Pneumonia or pneumonia is a viral disease that affects the lung tissue and interferes with the normal exchange of oxygen between air and blood. Inflammatory secretions that enter the alveoli do not allow the body to receive a sufficient amount of oxygen. And if the disease affects most of the lungs, acute respiratory failure develops.
Pneumonia affects people with weak immune systems, children and the elderly. Every year in Russia alone, 1.5 million people suffer from the disease, and 30% of them are young children and people over 70 years of age.
But pneumonia can and should be treated! And it is recommended to do this using an integrated approach. Treatment of any disease begins with a correct diagnosis. Therefore, at the first signs of the development of pathology, seek the advice of a specialist.
What are the first symptoms of pneumonia, how to approach treatment correctly and comprehensively, and what is required to diagnose the disease, we will tell you in this article.
Causes of pneumonia
Pneumonia develops when bacteria and viruses, as well as foreign agents, enter the lungs and affect part or all of the lung tissue. Pathological agents enter the human body through the respiratory route, and rarely through the blood.
Why does the disease develop quickly in the body of a person with reduced immunity? Bacteria are constantly present in our body, but protective mechanisms do not allow them to multiply, causing pathology. But if the immune system is weakened, harmful microflora increases in population, which leads to the appearance of an inflammatory process.
Viral pneumonia also often develops against the background of the spread of colds of the upper respiratory tract (bronchitis, tracheitis). Pneumonia can also be caused by hypothermia, stress, overwork, or smoking abuse. The risk of developing the disease increases in people with chronic diseases and obesity.
Classification of the disease
The International Classification of Diseases provides for the distribution of pneumonia into seven main types:
- unclassified adenoviral disease;
- unclassified bacterial pneumonia;
- pneumococcal;
- infectious;
- provoked by Haemophilus influenzae;
- arising against the background of other atypical diseases (gonorrhea, typhoid fever, whooping cough, measles, chickenpox, etc.);
- without taking into account the pathogen.
This classification is based on the type of pathogen that provoked the development of inflammation.
Signs of pneumonia in an adult
When the disease appears, a person’s body temperature rises, which can reach 38°, there is general weakness throughout the body, a headache, the patient wants to lie down and relax. After a few days, a strong paroxysmal cough appears and sputum appears.
Pain in the chest, especially at the site of inflammation, as well as the appearance of shortness of breath indicate the seriousness of the situation and clearly indicate pneumonia.
General signs are listed here, but the nature and timing of their manifestation may differ depending on the type of pneumonia. With viral pneumonia, the first symptoms appear quickly and the patient feels a sharp deterioration in health. From the very beginning of the disease, muscle pain, high body temperature, severe headache, and a painful dry cough are observed.
Bacterial pneumonia, on the contrary, develops gradually. The disease begins only 2 weeks after the first symptoms appear. After this, there is a sharp relief, an improvement in the general condition of the patient, then the temperature rises sharply again, a headache occurs, the cough intensifies, and purulent sputum appears.
One of the serious types of the disease is atypical bilateral pneumonia, which extensively affects the lung tissue and develops respiratory failure. In terms of its symptoms, bilateral pneumonia resembles a cold viral infection, and the characteristic wheezing is not yet heard in the lungs. Many begin to treat themselves, which aggravates the condition.
At first, the sick person thinks that his condition has improved, the symptoms of the pathology begin to go away. But then the cough worsens and the second wave of the disease begins.
Symptoms may vary slightly in older people. First of all, a dry cough and shortness of breath appear during minor physical exertion on the body or even at rest. Often the disease occurs without fever in older people.
Flow options
The following types of pneumonia are distinguished:
- community-acquired pneumonia (acquired outside a hospital);
- hospital-acquired pneumonia (acquired in a medical institution);
- aspiration pneumonia;
- pneumonia in patients with severe immune deficiencies (HIV infection, congenital immunodeficiency, drug immunosuppression).
Mild pneumonia is characterized by mild symptoms of intoxication, low-grade body temperature, absence of respiratory failure and hemodynamic disturbances. Infiltration is localized within one segment of the lungs, leukocytes from 9.0 to 10.0 ×109/l, the patient has no concomitant diseases.
With moderate severity of pneumonia, the symptoms of intoxication are moderate, body temperature rises to 38 degrees, respiratory rate is no more than 22 per minute, heart rate is up to 100 beats per minute. Pulmonary infiltrate is located within 1-2 segments.
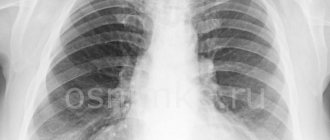
Severe pneumonia is characterized by pronounced signs of intoxication. The patient's body temperature is above 38 degrees, there is respiratory failure of II - III degree and hemodynamic disturbances. The radiograph reveals bilateral pneumonic infiltration, the pathological process is rapidly progressing. The disease is complicated by pleural effusion, abscess formation of lung tissue, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, and sepsis.
Is pneumonia contagious?
The inflammatory process in the pulmonary system most often appears due to the multiplication of the virus and as a complication of influenza or acute respiratory viral infection. In such cases, it is impossible to get sick from pneumonia itself, but it is easy to catch the disease that became the root cause. That is, pneumonia itself is not contagious, and the development of inflammation in the lungs is an independent complication that arose against the background of a weakened immune system and improper self-medication.
Can pneumonia go away on its own without treatment?
Pneumonia or pneumonia is one of the most dangerous and common diseases of the respiratory system. The danger is that specialists do not always have time to make a diagnosis in time. People do not go to the doctor with a cough and fever, but prefer to stay at home for a couple of days until the disease spreads. The condition can worsen to bilateral pneumonia, which carries severe consequences, long-term treatment or chronic diseases.
A hundred years ago, before the discovery of penicillin, pneumonia took the lives of those who fell ill. Science and medicine do not stand still - our lives have changed dramatically in a hundred years. People have antibiotics in every medicine cabinet, and hospitals carry out operations using modern equipment. However, according to the Russian Academy of Sciences, pneumonia is still on the list of the deadliest infectious diseases and should not be underestimated.
Pneumonia will not go away on its own. This disease can lead to death, so seeing a doctor is vital. Treatment for pneumonia should be prescribed by a doctor. It is he who determines whether antibiotics are needed and which ones, and also decides on the severity of the disease.
With pneumonia there is always a high temperature and a strong cough, is this true?
This is a very big and dangerous misconception. Errors in diagnosing the disease are one of the main causes of mortality from pneumonia. According to doctors, up to 30% of cases of pneumonia are not diagnosed or detected too late, since people do not see the need to see a doctor before a high temperature appears. As a result, this leads to a deterioration in the person’s condition and the development of severe complications. Asymptomatic, hidden, but real pneumonia often develops in children and the elderly. The main and most dangerous problem in diagnosing pneumonia in elderly patients is that the disease successfully disguises itself as various chronic diseases. In this case, it passes without the most important marker of the disease for us - without fever. How then do you understand that pneumonia is going away in an adult? - Monitor your body, and promptly consult a doctor if your health worsens.
If you have what signs you should consult a doctor?
- increased sweating;
- weakness;
- dyspnea.
By the way, the myth that pneumonia is necessarily accompanied by a severe cough is just a myth. This problem is mostly characteristic not of the older generation, but of children. There are often cases when pneumonia progresses, but there is no cough. If you do not consult a doctor in time and do not make a diagnosis, the child may experience chronic consequences.
Pneumonia in children can be identified by the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath and chest pain when moving;
- pain when turning the body
- inability to take a deep breath;
- tachycardia;
- exercise intolerance;
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- the person looks pale, but with a bright, unhealthy blush.
How is pneumonia transmitted?
The disease can be transmitted in different ways, including:
- Airborne method. During the disease, droplets form on the mucous membrane of the mouth and nose, which spread through the air during sneezing and coughing. You can become infected by airborne droplets in any public place: hospital, store, public transport. The pathogenic agent spreads through the air along with particles of mucus, sputum, and saliva.
- Contact. The infection is also transmitted through contact - shaking hands, hugging, kissing. People become infected when they touch contaminated objects or when they touch their mouth, eyes, or nose with dirty hands.
- Domestic. The infection can be transmitted through shared towels, dishes and bedding. Therefore, the patient needs to be provided with personal hygiene items, and, if possible, change and wash them more often.
- Fecal. The virus survives up to two days in fecal matter with normal bowel movements. You can easily acquire the disease from improper toilet cleaning or personal hygiene. To prevent infection, especially from young children, it is important to constantly wash your hands after cleaning the child's potty, change diapers frequently and thoroughly wash the area where bowel movements occur.
However, personal hygiene items must be handled very carefully. It has been proven that the viral microorganism can survive up to 4 hours on any surface. Morbid bacteria are not afraid of frost; even with bleach it can be destroyed only five minutes after direct treatment.
Prevention
Prevention is the prevention of infection with viral and infectious diseases. To do this, you should adhere to basic hygiene rules and use simple protective equipment:
- keep your hands clean, wash them as often as possible, especially after sneezing or coughing, use antiseptics;
- cover your nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing with a paper tissue;
- prevent pneumococcal infections with vaccines.
At the first signs of ARVI, influenza or other viral infectious disease, you need to stay home and promptly begin a course of treatment, which in many cases helps prevent the development of complications in the form of pneumonia.
Pneumonia and bronchitis: what is the difference?
Both diseases affect the human respiratory system, which means they have similar symptoms. It is often difficult to distinguish the two pathologies from each other.
| Pneumonia | Bronchitis |
| In most cases, it is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature to 38-39° and a feverish state. There is a slight increase in temperature. | Accompanied by a strong dry cough. In some cases, sputum may appear greenish or streaked with blood. Wet cough, sputum is light in color. |
| When listening to the chest, “wet” rales are heard. | When listening to the chest, “dry” wheezing is heard. |
Complications
As we have already mentioned, pneumonia is dangerous due to its complications, so treatment regimens for the disease in adults at home using folk remedies are not only ineffective, but can also be life-threatening for the patient. Conventionally, complications caused by tissue inflammation can be divided into two groups: pulmonary and extrapulmonary.
Pulmonary complications affect the respiratory system and include:
- acute respiratory failure;
- pleural empyema;
- gangrene or lung abscess;
- parapneumonic pleurisy;
- respiratory distress syndrome.
Extrapulmonary complications include disorders that occur outside the respiratory system:
- myocarditis;
- septic shock;
- meningitis;
- failure of internal organs and systems;
- DIC syndrome.
How is pneumonia diagnosed?
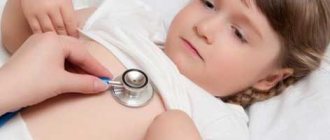
If a child suffers from the disease, you should seek examination from a pediatrician. If you are an adult, make an appointment with a therapist who will refer you to a specialist if necessary. The doctor will conduct an external examination, collect anamnesis, study the medical history and learn about the symptoms of the disease.
You will be sent for laboratory tests:
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Sputum analysis is carried out to determine the inflammatory process in the body, as well as the causative agent of pneumonia and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Among the diagnostic research methods you will be prescribed:
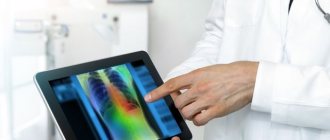
- Chest X-ray - shadows appear in the images in areas of tissue damage;
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used as additional measures when other methods do not allow an accurate diagnosis.
Methods for treating pneumonia
If pneumonia is bacterial in nature, antibiotics are prescribed. Their effectiveness can be assessed after 48-72 hours. If the temperature subsides, the cough becomes less frequent, and the patient begins to feel better, the treatment continues. You cannot interrupt the course of medications, and it is important to take them correctly as prescribed by your doctor. If antibiotics do not help, another treatment is prescribed or changed to a drug from another group.
For viral pneumonia, antibiotics are not effective, so antiviral drugs are prescribed. Vitamins and immunomodulators can be prescribed as auxiliary substances.
Once the patient's body temperature has returned to normal, physical therapy can be prescribed. It allows you to remove phlegm from the lungs. For this purpose, herbal medicines are often taken, for example, licorice root or complex breast mixtures.
Along with drug treatment, patients need bed rest, meals containing protein and vitamins, and plenty of warm drinks. For the best effect, therapeutic methods are recommended - electrophoresis, inhalation, massage, magnetic therapy, etc.