The role of the gallbladder in the body
The gallbladder is an organ of the digestive system, normally not exceeding 6–12 cm in length and 4–5 cm in width. It is a kind of reservoir for concentrated bile, regularly produced by liver cells - hepatocytes.
In addition to collecting and temporarily storing the secretion produced, the gallbladder performs absorption, concentration and contractile functions. In other words, what happens in it:
- absorption of water contained in hepatic bile,
- accumulation of bile acids,
- their uniform release after eating.
In the latter case, the smooth muscles of the organ contract and the bladder bile stored in it is sent in measured portions to the duodenum. Once in the intestines, it performs a number of functions:
- rebuilds digestion from gastric to intestinal, neutralizing the enzyme of gastric juice;
- mixes fats;
- activates lipase – a fat-splitting catalyst;
- ensures the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, calcium salts and amino acids;
- enhances the work of microscopic glands of the mucous membrane, responsible for the production of protective mucus;
- prevents the development of pathogenic microflora;
- stimulates parietal digestion with the participation of enzymes produced by the glands of the intestinal wall, and the motor activity of the small intestine.
However, it should be taken into account that for good digestion two prerequisites are necessary: normal contractile function of the gallbladder and stability of the quantitative and qualitative ratio of bile components.
Up to contents
Foods that interfere with the flow of bile
Rich broths prevent the outflow of bile.
Along with a wide selection of choleretic products, there are products that promote stagnation of bile and reduce the motility of the biliary tract. These products include: rich fish, meat and mushroom broths; pork, goose, lamb or duck fats; smoked, spicy and salty foods; millet and black bread, they contain coarse fiber that is poorly digested; chocolate, baked goods, cocoa, strong tea and coffee; peas, mushrooms, nuts, legumes, radishes, radishes, onions, turnips, garlic; ice cream, carbonated drinks.
What gallbladder diseases may cause stool retention?
The main reason for the development of so-called biliary constipation is insufficient flow of bile into the intestines. It is caused by a violation of the motor function of the gallbladder and, as a consequence, a change in the biochemical properties of bile.
There are several diseases of the biliary system that can provoke stool retention:
- biliary dyskinesia . Functional disorder associated with disruption of the activity of the hepatic and vesical sphincters (muscle rings) and a disorder of the contractile function of the organ;
- inflection of the gallbladder. This is a congenital or acquired pathology due to deformation of the organ in various parts;
- cholecystitis. An inflammatory disease that develops as a result of infection of the gallbladder with Escherichia coli, coccal microflora, Proteus, Giardia or hepatitis virus;
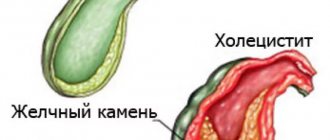
- cholelithiasis. Multifactorial pathology that occurs due to an imbalance in the ratio of bile components (decreased secretion of bile acids and increased production of cholesterol or bilirubin);
- postcholecystectomy syndrome. It is a consequence of removal of the gallbladder and restructuring of the biliary system.
Up to contents
Risk group for cholecystitis
Not everyone develops cholecystitis and, even if a person’s nutrition is far from ideal, he can live with a healthy gallbladder all his life. There are risk factors that increase the chances of developing the disease.
- Genes. If your relatives suffered from cholecystitis, you are also at risk.
- Weight jumps. Both weight gain and weight loss are stressful for the body. Often this process is associated with changes in diet - strict diets or overeating, fasting or eating more fatty foods.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Diabetes types 1 and 2.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Taking COCs, especially between the ages of 30 and 45 years.
- Pregnancy and other hormonal changes.
- Other gastrointestinal diseases are Crohn's disease, cirrhosis and fatty liver hepatosis, congenital pathologies of the gallbladder.
- Helminthic infestations.
Features of constipation in various gallbladder diseases
Stool retention, which occurs as a result of impaired intestinal motor function, in various diseases of the gallbladder may be accompanied by not entirely uniform clinical symptoms.
Constipation due to biliary dyskinesia
With a decrease in the tone of the gallbladder and a decrease in the contractile activity of the sphincters, spastic constipation may develop. It is characterized by difficult excretion of hard, fragmented (so-called sheep) feces. Patients may complain of bloating, flatulence, and periodic cramping abdominal pain caused by spasm of the muscles of the internal organs. Due to the prolonged retention of feces in the intestines, putrefaction processes intensify and intoxication of the body develops. It is manifested by weakness, increased fatigue and a general decrease in performance.
With increased contractile function of the gallbladder and accelerated excretion of bile, atonic constipation may develop and a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying may occur. In this situation, dense feces of large diameter cause pain during defecation, can injure the mucous membrane and lead to the formation of anal fissures.
Constipation due to bending of the gallbladder
When the gallbladder is deformed due to insufficient bile flow or its complete cessation, the digestion and absorption of fats is impaired. As a result, feces take on the appearance of hard, dry lumps. Due to problems with defecation, blood streaks are often found in the stool. This condition is also characterized by patient complaints of nausea, a bitter taste in the mouth and abdominal pain of varying intensity.
Constipation with cholecystitis
With infectious inflammation of the gallbladder, stool may be absent for up to 3-4 days. The pathological condition is often accompanied by gas formation and clinical symptoms similar to the manifestations of constipation when the organ is bent.
Constipation due to cholelithiasis
Stool retention in cholelithiasis, which occurs as a result of a decrease in intestinal contractile activity, is of a reflex nature. In this situation, spastic constipation may develop.
Constipation after cholecystectomy
Problems with bowel movements are one of the main consequences of gallbladder removal. Developing due to a violation of the outflow of bile into the intestines, a decrease in the activity of digestive enzymes and insufficient digestion of fats, constipation after cholecystectomy occurs of the atonic type. The stool may contain undigested pieces of food, mucus and streaks of blood.
Up to contents
When the gallbladder is inflamed. We talk about cholecystitis
Modern medicine has to deal with pathology of the biliary tract quite often. And the number of such diseases continues to grow. Today we will talk about cholecystitis: what kind of disease it is, what are its symptoms, the causes of its appearance, how it is detected and treated.
Nikolai Borisovich Patrushev, a gastroenterologist at Clinic Expert, Perm, answers our questions.
— Nikolai Borisovich, there is evidence that today 10-20% of the adult population suffers from cholecystitis, and there is a tendency for this pathology to further increase. Please tell us what it is?
— In one sentence, cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. Pathology of the biliary tract remains a pressing problem for today's medicine. Yes, there is a tendency towards an increase in incidence. Moreover: according to scientists, the number of diseases of the digestive system (which includes pathology of the biliary tract) will increase by 30-50% in the world in the next 15-20 years.
— What types of cholecystitis are known to modern medicine?
— There are two of them: acute and chronic cholecystitis. The first develops quickly, against the background of complete well-being. Abdominal pain appears, the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium. Nausea and vomiting may occur, and the temperature may rise. As a rule, acute cholecystitis is most often a manifestation of cholelithiasis. Such patients are hospitalized by ambulance in a surgical hospital.
Read more about gallstone disease here: Remove or leave? What to do if gallstones are found?
Chronic cholecystitis initially develops as an independent process, gradually and imperceptibly. Often, a patient is diagnosed with cholecystitis during an examination for completely different diseases. It should also be taken into account that diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract are characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations, duration of course, and prolonged exacerbations - this causes frequent seeking of medical help, making these ailments a social problem.
- What are the causes of cholecystitis? What causes it?
— Various factors are involved in the development of this pathology. In first place I would put a violation of the contractile function of the gallbladder. This leads to stagnation of bile, slowing down its evacuation from the gallbladder. Most often, the contractile function of the gallbladder is affected by psycho-emotional overload, neurotic reactions and prolonged stressful situations, physical inactivity.
The infectious factor also matters. Infectious agents penetrate the gallbladder from chronic foci of inflammation in the body - for example, in diseases of the ENT organs, stomach, duodenum, and from other parts of the intestinal tube.
Helminthic infestations, such as opisthorchiasis, also contribute to the development of cholecystitis. Previous hepatitis A (Botkin's disease) can also lead to inflammation of the gallbladder.
This disease can also be provoked by the reflux of pancreatic juice into the cavity of the gallbladder - a so-called chemical burn of the gallbladder mucosa occurs, which can lead to its inflammation.
Read materials on the topic:
How to protect yourself from Botkin's disease? Is there a stress vaccine? Childhood is for movement! What does physical inactivity lead to?
— Please tell us about the signs of cholecystitis. How does it manifest itself?
— Cholecystitis can occur with varying degrees of severity. The symptoms will depend on this, as well as on the stage of the disease. First of all, the pathology manifests itself as pain. These pains occur due to spasm of the gallbladder or due to its stretching.
Pain appears in the right hypochondrium, usually 40 minutes - 1.5 hours after an error in diet (for example, when eating spicy, fatty foods, fried foods, overeating). The pain is felt for about half an hour and, in mild cases, goes away on its own. In severe forms, the pain is more intense and prolonged.
Pain can also be provoked by a person spending a long time in a sitting position - driving a car, at a computer. From the right hypochondrium, such pain can radiate upward - to the right shoulder, neck, right shoulder blade.
In addition to pain, the patient may be bothered by so-called dyspeptic disorders: belching, nausea, metallic taste in the mouth, sometimes vomiting (if it occurs repeatedly, bile may appear in it). Abdominal bloating and alternating constipation and diarrhea may occur.
Also, cholecystitis may be accompanied by irritability, insomnia, and decreased performance.
The more severe the form of cholecystitis, the brighter and longer the listed symptoms will be expressed.
— Is there asymptomatic cholecystitis? That is, nothing bothers the person, and the disease is detected only when conducting any diagnostic studies - for example, as part of a preventive examination
- Yes, this happens. In 50% of cases, cholecystitis occurs latently and asymptomatically. Signs of gallbladder pathology before clinical manifestations of the disease can only be indicated by ultrasound data. Therefore, this study must be included in the screening program for diseases of the digestive system.
In addition, there are atypical clinical forms that can mislead the doctor, simulating various diseases of other organs and systems, for example, cardiovascular, endocrine and others (so-called “masks”). And when we start to understand, it turns out that we are talking about the pathology of the gallbladder. The most well-known and studied is the so-called cardiac mask of cholecystitis (or cholecystocardiac syndrome): every third or second patient with cholecystitis may complain of heart problems. These are rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, pain in the heart area. The electrocardiogram in such patients is without any abnormalities.
Cholecystitis can also occur under the guise of thyroid pathology - here the patient’s complaints will be similar to thyrotoxicosis (irritability, excessive sweating, the same rapid heartbeat, trembling of the fingers, increased body temperature to 37-37.5 degrees). In this case, the thyroid gland may turn out to be somewhat enlarged, and here it is necessary to figure out whether the symptoms are caused by its pathology, or whether the problem is still in the gallbladder.
Cholecystitis may also have an allergic mask, and a number of others. To understand this, the doctor must have considerable practical experience and correctly build a diagnostic search.
- Let's talk about diagnosing cholecystitis. What does it include? How can a doctor detect this pathology?
— Today, the most accessible and common method for diagnosing cholecystitis is ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to assess the condition of the walls of the gallbladder: if they are thickened by more than 4 mm, this is already a clear sign of cholecystitis, if less, perhaps the pathology is only at the beginning of development. The doctor also evaluates the contractility of the gallbladder.
An ultrasound will also help identify gallstones. If they are detected and cholecystitis is also present, then they speak of stone (calculous) cholecystitis.
You can sign up for an abdominal ultrasound here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
There are other research methods. For example, probing of the duodenum (duodenal intubation). It allows you to evaluate the biochemical composition of bile, test it for infection and identify microbes that cause inflammation in the gallbladder.
— How can doctors help a patient with this disease? How is cholecystitis treated?
“We can only help after, during a full examination, we find out as fully as possible all the reasons that led to the appearance of cholecystitis in the patient. The treatment program is structured as follows. In the first place is therapeutic nutrition. First of all, this is a fractional meal, five to six times a day. The gallbladder “loves” that we take food at the same hours: by doing this we train it and prevent stagnation of bile in it. It is important that the food is not hot or cold, but warm.
The selection of medications is carried out taking into account the function of the gallbladder, in particular its contractility. If the function is increased, if there are sharp spastic pains, antispasmodic drugs are recommended. When, during normal contractile function of the organ, we find signs of viscous, stagnant bile, drugs with a choleretic effect are used.
If studies show poor contractility of the bladder, then the treatment program includes drugs that stimulate its function and help it work correctly.
In certain cases, antiparasitic, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. The doctor decides all this, depending on the results of the study.
Let's not forget about other methods of treating cholecystitis - the same sanatorium-resort treatment. Chronic patients need to go to resorts for at least three or four years in a row - as they used to say, “to the waters.” It is very useful. But you need to go there with all medical documents, then the patient will be given the right diet and water intake (type, quantity and temperature).
— What can you eat with cholecystitis and what can’t you eat?
— Proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be exactly as much as necessary for the normal functioning of the body. The diet should include lean meats (beef, rabbit), fish (preferably boiled or steamed), low-fat cottage cheese, and wheat bran. Among cereals, preference is given to oatmeal and buckwheat.
Let's not forget about fresh vegetables and fruits (it's better to have melon, pumpkin, watermelon, carrots, apples).
Fatty, fried foods, smoked foods, marinades, pickles, and alcoholic drinks, including beer, are excluded. This list also includes carbonated drinks, hot seasonings and egg yolks (the latter for periods of exacerbation).
Fasting days (1-3 per week) will not hurt: these can be rice-compote, cottage cheese, watermelon days. In addition, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
— How to prevent the development of cholecystitis? Please tell us about prevention
— Probably, much is clear already from the above. Basic prevention differs little from the prevention of many other diseases. This is a healthy lifestyle, rational nutrition - we eat often, not on the run, we chew food thoroughly, slowly.
Agree, seemingly simple, truisms. But, believe me, first of all, they are important in terms of preventing cholecystitis.
Interviewed by Igor Chichinov
If you need a consultation with a gastroenterologist, you can make an appointment here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
Biliary dyskinesia: what is hidden behind this diagnosis? Why do people turn yellow? MRI of the liver: pros and cons
For reference:
Patrushev Nikolay Borisovich
Gastroenterologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences Graduate of the Perm State Institute in 1988. Primary specialization in gastroenterology - 1995. From 2005 to 2014. worked at the Central Research Institute of Gastroenterology (Moscow). First - a doctor in the department of chronic liver diseases, then the head of the consultative and diagnostic department of the institute. Since 2021 – gastroenterologist at “Clinic Expert” Perm. Receives at the address: Perm, st. Monastyrskaya, 42a.
Diagnostics
To find out the true cause of constipation, the patient is prescribed a diagnostic examination. This may include:
- clinical and biochemical blood and urine tests;
- coprogram (stool analysis);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- cholecystography (x-ray of the gallbladder);
- colonoscopy (endoscopic examination of the large intestine);
- duodenal intubation (examination of the contents of the duodenum).
Up to contents
Features of the treatment of constipation in diseases of the gallbladder
Treatment of constipation that develops against the background of the above-mentioned diseases requires an individual comprehensive approach, which may include the following measures:
- nutrition correction (compliance with therapeutic diet No. 5 and 5a);
- organizing an optimal drinking regime (you should drink about 1.5–2 liters of clean water per day);
- increase in physical and motor activity;
- therapeutic exercises;
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures (electrical stimulation of the intestine - exposure to electric current, during which the intestine contracts, simulating natural urges);
- drug therapy. May include taking laxatives, as well as drugs that enhance the formation of bile (choleretics) and stimulate the contractile function of the gallbladder (cholekinetics).
Up to contents
Choleretic property of bran
If the liver or gallbladder is malfunctioning, it is useful to take bran as a dietary supplement. Bran consists of grain shells and unsorted flour, which provides a high content of dietary fiber. Bran enhances mechanical stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract. Bran contains B vitamins, keratin, vitamin E and PP, as well as copper, magnesium, potassium and other trace elements. You can take bran with food or between meals; add it to yogurt, kefir or other dairy products. You should start taking it with a teaspoon, the maximum dose per day should not exceed 50 grams.