What is a dental abscess and how to prevent this disease? In this article we talk about the causes, symptoms and treatment of abscess on the gums, as well as recommendations on how to reduce the likelihood of encountering a purulent infection.
Abscess on the gum and its symptoms
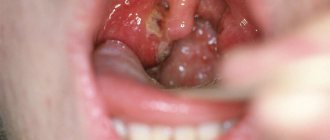
An abscess is a painful process of suppuration in a place where an infection occurs. Most often, inflammation occurs in the area of the diseased tooth. The compaction with pus is a protective mechanism that prevents the infection from spreading throughout the body. If you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner, the abscess can destroy the jaw bone, as well as the periodontal structure, which sometimes leads to tooth extraction.
The first signs of infection in the gums are pain and discomfort while eating. Symptoms of an abscess on the gum:
- continuous throbbing pain;
- pain when pressing on a tooth;
- discomfort when eating hot/cold foods;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- swelling and redness of the face;
- bleeding from the gums;
- mobility and change in the natural color of the tooth;
- lump on the gum and swelling of the face;
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical studies:
- Collecting the patient's medical history. The doctor listens to complaints and asks questions about symptoms and other manifestations.
- Inspection. It is carried out to identify the causative tooth. The doctor evaluates the color of nearby tissues, the symmetry of the face, and checks the opening and closing of the jaw.
- Palpation of lymph nodes. Their increase indicates the presence of inflammation.
- Measurement of temperature and blood pressure. Deviation of indicators from the norm indicates intoxication of the body.
- X-ray (spot shot and orthopantomogram). It is carried out to establish the localization of the purulent focus.
- Electroodontodiagnostics. Necessary to assess the condition of the dental nerve in the causative tooth.
- Lab tests.
If necessary, general clinical studies are prescribed, such as an electrocardiogram and fluorography.
Material is taken from the opened lesion to assess the sensitivity of the microflora to the effects of antibiotics.
Types of dental abscess
- Desnevoy
- Periodontal
- Periapical
- Pericoronal
- Combined (periodontal-endodontic)
Desnevoy
A superficial formation on the soft tissues in the area of the gingival papillae between the teeth. Inflammation is associated with the ingress of food, foreign objects, or trauma to the gums with a toothbrush or floss. A gum abscess is relatively easy to correct, but if not treated early, complications can arise.
Periodontal
This is an internal inflammation of the soft tissues of the gums, often caused by periodontitis. In this case, the infection is localized between the outer wall of the alveolar ridge and the gum when the dental pulp is healthy. A purulent exudate forms in the affected gum, which forms a lump in the periodontal pocket. There is no place in the gum for fluid with infection to escape, so the soft and bone tissues near the site of suppuration are gradually affected.
Periapical
The most common type of abscess, the cause of which is complicated caries or untreated periodontitis. The infection affects the root system of the tooth, resulting in pus accumulating at the apex of the root. When the immune defense is weakened, the inflammatory process affects the periosteum of the tooth, spreads to the soft tissue of the mucosa and leads to the formation of a fistulous tract and a purulent lump on the gum.
Pericoronal
Inflammation occurs in the soft tissues above the erupting tooth when food debris and bacteria get there. Pericoronitis can cause swelling of the neck, jaw, and also lead to angina pectoris (impaired respiratory function).
Combined (periodontal-endodontic)
Damage to the gums in the pulp and soft tissues, which causes periodontitis on adjacent teeth.
Consultation, image and treatment plan free of charge
Enter your phone number, we will call you back and select a convenient appointment time for you. Or call us yourself - +7
Already received your application
We will definitely contact you as soon as possible and advise you on all your questions.
No time to wait? Call:
+7
Causes of gum abscess
The human oral cavity contains about 30 strains of microorganisms, represented by more than 700 species of bacteria. Under normal conditions, microbiocenosis does not harm its owner. A dental abscess occurs only in the presence of certain factors:
- traumatic disruption of the periodontal junction;
- infectious dentogingival pathologies;
- transmission of microorganisms through the bloodstream from other infectious foci (meningitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, etc.);
- gum damage during segment therapy;
- trauma to the crown or root of the unit;
- peri-implantitis (inflammation around the implanted tooth root).
The likelihood of developing the disease increases with poor oral care, hypothermia, accumulation of tartar inside deep periodontal pockets, and smoking. Professional hygiene and gum treatment in Moscow is carried out by doctors of the North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1. A timely visit to the clinic will reduce the risk of the formation of a purulent formation.
Treatment of gum suppuration
Minor or severe pain requires the help of a dentist. The choice of methods to eliminate suppuration remains with the doctor. Treatment begins after a survey, external examination, and X-ray diagnosis of the patient. The specialist’s main goal is to remove accumulated pus as a source of infection. Depending on the severity, surgical treatment may be required.
Surgery
Treatment methods depending on the type of inflammation:
- With a gingival abscess, the pocket with pus is opened, and then cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
- In cases of periodontal inflammation, it may be necessary to cut the boil to gain access and eliminate the infection. The pus is removed through auxiliary dental canals so that the infection does not spread further through the blood vessels. After eliminating the purulent process and residual infection, curettage of the periodontal pocket and other procedures for the treatment of periodontitis are performed.
- Patients with a periapical abscess are most often prescribed cleaning and refilling of the root canals according to the periodontitis treatment regimen, as well as removal of pus by opening and draining the flux.
- To eliminate a pericoronal abscess, it is necessary to remove the tissue that is preventing the tooth from erupting.
Don't forget antibiotics!
After surgery, the doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial therapy: anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, as well as a course of home antiseptic rinses.
Read more about surgical and conservative methods of treating abscess.
Treating an abscess at home
At home, it is impossible to completely cure gum suppuration, but you can significantly reduce the pain.
Before visiting the dentist, you can use the following home remedies:
- a decoction of chamomile and oak bark for rinsing the mouth;
- rinsing with a solution of salt, soda or chlorhexidine;
- local application of ointments and internal administration of analgesics.
Prevention
In general, the effectiveness of treatment depends on at what stage of the disease the patient sought medical help and his general health. It is very important to follow all doctor’s orders and treatment procedures immediately after they are prescribed. A timely surgical operation and the absence of complications after it are a guarantee of healing the abscess within one to two weeks.
Preventive measures to prevent this disease are very simple:
- Maintain hygiene, which includes high-quality and proper care of teeth and gums (brushing teeth and tongue at least twice a day, cleaning interdental spaces with dental floss after meals, regular use of mouth rinses);
- Treat carious teeth and other oral diseases in a timely manner;
- Protect the jaws and oral mucosa from injury;
- Have a complete diet, including vitamins and vital microelements.
Simple tips, the implementation of which depends only on your desire, will help in the future to avoid serious consequences caused by an abscess. And remember: oral health directly affects the beauty and charm of your smile.
Types of dental abscess
- Osteomyelitis
- Phlegmon
- Tooth loss
Osteomyelitis
When pus remains in the soft tissues, complications arise. Dense formations with pus form in the bone tissues, and swelling of the lymph nodes also occurs.
Phlegmon
A life-threatening complication occurs when the infection spreads into the soft tissues of the gums. The growth of pus leads to chronic pathologies.
Tooth loss
If the infected fluid spreads to the base of the tooth, painful swelling appears, which may lead to tooth extraction.
What is an oral abscess?
An oral abscess is an acute inflammatory disease characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the tissues of the gums, tongue or cheeks. The abscess is accompanied by local swelling and hardening of soft tissues, severe pain on palpation, fever and general weakness. The disease is diagnosed by a dentist after a visual examination of the tissue, after which immediate surgical intervention is required: opening the abscess, followed by cleaning and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
Oral abscess is one of the most common complications in the practice of dental surgery. It can be observed in patients of different ages. Untimely treatment can lead to the transition of inflammation to the chronic stage. Against this background, sepsis and phlegmon can develop. That is why, if the slightest symptoms of an abscess occur, you should immediately visit a dentist.
Stages of development and classification of gum abscess
A gum abscess most often has an acute course, characterized by a clear clinical picture with increasing pain and swelling. Sometimes, in the absence of treatment, the process may subside, the clinic becomes weakly expressed and erased. This means that the abscess has become chronic.
Depending on the location of the purulent focus, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- Periodontal abscess. Localized inside the hypertrophied periodontal pocket (between the alveolar process and the gum). The cause of the pathology is subgingival deposits, which are a breeding ground for the proliferation of bacteria.
- Periapical (root). The leading cause of occurrence is inadequate root canal treatment, leading to periodontal inflammation. Granulations form near the root apex. Progressive inflammation spreads to the periosteum and periodontal tissue. A connective tissue capsule with purulent contents is formed. Over time, a fistula forms with pus coming to the surface in the form of a lump.
- Desnevoy. The purulent cavity is located near the papillae between the segments. A possible cause is an injection into the gum.