- home
- general surgery
- Cholelithiasis
- Laparoscopic surgery to remove the gallbladder
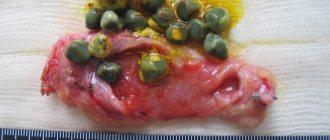
One of the most frequently performed operations in abdominal surgery is cholecystectomy—removal of the gallbladder. To date, such an intervention is the only way to safely treat gallstone disease. GSD is a disease of the biliary tract, in which stones (calculi) form in the gallbladder and ducts. Recently, the number of people suffering from cholelithiasis has been steadily growing; among older people, almost every third person has gallstones.
Different in shape and size, stones can be single, and their number can reach several dozen. But even the presence of one stone is accompanied by a health risk, including complications: block of the cystic duct and the development of acute cholecystitis, the development of obstructive jaundice or pancreatitis with obstruction of the outlet bile duct, rupture of the bladder, peritonitis, etc.
Operation
It should be noted that if there are stones - one or more - it is impossible to preserve the organ; the gallbladder is always removed, since there are no technologies that allow removing stones from the gallbladder and avoiding relapse in the future. Cholecystectomy can be performed using two methods:
- traditional - manipulations are carried out through a 15-20 cm incision. The indication for removal of the gallbladder using this technology is the presence of complications. However, in my practice, the need for such an operation was extremely rare; I always give preference, if possible, to low-traumatic methods.
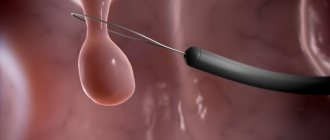
- laparoscopic surgery - currently this technique is recognized as the “gold” standard for gallbladder removal. Laparoscopy can be performed through several punctures on the anterior abdominal wall, through a puncture in the paraumbilical area (near the navel) or transvaginally. Our clinic also performs minilaparoscopic cholecystectomy, when tissue trauma is minimal.
During laparoscopic intervention, all manipulations are performed using video endoscopic equipment, all actions are carried out with high precision, since visual control is possible. During the operation, I also actively use the technology of dosed ligating action on the tissue “LigaSure” and the hemostatic system “PerClot”, which allows for reliable hemostasis in the area of the bladder bed, especially in difficult situations when the venous sinuses are located near the surface of the liver; the risk of significant blood loss during surgery is minimized.
At the final stage of the operation, the gallbladder is removed using a special plastic container inserted into the peritoneal cavity. To prevent the formation of adhesions, I use modern anti-adhesion barriers. After removing the trocars, the wound is sutured. The duration of the intervention is no more than 25-40 minutes; discharge is possible on days 2-3. After laparoscopic surgery, unlike open surgery, recovery takes 7-14 days.
For a free written consultation, you can send me a complete description of an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, preferably a gastroscopy, to my personal email address; you must indicate your age and main complaints. In rare cases, if stones in the ducts are suspected, it is necessary to perform an endoscopic ultrasound examination of the ducts and pancreas. Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.
Indications for gallbladder removal
Cholecystectomy is performed for cholecystitis and cholelithiasis to remove gallstones and combat the complications they cause. Your doctor may recommend surgery in the following cases:
— Chronic calculous cholecystitis (gallbladder stones, cholelithiasis)
— Polyps and cholesterosis of the gallbladder;
— Stones in the bile duct (choledocholithiasis)
— Inflammation of the gallbladder (acalculous cholecystitis)
— Asymptomatic cholecystolithiasis (no symptoms in the presence of gallstones)
Cholecystectomy performed routinely is a fairly simple operation that rarely entails complications. In most cases, the patient can go home 1-2 days after the operation.
Emergency removal of the gallbladder is carried out when there is an immediate threat to the patient’s life, when complications of cholecystitis that have arisen make attempts to achieve stable stabilization of the patient’s general condition futile:
- with peritonitis;
- gangrenous cholecystitis;
- perforation of the gallbladder wall
Types of operations using laparoscopy
- One of the unique techniques is the NOTES technology - removal of stones transvaginally, without incisions in the abdominal wall. For access, the posterior vaginal vault is used, where an incision about 1 cm long is made. During transvaginal laparoscopic surgery to remove the gallbladder, after introducing instruments and optics into the intervention area through an incision on the vaginal vault, cholecystectomy is performed in a standard way. After removing the bladder through the same access using a plastic container, a single suture is placed on the incision, which resolves after 3-4 weeks. Among the advantages of this technique: painlessness in the postoperative period;
- hospitalization takes one day;
- after the operation, the patient’s activity is not limited;
- excellent cosmetic result.
The only restriction is the exclusion of sexual relations in the first month after the operation. However, the intervention does not affect sexual function, since the reproductive organs are not affected. But it should be noted that this technique is not recommended for patients who have a history of multiple surgeries on the pelvic organs.
However, there are contraindications for performing surgery using this technology:
- acute cholecystitis;
the presence of pronounced adhesions in the area of the neck of the gallbladder and Calot’s triangle;
In patients over 45 years of age or who are overweight, the possibility of surgery using this technique is decided individually.
Due to the low-invasiveness of the techniques, in our clinic it is possible to perform simultaneous operations - simultaneous performance of several interventions during one anesthesia. Thus, a patient who has several diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs requiring surgical treatment can be treated with one operation. At the same time, the load on the body is much lower. Unlike operations performed with a 5-6 week interval between each one, hospitalization and recovery with simultaneous surgery take much less time.
To perform a cholecystectomy, the surgeon must be fluent in all techniques, since every person’s body is unique. Each patient who turns to me for help can count on an individual approach. I select the surgical treatment method taking into account the state of health and individual characteristics of the body. For better diagnostics and selection of the optimal solution, we have developed a special program, which is already registered on Russian territory.
As for laparoscopy, in this case manipulations are performed in a limited space, which also requires experience from the surgeon. Since 1994, I have personally performed more than 6 thousand laparoscopies for the treatment of cholelithiasis, of which more than 100 were performed using the transvaginal technique. The results of treatment are summarized in more than 30 scientific publications: both domestic and foreign. I described in detail the indications and technique of all types of operations for cholelithiasis in a monograph published in 2017 - SURGERY FOR GALLSTONES: laparoscopy, minilaparoscopy, single port, transvaginal access, simultaneous operations. -M.: Publishing House "MEDPRACTICA-M", 2021, 312 p.
I also regularly conduct seminars on laparoscopic removal of the gallbladder, which are attended by specialists from medical institutions of various importance: from regional hospitals to large research centers.
After cholecystectomy
You should prepare in advance for postoperative recovery. Most people go home the day after a cholecystectomy, but complications may increase the length of your hospital stay. In some cases, the surgeon may have to make an incision in the abdominal wall to remove the gallbladder. In this case, the patient will have to stay in the hospital for a longer period. It is not always possible to say exactly how the operation will proceed. If you have to stay in the hospital longer, you should immediately take personal items with you, for example, a toothbrush, comfortable clothes, books or magazines, so that you don’t get bored.
Arrange for someone to take you home after discharge and look after you. Ask a friend or family member to drive you home and stay with you the first night after surgery.
Thanks to cholecystectomy, the pain and discomfort caused by gallstones will go away. Conservative treatment, such as changing your diet, does not prevent the formation of gallstones. Cholecystectomy is the only way to prevent the formation of gallstones.
After cholecystectomy, some patients experience mild diarrhea, which then goes away. Most patients do not experience digestive problems after cholecystectomy. The gallbladder is not an organ necessary for healthy digestion.
How quickly a patient can return to normal activities after cholecystectomy depends on the surgical procedure and overall health. Patients who have undergone laparoscopic cholecystectomy can return to work within a few days. Patients who have had an open cholecystectomy need several weeks to recover and return to work.
Postoperative period
Features of the recovery period after surgery are determined by the technique of its implementation. With laparoscopic intervention it is relatively easy. After just 6 hours you can sit down on the bed and gradually get up under the supervision of medical staff. The next day you can safely move around the department. As for food, they begin to eat light food on the second day after cholecystectomy. The drainage can be removed on the same day. On average, recovery takes about a month, but the time frame may increase depending on the general condition of the patient. Open surgeries sometimes require longer bed rest and pain relief.
Reviews
Almost all reviews from our patients are positive - the operation is considered effective, fast and low-traumatic. Unpleasant points that patients pay attention to:
- Abdominal pain due to bloating;
- Difficulty breathing because the lungs have been compressed;
- You have to fast at first.
All these sensations pass quickly. Operated patients agree that these symptoms can be tolerated; they are incomparable to the benefits of surgery.
Diet
An important point in the recovery period is diet. During this period, it is recommended to give up alcohol, heavy foods (fats, marinades, smoked foods), and light carbohydrates. Small meals 4-6 times a day are recommended.
In the federal network of expert oncology clinics “Evroonko”, cholecystectomy is performed laparoscopically if there are no contraindications. We use expert-class equipment, staffed by highly qualified specialists.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Preparatory drug therapy
If necessary, to prevent complications, as well as improve the functional state of the structures of the hepatobiliary system, the doctor may prescribe preparatory drug conservative therapy, which usually lasts several days. Such treatment may include antibacterial agents of various groups, antispasmodics, choleretics or cholekinetics, which improve the process of formation and outflow of bile from the structures of the hepatobiliary system. The doctor determines the duration of such preparatory treatment, the type of medications, and their dosage individually, which depends on the severity of the inflammatory process, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
Proper preparation before removal of the gallbladder is the key to successful completion of the operation, as well as reducing the duration of the postoperative period.
When is laparotomy cholecystectomy inappropriate?
Absolute contraindications:
- Poor blood clotting;
- Pathology of vital functions in the stage of decompensation;
- The patient is in critical condition.
Relative contraindications are determined, as a rule, by the availability of modern equipment at the clinic, the individual characteristics of the patient and the experience of the surgeon. The question of using the technique is a joint decision of the surgeon and anesthesiologist.
There are situations when it is not possible to perform an operation due to anatomical abnormalities or an inflammatory process. In these cases, open surgery is performed.
Reviews of doctors providing the service – Cholecystectomy
Hello.
I would like to share my impressions after 3 brilliantly performed operations by the surgeons of the Multidisciplinary Clinic of CELT Dr. Bronshtein, Yuri Anatolyevich Prokhorov and the chief surgeon of CELT, Oleg Emmanuilovich Lutsevich, and express my gratitude to them from the bottom of my heart for the wonderful... Read full review Alexander Markovich A
07.08.2020
Hello. I would like to share my impressions after 3 brilliantly performed operations by the surgeons of the CELT Multidisciplinary Clinic Dr. Bronshtein, Yuri Anatolyevich Prokhorov and the chief surgeon of CELT, Oleg Emmanuilovich Lutsevich, and express my gratitude to them from the bottom of my heart for the wonderful... Read full review
Alexander Markovich A
07.08.2020
Operational risks
Cholecystectomy, like any other operation, may be accompanied by the development of complications and unwanted reactions. They can be divided into several groups:
Complications from the wound:
- Hematomas and hemorrhages.
- Wound infection. Accompanied by redness of the skin, thickening and the release of pathological discharge. Requires urgent medical attention.
Complications from the abdominal cavity:
- Residual choledocholithiasis. As we know, gallstones can form not only in the gallbladder, but also in the ducts. At the preoperative stage, they try to detect them and solve this problem during cholecystectomy. But in some patients it is not possible to detect stones either preoperatively or intraoperatively. Remaining stones can cause complications, such as obstructive jaundice. Then repeated intervention is required.
- Bile leakage. In the early postoperative period, bile may be separated from the gallbladder bed. To divert it, a drainage is inserted into the wound at the end of the operation. Usually this situation lasts 2-3 days and stops on its own. The only thing required here is observation in a hospital.
- Damage to the bile ducts. As a result, bile leakage may develop. Then the drainage discharge remains for more than 2-3 days. In this case, repeated surgery and long-term rehabilitation are required.
Despite the fact that any surgical intervention may be accompanied by the development of complications, it is still worth noting that their risk is negligible when the operation is performed by an experienced surgeon in a well-equipped operating room.
What are the features of laparoscopic removal?
Today, laparoscopic surgery is perceived positively in surgery because it has a number of advantages:
- with such an intervention the body is less injured;
- due to the closed type of operation, there is less risk of infection in the wound;
- the patient’s hospitalization is quite short - from 2 to 4 days;
- rapid recovery - within 3 weeks;
- small cuts during surgery heal quickly and have an aesthetic appearance;
- most patients would rather undergo this procedure than undergo direct surgery.