STDs are a group of diseases that include:
- “classic” sexually transmitted diseases (syphilis, gonorrhea);
- “new” diseases, the identification of which has become possible recently due to advances in medicine and microbiology (herpes, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, human papillomavirus);
- skin diseases transmitted through sexual contact (pubic lice, scabies, molluscum contagiosum);
- diseases that are sexually transmitted, but primarily affect organs outside the reproductive system (AIDS/HIV, viral hepatitis B and C).
In total, this group includes more than 25 diseases.
Causes
The content of the article
STDs are common among the sexually active population, especially those who practice promiscuity. The development of the disease occurs due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the body:
- bacterial agents;
- yeast-like fungi;
- viruses;
- simplest organisms.
They are transmitted sexually from an infected partner, regardless of what kind of sexual contact is practiced - oral, anal or vaginal. The best way to protect yourself is to use a condom.
Some microorganisms are opportunistic, i.e. live in the human body constantly. They provoke the development of the disease when favorable conditions occur, for example, when immunity decreases.
Sometimes infection occurs through household contact - through personal hygiene items, bed linen, toilet rim, unsterilized instruments, when visiting public places, etc. Infection is also possible vertically (from mother to fetus) and hematogenously (through blood), which is mainly associated with drug addiction.
Risk of contracting STDs
The risk of contracting an STD can be significantly reduced by:
- remain faithful to a permanent partner;
- Get vaccinated against human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B before sexual activity;
- maintain personal hygiene - do not use someone else’s soap, towel, washcloth, underwear;
- use a condom during sexual intercourse;
- undergo an annual medical examination with your partner.
Syphilis
Syphilis is characterized by a staged course and damage to all body systems. The incubation period is usually a month, but sometimes it is reduced to 9 days or extended to six months.
Primary form (6-8 weeks):
- formation of hard chancre on the skin and mucous membranes: most often in the genital area, less often on the mammary glands, thighs, abdomen, face;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the affected area;
- in women - thick and foul-smelling discharge, itching in the vagina;
- general malaise of the body: elevated temperature, fever, pain in bones and joints.
If left untreated, symptoms may disappear. This does not indicate recovery, but signals the transition of the disease to a new stage.
The secondary form (2-5 years) is characterized by a relapsing course. The main external manifestation is a specific rash on the skin and mucous membranes (bright roseola, papules, plaques, ulcers). Roseola rashes are localized mainly on the neck, forming the so-called “necklace of Venus”.
Syphilitic rash
Other symptoms are also observed:
- hair problems (thinning, split ends, loss);
- weight loss;
- headache;
- poor appetite;
- nausea and vomiting;
- elevated temperature.
In the absence of treatment, the latent period temporarily begins again.
Tertiary form (10-20 years) – internal organs and the central nervous system are irreversibly affected. The main symptom is the formation of specific infiltrative tubercles on the tissues and mucous membranes of internal organs - gumma. They cause degeneration of the affected tissues.
Cognitive impairments similar to complications of dementia occur. First of all, it is dementia and mental disorders. Vision, memory, attention, coordination of movements, speech, and hearing deteriorate. Damage to the vascular and skeletal systems is manifested by syphilitic meningitis, hydrocephalus, and progressive paralysis. Deformation and disruption of the functioning of internal organs occurs: liver, kidneys, lungs, heart.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is characterized by damage to the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract, sometimes the rectum, oropharynx, and eyes. The incubation period for women is on average up to 10 days, for men – up to 5.
Fresh gonorrhea (up to 2 months from the moment of infection) in women has symptoms:
- vaginal discharge of a purulent or serous-purulent nature;
- itching, hyperemia, swelling of the mucous membranes, formation of ulcers on them;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet, pain and burning when urinating;
- spotting outside of menstruation;
- lower abdominal pain.
Often the clinical picture is mild or completely absent, which is why women consult a doctor untimely. In advanced cases, the inflammatory process can affect the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and peritoneum. Possible general intoxication of the body, fever, disrupted menstrual cycle, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.
Clinical symptoms in men are similar to women. In the later stages of the disease, the prostate, seminal vesicles, etc. are affected. There may be complaints of fever, chills, and painful bowel movements.
With chronic gonorrhea (more than 2 months from the moment of infection), adhesions develop in the pelvis, libido decreases in men, and the menstrual cycle and reproductive function are disrupted in women.
Diseases caused by Mycoplasma genitalium (mycoplasma infection)
The detection rate of Mycoplasma genitalium (Figure 3) in the general population ranges from 1 to 5%, while in women at high risk of infection it is up to 42%. Infection occurs through contact of the mucous membranes of the genital organs, anogenital area and oral cavity. In 40 - 70% of cases, the disease is asymptomatic, in other cases the clinical picture is the same as for chlamydial infection.
Figure 3 - Mycoplasma genitalium
Complications include pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy. Both chlamydia and mycoplasma damage the ciliated epithelium of the fallopian tubes, which is necessary for the advancement of the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. Due to the fact that the fallopian tube simply has nothing to ensure the movement of the egg, pregnancy develops in the tube, resulting in a life-threatening condition.
If pregnancy occurs, infection with Mycoplasma genitalium increases the risk of miscarriage and premature birth. Diagnosis is the same as for chlamydial infection.
In this article I deliberately do not present currently recommended treatment regimens, since I consider it necessary to visit a doctor in person. An assessment of the effectiveness of the treatment (confirmation of the absence of a microorganism) for both infections should not be carried out earlier than 2 weeks when using NASBA, or a month after the end of the course of therapy - PCR, RT-PCR; if the result is negative, re-screening is not necessary!
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is characterized by damage to the urogenital tract, and less commonly to the prostate gland in men. The incubation period averages from 3 to 30 days.
Trichomonas
Fresh trichomoniasis in women has the following symptoms:
- copious foamy and foul-smelling discharge that is yellow, green or gray in color;
- hyperemia, swelling, itching, burning of the vaginal mucosa and around the labia;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain and discomfort during intimacy;
- urination disorder (frequent, painful, incontinence, etc.).
In men, trichomoniasis often occurs in a latent form. During exacerbation, the clinical picture is similar to that of women.
The intensity of manifestations is significantly influenced by smoking, drinking alcohol, poor diet, taking antibiotics, and exacerbation of other chronic diseases. In women, symptoms worsen before menstruation.
If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic or Trichomonas carriage. Chronic trichomoniasis occurs over a long period of time with mild symptoms. In the case of Trichomonas carriage, no external signs are observed; the pathogen is detected in the laboratory. This is a conditional division, since trichomoniasis can change from one form to another.
A common problem when self-medicating STIs
When pathological discharge from the genital tract appears, the first thing patient N does, deciding that she has an exacerbation of thrush, independently uses suppositories, which:
- once helped in a similar situation;
- recommended by friends;
- were advertised on the Internet.
Will the smear required by the doctor to make a diagnosis, performed after using the drug, be adequate? Of course not! And now, if an antibiotic was used, a break from using the drug for 14 days is necessary to obtain biomaterial and make a diagnosis!
And patient N has itching and burning (the drug did not help, otherwise she simply would not have come)! So it turns out that the doctor is forced to treat the disease he suspects, based on the patient’s complaints, which is unacceptable in the 21st century.
Dear girls, women, pathological discharge from the genital tract can hide not only thrush (vulvovaginal candidiasis), bacterial vaginosis and aerobic vaginitis, but also STIs that cannot be treated with “thrush” suppositories!
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is characterized by damage to the genitourinary, respiratory, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal systems, and organs of vision. The incubation period is 2-30 days.
The first signs of the disease in women:
- mucous or purulent-mucous vaginal discharge that has a yellow color and a foul odor;
- itching and burning;
- lower abdominal pain;
- intoxication of the body.
In men, chlamydia manifests itself:
- mucopurulent or watery discharge from the urethra;
- itching and burning when emptying the bladder;
- swelling and redness of the external opening of the urethra;
- pain in the lower back and groin;
- deterioration of general condition.
In children, the inflammatory process usually affects the eyes, ears, and respiratory system. Chlamydia in newborns is extremely dangerous.
Who needs to be tested to identify STI pathogens?
- to both sexual partners at the stage of pregnancy planning,
- pregnant women,
- sexually active girls who want to become mothers in the deferred period,
- women who have had unprotected contact with a dubious partner,
- women who frequently change sexual partners,
- partners of persons infected with STIs,
- patients with inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs and their sexual partners,
- patients with pathological discharge from the genital tract,
- patients with infertility and pregnancy loss,
- patients undergoing surgical interventions on the pelvic organs.
In this article I will briefly touch on bacterial infections that are in the department of gynecologists; STIs of viral etiology are discussed in separate articles (“HPV has been detected!” and HSV – I will write soon). Gonorrhea and syphilis are the domain of dermatovenerologists, while HIV and viral hepatitis are treated by colleagues who are infectious disease specialists.
Mycoplasmosis
Mycoplasmosis is characterized by great polymorphism and has varied localization. The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to several months.
The clinical picture is similar in both sexes:
- pain, cutting, burning when urinating;
- hyperemia and swelling of the external urethral opening;
- frequent urination;
- irritation and redness of the vaginal mucosa in women;
- glassy or whitish discharge with a musty odor;
- pain during intercourse (in men it increases with ejaculation)
- general intoxication of the body;
- pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back.
The list of symptoms may be shortened or supplemented depending on the location of the pathogen. As the infection progresses, other internal organs are affected.
Tests for sexually transmitted infections
The main danger of STDs is the long incubation period and possible side effects. However, if the disease is diagnosed in time, its treatment is not difficult.
Modern medicine has several accurate and effective ways to diagnose STDs:
— A blood test helps determine the infectious pathogen, as well as assess the general condition of the patient. Especially necessary if you suspect HIV and syphilis.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. It is used to detect antibodies and antigens in the blood that are formed in the patient’s body as a result of infection.
- Analysis of urine. It is carried out to assess the condition of the urinary organs and identify thrush or, for example, gonorrhea.
— Smears on the flora of the mucous membrane. It is a basic and primary study that must be completed at least once a year.
— Bacterial culture. This analysis determines the causative agents of the disease, as well as their sensitivity to antibiotics.
— PCR study. This is a molecular genetic study based on repeated copying of DNA fragments. Allows you to identify even hidden infections.
Tests for sexually transmitted infections must be taken in the following cases:
— During an annual screening examination to determine the presence of hidden infections.
- After unprotected sexual intercourse, even if ejaculation did not occur in the vagina.
— When planning pregnancy to reduce the risk of miscarriage.
— In the treatment of infertility, since STDs are one of the main causes of this pathology.
Ureaplasmosis
Ureaplasmosis is more often diagnosed in women, since acute symptoms are not typical for men. The incubation period ranges from 7 to 20 days.
Symptoms of the disease in women:
- vaginal discharge atypical in quantity, consistency, color and smell;
- burning and pain when emptying the bladder, increased urge;
- lower abdominal pain;
- disrupted menstrual cycle.
In men, ureaplasmosis manifests itself:
- cloudy or mucous discharge from the urethra;
- pain and burning when urinating;
- itching along the urethra;
- erectile dysfunction.
Often the clinical picture is blurred, especially at the initial stage of development of ureaplasmosis. If left untreated, the inflammatory process affects the bladder, prostate, kidneys, seminal vesicles, etc.
Gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis is a disorder of the vaginal microflora. In men it develops very rarely: the presence of the pathogen in the body usually does not manifest itself in any way, only sometimes causing a sluggish inflammatory process with erased symptoms. The incubation period is 7-20 days.
Characteristic signs of gardnerellosis:
- vaginal discharge with a fishy odor, yellow, grayish-white or green;
- burning, itching and discomfort in the vagina and urethra, increasing during urination and sexual intercourse.
Other symptoms may be due to the development of complications of gardnerellosis.
Basic measures to prevent STDs
Treating STDs is much more difficult than preventing them from occurring. A condom will not completely protect you from infection. But it significantly reduces the risk of infection. Therefore, use a condom every time you have sexual intercourse with a regular or new partner. Also, as a preventive measure for STDs, doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Practice good hygiene regularly. Each person should have their own towel and underwear.
- Do not skip preventive examinations from specialists. A man should make an appointment with a urologist at least once a year.
- It is advisable not to change partners frequently, to be faithful to your spouse, and to avoid casual sexual contact.
- Boost your immunity in accessible ways. Even if the virus is in the blood, good immunity will prevent it from actively manifesting itself.
As you can see, most sexually transmitted diseases are dangerous for both men and women. Some of them manifest themselves asymptomatically, which is the most dangerous thing, while others are accompanied by characteristic symptoms. The incubation period for STIs varies among men; for some infections it can reach a year. Therefore, it is recommended at any age to follow the rules for preventing STDs and not to miss preventive examinations with doctors. If you do develop an infection, do not hesitate to begin treatment as soon as possible.
If you don’t know where to go with a problem, call our clinic by phone. Specialists from the First Clinic of Orekhovo will help solve your health problems and answer any questions you may have. We can provide you with the necessary tests, tests, and hardware scans. There is no need to go anywhere or wait for a long time. To make an appointment, use the special form on the clinic’s website or call one of the contact numbers.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis (thrush) is characterized by damage to the skin and mucous membranes, less often internal organs. The incubation period is 1-8 days.
Candidiasis
The clinical picture depends on the localization of the pathological process. This may be the skin and its appendages, the oral cavity, the genitourinary system, and internal organs. The main symptom is a white coating on the affected area.
Urogenital candidiasis in women manifests itself:
- itching and burning of the external genitalia;
- white cheesy vaginal discharge;
- pain during intercourse.
Signs of the disease in men:
- itching, soreness, swelling and redness in the area of the glans penis;
- pain during sex and urination;
- white-grayish coating on the penis.
After 2 months from the moment of infection, candidiasis becomes chronic. On the mucous membranes, the development of foci of dryness, hyperpigmentation, infiltration, and tissue atrophy is observed.
Complications and consequences
Any signs of sexually transmitted infections in men should be a reason to consult a doctor. Only a doctor can see a clear clinical picture, diagnose and prescribe treatment for STIs. It is dangerous not to be treated or seek medical help for STDs, as they can lead to serious complications:
- infertility and impotence;
- prostatitis, cystitis, urethritis and other diseases of the genitourinary system; the occurrence of adhesions and other pathological changes in tissues;
- development of malignant neoplasms;
- the disease can become chronic.
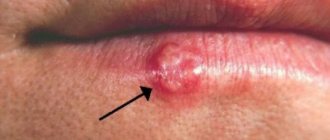
Genital herpes
Genital herpes ranks second in frequency among STDs. The incubation period is from 2 to 26 days.
The main symptom of the disease is a rash in the genital area.
Their localization:
- in men - the foreskin and glans penis, urethral mucosa, coronary groove, area around the anus, upper part of the inner thighs, scrotum;
- in women - the perineum, labia, inner thighs, vagina, uterus, urethral and cervical mucosa, area around the anus.
The bubbles are small, grouped and tend to coalesce. After 2-4 days, the liquid in them becomes cloudy, the cavity ruptures, and painful erosive-ulcerative elements form. Over time, they dry out and become crusty. Healing occurs within two weeks.
Symptoms of herpes often include fever, weakness, malaise, headache and muscle pain, frequent and painful urination, and enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
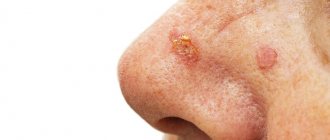
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
The virus, having entered the human body, can wait for favorable conditions for a long time. When activated, it provokes the development of benign formations - warts, papillomas and condylomas. They can appear on any part of the body and have different shapes, colors and sizes.
Signs of pathology:
- growths on the skin and mucous membranes (often in the genital area);
- redness and itching of the affected area;
- pain and discomfort during intimacy.
The virus has more than 100 strains. Some of them are oncogenic. Thus, HPV sometimes provokes the development of cancer of the vagina and vulva, and in men – cancer of the penis.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
CMV is part of the herpesvirus family. It differs from its counterparts in that it spreads throughout the body and affects internal organs - kidneys, heart, liver.
The disease manifests itself as a persistent cold, namely:
- weakness;
- chills;
- malaise;
- headaches and joint pains;
- runny nose;
- enlargement and inflammation of the salivary glands;
- excessive salivation;
- the appearance of a skin rash.
CMV is often asymptomatic or oligosymptomatic. The pathology poses a particular danger during pregnancy. It can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, or cause severe congenital deformities in the baby.
Vertical route of transmission of STDs
Vertical is the route of transmission of infection from a pregnant woman to the fetus. It is possible that the pathogen can travel through the mother's blood through the placenta or become infected during physiological childbirth.
Many toxic and infectious agents are not able to cross the placental barrier and circulate only in the blood of a pregnant woman. The pathogens of syphilis, genital herpes, cytomegalovirus, chlamydia, and gonorrhea spread through the fetoplacental bloodstream.
Mother's illness without timely treatment leads to intrauterine infection and developmental defects. These are bronchopneumonia, otitis media, conjunctivitis, congenital syphilis, congenital chlamydia, brain cyst. Stillbirths and neonatal deaths are possible.
It is because of these risks that all pregnant women should be tested for STDs. An infected pregnant woman undergoes special treatment, which reduces the risk of disease in the fetus. For the same purpose, caesarean section is chosen as the method of delivery.
Also for women, one of the most dangerous complications of STDs is post-infectious damage to the fallopian tubes, leading to infertility.
HIV
HIV is characterized by disruption of the immune system. Due to the suppression of the body's protective properties, secondary infections and malignant formations develop. The disease occurs in 5 stages, the last of which is AIDS.
Structure of the HIV virus
The first signs of HIV:
- causeless weight loss;
- frequent colds;
- chronic diarrhea;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, persistent cough;
- chest pain;
- private headaches;
- cognitive disorders;
- depressive states;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- increased sweating and feeling hot;
- blurred vision;
- skin rash, fungal infection that cannot be treated, etc.
The course of the disease is varied. It can last several months or stretch up to 20 years.
Contact route of transmission of STDs
Is it possible to become infected with sexually transmitted diseases at home?
Contact transmission occurs in some sexually transmitted diseases. The so-called “household syphilis” is transmitted through dirty dishes, stale bedding, underwear, and towels.
In the same way (excluding dishes) you can become infected with genital herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), chlamydia, candidiasis (thrush). Most often, girls become infected through household contact.
In adults, domestic infection is preceded by a decrease in immunity after illness, transplantation and autoimmune disorders, and HIV-positive status. Gonococci, chlamydia and Treponema pallidum survive in water. Therefore, there is a low risk of illness when swimming in stagnant water.
The water in the pools is disinfected. But if the source of infection and a susceptible organism are located together in a limited area, infection is also possible.
Environmental factors contributing to household infection:
- underwear, towels, sheets, duvet covers
- utensils for general use
- washcloths, body wash sponges
- shared bath, swimming pool, sauna
- public toilet
Thrush can be transmitted from unwashed vegetables and fruits, and dirty nipples of newborns.
Most microorganisms die in the external environment. So for infection, the recipient must use the same environmental factors immediately after the source of infection.
Most often transmitted by contact are scabies, pubic lice, and less commonly, syphilis. In other cases, domestic infection is unlikely. Contact-household route is excluded for mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, viral hepatitis B and C, HIV.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, accompanied by damage to its tissue. The latent course of the disease or lack of treatment ends in the transition to a chronic form. The outcome in this case is unfavorable - cirrhosis and liver cancer.
The most typical symptoms of hepatitis:
- lethargy, weakness and deterioration of general condition;
- jaundice;
- causeless weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- elevated temperature;
- rash and itching;
- heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, extending under the right shoulder blade;
- dryness and bitterness in the mouth;
- belching;
- nausea and vomiting;
- joint pain;
- dark urine and discolored stool.
The clinical picture may vary depending on the type of disease.
Current measures to curb the spread of STIs are not enough
Changing behavior is challenging
Despite significant efforts to identify simple interventions that can reduce risky sexual behavior, behavior change remains challenging. Research has identified the need to target carefully defined populations, conduct extensive consultation with identified target populations, and involve them in the design, implementation, and evaluation of interventions.
STI screening and treatment services remain underdeveloped
People seeking STI screening and treatment services face many challenges. These challenges include limited resources, stigma, poor quality of services and low or no follow-up of intimate partners.
- In many countries, STI services are provided separately and are not integrated into primary health care, family planning and other routine health care services.
- In many settings, screening for asymptomatic infections is often not possible due to a lack of trained personnel, laboratory capacity and appropriate medications.
- Marginalized populations with the highest rates of STIs, such as sex workers, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, prisoners, mobile populations and adolescents, often lack access to adequate sexual health services.
Lymphogranuloma venereum
This disease is characterized by purulent-inflammatory lesions of the lymph nodes and soft tissues of the urogenital area. The incubation period is from 2 days to 2 months. The disease develops in stages.
First phase (2-3 weeks):
- the appearance of erosive and ulcerative elements. Localization in men - glans penis, groin, urethra;
- in women - vulva, vagina, cervix. After oral or anal sex, lesions usually spread to the lips, tongue, rectum, fingers;
- partial enlargement of lymph nodes.
Second phase (1-2 years):
- compaction and fusion of regional lymph nodes, their pain;
- formation of a dense lumpy conglomerate up to 6-8 cm in diameter;
- opening of suppurations.
The third phase is characterized by severe destructive disorders of the regional lymph nodes, liver and spleen. Fistulas may occur in the pelvic area.
Lymphogranuloma venereum is not considered a common disease. Usually occurs in people 20-30 years old.
Sexual transmission of STDs
The main route of transmission of STDs is sexual.
Most pathogens of this group of diseases are sensitive to environmental conditions. Therefore, for sexually transmitted diseases only direct contact is possible, while for others it is preferable. These diseases are transmitted through unprotected sex with penetration: oral, vaginal, anal.
WHO considers anal sex to be the most dangerous due to frequent trauma to the mucous membrane.
In addition, some viruses “prefer” the rectal epithelium (this phenomenon is called tropism). The risk of infection is slightly lower during oral sex. However, it is in the oral cavity that there are foci of chronic infection (tonsillitis, carious teeth), which increases the risk of infection during sexual intercourse.
Also, the oral mucosa often has microcracks through which the pathogen penetrates. The likelihood of infection increases with kissing, petting (mutual masturbation), and the use of sexual toys. Even if the coitus itself took place with a condom. You can become infected through mutual masturbation, through kissing, fellatio and cunnilingus.
Is it even possible to get sexually transmitted infections with a condom?
What can you become infected with?
Yes.
The fact is that a condom only covers the penis. And with genital herpes, syphilis, condylomas, contact with the affected areas is not protected. Violations of the integrity of the skin of the pubis, abdomen, thighs, and buttocks provide an entry point for infection when interacting with infected material.
Diagnostics
Most STDs have a fairly similar clinical picture, so diagnosis based only on history and external manifestations is impossible.
The diagnosis is made based on the results of a number of tests:
- blood test for microflora;
- bacteriological culture;
- immunological blood test;
- Mutual investment fund method;
- PCR study.
The diagnostic plan is drawn up depending on the symptoms.
Depending on the suspected disease, different diagnostic materials are required for testing:
- genital smear;
- scraping or smear from the urethra;
- sperm, prostate juice;
- blood (usually from a vein);
- urine.
Diagnosis of STDs
The probability of a combination of several STDs at once is quite high, so one patient may be prescribed a full list of tests.
Methods for diagnosing and treating STIs in men
Diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases includes a number of medical measures:
- blood test;
- smear for STDs - taken from the urethra, semen;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - allows you to detect DNA fragments in smears and identify the disease;
- culture, which allows identification of the pathogen;
- serological diagnostic methods, which include tests for PIF and ELISA, which make it possible to detect antibodies to various pathogens and understand what a person is sick with.
The material for laboratory research in our clinic can be blood, saliva, semen, urine, scrapings from mucous membranes. We prepare the patient in advance to collect materials for testing. Sometimes this means avoiding sexual activity for 48 hours and not urinating for a while. In other cases, no preparation is required other than maintaining good personal hygiene.
Treatment of sexually transmitted infections is always individualized. Our specialists take into account the characteristics of the patient’s body, the severity of the disease, the presence or absence of complications. Typically, therapy includes increasing immunity with the help of immunostimulants, vitamins, minerals, and physical therapy. Medicines are also used, including antibiotics and antivirals.
If one of the partners has a sexually transmitted disease, the other partner must also pass all the necessary tests. This needs to be done even if he has no worrying symptoms.
Treatment
The main thing in the treatment of STDs is its timeliness. This will not only increase the chances of a successful recovery, but will also protect against the development of complications. It is also important that therapy should occur for both partners at the same time.
Treatment tactics are selected individually depending on the type of disease and the condition of the body.
To combat pathology, the following may be prescribed:
- specific drugs aimed at destroying a specific pathogen;
- vitamin complexes, restoratives, immunostimulants;
- painkillers;
- rinsing, tampons, suppositories, ointments, douching and cauterization;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- laser therapy, cryodestruction, radio wave exposure, electrocoagulation, surgery (to remove warts, papillomas and condylomas, suppurations and abscesses).
Some viral diseases cannot yet be cured. These are all types of herpes, HIV, HPV. Their treatment is aimed at reducing the harm they cause and prolonging a person’s life.
Some STDs are prone to relapse when favorable conditions occur, since they are provoked by opportunistic microflora. These are candidiasis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis and others.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter