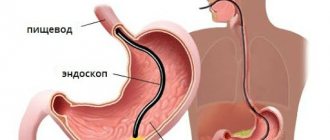
The method of examining the respiratory tract and respiratory organs endoscopically is called bronchoscopy. The essence of the method is to insert a flexible hose with a camera at the end into the trachea and then into the bronchi. The image from the camera is transmitted to the screen, thanks to which diagnosticians can identify problem areas, locations of tumors and other pathologies. In terms of making a correct diagnosis, pulmonary bronchoscopy cannot be replaced by MRI, CT, radiography and other studies.
This technique for detecting respiratory diseases is not used for common colds or bronchitis. It is necessary in cases where the patient’s inflammation lasts for several weeks or months and cannot be corrected with medication. In the first Danilovsky multidisciplinary medical center on Avtozavodskaya, bronchoscopy is performed by real professionals using high-quality equipment. No pain or harm for patients during the procedure!
FREE WITH ANNUAL MEMBER
What is bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the respiratory tract: larynx, trachea and bronchi in order to identify diseases of the mucous membranes of these organs.
The procedure is carried out using a bronchoscope - a flexible or rigid tube with a diameter of 3-6 mm, equipped with a lighting lamp and a photo-video camera. Modern devices are based on fiber optic technology, which ensures high diagnostic efficiency. The image is displayed on a computer monitor, so it can be enlarged tens of times and the recording can be saved for subsequent dynamic observation. The optical system of the device allows you to examine the respiratory tract up to the second branch of the bronchi and in 97 percent of cases make an accurate diagnosis. Bronchoscopy is used in the diagnosis of chronic bronchitis, recurrent pneumonia, and lung cancer. If necessary, tissue samples can be taken for biopsy during bronchoscopy. The technique of bronchoscopy provides the possibility of using the procedure for medicinal purposes - for:
- removal of foreign bodies from the bronchi;
- cleansing the trachea and bronchi from pus and mucus;
- washing and administration of medicinal solutions (antibiotics, glucocorticoids, mucolytics, nitrofurans);
- expansion of the narrowed lumen of the bronchi;
- removal of small tumors.
To treat respiratory diseases and take material for histological examination, the bronchoscope is equipped with the necessary surgical instruments.
If necessary, two studies are performed together - bronchoscopy and bronchography. Bronchography is an x-ray method in which a contrast agent is injected into the airways through a catheter or fiberoptic bronchoscope. The study allows us to study in detail the structure of the bronchial tree (especially those parts of it that are inaccessible for endoscopic examination) and evaluate its motor function during breathing.
Recommendations for nursing staff on preparing a patient for endoscopic examinations.
Algorithm for preparing for bronchoscopy .
Introduction The psychological state of the patient is a fundamental condition, along with quality preparation, for safe and effective endoscopy. Thanks to the achieved positive psychological result in the examination, the feeling of anxiety before the examination and during the endoscopic examination is leveled. Communication between the medical professional and the patient before these types of examinations is of no small importance. First of all, from an emotional point of view, it is important for patients to know: what kind of doctor will examine them, his experience, qualifications, and how the examination will take place. It should be noted that modern technology for conducting endoscopic examination requires the utmost concentration of attention from the medical worker to monitor the general condition of the patient being examined and has the ability to provide him with psychological assistance in a timely manner. A medical worker at the stage of preparation for an endoscopic examination, through adequate psychological contact, has the opportunity to minimize the patient’s feeling of anxiety. The department's medical worker explains to the patient the essence of the study and the corresponding rules of behavior.
Preparation for the procedure: 1. Inform the patient that:
- 3-4 days before the study, it is necessary to exclude alcohol intake (as it sharply worsens the tolerability of the study and distorts the picture of the mucous membrane of the organs in question due to its irritating effect, and also strengthens the cough and gag reflexes)
- on the eve of the study, the last meal at 19:00 is a light dinner (tea, broth, fermented milk products, juice, bread);
- You can take medications prescribed by your doctor
- the evening before the examination, you should stop smoking (nicotine increases the gag reflex and salivation, which will make breathing difficult during FEBS, and it also reduces the potency of local anesthetics used during bronchoscopy)
- if you are worried before the study, then the night before going to bed you can take sedatives prescribed by your doctor or weak sedatives (valerian tablets, novopassit, etc.)
- on the day of the examination - fasting, it is necessary to avoid drinking any liquids, if absolutely necessary - the last drink of water 1 hour before the examination (boiled water - no more than 100 ml)
- Taking medications by mouth on the day of the examination is possible 1 hour before the examination, wash them down with a small amount of water
- Less than an hour before the test, you are allowed to take medications sublingually and use an inhaler.
- Patients with diabetes who regularly use insulin should skip the morning injection.
- Patients suffering from epilepsy or seizures should start taking anticonvulsant medications prescribed by their doctor 2-3 days before the study. 3-4 hours before the test, you must take this drug in crushed form with a small amount of water (up to 100 ml). It is necessary to warn your doctor about the possibility of developing a seizure.
- at the FBS you need to take: a towel, an outpatient card or medical history, protocols of previous studies, a referral, radiographs of the lungs, medications that you regularly use for heart pain, choking (nitroglycerin, inhaler, etc.)
- Before the examination, be sure to warn the doctor performing the examination that you have serious diseases or intolerance to anesthesia drugs
- Before the examination, you must unbutton your shirt collar, which may make breathing difficult during the examination.
- Before the examination, as prescribed by the doctor, an intramuscular or intravenous injection of the drug is performed, after which you may feel drowsiness, a slight increase in heart rate, and dry mouth.
Figure 1. Performing bronchoscopy
Algorithm of action during the procedure: 1. Explain to the patient the purpose and progress of the study, the rules of behavior during the study and obtain his consent. 1. Provide psychological preparation to the patient. 2. Inform the patient that the test is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. He should exclude food and water the night before, and not smoke. 2. Make sure that the patient removes removable dentures before the examination. 3. Show the patient to the endoscopy room at the appointed time with a towel, medical history and a referral. 4. Irrigate the mucous membrane with 10% lidocaine spray. 5. Follow SOPs for conducting the study. 6. Take the patient to the room and warn him not to eat or smoke for two hours after the examination. 7. Inform the patient that: - after the study, do not take water or food for 30 minutes (until the feeling of a “lump in the throat” disappears), then do not consume spicy, rough food and alcohol - after the biopsy for 12- Do not consume hot food or drink for 18 hours. - after the examination, hoarseness is possible, which will disappear within a few hours.
Types of bronchoscopy
Depending on the purposes of the study, two types of procedures are used:
- Flexible bronchoscopy - it is performed using flexible tubes (fiber bronchoscope). Thanks to its small diameter, the fiber bronchoscope can move into the lower sections of the bronchi, practically without injuring their membrane. Flexible bronchoscopy is used to diagnose diseases of the respiratory tract, including its lower sections. High-quality visualization of mucous membranes allows not only to diagnose pathologies, but also to remove small foreign bodies. This type of research can be used in pediatrics. General anesthesia is not required for flexible bronchoscopy.
- Rigid bronchoscopy – for its implementation, a device with a system of rigid hollow tubes is used. Their diameter does not allow examining small bronchi, unlike the fibrobrochosop. A rigid bronchoscope has a wider range of therapeutic capabilities and is used for:
- fight bleeding
- expansion of the lumen of the bronchi,
- removal of large foreign objects from the respiratory tract,
- removing mucus and fluid from the lungs,
- lavage of the bronchi and administration of drug solutions,
- removal of tumors and scars.
General anesthesia during rigid bronchoscopy is performed, so the patient does not feel any discomfort.
Methodology
The duration of bronchoscopy is 30-40 minutes.
Bronchodilators and painkillers are administered to the patient subcutaneously or by spraying, facilitating the advancement of the tube and eliminating discomfort.
The patient's body position is sitting or lying on his back.
It is not recommended to move your head or move. To suppress the urge to vomit, you need to breathe often and not deeply.
The bronchoscope is inserted through the oral cavity or nasal passage.
In the process of moving to the lower sections, the doctor examines the internal surfaces of the trachea, glottis and bronchi.
After the examination and the necessary manipulations, the bronchoscope is carefully removed, and the patient is sent to the hospital for some time under the supervision of medical staff (to avoid complications after the procedure).
Indications for bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is used for diagnostic purposes in the presence of:
- unmotivated painful cough;
- shortness of breath of unknown origin;
- hemoptysis;
- frequent bronchitis and pneumonia;
- suspicion of a foreign body in the bronchi or tumor;
- cystic fibrosis and tuberculosis;
- bleeding from the respiratory tract.
For therapeutic purposes, bronchoscopy is performed in the following cases:
- entry of a foreign body into the trachea or bronchi;
- coma and other states of respiratory failure;
- bleeding - to stop it;
- the presence of viscous sputum, pus or blood;
- a tumor that has blocked one of the bronchi;
- the need to administer antibiotics and other drugs directly into the respiratory tract.
Bronchoscopy for pneumonia can be prescribed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Complications of the procedure
Bronchoscopy is a safe procedure and rarely causes complications. And the complications that may arise include: bronchospasms, which can worsen breathing; irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias); infections such as pneumonia (usually these can be treated with antibiotics); constant hoarseness.
If a biopsy was performed during bronchoscopy, complications that may occur include: partial collapse of the lung (pneumothorax), bleeding caused by the biopsy forceps used to collect tissue, infection from the biopsy procedure.
Contraindications for bronchoscopy
Due to the fact that the bronchoscopy technique is a surgical intervention, this procedure has a number of contraindications.
The following are absolute contraindications:
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia;
- Hypertension;
- Recent heart attack or stroke (less than 6 months);
- Chronic pulmonary or heart failure;
- Severe arrhythmia;
- Mental disorders (epilepsy, schizophrenia, etc.);
- Aortic aneurysm;
- Narrowing of the larynx (stenosis).
In some situations, bronchoscopy should be postponed:
- During pregnancy (after the 20th week);
- During menstruation;
- With exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- When blood sugar increases in patients with diabetes.
The need for bronchoscopy and the possibility of performing it can only be determined by a pulmonologist or therapist.
Advantages of bronchoscopy at MEDSI
- MEDSI clinics are equipped with expert-class equipment for performing bronchoscopy;
- The study is carried out by a team of highly qualified experienced specialists: a pulmonologist, a physician assistant and an anesthesiologist;
- The high accuracy of bronchoscopy makes it possible to diagnose respiratory diseases in 97 percent of cases;
- The procedure is painless, as it is carried out using effective anesthetics, and, if necessary, in a state of medicated sleep;
- The patient's condition during bronchoscopy is under the control of doctors using special equipment for this.
Preparation for the procedure
Before starting the procedure, the patient needs to remove dentures, glasses, contact lenses, hearing aids, if any of the above are available. During bronchoscopy, a local anesthetic spray is used, which is applied to the throat and nasal cavity. The patient may also be given a sedative to help them relax.
A patient scheduled for bronchoscopy should not eat or drink 6-12 hours before the procedure, so it is worth undergoing bronchoscopy in the first half of the day. It is worth talking to your doctor about which medications you should stop taking before the procedure.
Before the procedure, you should empty your bladder. You need to remove all or most of your clothing. The procedure is performed by a pulmonologist and an assistant. During the procedure, heart rate, blood pressure and blood saturation levels will be checked. A chest x-ray must be performed before the procedure.
Before performing a bronchoscopy, the doctor may prescribe other tests, such as a complete blood count, coagulogram, and pulmonary function tests.