Probably, summer is given to us in order to enjoy sunny days, get out into nature, admire its colors, travel and, of course, bask in the rays of the gentle sun. Some people use their summer vacation to visit southern countries, swim in the sea, lie on the beach and sunbathe. But both at home and at a party, one danger awaits us - an allergy to the sun. Why does it occur? How does it manifest? And what should you do if, after being in the sun, your skin suddenly becomes covered with red spots and itches mercilessly?
What is photodermatitis?
A sun allergy has little in common with a true allergy. The disease is caused by increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight, but as such an allergen, that is, a foreign substance that directly causes the development of a true allergic reaction, does not exist. That is why the processes occurring in the skin during photodermatitis are called pseudo-allergic.
And yet, there are some common points between true allergies and photodermatitis. Substances that provoke the appearance of skin rashes after sunbathing still exist, however, they do not come from the outside, as in a true allergy, but are formed in the skin itself under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and become an irritant to the human immune system.
Sources
- Bolotnaya L.A. Photodermatoses // Dermatovenereology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology. —2009. — No. 1-2 (12). — pp. 188-197.
- Princely N. And there are spots from the sun // Asthma and allergies. - 2010. - No. 2. - P. 6-7.
- Macharadze D.Sh., Tsintsadze N.N. Solar urticaria and other photodermatoses // Medical advice. - 2011. - 5-6. — P. 30-34.
- Osipova V.V. Photodermatoses: photoallergic reactions // Asthma and allergy. - 2014. - No. 2. - P. 3-5.
- Polymorphic photodermatosis. Clinical recommendations. - M., 2015. - 15 p.
- Sidorovich O.I., Tsyvkina E.A. Photodermatoses: prevention and treatment // Medical advice. - 2021. - No. 18. - P. 132-134.
- Fedotov V.P. Photodermatoses (clinical lecture) // Dermatovenerology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology. - 2015. - No. 3-4. — pp. 143-157.
- Yarovaya N.F. Photodermatoses // Attending physician. - 2009. - No. 6. - P. 61-66.
Cosmetics may cause sun allergies
Depending on the mechanism of occurrence, photodermatitis is divided into exogenous and endogenous.
With exogenous photodermatitis, substances located on the surface of the skin act as a trigger. Together with ultraviolet radiation, they cause the formation of allergens in the skin and the appearance of disease symptoms.
The following may act as a “provocateur”:
- sunscreens, especially if they contain para-aminobenzoic acid;
- cosmetics and perfumes;
- essential oils, for example, bergamot oil, St. John's wort, rose, sandalwood;
- dill and parsley juice;
- boric and salicylic acids, phenol, mercury preparations;
- polyunsaturated fatty acids in vegetable oils.
When packing your cosmetics bag for the sea, you should carefully select products and exclude those that can provoke allergies to the sun.
Another example of exogenous photodermatitis is meadow allergy. Its cause is furocoumarins in the pollen of meadow flowers and grasses that settle on human skin.
Diagnostics
If you notice a rash on your skin after sunbathing, you should immediately consult a doctor. Identifying the fact of photosensitivity during a conversation with the patient, dermatological examination and dermatoscopy of the present rashes will provide the doctor with the opportunity to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment for solar dermatitis.
Determination of the type of photosensitizing substance is carried out by application tests with photoallergens. The allergen is applied to the patient's skin in two rows, after which a light bandage is applied to the area where the research is being carried out. After 24 hours, one row is exposed to ultraviolet irradiation, and the second will be the control.
In order to identify the endogenous causes of the disease, it may be necessary to conduct a biochemical analysis of the patient’s blood and urine, an analysis of the Zimnitsky test, a study of hormonal changes, excretory urography, ultrasound and CT of the kidneys, and ultrasound of the abdominal organs. To completely exclude such an insidious disease as systemic lupus erythematosus, antinuclear factor, C-reactive protein and lupus anticoagulant can be determined in the patient’s blood.
When the causes of photodermatitis lie inside
Endogenous photodermatitis develops under the combined action of sunlight and substances accumulating in human skin.
Their causes may be:
- chronic liver diseases;
- metabolic diseases of hereditary and acquired nature;
- diseases of the adrenal glands and kidneys.
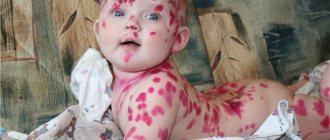
Young children are more likely to develop photodermatitis, when the internal mechanisms of skin protection are not yet formed, as well as people with fair skin.
Many medications cause increased sensitivity to sunlight: Tetracycline, Doxycycline, Amiodoron, Trazicor, Ibuprofen, Aspirin, oral contraceptives, cytostatics and even some antiallergic drugs.
The likelihood of developing a sun allergy increases sharply after cosmetic procedures, such as cleansing, peeling, mesotherapy, contouring, and tattooing.
Clinical researches
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children and adults with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Based on the results of joint research, the following information is placed on product packaging: “Recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.”
Sources:
- Ratner Desiri, Avram M.R., Avram M.M., Procedures in Dermatology. Clinical cosmetology, GEOTAR-Media, 2021.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, Notabene, 2017.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Illustrated clinical dermatology. Brief alphabetical reference book, Lux Print publishing house, 2010.
Photos of dermatitis
Photo album on the diseaseHow not to confuse sun allergy with sunburn?
Most often, manifestations of photodermatitis occur with the first rays of spring and worsen after sunbathing throughout the summer.
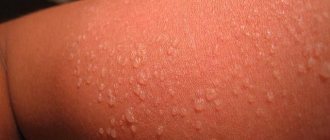
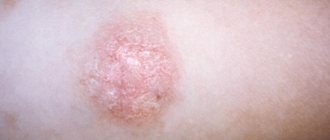
Typically, from the moment of exposure to sunlight until the appearance of allergy symptoms, it takes from several hours to two days. The rash is preceded by itching of the skin; it can occur already during sunbathing. Then, after about a day, a rash appears on the irradiated areas of the skin. Most often, it has the appearance of urticaria, that is, small tubercles merging into blisters; less often, blisters form, after opening which, erosions remain on the skin, healing after 2-5 days with the formation of crusts, and leaving behind persistent pigmentation. Considering that the whole picture of photodermatitis unfolds against the background of general redness of the skin, it is quite easy to confuse an allergy to the sun with ordinary sunburn. Treatment for these conditions varies, so if in doubt, it is better to immediately consult a dermatologist.
There is also a chronic form of sun allergy, which in its course resembles eczema, accompanied by severe itching. This type of sun intolerance is more common in middle-aged and older men.
Solar cheilitis
There are several varieties of this disease with their own characteristics. In particular, eczematous cheilitis resembles classic eczema and appears on the lower lip in the form of blisters against a background of reddened and swollen skin. Over time, the bubbles merge into a single spot, open, and erosions form in their place. At the same time, the skin peels, cracks, and becomes covered with crusts after bursting blisters. The disease can be noticed by thickened, protruding lips7.
Another type is xerotic cheilitis, it develops slowly and lasts a long time. Dry, thin gray scales form along the edges of the lips. They disappear and new ones quickly appear in their place. With a long course, the formation of abrasions and wounds is possible.
Important!
Solar cheilitis is often observed in those who are exposed to UV radiation for a long time and often. This can cause malignancy.
Doctor, is this forever?
Treatment of sun allergies involves eliminating exposure to ultraviolet radiation. In the case of solar urticaria, antihistamines help, and there are special medications that thicken the skin and reduce its sensitivity to sunlight. Treatment in this case consists of gradually accustoming the skin to the sun while taking medication.
To relieve exacerbation of photodermatitis, local treatment is prescribed in the form of ointments, sometimes hormonal, and internal treatment: vitamins B, E, C, nicotinic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antihistamines. Usually the course of treatment continues for several days or weeks. During this time, it is recommended to spend less time in the sun, wear a wide-brimmed hat, clothes with sleeves and sunglasses.
If sun allergy is left untreated, repeated episodes will lead to the development of photodermatosis. When you have managed to stop the allergy attack by carefully taking care of protecting your skin, eliminating provoking factors and strictly following the sunbathing regime, you have the opportunity to bask in the gentle rays. Sun allergies can be controlled and prevented, and children may even outgrow this disease.
medkrug.ru
Solar dyshydrosiform dermatitis
This type of photodermatitis, in its symptoms and course, resembles solar eczema. It develops slowly - within 10-20 days. It most often affects people with hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). Outbreaks occur in late spring and summer when the weather gets hot. The peculiarity of this photodermatitis is the localization of the rashes: on the sides of the fingers, palms and soles. The rash appears first on the arms, then on the legs. The rashes are located symmetrically, as with solar eczema. The rash consists of deep blisters of both small and large sizes. They are covered with a stratum corneum and rarely open. As the disease progresses, the blisters coalesce into spots. Peeling of the skin is typical, and a fungal infection is possible.
People prone to photodermatitis should limit exposure to open sun. Photo/Depositphotos
Folk remedies
After consulting with a specialist, treatment of photodermatosis can be supplemented with traditional medicine procedures.
- To relieve symptoms such as swelling and inflammation, compresses made from grated horse chestnut and carrot pulp are used.
- A decoction of calendula, chamomile and plantain will literally do the impossible; it will not only relieve inflammation, help regenerate the dermis, but also reduce stress. Take an assortment of herbs about 400 g, pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for about an hour, take 1 glass per day on an empty stomach;
- Burning and itching can be reduced by using lotions with kefir and apple cider vinegar.
- Treatment with herbal baths: currant leaf, chamomile has a beneficial effect on the skin.
- Prepare an ointment based on St. John's wort; it will not only relieve inflammation, but also act as an antiseptic. To make it, squeeze the juice from the flowers, put on the fire and bring until the mass evaporates by half, add butter to the broth in a ratio of 1 to 4;
- To soften the skin and give elasticity to the epidermis, you can use sea buckthorn and peach oil.
- Potatoes, the most beneficial and at the same time cheapest remedy, to use it, grate a small tuber on a fine grater, lubricate the damaged areas with the resulting pulp.