregnancies. Ectopic pregnancy During conception during treatment with clomiphene, in a number of cases, an ectopic pregnancy developed (in the ovaries or tubal). There are reports of cases of multiple pregnancies in which there was intra- and ectopic pregnancy. Uterine fibroids Examination of patients with uterine fibroids treated with Clostilbegit should be carried out with caution due to the possible further growth of fibroids. Pregnancy loss and birth defects According to the literature, the average incidence of birth defects in mothers receiving clomiphene (before or after conception) is no different from that observed in the average comparison population. Cases published in the literature (spontaneous reports) indicate that when ovulation is induced with clomiphene, defects in neural tube development are more common among congenital developmental defects, however, studies at the population level do not confirm these observations. Doctors should inform patients in a manner that is accessible to patients about the possible dangers and risks associated with both natural pregnancy and its induction with clomiphene. Patients should be informed that certain factors and conditions may be risk factors for their pregnancy. Such factors include: the age of the woman and men, previous spontaneous abortions, the RH genotype, the menstrual cycle and impaired reproductive function (regardless of the cause) in the history, organic heart disease, diabetes, pathogens of infections (for example, rubella), the presence of congenital defects in family and other risk factors. Based on the results of the examination of patients, they may be shown a genetic examination. The results of population studies were published about a possible increase in the risk of developing Down syndrome during the ovulation induction and on increasing the frequency of trisomy among spontaneous abortions of women with reduced fraud, which received drugs for induction of ovulation (not a single patient received monotherapy with clomiphene without additional inducing drugs). However, the number of messages is still not enough to confirm or refute increased risk. This issue can be resolved using an amniocentesis carried out according to ordinary indications (age, family history). In clinical studies of uniform or multiple pregnancy in patients receiving clomiphen, the fetus was established - 21.4%(abortion frequency of 19%), ectopic pregnancy - 1.18%; molar pregnancy - 0.17%; The fruit is “paper” (Foetus papyraceus) - 0.04%; Pregnancy with one or more stillborn - 1.01%. In clinical studies, Klomifen was used after conception in 158 cases out of 2369 pregnancies ending. Of these 158 pregnancies, 8 newborn (of 7 pregnancies) had congenital defects. There were no differences in the frequency of congenital defects in patients, to whom Klomifen was prescribed until 19 days after conception or between the 20th and 35th days after conception. This frequency corresponds to the expected frequency interval at the general population level. Ovary cancer has rare messages about the development of ovarian cancer when using drugs that improve fertility. The primary risk factor is the violation of fertility itself. Epidemiological data indicate that prolonged use of clostilbegite can increase this risk. Thus, the recommended duration of treatment should not exceed. Lactose each clostilbegite tablet contains 100 mg of lactose. This should be taken into account when prescribing the drug to patients with lactose intolerance. In case of rare hereditary diseases, including persons with fructose intolerance, LAPP-lappase enzyme deficiency and malabsorption of glucose-galactose, the drug cannot be used. Pregnancy and lactation, when confirming pregnancy, the intake of Klostilbegit should be canceled. Clostilbegit is released with breast milk, so its use during lactation requires a thorough analysis of risk and benefits. In order to avoid the unintentional purpose of clostilbegite in the early stages of pregnancy, during each treatment cycle, the presence of ovulation should be determined using the corresponding tests. Before each new course of treatment with Klostilbegit, a pregnancy test should be carried out. Features of the effect of the drug on the ability to drive a vehicle and potentially dangerous mechanisms in connection with transient visual impairments at the beginning of treatment with the drug, it is not recommended to drive a vehicle and other potentially dangerous types of activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions, in particular, with changing lighting intensity. Overdose symptoms: nausea, vomiting, vasomotor tides, visual impairment (decrease in visual acuity, outbreak of light, scotoma), an increase in the ovaries and pain in the pelvic or abdominal organs. Treatment: After the cancellation of the drug, symptomatic treatment is recommended. There is no data on the possible excretion of the drug through dialysis. The output form and packaging of 10 tablets in a brown-glass bottle-made PE lid with the first opening cover and equipped with a shock absorber. A self-adhesive label is placed on the bottle. 1 bottle, along with instructions for medical use in the state and Russian languages, is placed in a cardboard box. Storage conditions are stored at a temperature of 15 ° C to 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children! The shelf life of 5 years is not used after the expiration date. Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies By prescription 1106 BUDAPEST, st. Keresturi, 30-38 Hungary Phone: (36-1) 803-5555, fax: (36-1) 803-5529 Registration certificate owner JSC "EGIS Pharmaceutical Plant", Hungary Address of the organization accepting claims from consumers on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan quality of products (goods) Representative office in the Republic of Kazakhstan CJSC "EGIS Pharmaceutical Plant" 050060, Almaty, st. Zharokova 286 G tel: +, +, fax: + 7 (727) 247 61 41, e-mail