pharmachologic effect
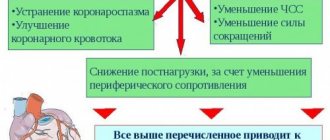
The active component, being an antagonist of calcium ions , causes blocking of calcium channels in the cells of cardiomyocytes and arteries. Thus, nifedipine affects the cardiac and peripheral vessels, causing them to expand. Does not affect the tone of the smooth muscle muscles of the veins. Such a reaction helps to lower blood pressure , reduce peripheral vascular resistance (mostly arterioles), reduce the oxygen needs of cardiomyocytes and, accordingly, all this leads to a significant reduction in the load on the heart as a whole. One of the functions of nifedipine is also the inhibition of platelet .
How it affects the body
The medicine is a calcium antagonist and belongs to the group of slow calcium channel blockers (SCBC). The substance slows down the process of calcium penetration into the muscle cells of the heart, as well as into the cells of vascular muscles. Under the influence of the drug, the myocardium consumes less oxygen. Nifedipine lowers blood pressure and total peripheral vascular resistance, and the ability of the myocardium to contract is also slightly reduced.
Thanks to the medicine, the tone of the smooth muscles located in the vessels slightly decreases, therefore the peripheral and coronary arteries dilate. Due to this, blood flow in the coronary vessels is normalized. Myocardial conductivity is not inhibited. But you need to remember that Nifedipine does not act against arrhythmia and does not normalize heart rhythm.
Indications for use
Phenigidine is prescribed for blood pressure, an increase in which is associated with the following cardiovascular diseases:
- arterial hypertension;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- Raynaud's disease.
The medication is used to quickly relieve a hypertensive crisis and prevent attacks of angina pectoris ( ischemia ).
What else can Phenigidine be used for? In pulmonology, the drug is prescribed for:
- pulmonary hypertension;
- broncho-obstructive syndrome.
Contraindications
- low systolic pressure ( hypotension );
- severe heart failure
- collapse;
- individual hypersensitivity to the active substance or similar dihydropyridines;
- aortic stenosis;
- cardiogenic shock;
- myocardial infarction in the acute period;
- period of pregnancy and lactation .
Side effects
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- asystole;
- redness of the skin of the chest and face;
- tachycardia;
- bradycardia.
Possible disturbance of central nervous system reactions:
- moderate drowsiness ;
- sleep disorders;
- blurred visual perception;
- dizziness;
- limb tremors;
- migraine headache.
From the gastrointestinal tract:
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- depression of liver function.
Side effects
The medicine may cause some side symptoms. To relieve them, your doctor may prescribe additional medications.
Side effects:
- increased heart rate;
- skin redness;
- feeling of warmth or heat on the skin;
- hypotension;
- slight swelling;
- skin rash;
- ventricular tachycardia;
- slow heart rate;
- increased attacks of angina pectoris;
- cardiac arrest, asystole;
- heartburn, nausea, diarrhea;
- swelling of the gums;
- liver dysfunction;
- muscle pain;
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- tremor of the limbs;
- visual disturbances;
- thrombocytopenia;
- leukopenia;
- renal dysfunction;
- increase in the daily amount of urine excreted;
- sudden enlargement of the breast (gynecomastia).
After an intravenous injection, the patient may feel a burning sensation. After intracoronary administration of the drug, within the first minute the patient’s pulse may sharply increase and blood pressure may drop. These unpleasant sensations disappear after 5–15 minutes.
Instructions for use of Phenigidine (Method and dosage)
The dosage is determined individually, taking into account several factors (age, concomitant diseases, general reaction of the body, etc.). As a rule, the minimum dosage is 10 mg (in some cases 20 mg), the number of doses is up to 4 times a day. For coronary artery stenosis, the minimum dose is 50-100 mcg. The instructions for Phenigidine provide for the maximum safe number of tablets per day - no more than 12 pieces.
To relieve attacks of angina pectoris and hypertensive crisis, it is necessary to take the drug sublingually until completely dissolved. Additionally, it is recommended to take a lying position for at least 1 hour.
Dose adjustment is carried out with extreme caution, gradually increasing or decreasing the amount of the active substance. To avoid side effects, it is advisable to take the drug with food.
The course of therapy is determined according to indications and usually lasts 1-2 months. Next, the attending physician selects another treatment regimen.
Release forms
There are two main forms of release of Nifedipine - tablets and gel-emulsion. Most often, patients are prescribed tablets. They contain a high content of active substance. Gel emulsion is an auxiliary preparation.
Tablets weighing 10 g can be packaged in blisters of 10 pieces each. These blisters are packed in cardboard boxes. Also, tablets of 20 or 50 pieces can be placed in plastic jars.
The gel emulsion is stored in a tube weighing 40 g. This medicine in this form of release is used only for the treatment of hemorrhoids.
There is also Nifedipine in the form of a solution for intravenous injection, as well as in the form of boluses that are injected into the coronary vessels.
Overdose
In case of an overdose, a dangerous decrease in systolic blood pressure occurs. The following symptoms are observed:
- bradycardia;
- collapse;
- arterial hypotension (can lead to loss of consciousness);
- disturbance of rhythm and conduction of the heart;
- headache.
If there are symptoms of poisoning, you should immediately perform gastric lavage and take activated charcoal . In especially severe cases, patients are prescribed a 10% calcium chloride solution intravenously.
Overdose symptoms
You should not take more than 120 mg tablets per day. The maximum dose of intravenous solution is 30 mg.
Signs of overdose:
- a sharp slowdown in heart rate;
- bradyarrhythmia;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- hypotension;
- collapse;
- cardiogenic shock;
- convulsions;
- loss of consciousness;
- hypoxia;
- acidosis;
- slowing of cardiac conduction;
- hyperglycemia;
- coma.
Symptoms appear 3-4 hours after taking the tablets. In case of overdose, the patient's stomach is washed and activated charcoal is administered. He is then given intravenous injections of atropine with calcium gluconate, calcium chloride and norepinephrine to relieve intoxication. Due to proven ineffectiveness, hemodialysis is not performed.
Interaction
The drug has a more pronounced effect when taken simultaneously with other drugs to lower blood pressure, nitrates, diuretics, tricyclic antidepressants, Ranitidine , Cimetidine . In combination with beta-blockers, it can cause circulatory problems in the heart muscle and increase arterial hypotension.
The effectiveness of nifedipine is reduced when taken simultaneously with calcium supplements, Phenytoin , Rifampicin , Phenobarbital , Carbamazepine .
When taken simultaneously with Digoxin , Quinidine and Theophylline, the concentration of the latter in the blood plasma changes. Ethanol can enhance the effect of nifedipine, thereby causing dizziness, weakness, and coronary circulatory disorders.
Interaction with other drugs
Blood pressure drops sharply when Nifedipine is taken simultaneously with other antihypertensive drugs, as well as diuretics, diltiazem, and drugs based on phenothiazine and its derivatives.
Attention and memory may be affected when Nifedipine is used with anticholinergic medications.
This medicine should not be combined with beta-blockers, otherwise severe hypotension and even heart failure may occur.
In combination with magnesium salts, the patient experiences severe muscle weakness.
The effective effect against angina pectoris is enhanced when the drug is combined with nitrates.
Due to the intake of digoxin and theophylline, the amount of these substances in the blood increases.
You should not take Nifedipine together with medications containing calcium. These substances have opposite properties, which reduces their effectiveness. Side effects of the drug are enhanced in combination with fluoxetine and vincristine. Also, the effect of Nifedipine is reduced in combination with rifampicin, so these two drugs are incompatible with each other.
The level of nifedipine in the blood decreases if you take the medicine together with phenytoin, phenobarbital or carbamazepine. Conversely, concentrations increase in combination with itraconazole, cimetidine, fluconazole and ranitidine.
The QT interval on the ECG is prolonged when Nifedipine is taken simultaneously with quinidine. This occurs because the amount of quinidine in the blood decreases sharply, and when it is discontinued, it suddenly increases.
Severe hypotension, dizziness and other unpleasant symptoms occur if the patient drinks Nifedipine and drinks containing ethyl alcohol. This drug should not be combined with grapefruit juice.
special instructions
Phenigidine must be used under the strict supervision of a physician, and in case of myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus , diseases of the hepatic system, pathology of cerebral circulation, hypovolemia, hemodialysis - only in a clinical setting.
The dose is increased and decreased gradually. Abruptly stopping treatment can be dangerous. For the elderly, a dose reduction is recommended due to reduced metabolism. For speedy absorption, it is recommended to dissolve the tablet under the tongue until completely dissolved. During treatment, alcohol and substances that lower blood pressure are not allowed.
During the treatment period, it is not recommended to drive various types of transport, machinery or carry out work that requires increased attention and concentration.
Carefully
Patients suffering from certain diseases should be extremely attentive to their health. They will have to drink Nifedipine with caution:
- elderly patients;
- hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy;
- severe liver diseases;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- kidney dysfunction;
- mitral valve stenosis;
- chronic heart failure;
- diabetes;
- stenosis of any part of the intestine;
- disturbances in the functioning of cerebral vessels.
Taking the medication in these cases should be strictly under the control and supervision of the attending physician.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Lacipil
Cordafen
Azomex
Nimodipine
Felodipin
Nifedipine
Farmadipin
Amlotop
Nimotop
Tenox
Nifecard HL
Cordipin
Felodip
Normodipine
Norvask
Cordaflex
Lerkamen
Corinfar
Vero-Amlodipine
Amlodipine
There are many analogues of Phenigidine with a similar mechanism of action:
- Nifedipine
- Cordipin
- Myocardium
- Nifecard
- Corinfar
Reviews about Phenigidine
Analysis of information on medical portals led to the conclusion that this drug is considered outdated, and many restrictions on use force doctors to prescribe safer and more modern analogues. Reviews report that the development of side effects is quite common. In this regard, many forum participants are worried about their health, but at the same time unanimously confirm the effectiveness of this drug, especially during attacks of angina pectoris and a sharp increase in systolic pressure.
Phenigidine differs from other antihypertensive medications in the presence of additional effects, because the active substance not only reduces blood pressure, but also has an antiatherosclerotic effect. The opinions of patients on this matter are divided: some choose an effective drug for hypertensive crises, turning a blind eye to pronounced side effects, while for others it is preferable to take safe, modern drugs that not only smoothly lower blood pressure, but also do not cause negative reactions.