Stomatitis: features of the disease
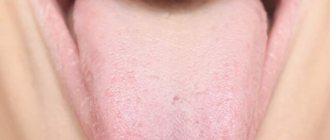
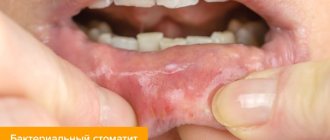
Stomatitis is a disease related to dental pathologies in which inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs. Infection of the tongue with stomatitis in adults is also called “glossitis.”
The inflammatory process affects the mucous membrane and causes severe symptoms:
- redness and swelling of the tongue;
- formation of white plaque;
- severe pain;
- the formation of many small blisters and ulcers.
Due to severe sensitivity and soreness of the tongue, the patient cannot eat food, fever, insomnia and irritability are possible.
Stomatitis under the tongue in adults, as in other parts of the oral cavity, is classified into two types.
- Aphthous. A form of inflammation in which the tongue becomes covered with papules and ulcers that turn into erosions (aphthae).
- Herpetic. The inflammatory process is manifested by swelling and redness of the tongue. Small bubbles are localized in groups.
Prosthetic stomatitis and ulcerative-necrotic form of pathology are extremely rare.
Without treatment, the signs of stomatitis completely disappear, but this does not mean that the patient is cured of the pathology. The inflammatory process becomes chronic and when the immune system is weakened or exposed to an irritant, a relapse occurs.
Main symptoms
Sometimes the presence of cracks and grooves in the tongue is not accompanied by unnatural or painful sensations and can only be detected during examination by a dentist, ENT specialist or therapist. But this doesn't always happen. Patients often complain of the following related problems:
- pain;
- burning sensation;
- feeling that the tongue is loose;
- there is blood and ichor;
- elevated temperature;
- swelling and itching appeared;
- it becomes painful to chew;
- there is a problem with speech;
- increased salivation appeared;
- change in natural color;
- taste disturbance;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
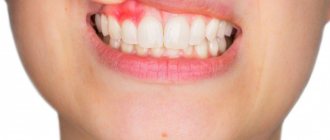
If cracks appear on the tongue, and the phenomenon is accompanied by one of the listed symptoms, then they speak of a progressive disease. This inflammatory process is referred to as glossitis; the prognosis for recovery from it is usually favorable. The appearance of erosions, furrows and ulcers indicates damage to the deep parts of the tongue. In this case, you should definitely contact a specialist.
Sometimes the tongue cracks and becomes covered with ulcers due to general damage to the ENT organs. Thus, tonsillitis or fungal pharyngitis can cause swelling and the appearance of white grooves. This condition is not isolated as an independent disease. Treatment in such cases begins with eliminating the underlying problem.
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis under the tongue in adults is a reaction of the immune system to certain types of irritants, which are any substances. The causes of stomatitis have not been clearly identified; presumably, the body exhibits an individual reaction to certain substances or microorganisms.
Possible causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults:
- bacteria and infections of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of an infectious or viral type;
- respiratory diseases (ARVI, influenza, etc.);
- frequent injury to the tongue by orthopedic or orthodontic structures;
- damage to the tongue due to a chipped tooth;
- fungal infection;
- bad habits (smoking or alcoholism);
- burning the tongue or eating “spicy” foods.
In addition to the listed causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, inflammation of the mucous membrane can be caused by the herpes virus (herpetic stomatitis).
Tongue in cracks - reasons
- Bacterial and viral infections
This doesn't just apply to infections in the mouth. Viruses and bacteria spread throughout the body, and the infection manifests itself in the tongue. Most often, cracks in the tongue are caused by the herpes virus. - Anemia
Iron deficiency can cause glossitis. Iron is transported by a special protein - myoglobin, which is responsible for the healthy state of muscle tissue. If there is not enough iron, all muscles suffer, including the tongue. - Allergic reaction
The body's response to various allergens: food, medications, sometimes even toothpaste components - can cause inflammation. - Mouth injuries
Burns, cuts, and any mechanical injuries become an environment where bacteria multiply, which means inflammation occurs. - Vitamin deficiency
It has been scientifically proven that a deficiency of B vitamins can lead to cracked tongue.
Treatment Basics
If an adult has a swollen tongue, the surface is covered with plaque, or has severe hypothermia, you should consult a dentist. Even in the absence of neoplasms in the oral cavity in the form of papules, ulcers or erosions, a specialist will be able to determine the development of the inflammatory process. With timely treatment, the risk of pathology becoming chronic is minimal.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults is carried out exclusively conservatively. Depending on the causes of the disease and the clinical picture, the doctor will determine a treatment regimen and prescribe effective drugs of systemic and local action.
The dentist’s task is not only to eliminate symptoms and inflammation, but also to identify the cause. If the provoking factor has a constant impact, then stomatitis under the tongue will constantly recur.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults begins with the relief of concomitant diseases - the root causes.
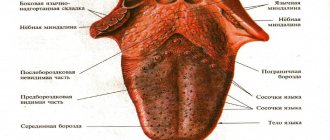
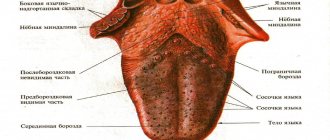
What it is
Officially, painful cracks on the tongue and along the edge of the tongue are called glossalgia. This is a fairly common neurosomatic disease.
Most common symptoms:
- dryness in the tongue area;
- itching and burning;
- swelling;
- soreness.
The insidiousness of glossalgia is that it does not go away on its own; without appropriate treatment it is impossible to get rid of a crack in the tongue.
At an early stage of the disease, the doctor may not notice pronounced cracks in the tongue, since they are microscopic and mainly manifest themselves as burning and pain. If you do not respond to this symptom in a timely manner, over time a crack may form at the tip or in the middle of the tongue, longitudinally, as well as cracks under the tongue and on the sides. In this case, the doctor also notes swelling and swelling of the tongue, atrophy of the salivary glands and filiform papillae on the surface of the tongue. The sooner you start treatment, the easier it is to get rid of glossalgia, so if you have cracks in your tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment for stomatitis is comprehensive.
- Anesthesia. To eliminate pain, the dentist may prescribe topical medications containing lidocaine or analgesics.
- Antiviral therapy. If the disease is caused by a herpes virus, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs of the appropriate group of effects.
- Antibacterial therapy. In case of bacterial stomatitis, local treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions and dental ointments with antibacterial action is mandatory.
- Antifungal therapy. Stomatitis can be the result of fungal activity in the mouth. This form is more common in children, but is not excluded in adults. The specialist prescribes the patient a strict regimen of antifungal drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. It is carried out in cases of severe inflammation. The dentist recommends taking anti-inflammatory systemic drugs that have a targeted effect depending on the pathogen or cause of tongue stomatitis.
- Diet. Patients with stomatitis are prescribed a diet that excludes foods that can aggravate irritation of the mucous membrane and tongue. So dentists recommend avoiding hot, spicy, sour and salty foods. Smoking and drinking alcohol should be avoided.
Together with the treatment of stomatitis, treatment of diseases of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, inflammation of the gums, caries, etc. can be carried out.
Treatment in the clinic
Before prescribing medications and procedures, it is necessary to find out why cracks occur. After this, a plan is drawn up, which may include:
- Treatment of a common disease
- Antifungal medications
- Iron tablets
- Vitamins
- Corticosteroids
- Immunostimulants
- Antihistamines
The surface of the tongue is disinfected with antiseptic solutions. Painkillers are used to reduce pain.
If mechanical injuries occur as a result of unsuccessful prosthetics, it is recommended to replace the structure.
General recommendations
For stomatitis in adults, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The dentist can perform initial treatment of the oral cavity, then the patient will need to perform all the manipulations independently at home.
Antiseptic treatment of the entire oral cavity is a prerequisite for the successful treatment of stomatitis and the rapid recovery of the affected mucosa. For “disinfection”, solutions containing chlorhexidine, furatsilin or metronidazole are used. Dentists also recommend rinsing with a soda solution every 2-3 hours.
Locally in the affected areas, it is necessary to remove heavy plaque using gauze and apply anti-inflammatory and regenerating gels or ointments to the areas where ulcers accumulate. The procedure is unpleasant, but significantly speeds up recovery.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, subject to all prescriptions and recommendations of the dentist, takes no more than 10 days. Symptoms of the disease disappear after 3–5 days; a few more days are required to restore the affected tissues.
Congenital fissures
It happens that a patient has cracks in the tongue since birth or childhood, which practically do not cause him any concern. Such cracks are usually transverse and are caused by the development and formation of the tongue.
Some patients have a so-called folded tongue, a congenital feature of tongue development. It is usually considered normal and does not require any treatment. The exception is red cracks in the tongue, which form at the bottom of the folds and cause pain to the patient. This happens with insufficient oral hygiene, so those with a folded tongue must carefully clean not only their teeth and gums, but also their tongue from plaque. If the owner of a folded tongue has developed cracks, treatment should be prescribed by a competent doctor, taking into account the design features of the patient’s tongue. To prevent the formation of folds in the depths, more attention should be paid to the sanitation of the oral cavity.
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is a chronic pathology characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa. Its main symptom is a rash of aphthae or ulcers, which are noticeably painful. Aphthae usually appear periodically in the following areas:
- Language;
- Cheeks;
- Hard and soft palate;
- Mucous membrane of the lips.
If ulcers are periodically injured, they can develop into full-fledged, difficult-to-heal wounds, in place of which noticeable scars remain. The normal healing time for aphthae is no more than a week from the moment of its appearance.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis are as follows:
- Chronic colitis;
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Chronic stress;
- Injury to the mucous membrane;
- Hormonal imbalance during menstruation.
With a normally functioning immune system, ulcers heal on their own in one, or in extreme cases, two weeks. If healing does not occur, you must visit a doctor to prescribe the correct treatment. As a rule, the basis of therapy is taking vitamin C, which has a positive effect on the immune system.
Home Remedies
Folk remedies are not able to eliminate the cause of cracks, especially if it is a common disease. In rare cases, the body can defeat a bacterial infection on its own. Therefore, medications from a home medicine cabinet can only be considered auxiliary. These include:
- Gargling with decoctions of sage and chamomile
- Lotions with sea buckthorn or olive oil
- Propolis
- Potato juice applications
Incorrectly selected folk remedies can reduce the effect of drug treatment.
Be sure to consult your doctor.
Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis
Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis is also called Setton's aphthae. Its symptoms are:
- Seals appear in the submucosa of the oral cavity;
- Instead of compactions, ulcers with raised edges develop over time;
- The ulcers become inflamed, causing blood and lymphatic discharge.
Places where such afts accumulate are the upper and lower lips, cheeks and sides of the tongue. The pathology is characterized by extremely severe pain. Patients find it so difficult to eat that many give up eating completely. Difficulties also arise during conversation. The healing process of aphthae lasts a long time - sometimes up to several months, and the pathology itself persists for up to several years.
Top five dental clinics
All clinics on the list are multidisciplinary. They are engaged in prevention, treatment, prosthetics and implantation.
| Dental center | Clinic address | General information |
| Cerecon | Moscow, Andropova Ave. 8 | Metro Technopark. Opening hours: 24 hours a day |
| ROOT | Moscow, st. Rustaveli, 14 building 9 | Metro Butyrskaya. Opening hours from 10:00 to 22:00 |
| Alpha-Dent | Moscow, Beskudnikovsky blvd., 24, bldg. 1 | Metro Petrovskoye-Razumovskoye. Open all days of the week. |
| MegaStom | Moscow, Bolshoi Kozlovsky lane, building 10, building 2 | Metro Red Gate. They don't work on Sundays |
| Denta amo | Moscow, st. Grekova, 9 | Metro Medvedkovo Open daily from 9 to 9. |