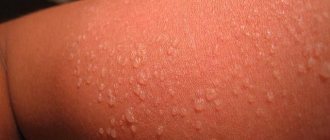
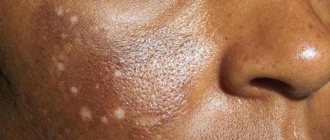
An allergy is a specific reaction of the body to any irritant (allergen). The response of the immune system can manifest itself not only in the flowering of plants and pets, but also in hypothermia. Cold allergies occur when exposed skin is exposed to low temperatures and is otherwise called cold urticaria. The hands and face are most susceptible to this pathology1.
Symptoms of an allergy to cold
The reaction can occur upon contact with cold objects or prolonged exposure to frost. Most often, manifestations occur in winter. The likelihood of such a reaction increases in damp, windy weather. Sometimes the peak of development of an allergy to cold occurs at the moment when the patient gets into the heat. Main symptoms:
- pink or red rashes;
- itching;
- swelling in exposed areas of the body.
Sometimes patients experience a systemic allergic reaction - redness of the skin throughout the body. Its characteristic symptoms are:
- chills;
- tachycardia;
- swelling of the fingers and toes;
- a feeling of heaviness in the chest and throat (tightness);
- and even loss of consciousness2.
What is cold allergy and why does it occur?
This pathology, in its essence, is an inadequate response of the immune system to the effects of low ambient temperature or water. For what reason such changes occur is currently not known for certain. Some scientists suggest that cryoglobulins, special proteins that are produced in the cold and activate histamine, thus triggering a cascade of allergic reactions, play an important role in the mechanism of the allergic reaction.
The foundation for this pathological process is various somatic pathologies: chronic diseases of the respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems, infectious and parasitic diseases. An extremely important role is played by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to intestinal dysbiosis, gastritis, cholecystitis, enterocolitis, etc. In principle, almost any long-term health disorder can provoke an allergic reaction.
Allergy to cold on the face
It is very important to learn to recognize this type of allergy, as it can masquerade as colds or dermatitis. The main symptoms appear as follows:
- Finding yourself outside in the cold, a person begins to experience a headache.
- Spasms (tone) of the muscles of the face and neck appear.
- Nausea sets in.
- In particularly severe cases, extensive facial swelling may develop, which is accompanied by redness.
- Spots and blisters appear, like a burn, and severe itching occurs.
- People suffering from cold urticaria experience a runny nose with watery nasal discharge and frequent sneezing.
Also, the cold may cause pain in the eye area and watery eyes. This phenomenon is called pseudoallergic conjunctivitis.
Diet for cold dermatitis
Poor nutrition, stomach and intestinal diseases are a common cause of the development of cold dermatitis. To get rid of the disease and prevent its recurrence, you should follow a diet and try to give up the following foods:
- Fast food and quick snack: chips, crackers, nuts, etc.;
- Citrus fruits often cause allergies;
- Store-bought juices and sweet sodas contain dyes and preservatives;
- Limit baked goods (especially rich ones);
- Chocolate, candy, cakes, honey;
- Any mushrooms;
- Seasonings;
- Store-bought sauces;
- Eggs are considered a strong allergen;
- Milk – many people are allergic to lactose;
- Seafood - except fish, whose meat is considered dietary;
- Fatty foods and fatty meats.
Can be used:
- Poultry meat – chicken, turkey;
- Dairy products;
- Greens – parsley/dill, etc.;
- Vegetables - zucchini, cabbage, and pumpkin are especially useful.
- Cereals.
Steam cooking is recommended. It is acceptable to add a small amount of olive oil and salt for taste.
By adhering to the basics of proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle, you can avoid many dermatological diseases or alleviate their course, avoiding complications.
Allergy to cold on hands
It is quite rare. The reasons for its occurrence have not been fully studied, so it is impossible to say with certainty why exactly cold allergies occur in the hands. It is known that a reaction occurs in patients with increased sensitivity of the body to cryoglobulin. This is a protein in the blood that can appear in various diseases, myeloma, nephrosis, cirrhosis, rheumatism. When exposed to cold, it triggers a pathological reaction3.
It all starts with a feeling of slight discomfort and scratching. A little later, the skin of the hands becomes dry and rough. Small cracks appear, followed by pink-red rashes and swelling. All these manifestations become most pronounced after warming up the hands, but within an hour, as a rule, no trace remains of them. In some cases, symptoms may persist for a week.
Heat urticaria: what is it?
Heat urticaria is an itchy rash (blisters) that occurs when the skin is exposed to high temperatures. The presence of this form of allergy can be determined using special tests. But there are more accessible and simpler diagnostic methods.
For example, it is enough to apply a hot object to the skin of the forearm for only 5-7 minutes. If redness, itching or swelling appears on the skin within 15-20 minutes, the diagnosis of “heat urticaria” can be considered confirmed. In children and adults, this allergic reaction may also occur in the form of fever.
Allergy to cold in a child
The body's reaction to hypothermia can occur at any age. In children it manifests itself differently and is of a purely individual nature. For example, with the first case of a reaction to cold, children tolerate allergies much easier than with repeated attacks of the pathology (relapses). Clinical manifestations depend on the form of the disease and severity. Cold allergies in children are not much different in appearance from skin lesions such as seborrheic eczema (a skin disease characterized by inflammation, rash and severe itching) or atopic dermatitis (a disease caused by a genetic factor, accompanied by a rash and severe itching)4,5.
Children with weak immune systems are most susceptible to reactions. In the vast majority of cases, a child develops cold urticaria:
- due to genetic inheritance;
- after viral infections;
- with a tendency to skin diseases6.
Treatment of cold dermatitis with folk remedies
In folk (alternative) medicine, there are many recipes to combat many skin pathologies. Ointments, tinctures, lotions or decoctions are made based on herbs or other natural ingredients. Almost all of these remedies are ineffective against cold dermatitis, and are sometimes dangerous, especially when treating children. The possibility of using any folk remedy as an addition to the main drug treatment should be discussed with your doctor.
Only the attending physician can advise the remedy and the advisability of its use.
Treatment of allergies to cold
As with any other type of allergy, the first step is to get rid of the irritant. No allergen – no reaction. But it is not always possible for a person to determine what exactly a cold allergy is caused by.
First of all, you should take an antihistamine to stop the attack and prevent its development. If the allergen is known, it must be excluded or, at least, contact with it must be reduced as much as possible. In the case of allergies to cold, doctors recommend:
- Minimize exposure to cold.
- Approximately 30 minutes before leaving the house, lubricate your face and hands with protective cream.
- Instead of soap for washing, use gentle gels and foams. Regular toilet soap causes dry skin, making it more sensitive to cold.
- To avoid general hypothermia of the body, it is necessary to dress according to the weather, do not neglect hats and protect your hands from the cold. Preference should be given to clothing made from natural materials. Eliminate synthetic underwear and nylon tights from your winter wardrobe.
If preventive measures are not enough to eliminate an inadequate reaction to cold, and it is impossible to completely eliminate the presence of the allergen, symptomatic treatment is necessary.
Depending on the type of reaction, either corticosteroids for topical use (ointments, gels and sprays) or antihistamines (suspensions, tablets) are prescribed. If necessary, treatment lasts throughout the entire cold period of the year.
One of the modern antihistamines for the treatment of allergies is Cetrin®. The action of the drug is based on blocking the receptors to which histamine, which is responsible for the development of an allergic reaction in the body, binds. Moreover, the effect of Cetrin® does not depend on the cause of the allergic reaction, so it can also be used for cold allergies.
As for the dosage, in accordance with the recommendations, the drug Cetrin® must be consumed, adhering to the following rules:
- children over 6 years of age – ½ tablet 2 times a day or 10 mg 1 time a day;
- adults – 1 tablet 1 time per day1.
The medicine must be taken with water (at least 200 ml). Chewing is not recommended. It is recommended to follow a certain diet and preventive measures:
- Eliminate from your diet spicy, fried foods and foods that can irritate the gastric mucosa.
- Include foods rich in polyunsaturated acids. The highest content is in flaxseed, cod liver, olive and rapeseed oil. It is also useful to include fatty sea fish (mackerel, tuna, herring) in your diet.
- Hardening the body can be a good preventative measure for cold allergies.
By following the recommendations, you can significantly reduce the intensity of pathological manifestations or completely get rid of allergies to cold.
Bibliography
- Goryachkina L.A. Urticaria / L. A. Goryachkina, N. M. Nenasheva, E. Yu. Borzova // Moscow, Newspaper “News of Medicine and Pharmacy”. – 2010. – No. 8. – 321 p.
- Nusinov E.V. Hives. Atopic dermatitis: methodological recommendations for students of medical, pediatric and dental faculties / E.V. Nusinov; edited by V. M. Chervenets. – M.: Alquist editorial office, Tver, 2012 – 22 p.
- Muzychenko A.P. Urticaria: educational and methodological. Manual / A. P. Muzychenko. – M.: BDMU, Minsk, 2014. – 16 p.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the management of patients with eczema / Ed. V. A. Okhlopkova. – M.: Moscow, Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists, 2013. – 18 p.
- Atopic dermatitis: hand. for doctors / Ed. Yu. V. Sergeeva. – M.: Moscow, 2002.
- Nusinov E.V. Hives. Atopic dermatitis: methodological recommendations for students of medical, pediatric and dental faculties / E.V. Nusinov; edited by V. M. Chervenets. – M.: Alquist editorial office, Tver, 2012 – 22 p.
- Instructions for use of the medicinal product for medical use Cetrin®. – Registration number: P N013283/01.
Treatment of cold dermatitis
Before starting treatment, it is imperative to carry out a diagnosis, since cold dermatitis has similar symptoms to other diseases - allergic urticaria, chicken pox, atopic dermatitis. The doctor uses the following diagnostic methods:
- Dermatoscopy is a device for tenfold magnification and study of tumors.
- Measuring the pH level - to exclude a fungal or bacterial infection, and determine what caused the development of dermatitis.
- General blood and urine analysis.
Additionally, additional examinations may be prescribed - ultrasound, smear, gastroscopy. It is quite difficult to establish a diagnosis on your own, so it is recommended to visit a dermatologist; the doctor, based on the tests obtained, will prescribe a treatment regimen taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body.
The main treatment is to protect the skin from exposure to low temperatures and complex treatment aimed at:
- Relieving symptoms - often antihistamines (tablets or ointments) eliminate itching, swelling and redness of tissues;
- Retinoids - to heal formed cracks, accelerate tissue regeneration and normalize the functionality of dermal cells (gels, creams);
- Vitamin complexes - to boost immunity;
- Prebiotics – to eliminate dysbiosis;
- Cosmetics for skin care and protection from negative factors.
Self-prescribing and taking medications is unacceptable; any medications should be prescribed only by a doctor, this will avoid negative consequences.