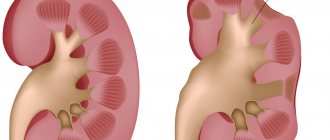
What is salpingoophoritis
The body of a healthy woman independently copes with attempts to invade foreign infections. The pathogen will not achieve its goal if the internal environment of the vagina is acidic and enough opportunistic microorganisms have been formed. An obstacle to its penetration will be the natural layer of dense mucus in the cervical canal (the transition of the cervix into the body of the uterus) and the regular rejection of the endometrial layer during menstruation.
If this set of natural defense mechanisms is disrupted, the infection is more likely to enter the body. Pathogens enter in two ways:
- Actively, attaching in the fallopian tubes to moving objects - sperm, trichomonas;
- Passively, with blood and lymph flow, as well as ascending (through the vagina).
Once in the ovary, the infection destroys its cells and causes inflammation and swelling - this disrupts the function of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
A sick woman’s body temperature rises, blood counts change, and due to intoxication of the body, general health worsens.
Inflammation progresses from bottom to top, from the fallopian tube to the ovary and ligaments. In this case, exudate is released from the blood vessels and accumulates in the lumen of the fallopian tube. The villi in the fimbrial region stick together, and an elastic protrusion is formed in the form of fluid-filled sacs - sactosalpinx.
If treatment is not started, the amount of exudate in the sacs continues to accumulate and become purulent - a pyosalpinx is formed.
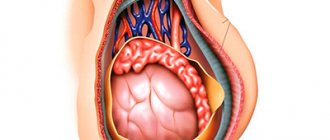
When the infection reaches the deformed area of the fallopian tube, purulent melting of the villi occurs and cavities are formed. In the absence of medical assistance, inflammation seizes the ovary, and a process of necrosis occurs. If the affected ovary comes into contact with the pyosalpinx, an abscess forms.
Next, purulent inflammation spreads to the peritoneum and forms abscesses between the intestinal loops - pelvioperitonitis occurs.
Salpingitis and oophoritis
Often salpingitis occurs not alone, but together with oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries). The causative agents of oophoritis include various microorganisms, often found in combination and at the same time quite resistant to antibiotics.
With such a combined disease, the process of soldering the fallopian tube altered due to the inflammatory process with the ovary occurs and a single extensive inflamed formation is formed, which has very serious consequences.
Classification and symptoms of the disease
Salpingo-oophoritis can be acute, subacute and chronic.
In the acute stage of the disease:
- temperature rises;
- general condition deteriorates sharply;
- abdominal pain occurs;
- urine separation is impaired;
- possible diarrhea or constipation;
- The discharge contains pus and smells unpleasant.
The pain intensifies during examination by a gynecologist and is often projected onto the anus. During the examination, the doctor will determine limited mobility of the uterine appendages; a blood test will show an increased number of leukocytes, ESR, and C-reactive protein.
Symptoms of right-sided adnexitis are similar to those of appendicitis. The final diagnosis can be established after diagnostic studies.
Acute bilateral salpingoophoritis is accompanied by acute pain throughout the peritoneum and acute intoxication.
The subacute (non-specific) stage does not produce pronounced symptoms. This is an intermediate form between acute and chronic disease. The following may be observed:
- weakness;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- urinary problems;
- itching of the genitals;
- swollen and painful lower abdomen.
The subacute form does not last long and the woman may not have time to start treatment or confuse the symptoms with a cold. Then the disease becomes chronic and intractable.
Chronic adnexitis is a consequence of an untreated disease or a consequence of untreated acute adnexitis. During the remission stage, the disease may not manifest itself in any way; exacerbations are possible with hypothermia, ARVI and stress.
A woman suffers from dull aching pain in the lower abdomen. They intensify before menstruation, in case of hypothermia or illness. Since ovarian function is impaired, the menstrual cycle is inconsistent. Discharge from the genital tract is mucopurulent.
Women suffering from chronic adnexitis find it difficult to become pregnant and bear a child. The pregnancy may be ectopic or end in spontaneous abortion. Unpleasant sensations often occur during sex. Constipation or chronic colitis, biliary dyskinesia, cholecystitis, and pyelonephritis are added to the underlying disease.
On palpation, the appendages are painful and enlarged in size. Often the disease is accompanied by inflammation of the vaginal mucosa or inflammation of the cervical canal.
Acute salpingitis
The disease begins with an increase in temperature to high numbers, as well as with general malaise. Heartbeat increases.
Symptoms of acute salpingitis:
- vomit;
- nausea;
- Strong headache;
- pain in the groin area is an important diagnostic symptom. Its localization depends on which of the tubes the inflammatory process has developed;
- pathological discharge. With gonococcal salpingitis, purulent discharge appears, with trichomonas - foamy and abundant. If acute salpingitis is very severe, then the appearance of bloody discharge is noted. It is worth noting that the discharge in this disease is always abundant, and it is accompanied by burning and itching.
Acute salpingitis occurs and progresses due to infection entering the oviduct. The path of entry into the pipes is ascending or from a lesion that already exists in the woman’s body (appendicitis, oophoritis). In most clinical cases, acute salpingitis develops against the background of an ectopic pregnancy. The symptoms of this disease are very pronounced.
Causes
Most often the disease is caused by chlamydia and gonococci. But there are a great many microorganisms that can cause inflammation; they are usually divided into specific and nonspecific.
Among the specific ones:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- diphtheria;
- gonococci;
- Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis);
- trichomonas, actinomycetes, candidiasis pathogens;
- ureaplasma, chlamydia. mycoplasma;
- .viruses.
Nonspecific microorganisms:
- staphylococci, streptococci;
- Escherichia coli, enterococci;
- Klebsiella, Proteus.
Often the disease is caused by more than one pathogen, a complex of microorganisms. It unites completely pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic mycobacteria that habitually exist in the genital tract of every woman. Conditionally pathogenic microorganisms themselves can also cause inflammation, but this only happens if the body is weakened.
Salpingo-oophoritis is more likely to occur in women whose immunity is undermined by chronic stress, physical and mental stress, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Chronic somatic diseases also significantly increase the risk of disease.
Causes of acute adnexitis:
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- surgeries on the pelvic organs;
- use of an intrauterine device;
- abortions and difficult births;
- therapeutic and diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity;
- severe diseases (tuberculosis, diphtheria, pneumonia).
Prevention of genitourinary diseases
To avoid “female” diseases, it is imperative to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- Try to avoid hypothermia (if this is impossible for certain reasons, then you need to protect the genital area and legs);
- Protect yourself from infectious diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse;
- Do not forget that salpingoophoritis is caused by medical abortions and other procedures that increase the risk of an infectious disease.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Diagnostics
In the acute stage of the disease, it is almost impossible to clarify the diagnosis by palpation of the abdomen - peritoneal tissue is involved in the pathological process, the situation is aggravated by edema. When examined on a gynecological chair, purulent discharge and signs of inflammation of the cervix are visible in the vagina.
An accurate method for assessing ovarian function is histological analysis of a scraping of the endometrium (the inner mucous membrane of the uterine wall). The material is taken by curettage, 2-3 days before the onset of menstruation.
If a tumor is suspected, the doctor will order a biopsy - taking a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope.
It is possible that culdocentesis will be indicated - a puncture of the posterior vaginal vault to collect exudate.
The method for clarifying the diagnosis is ultrasound examination and fluoroscopy - pneumogynecology, plain radiography, metrosalpingography (a procedure using a contrast agent).
The hormonal function of the ovaries will be clarified by tests - colpocytology and determination of the karyopyknotic index.
The main tests that need to be taken if acute salpingoophoritis is suspected:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- bacterioscopy of vaginal smears;
- bacteriological examination of secretions for the presence of bacteria and fungi.
Diet
During the acute and subacute stages of adnexitis, patients should follow a hypoallergenic diet. It is advisable to exclude from the diet:
- mushrooms;
- chicken egg whites;
- chocolate;
- baked goods, sweets;
- citrus fruits, etc.
Limit the amount of table salt. Food must be processed by boiling or stewing.
If salpingoophoritis does not have pronounced symptoms, it is not necessary to adhere to a diet. But nutrition should always be complete, with sufficient vitamins and proteins.
Treatment of salpingoophoritis
The acute stage of the disease and exacerbation of chronic adnexitis are treated in a hospital using broad-spectrum antibiotics or antimicrobial drugs. The medicine is prescribed individually; the causative agent of the disease must first be determined and a sensitivity test to the drug must be carried out. At the same time, the doctor detoxifies the body and relieves pain in the pelvic organs involved in the inflammatory process.
Patients are recommended bed rest and complete rest. After the acute process is removed, the situation will be helped to stabilize:
- electrophoresis with potassium, magnesium or zinc;
- ultrasound procedures;
- vibration massage;
- taking biostimulants.
If therapy does not help, laparoscopy will be prescribed. In case of rupture of purulent formations, invasive surgical intervention is indicated - laparotomy. The affected tissue is removed through an incision in the peritoneal wall.
Chronic adnexitis is treated with balneotherapy and physiotherapy: ultrasound, pulsed currents, exposure to a magnetic field, mud therapy, mineral baths, reflexology.. The treatment program is drawn up by a doctor, he takes into account the prevailing symptoms, the presence of adhesions, and the characteristics of the menstrual cycle.
At this stage of the disease, antibiotics are not used; priority is given to anti-inflammatory and desensitizing therapy and pain relief. women need to strengthen the body, take vitamins and immunostimulants, and work with a psychologist.
During the acute phase of the disease, it is important to follow a diet: Avoid fried and smoked foods, eat foods containing vitamin C and fiber. Fermented milk products, vegetable oils, vegetable and fruit juices are useful. Drink at least 2.5 liters of fluid per day.
Important! Salpingoophoritis cannot be cured with folk remedies. Strictly follow your doctor's recommendations!
Cost of treatment of right-sided adnexitis
The cost of treating adnexitis at the Healthy Family clinic is calculated individually in each case. It depends on the stage at which the woman sought help and on what type of treatment was chosen by the doctor.
Mostly therapy is prescribed on an outpatient basis, but in particularly difficult cases, the attending physician may insist on hospitalization and keeping the woman in hospital under observation. In acute cases of the disease, mainly antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Their selection is made taking into account the susceptibility of the pathogen to antibiotics. If after diagnostics it is not possible to establish the cause, then complex medications may be prescribed. The most positive combination of 3rd generation cephalosporins, tetracyclines and metronidazole has proven itself. But you should definitely remember that only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics. Self-medication often leads to worsening of the condition and complications of the disease.
In the chronic form, antibacterial drugs are also used. Additionally, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Along with these medications, doctors recommend using products that restore the microflora of the vagina and intestines. They can be used either orally or vaginally.
Physiotherapeutic treatment has proven positive. Specialists can prescribe:
- electrophoresis;
- ozokerite;
- massages;
- physical therapy.
Undergoing physiotherapeutic treatment allows you to avoid exacerbations and reduce the negative symptoms of chronic adnexitis. Nutritional correction also has a beneficial effect. Refusal of junk food and inclusion of useful microelements in the diet allows you to stabilize the body’s condition. And additional intake of vitamins and minerals will restore the body’s defenses and quickly overcome the infection.
Diagnostic measures
Treatment of salpingoophoritis is performed under the supervision of a gynecologist after confirmation of the diagnosis. The doctor takes into account objective data, the patient’s complaints, and the results of laboratory and instrumental tests. Girls with signs of inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries are prescribed:
- gynecological examination;
- microbiological examination of smears from the urethra, vagina and cervix;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- radiography of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries;
- functional tests.
If there are appropriate indications, the doctor may insist on conducting a diagnostic operation to clarify the location of the abscess and examine the fallopian tubes.
General information
Adnexitis can occur in one or two-sided form. The pathology is one of the five most common diseases of the genitourinary system in women. The causative agents of the inflammatory process are microorganisms of various types: bacteria, viruses or fungi. Pathogenic microflora is resistant to the main groups of antibiotics.
Unilateral inflammation is formed as a result of staphylococci and E. coli entering the fallopian tubes, bilateral inflammation - gonococci and tubercle bacilli. The risk of developing the disease increases significantly with hypothermia of the patient's body, the presence of primary infections of the genitourinary system, violation of personal hygiene rules and sexual contacts without the use of barrier methods of contraception.