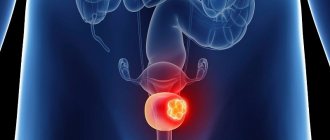
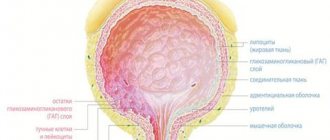
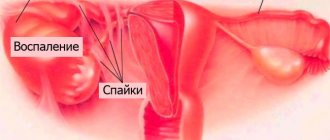
Inflammation of the bladder or cystitis usually occurs as a result of the upward spread of bacteria from a more distant part of the urinary system - the urethra. The germs settle in the bladder and can then spread to the kidneys, causing further complications.
In general, women are more prone to urinary tract infections due to the difference in the anatomical structure of the urethra, which is shorter than that of men. Therefore, women are more likely to have uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
In men, bladder inflammation causes a more complex clinical picture, since it often affects the prostate and requires longer-term drug therapy.
Causes of bladder inflammation in men
The content of the article
Acute inflammation of the bladder occurs in men aged 15 to 50 years with a frequency of 5 to 8 cases per 10,000 men. The etiology of bladder inflammation is the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the sterile space of the urinary system.
The bacteria are located near the urethra. There are situations and factors that contribute to their unhindered penetration into the urethra and bladder:
- frequent unprotected sex with multiple partners;
- diabetes – weakened immunity contributes to the development of bladder inflammation, bacteria benefit from a “sweeter” environment for growth;
- use of spermicides as contraceptives;
- uncircumcised men;
- unprotected anal intercourse;
- kidney stones that block the passage of urine.
Acute cystitis - symptoms and treatment
Treatment algorithm for acute cystitis:
- drink plenty of fluids at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day;
- exclude sexual contact for the entire period of the disease;
- antibacterial therapy.
If cystitis is recurrent, then the antibiotic is selected based on the results of urine culture.
Antibacterial drugs:
- Fosfomycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that shows high activity against most bacteria: Pseudomonas aеruginosa, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis), Streptococcus spp. (including Enterococcus faecalis) [11].
- An alternative to fosfomycin are drugs from the nitrofuran group (Nitrofurantoin, furazidine potassium salt). The drugs are effective against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and other bacteria, as well as fungi of the genus Candida. Resistance to nitrofurans rarely develops.
- Less often they resort to prescribing systemic oral antibacterial drugs, such as cefixime, a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Antibiotics of the fluoroquinolone group (levofloxacin, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, etc.) and cephalosporins (cefixime, cefuroxime, etc.) are associated with a large number of adverse reactions and can lead to the development of resistant bacterial forms, and therefore should not be the first line of treatment for acute uncomplicated cystitis [12] [19].
Etiological treatment (aimed at eliminating the cause and conditions for the development of the disease)
In case of relapses of acute cystitis, bacteriophage preparations have recently been increasingly used - drugs based on viruses that selectively destroy bacteria, like sniper fire. Most often, bacteriophages multiply inside bacteria and cause them to disintegrate into fragments.
Treatment with bacteriophages is safer than with antibiotics, but it should be taken into account that targeted destruction of bacteria requires bacteriological examination of urine to determine the pathogen and its sensitivity to phages [2].
In patients with recurrent cystitis, which is directly related to sexual intercourse (postcoital cystitis) and in the presence of a deeply located external urethral opening, surgical treatment is used. An operation aimed at moving (transposing) the urethra has a high success rate.
Pathogenetic treatment (aimed at eliminating or suppressing the mechanisms of disease development)
Uro-Vaxom vaccine , taken orally (by swallowing). The product has an immunobiological property that protects against the effects of E. coli and triggers a nonspecific immune response (activates macrophages and cellular phagocytosis). When prescribing a vaccine, it should be taken into account that the effectiveness remains with a repeated course of taking the drug [4].
D-mannose is a monosaccharide that, after absorption from the intestine with urine, enters the bladder, where it blocks the attachment of bacterial pili (thread-like outgrowths of bacteria). As a result, bacteria leave the body along with urine. D-mannose is a dietary supplement, not a medicine, but this drug has proven effectiveness and is recommended by the European Association of Urology [17].
Hormone replacement therapy. In postmenopausal women, estrogen levels sharply decrease. Estrogens are one of the factors protecting the bladder mucosa; when they decrease, the protective mechanisms of the mucosa are weakened. It is possible to administer hormonal drugs containing estrogens through the urethra or vagina.
that have anti-inflammatory, weak diuretic and antiseptic effects are used as auxiliary agents Among herbal remedies, “Canephron” is effective - a complex preparation of plant origin, which includes centaury herb, lovage root and rosemary leaves. The drug has diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, antimicrobial, vasodilator and nephroprotective effects [1].
In case of severe hematuria, hemostatic drugs may be prescribed. The most effective in this group are antifibrinolytic drugs - aminocaproic and tranexamic acids [11].
If the cause of acute cystitis is obstructive uropathy (difficulty passing urine associated with a narrowing of the lumen of the urethra), then after stopping the acute period and eliminating the infectious agent, surgical correction is performed - installation of a cystostomy (special drainage tube), urethroplasty, etc.
Symptomatic treatment (reducing the manifestations of the disease)
NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are a large group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects, reduce pain, fever and inflammation. The most well-known representatives of NSAIDs: aspirin, paracetamol, ibuprofen, diclofenac.
More modern drugs from the NSAID group, which have the same positive properties and have much fewer side effects: nimesulide, meloxicam, Celebrex [10].
Phenazopyridine - this drug, entering the bladder with urine, acts on the mucous membrane of the lower urinary tract, exerting a local effect. This helps reduce pain over the pubis, burning and reduce the frequency of urination. The effect appears quickly, in a matter of hours.
If you are ill, you must follow a diet excluding spicy foods. It is advisable to eat foods that are rich in vitamins and increase daily diuresis (for example, cranberries), as well as a sufficient amount of fluid to maintain daily urine output in a volume of 2000-2500 ml [1].
Symptoms of bladder inflammation in men
Typical symptoms:
- pain or burning when urinating;
- frequent urge to urinate, but without satisfactory urination;
- sudden need to urinate;
- blood in urine;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Contact your urologist if you recognize any of these symptoms, and especially if you have:
- heat;
- pain in the pelvis or anal area;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- chills;
- nausea, vomiting.
These symptoms are urgent. It is possible that the inflammation has already spread from the bladder to the kidneys and prostate.
Complications of bladder inflammation:
- acute kidney pyelonephritis;
- acute prostatitis;
- sepsis;
- renal failure;
- Prostate abscess is a collection of pus.
Treatment
Acute cystitis often turns into a chronic protracted form due to self-medication. On TV, medications are often advertised that should instantly help cope with the disease. And when a person suffers from cutting pain every time he goes to the toilet, he grabs at any straw. But self-prescribing such drugs only temporarily eliminates or reduces symptoms. The inflammatory process in the urethra remains, and as a result, repeated cystitis after some time. In this case, laboratory diagnostics are not performed, which means it is impossible to determine the success of treatment.
Important! If you suspect cystitis, do not self-medicate, consult a doctor - a urologist or therapist.
Drug therapy
To eliminate the inflammatory process, you need to act on the pathogenic microorganisms that caused it. Therefore, taking medications is an important and main part of therapy, since medications are excreted by the kidneys, which means they pass through the urinary tract. Here it is important not to do harm, so the drugs are selected by the doctor taking into account the clinical picture and test results.
The main group for infectious diseases consists of antibiotics from different groups. If there is no positive dynamics after 3-4 days, a change in the drug is necessary. Uroantiseptics are also additionally prescribed. These are herbal preparations that are concentrated only in the genitourinary system, are not absorbed into the blood and have an antiseptic effect.
If the causative agent is a fungal infection, then taking antifungal agents is advisable. When hormonal disorders are confirmed, estrogens are used.
Diet
It is important to adhere to the drinking regime. Cranberry juice is especially effective and healthy. It has a good diuretic and bactericidal effect. A large amount of liquid accelerates the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms and restores the normal process of urination. In case of any inflammatory process, spices, spicy, smoked and fatty foods are contraindicated. Temporarily you need to give up pickles, mayonnaise, and meat products. Vinegar has a very bad effect on blood vessels, so all sauces and products containing it are also prohibited.
It is necessary to reduce the amount of salt, sugar, yeast products, and completely eliminate alcohol. Kefir, cottage cheese, milk, plant foods, fresh vegetables, steamed or boiled fish, and cereals are welcome.
Herbal medicine (herbal treatment)
Herbal decoctions and infusions are selected together with a doctor. They only complement drug therapy, but cannot be used instead of tablets. Herbs are widely used for mild forms of cystitis, as well as during periods of remission in chronic illness. Recommended herbs for cystitis include lingonberry leaf, dill seeds, bearberry, and horsetail.
Herbal infusions should be taken with caution in the presence of chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system. Diuretics are especially prohibited for urolithiasis.
Additional treatment
To reduce the painful syndrome, symptomatic therapy is used. These are analgesics and antispasmodics. In advanced cases with a long, debilitating course, sedatives or antidepressants are recommended. They help relieve tension, fear of going to the toilet, reduce irritability, and improve sleep quality.
It is also effective to wash the urethra or instillate it. This procedure is performed by a doctor. For this, special antiseptic solutions are used. For the treatment of male cystitis, lavage is rarely used, since the narrow structure of the urethra complicates the procedure.
Recommendations
Symptoms should begin to subside within a day or two of starting therapy. It is also recommended to drink plenty of fluids to urinate more and avoid sexual intercourse while taking antibiotics.
Some recommend using cranberry preparations to treat or prevent urinary tract inflammation. But there is no reliable medical research to prove whether this is correct. Therefore, it is best to follow your doctor's recommendations and take antibiotics.
If a man has frequent bladder infections, it would be a good idea to talk to his doctor to find out the cause and prevent recurrence. In such cases, there may be anatomical abnormalities or stones in the kidneys, bladder or urethra that help harbor bacteria.
Methods for diagnosing cystitis
Diagnosis of cystitis is carried out using laboratory and instrumental studies.
Laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory diagnosis of cystitis includes a general blood test and clinical urine test. In some cases, a urine test according to Nechiporenko may be required. In order to identify the causative agent of the disease, a cultural study (bacteriological culture of urine) can be carried out.
Ultrasound of the bladder
Ultrasound of the bladder is the simplest and most informative study. It allows you to assess the degree of damage to the bladder wall, the extent of the process, and detect stones and tumor processes that may accompany cystitis.
More information about the diagnostic method
Cystoscopy
In cases of frequently recurring cystitis, cystoscopy may be performed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Risk factors
There are factors that increase the likelihood of developing cystitis. This happens when:
- sedentary lifestyle.
- regular hypothermia of the body.
- Constant use of tight underwear.
- Frequently changing sexual partners when contraceptives are not used.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules.
- Chronic disease of one or another internal organ.
- Overwork, hypovitaminosis.
- Impaired bladder emptying.
- Reduced protective functions of the body.
- The presence of a foreign body located in the bladder.
Relieving an attack of cystitis
In the acute form of cystitis, each attack is very painful. The first main rule, thanks to which an attack is alleviated, includes drinking large amounts of fluid. It promotes the rapid removal of pathogenic microorganisms from the body, as a result of which the man’s condition is alleviated.
In more severe cases, you can use medications. The best solution is antispasmodics. The spasm is eliminated, the tone of the smooth muscles of the bladder is reduced. Painful sensations are eliminated not only by antispasmodics, but also by analgesics.
Self-administration of antibiotics is strictly prohibited. This can change not only the picture of laboratory examination, but also complicate the identification of the source and cause of the disease. By self-medicating, you can only get rid of the symptoms for a while, but cystitis will become chronic.