Signs of gonorrhea in women, treatment and prevention
Gonorrhea in women most often occurs during their reproductive years. This sexually transmitted infectious disease can lead to infertility or problems with pregnancy, so gonococcal infection requires immediate treatment for both sexual partners. This sexually transmitted disease is also called gonorrhoea or gonorrhoea.
According to WHO statistics, gonorrhea is a very common infection. Each year, approximately 200 million people are diagnosed with the disease. In the Russian Federation in the 90s, there was a slight decrease in the growth of the number of cases, but after a few years the situation began to worsen. And now the incidence reaches more than 100 cases per 100 thousand people.
Despite modern treatment methods, the disease cannot be completely controlled: the causative agent of gonorrhea mutates, gradually acquiring resistance to the latest antibiotics.
The causative agent of gonorrhea and transmission routes
The causative agent of gonorrhea is the gram-negative bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which belongs to paired cocci and has a bean-shaped shape. Gonococci are located inside cells, within the cytoplasm of leukocytes. These organisms are characterized by increased sensitivity to various external factors. They die when the temperature rises to just 55 degrees. Also harmful to them is exposure to sunlight and drying out. Treatment with antiseptic solutions gives a good effect. The bacterium remains viable in fresh pus. After it dries, the gonococcus dies.
Ways of transmission of gonorrhea:
- The main route of transmission is sexual, when pathogens are transmitted during unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse. 20 - 50% become infected with gonorrhea during a single unprotected traditional sexual intercourse. Much less - during oral intercourse.
- The disease is transmitted from a sick mother to the newborn during childbirth. Gonorrheal conjunctivitis of a newborn occurs with the formation of ulcers that heal with a scar. The disease is complicated by blindness.
- During unconventional sexual intercourse, gonorrheal inflammation develops in the rectum, pharynx and tonsils. The disease can be transmitted through vibrators and sex toys of an infected person.
- Due to the instability of bacteria in the external environment, the disease is not transmitted through kisses, personal belongings of the patient, cutlery, toilets and in swimming pools.
- Very rarely, the source of infection for little girls is the personal belongings of a mother with gonorrhea.
The causative agents of gonorrhea are not able to move, they do not form spores. These organisms have very thin threads, thanks to which they can be held on the surface of epithelial cells, red blood cells, and male germ cells - sperm. On top, each bacterium is covered with a layer of a special substance and is, as it were, located in a capsule. Therefore, the destruction of such organisms is difficult. Treatment is complicated by the fact that the pathogen can be located inside epithelial cells, Trichomonas and leukocytes.
Routes of infection
Like any other sexually transmitted disease, gonorrhea is transmitted in the vast majority of cases through unprotected sex. The risks of infection in the home cannot be ignored.
Sexual tract
The very name of the group of diseases, which includes gonorrhea, speaks for itself: their main cause is sex with an infected partner. Intimate contacts account for 99% of infections in both men and women. Unprotected sex with a carrier of infection does not always lead to illness, but a woman is much more likely to get sick after such an intimate encounter than a man.
Contagiousness of gonorrhea, i.e. the ability of gonococci to be transmitted from one person to another is 50-70% in women, i.e. More than half of them are guaranteed to be infected if they have sexual intercourse with a sick partner. For men, this figure is slightly lower – 25-50%.
Important! One should not have any illusions about the possibility of infection only through traditional vaginal intercourse. Oral or anal sex will also open the way for bacteria. In some cases, multiple organ infection is observed. Gonococci enter the partner’s body not only during full sex, ending in ejaculation, but also during intimate caresses.
Who is at risk?
Risk factors for contracting gonorrhea include:
- carelessness when choosing a partner,
- neglect of basic means of protection (sex without using a condom),
- presence of other sexually transmitted diseases or HIV,
- antisocial lifestyle, prostitution,
- for men - sex with men.
Doctors recommend regularly, once a year, to be screened for gonorrhea if you are a sexually active woman over the age of 15 who changes sexual partners (Fig. 2). Being careful during sexual intercourse and mandatory use of a condom should be a priority for every woman, and there should be no exceptions to this rule.
Figure 2. Incidence of gonorrhea in the United States in 2021, distribution by sex and age. Source
Household way
Infection with gonorrhea in everyday life is much less common in medical practice, since gonococci quickly die in the external environment and are unstable to physical and chemical influences.
The main cause of household infection is failure to comply with basic personal hygiene rules. The infection can enter the body by using towels and washcloths that a sick person used to wash and dry themselves, wearing someone else’s underwear, etc. Due to the anatomical features of the structure of the external genitalia, girls develop domestic gonorrhea much more often than boys.
A risk factor for infection of a newborn baby is the passage of an infected mother through the birth canal during natural childbirth. No cases of intrauterine infection have been identified in clinical practice. In newborns, gonococci most often affect the eyes, causing inflammation of the conjunctiva (gonoblenorrhea). For preventive purposes, immediately after birth, the baby’s eyes are washed with albucid or a 1% solution of silver nitrate.
I often diagnose gonoblenorrhea in adult women with a latent or mild form of gonorrhea. The infection reaches the conjunctiva through a towel used for intimate hygiene or through the hands.
Incubation period
The latent (incubation) period for gonorrhea ranges from 2 to 5 days for men and from 5 to 10 days (and even 30 days) for women. During this time, gonococci enter from the mucous layer into the submucosal layer, causing its destruction.
From there, the infection spreads through the lymphatic tract and enters the blood. Spreading retrogradely, gonococci penetrate through the fallopian tubes into the ovaries, causing their inflammation (adnexitis) and into the abdominal cavity. With sharply reduced immunity, gonococci can spread through the bloodstream and cause sepsis and damage to certain organs - joints, mucous membrane of the eyes, skin, heart and membranes of the brain.
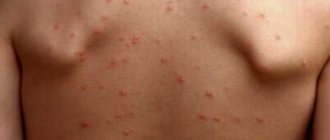
The first signs of gonorrhea, photos
Immediately after infection, gonococcal infection has no clinical manifestations. With gonorrhea in women, symptoms and treatment are determined by the localization of the inflammatory process.
Most often, this disease affects the urethra and develops gonorrheal urethritis with the following symptoms:
- pain (often pain and burning) when urinating;
- itching in the genital area and, in particular, the urethra;
- increased frequency of urination;
- excretion of urine in small portions;
- persistent feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- purulent inclusions in the urine.
It also happens that gonorrhea provokes cervicitis, an inflammatory process in the cervix. The main symptom of this condition is leucorrhoea, sometimes with purulent inclusions. Otherwise, the disease is asymptomatic and painless.
The third most common set of symptoms for gonococcal lesions in women is gonorrheal proctitis, the symptoms of which are:
- painful sensations (sometimes with itching and burning) in the anus;
- a feeling of heat as a result of a local increase in temperature in the anal area;
- the need for frequent bowel movements, often without cause.
Where to go if you have gonorrhea
If there is a genital form of pathology, a woman will need to make an appointment with a gynecologist or venereologist.
The doctor will tell you which doctor treats this pathology and give a referral.
As a rule, the extragenital form of gonorrhea is often discovered at an appointment with other specialists.
A dentist may detect an inflammatory process in a woman’s mouth, the symptoms of which will be atypical for nonspecific stomatitis or gingivitis.
An otolaryngologist will detect symptoms of gonorrhea if you complain of sore throat and sore throat.
The ophthalmologist will make an assumption about the disease in case of specific eye damage.
The proctologist may also, after collecting a history from which it is clear that the patient has resorted to unconventional sex, may suspect the presence of gonorrhea.
Be that as it may, a specialist does not have the right to make a final diagnosis only on the basis of an initial examination and anamnesis.
In any case, the doctor will take smears and send them for bacterial culture, microscopy, PCR and PIF examination.
To find out which institutions treat sexually transmitted diseases and where to go anonymously, you can find information on the Internet.
In addition, in every city there is a skin and venous dispensary where venereologists conduct consultations.
Chronic form of the disease
In women, the chronic form of the disease occurs when the acute form is left untreated for a long time. Treatment of chronic gonorrhea is very difficult due to possible complications. You can completely get rid of the infection in any case, but it is worth remembering that the processes it causes in the body may be incurable. For example, long-term cervicitis that often accompanies gonorrhea gradually leads to the appearance of adhesions in the cervical area, preventing conception and bearing a child. Sometimes this problem can only be eliminated through surgery.
Chronic gonorrhea is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms and can be detected accidentally during an examination for the presence of any other infection. Antibiotics are also the mainstay of its treatment. The probability of a complete recovery if all necessary medical recommendations are followed is 100%.
Tripper during pregnancy
Gonorrhea in pregnant women is manifested by inflammation of the vagina and cervix, premature opening of the membranes or their inflammation, labor fever, and septic abortion. Quite rarely, before the 4th month of pregnancy, gonococcal infection can occur as salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes). Characteristic is the development of gonorrheal vaginitis, which usually does not occur outside of pregnancy and is associated with hormonal changes in the vaginal epithelium.
The symptoms are similar to thrush, but standard medications do not help. Danger for the child is intrauterine infection with gonococci, postpartum gonorrheal conjunctivitis, and in girls – gonorrhea of the genital organs. Pregnant women with gonorrhea are treated in a hospital.
Sources
- Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Protection of Consumer Rights and Human Welfare [Electronic resource] // Infectious morbidity in the Russian Federation - Moscow, 2021.
- Kubanova A. A., Kubanov A. A., Melekhina L. E. Dynamics of changes in intensive rates of incidence of sexually transmitted infections in the assessment of the epidemiological process and health status of the population of the Russian Federation for 2006–2016. //Bulletin of Dermatology and Venereology. 2018;94(1):27–37.
- Aniskevich A.V., Shimanskaya I.G. Antibacterial therapy of gonococcal infection: problems, issues of choosing etiotropic therapy //Military Medicine. – 2021. – No. 3. – P.28-33.
- Yargin S.V. On the treatment of gonorrhea: recent history //Chief Physician. – 2021. – No. 3(56) – P. 50-52.
- Olga Belokon. I am a woman. All about women's health, contraception, hormones and much more. – 2020
Complications
Complications of gonorrhea in women are very serious:
- the formation of cervical erosion - a non-healing defect of the mucous membrane;
- bartholinitis - inflammation of large paired glands in the vestibule of the vagina, often requiring surgical intervention;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- frigidity - decreased libido;
- spread of infection to the uterine cavity and appendages (operation is often performed);
- death of the eyeball of a baby infected during childbirth;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes and ectopic pregnancy;
- infertility, often persistent;
- joint damage;
- miscarriage due to infection in early pregnancy;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus, premature birth and sepsis of newborns due to infection in late pregnancy;
- in the most severe cases - peritonitis, damage to the heart and brain.
Diagnosis of the disease
The beginning of diagnosing gonorrhea is by interviewing the patient and taking an anamnesis. Next, the patient is examined to detect the causative agent of the disease, and the clinical manifestations of the disease are examined. However, the most accurate result is shown by the test results.
A bacterioscopic study consists of staining a smear using a special method that detects pathogenic microorganisms in acute gonorrhea with almost 100% accuracy. Chronic gonorrhea is much more difficult to detect. The bacteriological method makes it possible to determine the sensitivity of the found bacteria to antibacterial drugs, which is necessary for further treatment.
In this situation, in addition to standard tests, the urethral secretions, urinary ducts and rectal lavage are examined. All this together gives a clear picture of the disease and allows it to be treated most effectively.
Diagnosis of gonorrhea in women
To make a correct diagnosis, it is not enough to know what symptoms indicate infection with gonorrhea.
To clarify the diagnosis, a study of discharge from the genital tract is mandatory.
A smear is taken for analysis.
Since in the chronic course of gonorrhea the symptoms of the disease do not appear, gonococci may be absent in the analysis.
Therefore, doctors resort to provoking an exacerbation of the infection.
The following methods of provocation are distinguished:
- Physiological method - taking a smear in the last days of menstruation
- Nutritional – on the eve and on the day of the test, a woman is recommended to include spicy foods, pickles and alcohol in her menu
- Biological method - intramuscular injection of pyrogenal or provocation with a gonococcal vaccine
- Thermal – diathermy is carried out for 3 days in a row
- Chemical method - treatment of the cervical canal and urethral mucosa with silver nitrate
Smears are taken in three sessions every other day, two, three.
- Diagnosis of the disease begins with collecting anamnesis and interviewing the woman
- The doctor then examines the woman to recognize the visible signs and symptoms of gonorrhea.
- To clarify the diagnosis, smears are taken for bacterioscopic examination. Using culture, a laboratory technician determines the sensitivity of microorganisms to the effects of antibiotics so that the doctor can prescribe effective drugs
In addition to bacterial culture of vaginal secretions, the flora of the urethra and rectum is examined.
This approach to diagnostics allows us to obtain the most complete and reliable picture of the pathological process.
Treatment regimen for gonorrhea
The main principle: it is imperative to treat sexual partners who have been diagnosed with gonococci using the cultural method. Acute and chronic gonorrhea require an etiotropic approach, that is, an impact on the cause of the disease.
Therapy with antibiotics taken orally is always carried out against the background of hepatoprotectors (Karsil) and probiotics (Linex, yogurt). Local remedies with eubiotics (intravaginal) - acylact, lacto- and bifidumbacterin. It would also be useful to prescribe antifungal drugs (fluconazole).
It is better to immediately stop the temptation to heal yourself, since the antibiotic may not work and gonorrhea will become chronic, and medications are increasingly causing allergies and its complication - anaphylactic shock - develops at lightning speed. And most importantly: only a doctor can reliably diagnose gonorrhea, based on objective data.
Of the antibiotics in the treatment of gonorrhea in women, preference is given to drugs of the penicillin, cephalosporin, and fluoroquinolone series:
- Ceftriaxone 0.25 g or gentamicin 2.0 g IM
- Sumamed 2 g (analogs Zi-factor, Azitrox, Hemomycin, Azicide, Ecomed)
- Cefixime 0.4 g or ciprofloxacin 0.5 g orally
Acute ascending gonorrhea is treated with the following drugs6
- Ceftriaxone 1 g IM 1 time per day for a week, ciprofloxacin 500 mg IV 2 times a day for 7 days, ofloxacin 0.4 g 2 times a day for a week.
- It is possible to use other antibiotics (tetracycline, clindamycin, rifampicin, bicillin, josamycin, ofloxacin, etc.)
- Treatment of chronic gonorrhea is supplemented with immune stimulants and gonococcal vaccine (pyrogenal, methyluracil, levamisole, prodigiosan).
- Autohemotherapy effectively activates the body's defenses.
Since gonorrhea is often combined with trichomoniasis and/or chlamydia, Doxycycline is added to therapy for 10 days and Metronidazole drugs for 5 to 7 days. Local treatment consists of washing the urethra with a 0.5% solution of silver nitrate, douching the vagina with solutions of manganese, protargol, chlorhexidine, miramistin and chamomile decoction.
In some cases, new treatment regimens are used, using 2 drugs - Azithromycin (orally) + Gentamicin (injections) or another combination - Gemifloxacin + Azithromycin orally.
This is due to the fact that in the last decade, WHO has been concerned about the increase in cases of development of resistance of the gonorrhea pathogen to certain antibiotics; for example, the UK's chief health expert, Sally Davis, stated that in 2013, 80% of clinical cases were determined to be resistant to tetracyclines.
Sexual contact and alcohol are prohibited for the entire treatment period!
How to recover
Treatment for gonorrhea has changed greatly today. This is mainly due to the development of resistance of gonococci to penicillin antibiotics, which in the past formed the basis of therapy. Antibiotics that have a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect on gonococci are of primary importance. Enzyme and immunotherapy (injections of specific and nonspecific drugs), local remedies (rectal suppositories, microenemas, douching) are also necessary. During pregnancy, the dosage of antibiotics depends on the duration of pregnancy, the nature of the procedures also changes (for example, drugs are not injected directly into the cervical canal).
Self-treatment of gonorrhea at home is unacceptable. This can lead to its transition to a chronic form and the occurrence of irreversible processes. Some girls believe that it is enough to find an article on this topic on the Internet or on a medical forum - and you don’t have to bother with a visit to the doctor, get tested, or “don’t waste your money.” But such people can pay with their health for such views. In the meager texts of published, even very correct standards for the treatment of gonorrhea, many of the nuances on which its result depends are often missed.
Treatment for gonorrhea should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor. Proof of successful therapy is the disappearance of signs of the disease and the absence of gonococci in tests performed 1-2 weeks after the end of taking antibiotics. In women, in addition, 2 additional studies of the same are carried out: during the next menstruation and immediately after it.
Immunity to this disease is not developed. If it is not treated correctly, gonorrhea takes a chronic, protracted course and is aggravated under the influence of alcohol, spicy food, sexual arousal, intimate intercourse, etc.
International standards in treatment
Currently, according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the US Center for Disease Control (CDC), the antibiotics of choice in the treatment regimen for gonorrhea are: ceftriaxone, cefixime, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, spectinomycin and azithromycin. An uncomplicated form of gonorrhea can be cured fairly quickly with the help of these antibiotics.
Since in approximately 30% of cases gonorrhea is combined with chlamydia, according to CDC recommendations, after taking a single dose of an antigonorrhea drug, a course against it should be taken. If a microbe is detected in one of the partners, the other one must also be treated, even if he has not been diagnosed with gonorrhea. Treatment of chronic and complicated forms is carried out with higher doses of the same antibiotics. Patients should always remember that only a qualified specialist can take into account all the features and determine the most effective drug, its dose and duration of treatment (taking into account these tests).
Do you suspect you have gonorrhea? Tests, anonymous examination and treatment as soon as possible in our clinic - make an appointment with a gynecologist right now!
Emergency prevention
If a woman has had unprotected sexual intercourse and is afraid of becoming infected with gonococcus, it is recommended to take emergency preventive measures, including:
- emptying the bladder (preferably twice);
- thorough treatment of the inner thighs and external genitalia with warm water and soap;
- injection of Miramistin or Betadine solutions into the urethra (no more than 1-2 milliliters) and into the vagina (up to 5 milliliters), if no more than two hours have passed since dangerous contact;
- treatment with an antiseptic (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, weak potassium permanganate) of the perineum and inner thighs.
No later than 48 hours after a possible infection, you should contact a venereologist, who will conduct an examination and write out a treatment regimen consisting of therapeutic effects in specific areas.
Routine prevention of gonorrhea
Preventing infection with gonococci and blocking the spread of the disease are the main goals of gonorrhea prevention. The risk of infection during sexual intercourse is reduced by using a condom and subsequent use of chlorine-based antiseptics (miramitan). Washing with plain water and soap is ineffective, as are spermicides. The best way to maintain health remains a reliable partner, preferably in the singular.
Safe sex with gonorrhea without a condom with a patient or carrier of the infection is possible, but such actions can hardly be called full sexual intercourse. Experts include body massage, dry kissing, oral contact with the body with the exception of the external genital area, self-masturbation and individual sex toys.
Identification of patients with gonorrhea and carriers takes place during routine examinations, registration of medical records, and during the registration of pregnant women. All sexual partners should undergo examination if symptoms of gonorrhea appear within 30 days after contact, and in the asymptomatic form - within 60 days before diagnosis, if at least one of them shows signs of the disease. Mothers whose children have gonorrhea are examined, and girls if their parents or guardians have been diagnosed with gonorrhea.
Gonorrhea test
Treatment of gonorrhea in women and men primarily involves confirming the diagnosis - identifying the causative agent, as well as conducting bacteriological and bacterioscopic tests. To identify antibodies and antigens to gonococci, immunological, immunofluorescent and other studies are used.
To diagnose gonorrhea, smear tests, PCR and culture are taken from the urethra, cervical canal, vagina, as well as prostate secretions, scrapings from the rectum, etc. Depending on the specific case, it may be necessary to collect material from the eyes and joints. Preparation consists of thoroughly cleaning the genitals, without using disinfectants, and avoiding antibiotics.
In the chronic form of the disease, as well as in the presence of concomitant infections or with previously administered antibacterial treatment, the use of a cultural diagnostic method is indicated. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is also highly informative. The cultural method currently remains the “gold standard” for diagnosing gonorrhea in women and men. It consists of inoculating the discharge from the area of inflammation on special media and isolating a pure culture, followed by determining the sensitivity of the microorganism to antibiotics.
What tests for gonorrhea do women and men take:
- A smear of discharge;
- Gram microscopy;
- PCR analysis;
- RNA testing (NASBA);
- Bacteriological culture of a smear.
Smear test for gonorrhea in girls and virgin girls:
- From the urethra;
- From the vagina (without speculum);
- From the external genitalia;
- From the anus;
- From the oropharynx.
Diagnostics
What tests are there for gonorrhoea and their price?
| List of analyzes | What is the price |
| Smear for gonorrhea in women: 1 point 2 points 3 points | 450 500 550 |
| Male smear | 500 |
| PCR for gonorrhea | 450 |
| PCR smear (quantitative) | 850 |
| Gram smear | 750 |
| Sowing tank with selection of antibiotics | 1 750 |
| NASBA RNA analysis (early diagnosis) | 2 500 |
| Complex analysis of NASBA RNA Chlamydia / Gonococcus / Mycoplasma genitalium / Trichomonas | 7 500 |
You can get checked by a doctor and get tested for gonorrhea anonymously and urgently in Moscow at our clinic on Kutuzovsky Prospekt. We work daily, incl. on weekends! Taking tests and seeing specialists by appointment.