Several years before the onset of her first period, starting from 8-11 years old, the girl (and those around her) notice the following changes in appearance:
- The figure takes on a more rounded, feminine shape.
- The breasts begin to grow.
- The hips become wider.
- The first hair appears on the pubis and armpits.
- Problems with the skin begin as the sebaceous glands are activated, the peak of their activity occurs on the skin of the face, back and chest.
- Hair roots look oily even if the frequency of hair washing and detergent does not change. Dandruff often appears.
- Abundant milky vaginal discharge appears, usually without a specific odor, since its main function is to cleanse and moisturize the vagina.
What is Menstruation?
Menstruation (menstruation) - this word in Latin sounds like mensis , this is a physiological process during which the old layer of the endometrium (the lining of the uterus) is torn off and comes out through the genital tract in the form of menstrual fluid.
Most of this fluid is blood. It is the duty of every woman to know as much as possible about her health and be able to feel her body.
The menstrual cup is an ultra-modern product for feminine intimate hygiene. Gives a new degree of freedom during the period. Menstruation is no longer a reason to put things off. And it is true. Read on!
We always have in stock a simply gigantic assortment of bowls from various manufacturers.
Germany, Finland, Spain, Russia, China. Anatomically shaped, with valve, cup sets made of medical silicone and thermoplastic elastomer...
You can get acquainted with it and choose the one that suits you on the product page:
6) The main thing is to choose the right size of the menstrual cup
Manufacturers' websites have detailed instructions on how to determine the length of the vagina and choose the cup size yourself. The fact is that each manufacturer has its own size range; there is no universal scheme. Plus, the bowls are very soft and elastic. The first ones are less noticeable inside, but more difficult to remove. Keep in mind that you may not be able to insert and remove the cup the first time, but you will get the hang of it. I advise you to try using the cup before your period begins - this way you will determine for yourself the most comfortable position for inserting it.
It is important to store this hygiene product correctly (in a fabric bag) and process it promptly before use and after the end of menstruation.
After removing the tray, you need to rinse it under cold water, and then reinsert it, of course. Every month, the mouthguard must be sterilized in hot water for 3-5 minutes or use special sterilization tablets.
If you choose the right bowl size, you can use it at night and sleep peacefully.
It is the duty of every woman to know about it and be able to feel her body.
In addition to the article, our online store offers you modern intimate feminine hygiene products that will help you get through your period with maximum comfort and safety.
For example:
The menstrual cup is an ultra-modern product for feminine intimate hygiene. Gives a new degree of freedom during the period. Menstruation is no longer a reason to procrastinate or feel inconvenienced.
We always have in stock a simply gigantic assortment of silicone menstrual cups from various manufacturers.
Germany, Finland, Spain, Russia, China. Anatomically shaped, with a valve, with a “stem”, “ring”, “ball” tail type... sets of bowls made of safe medical silicone and thermoplastic elastomer...
You can get acquainted with it and choose the one that suits you on the product page:
Special reusable menstrual panties, protective with a waterproof layer, or hygienic, which can be worn without tampons and pads. It's easy to choose your size from products from more than 10 manufacturers.
In the photo, the panties are worn on the model inside out so that you can estimate the size of the absorbent and protective waterproof layers “from elastic to elastic.”
With high, medium or low waist. Slips, bikinis, and even thongs.
Visit our online store page with special underwear for your period: “Menstrual panties”
4) When choosing gaskets, focus not on the price, but on the composition
Pads don't have many advantages over tampons. It's all about comfort. Some women absolutely cannot use tampons - they are uncomfortable or even painful. Pads are also used by girls who are not sexually active.
They need to be changed every 4-6 hours depending on the amount of discharge. The disadvantages of these hygiene products are the “greenhouse effect” due to the tight fit to the perineum and lack of air circulation, irritation and even allergic reactions. You need to focus not on the price, but first of all on the composition: natural materials (cotton), a minimum of fragrances and flavors.
By the way, dermatologists now do not recommend using panty liners, as they can cause allergic reactions and dermatitis on the skin of the external genitalia.
What is menstruation?
Menstruation (from Latin mensis - month, menstruus - monthly), menstruation or regula - part of the menstrual cycle of the female body.
of the endometrium (uterine lining) is shed The countdown of the menstrual cycle begins on the first day of menstruation.
Why do we need periods?
The menstrual process is a period when the uterine epithelium is renewed every month.
During this process, irreversible changes occur in the epithelium, and it is removed from the body, since it can no longer be used. Instead, a new epithelium is formed in the body, which is successfully involved in internal processes.
Functional purpose:
Degeneration of cells. The menstrual process allows you to renew epithelial cells, which provides an important role for a girl’s reproductive ability.
Natural protective. The menstrual process involves a separate layer of the uterus, which is responsible for analyzing problems in eggs that are not fertilized and preventing the implantation of these eggs. Such eggs are excreted from the body along with the epithelium every month.
Menstrual blood does not clot and has a darker color than the blood circulating in the vessels. This is explained by the presence of a set of enzymes in menstrual blood.
Menstrual blood is the liquid discharge from the vagina during menstruation. Strictly speaking, a more correct term is menstrual fluid, since its composition, in addition to blood itself, includes the mucous secretion of the glands of the cervix, the secretion of the vaginal glands and endometrial tissue.
The average volume of menstrual fluid released during one menstrual cycle is, according to the Great Medical Encyclopedia, about 50-100 milliliters.
However, the individual spread ranges from 10 to 150 and even up to 250 milliliters.
This range is considered normal; more abundant (or, conversely, scanty) discharge may be a symptom of the disease. Menstrual fluid is reddish-brown in color, slightly darker than venous blood.
The amount of iron lost through menstrual blood is relatively small for most women and cannot on its own cause symptoms of anemia.
In one study, a group of women exhibiting symptoms of anemia were examined using an endoscope. It turned out that 86% of them actually suffered from various gastrointestinal diseases (such as gastritis or duodenal ulcers, in which bleeding occurs in the gastrointestinal tract).
This diagnosis may have been missed due to erroneous attribution of iron deficiency to menstrual blood loss. However, regularly heavy menstrual bleeding in some cases can still lead to anemia.
Menstruation (and menstrual cycles in general) usually does not occur during pregnancy and lactation. And the absence of menstruation at the expected time is a common symptom that suggests pregnancy.
During menstruation, a woman may experience physical discomfort. Before menstruation, you may experience irritability, drowsiness, fatigue, a slight increase in heart rate, and during menstruation - a slight slowdown in heart rate.
Premenstrual syndrome
Some women experience emotional changes associated with menstruation.
Sometimes there is irritability, a feeling of fatigue, tearfulness, and depression. A similar range of emotional effects and mood shifts are also associated with pregnancy and may be due to a lack of endorphins.
Estimates of the incidence of premenstrual syndrome range from 3% to 30%. In certain rare cases, in persons prone to psychotic disorders, menstruation may trigger menstrual psychosis.
It is important to know the days of your cycle, the description of which will help you get to know yourself better.
The female cycle by day, what happens on these days, every woman should know, because it will show when you are ready to conceive, when you are passionate or, on the contrary, cold, why your mood changes so much:
On the 1st day, the uterus throws out the spent endometrium, that is, bleeding begins.
A woman may experience malaise and pain in the lower abdomen. To reduce pain, you can take No-shpu, Buscopan, Belastezin, Papaverine.
On the 2nd day, heavy sweating begins.
On the 3rd day, the uterus is very slightly open, which can contribute to infection. On this day, a woman can also become pregnant, so sex should be protected.
From the 4th day , your mood begins to improve, your productivity appears, as your period is nearing completion.
What is the cycle by day in the second half?
Days starting from the 9th to the 11th day are considered dangerous; you can become pregnant.
They say that at this time you can conceive a girl. And on the day of ovulation and immediately after it is suitable for conceiving a boy.
On the 12th day, women's libido increases, which entails a strong sexual desire.
When does the second half start?
From day 14 , when the egg begins to move towards the male principle, ovulation occurs.
On the 16th day , a woman may gain weight as her appetite increases.
until the 19th day .
From the 20th day “safe” days begin. What are “safe days”? Exactly! “Safe” - in quotes!
These days, the possibility of getting pregnant decreases. Many women ask the question: is it possible for a woman to get pregnant before her menstrual cycle? The probability is low, but no one can give a complete guarantee.
The period of menstruation can change under the influence of many factors. No woman has an even cycle throughout her life. Even a cold, fatigue or stress can change it.
Many doctors warn that the body is capable of “giving out” repeated ovulation, so even 1 day before your period you can conceive a baby.
Menopause
Age of onset of menopause (cessation of menstruation): normal - 40-57 years, most likely - 50-52 years.
In temperate climates, menstruation lasts for an average of 50 years, after which menopause occurs; At first the regulations disappear for several months, then they appear and disappear again, etc.
There are, however, women who maintain menstruation until they are 70 years old. From a medical point of view, menopause is considered to have occurred if menstruation has been completely absent for a year.
What is the menstrual cycle?
In this video, in just 7.5 minutes, you can understand in detail the phenomenon of menstruation.
The mechanism of the menstrual cycle is described in great detail. Phases of the menstrual cycle. What hormones are controlled and what duration do they have?
If something is unclear, just look again.
Menarche.
The first appearance of menstruation (menarche) in a woman occurs at an average age of 12-14 years (with a range from 9-11 years to 19-21 years). Menstruation in hot climates begins between 11 and 15 years of age. In temperate climates - between 12 and 18 years of age and in cold climates - between 13 and 21 years of age.
The age of menarche reveals certain racial differences: for example, a number of studies have shown that Negroids experience menarche earlier than Caucasians living in the same socio-economic conditions.
After the first menstruation, the next one may be 2 or 3 months later. Over time, the menstrual cycle becomes established and lasts 28 days, but a cycle length of 21 to 35 days is normal. Only 13% of all women have a cycle of exactly 28 days. Menstruation lasts approximately 2-8 days. All discharge comes from the vagina.
On average, menstrual cycles usually begin between ages 12 and 15 and continue until approximately 45 to 50 years of age.
Since menstrual cycles are a consequence of changes in the ovary associated with the formation of oocytes, a woman is fertile only during the years that she has menstrual cycles.
This does not mean that sexual activity stops with the onset of menopause - only fertility disappears.
For practical reasons, the beginning of the menstrual cycle is considered to be the day when menstrual bleeding appears.
Menstrual discharge consists of collapsing endometrium mixed with blood from ruptured blood vessels.
Before the onset of menstruation, the following phenomena are observed:
- nagging pain in the sacrum, often in the lower back;
- headache;
- fatigue, weakness;
- nipple sensitivity;
- weight gain;
- Sometimes mucous discharge occurs.
Selection by day:
- 1 day - scanty discharge;
- 2.3 days – abundant;
- Day 4.5 - reduction in discharge;
- Day 6-7 – cessation of menstruation.
The menstrual phase lasts on average for 3-4 days. It is followed by two other phases of the menstrual cycle - the proliferation phase and the secretion phase (luteal phase, or corpus luteum phase).
The secretion phase begins after ovulation and lasts about 14 days. The duration of the proliferation phase is variable, averaging 10 days.
So, the menstrual cycle is usually called a period of time, the beginning of which is the first day of the appearance of menstruation, and the end is the day before the appearance of the next menstrual flow.
The normal menstrual cycle of a healthy woman has four phases, each lasting about 7 days. The duration of the entire cycle is 28 days. However, the duration of the menstrual cycle of 28 days is an average figure.
For each individual woman it can vary both up and down. But a cycle that lasts from 21 to 35 days is also considered normal.
If the cycle does not fit into these time periods, this is not the norm. In this case, you should contact a gynecologist and undergo a comprehensive examination under his guidance.
Menstruation and hormones
All processes during the menstrual cycle are controlled by hormones, so it is very important that the hormonal balance in the female body is always normal. Otherwise, you may need the help of not only a gynecologist, but also an endocrinologist.
Does your period hurt?
Many factors can affect how a woman feels during her period:
- Hereditary predisposition - some representatives of the fairer sex receive painful sensations or their complete absence during regulation as a “gift” from their mothers and grandmothers;
- Lifestyle - stress, irregular intimate life, poor nutrition, low or excessive physical activity can aggravate a woman’s condition during her menstrual period;
- General health – if a woman is sick, has a cold or her chronic diseases have worsened, then menstruation will only worsen her already poor health.
Since hormonal changes in the female body occur quite intensely during regulation, a woman’s sensations may be different depending on the day of her period.
On the first day, along with heavy discharge, aching or nagging pain may appear in the lower abdomen.
Such sensations are explained by contractions of the walls of the uterus, which, through such actions, tries to push out the exfoliated endometrium.
At this time, cardiovascular, nervous and digestive pathologies may worsen. Due to vasoconstriction, blood pressure may drop, especially in hypotensive patients. Due to hormonal changes, mood worsens, and due to the release of active prostaglandins, intestinal tone decreases and disorders occur.
During this time, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse, as there is a high risk of infection for both partners.
From 3 to 6 days , the volume of discharge decreases, the woman’s psycho-emotional state normalizes, she occasionally feels mild pain and other symptoms.
With the end of the regimen, the woman begins to feel great, not only her well-being improves, but also her mood, and her sex drive increases.
Phases of the menstrual cycle in more detail
The menstrual cycle consists of several phases. The phases of changes in the ovaries and endometrium are different. Each of them has its own characteristics and characteristics.
The preparation of the female body for gestation is characterized by cyclic changes in the endometrium of the uterus, which consist of three successive phases: menstrual, proliferative and secretory - and are called the uterine, or menstrual, cycle.
The menstrual phase is the first phase of the cycle
The menstrual phase, with a uterine cycle lasting 28 days, lasts an average of 5 days. This phase is bleeding from the uterine cavity that occurs at the end of the ovarian cycle if fertilization and implantation of the egg do not occur.
Menstruation is the process of shedding the endometrial layer. The proliferative and secretory phases of the menstrual cycle involve the processes of endometrial repair for possible implantation of the egg during the next ovarian cycle. The most unpleasant and often painful phase.
Proliferative or follicular phase - the second phase of the cycle
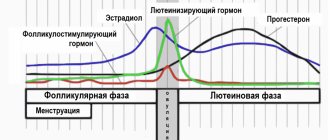
The proliferative phase varies in duration from 7 to 11 days. This phase coincides with the follicular and ovulatory phases of the ovarian cycle, during which the level of estrogens, mainly est-radiol-17p, in the blood plasma increases.
The main function of estrogens in the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle is to stimulate cell proliferation of tissues of the organs of the reproductive system with the restoration of the functional layer of the endometrium and the development of the epithelial lining of the uterine mucosa.
The proliferative (follicular) phase - the first half of the cycle - lasts from the first day of menstruation until the moment of ovulation. At this time, under the influence of estrogens (mainly estradiol), proliferation of cells of the basal layer and restoration of the functional layer of the endometrium occur.
The duration of the phase may vary. Basal body temperature is normal. Epithelial cells of the glands of the basal layer migrate to the surface, proliferate and form a new epithelial lining of the endometrium. In the endometrium, the formation of new uterine glands and the ingrowth of spiral arteries from the basal layer also occur.
During this phase, under the influence of estrogens, the endometrium of the uterus thickens, its mucus-secreting glands increase in size, and the length of the spiral arteries increases. Estrogens cause proliferation of the vaginal epithelium and increase mucus secretion in the cervix.
The secretion becomes abundant, the amount of water in its composition increases, which facilitates the movement of sperm in it.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, a woman’s body exhibits a very low concentration of the female hormones estrogen. Such a low level becomes a stimulus for the hypothalamus to produce special releasing hormones, which subsequently act on the pituitary tissue. It is in the pituitary gland that two main hormonal substances are produced that regulate the monthly cycle - follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
These chemicals enter the bloodstream and reach the woman's ovarian tissue. As a result of this interaction, the ovaries begin to produce the same estrogens that are not enough in the body in the first days of the menstrual cycle. A high level of estrogen in the blood is necessary for the process of active growth of follicles (female germ cells) to begin in the ovaries.
Stimulation of proliferative processes in the endometrium is associated with an increase in the number of progesterone receptors on the membrane of endometrial cells, which enhances proliferative processes in it under the influence of this hormone. Finally, an increase in the concentration of estrogen in the blood plasma stimulates the contraction of smooth muscles and microvilli of the fallopian tubes, which promotes the movement of sperm towards the ampullary part of the fallopian tubes, where fertilization of the egg should occur.
Every month, several such cells begin to mature in the female body, among which one dominant follicle stands out. It is the process of maturation and growth of the follicle that formed the basis for naming the first stage of the menstrual cycle, which is called follicular.
The duration of this stage may vary for each woman, but on average, with a 28-day cycle, follicle maturation takes about 14 days. The longer this stage lasts, the longer the woman’s entire menstrual cycle.
This period is considered the most unpredictable and the most “tender”. It is during the proliferative phase that the body responds sharply to all negative phenomena occurring to it.
Stress or illness can easily stop the process of follicle maturation and thereby lengthen the cycle, or, conversely, lead to rejection of the endometrium that has just begun to recover (imitation of menstruation).
Towards the end of the follicular phase, the level of FSH decreases, the middle of the cycle begins, and the body prepares for ovulation.
Video of the mechanisms of the menstrual cycle
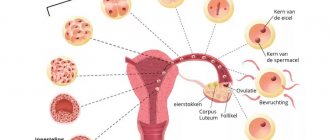
Ovulation is the third phase of the menstrual cycle
It begins after a sharp surge of LH (luteinizing hormone), the so-called luteinizing burst. After the dominant follicle bursts, an egg is released and begins its movement along the fallopian tube.
Once outside the follicle, the egg enters the fallopian or fallopian tubes (this process is called ovulation). The inner surface of the tubes is covered with villi, thanks to the movement of which the egg moves into the uterine cavity, preparing for fertilization and implantation.
Under the influence of LH, the cervical mucus softens and becomes looser, due to which sperm easily enter the uterine cavity and tubes.
The lifespan of an egg is 12-48 hours (while sperm live up to 5 days). If ovulation does not occur during this period, the egg dies.
Ovulation can be calculated and determined by the signs listed below:
- The woman begins to experience strong sexual desire.
- Basal temperature rises.
- The amount of discharge increases, it becomes mucous, viscous, but remains light and is accompanied by other symptoms.
- Moderate, nagging pain may occur in the lower back.
If at this moment the egg and sperm meet, an embryo is formed and the woman can become pregnant.
As mentioned above, during the second stage the dominant follicle grows actively and rapidly. During this time, its size increases approximately five times, as a result of which the enlarged cell protrudes beyond the ovarian wall, as if protruding from it.
The result of such protrusion is the rupture of the follicle membrane and the release of the egg, ready for further fertilization. It is at this stage of the menstrual cycle that the most favorable period for conceiving a child begins.
Calculating the date of ovulation is not difficult, especially if a woman has a stable and regular menstrual cycle. The day of ovulation occurs exactly 14 days before the first day of your period.
Luteal (secretory) - the fourth phase of the menstrual cycle
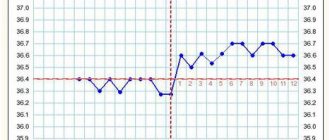
The secretory (luteal) phase - the second half - lasts from ovulation until the start of menstruation (12-16 days). The high level of progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum creates favorable conditions for embryo implantation. Basal body temperature is above 37 °C.
Changes occurring in the ovaries
The production of luteinizing hormone stops as suddenly as it began, immediately after ovulation. In place of the follicle, the corpus luteum is formed - a kind of endocrine organ that produces the pregnancy hormone - progesterone.
1) Severe pain during menstruation is a reason to consult a doctor
Severe pain often occurs in nulliparous girls. After childbirth, menstruation usually becomes less painful, this is due to changes in the anatomy of the internal genital organs (the position of the body relative to the cervix changes or, for example, during pregnancy the curvature of the uterus changes shape and size). Another common cause of pain is endometriosis, when cells in the inner layer of the uterine wall grow outside of it.
If your periods are painful, reduce your productivity and worsen your quality of life, consult a doctor - he will determine treatment tactics.
It is believed that a predisposition to pain is transmitted genetically. But this is an unproven fact.
More
- Scene;
- Period Remedy;
- Menstruation remedy two;
- Remedies for pain.
| [ + ] Menstruation is something about a woman. | |
| Methods | Abortion (Pros/Cons) • Two strips • Contraception (COC) |
| Diseases | Cervical cancer • HPV • Hidden infections |
| [ + ] Menstruation is an integral part of being human. | |
| Physiology | Physiological: Blood (Complement) • Urine • Feces • • Hormones • Death • Immunity • Carcinogenesis • Atherosclerosis • Pathogenesis Higher: Automatism • Sleep • Stress • Will (Laziness) Sexual: Sex • Orgasm • Sex hormones • Menstruation • Sperm • Pregnancy |
| Pathanatomy | Fibrosis • Cancer |
| Pathphysiology | Syndrome • Pain • Heredity • Mental automatism • Jaundice • Diarrhea • Myopia |
| Chemistry | Urea • Uric acid • Dihydrogen monoxide |
Earlier or later menarche
If a mother or grandmother’s first menstruation occurred, for example, at the age of 15, then the girl’s maturation will most likely follow the same “scenario.”
However, most often the failure of the natural mechanism occurs due to diseases or characteristics of the girl’s body.
Before menarche - before 11 years of age
Functional causes: most often overweight or obesity. One of the estrogen (female sex hormones) is produced in adipose tissue, which leads to early puberty.
Diseases:
- Hypothyroidism is decreased production of thyroid hormones.
- Follicular ovarian cysts.
- Tumor of the ovary, adrenal gland, or central nervous system.
- Lesions of the central nervous system: meningitis, encephalitis, trauma and others.
Late menarche - over 14 years of age
Functional reasons:
- With malnutrition or excessive thinness due to lack of nutrients, the synthesis of sex hormones is disrupted. The body “extracts” estrogens from adipose tissue, but it is also not enough. A healthy girl should have at least 17% fatty tissue of her total body weight.
- Frequent stress and prolonged psycho-emotional stress lead to a failure in the formation of sex hormones.
- With intense exercise, estrogen production decreases.
Diseases:
- Insufficient production of sex hormones by the ovaries is most often associated with congenital underdevelopment of the ovaries.
- Diseases: diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma (depending on the severity and controllability of the course).
- Congenital malformations of the reproductive system - for example, underdevelopment of the uterus or ovaries.
- Chromosomal or genetic diseases.
16) PMS can lead to depression
PMS is a complex set of symptoms that occur due to fluctuations in sex hormone levels. That is, this condition is far from a myth! PMS can manifest itself with a variety of symptoms: swelling, breast tenderness and irritability, and even severe depression.
Severe PMS leading to distress and depression is also called premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Its obligatory condition is the cyclical manifestation of symptoms: 5-10 days before menstruation and ending at the moment of their onset.
Another remarkable property: PMS is characteristic only of ovulatory cycles and, if for some reason there is no ovulation, then PMS is not expressed.
Content
- Uterus during menstruation
- Pain during menstruation
- Menstruation during lactation
- Periods while taking birth control pills
- Thrush during menstruation
- Should I use suppositories during my period?
- Is it possible to donate blood during menstruation?
- Sports during menstruation
- Why you shouldn't sing during your period
- What to do if you have pain during your period?
Any girl must know what menstruation is and what changes occur in the uterus during menstruation.
Such knowledge helps to control your body, identify in time the symptoms of various diseases that cause cycle disruption, and prevent unwanted pregnancy. In our article you can read about why the uterus hurts during menstruation, how menstruation occurs during lactation and while taking contraceptive medications, and also why you can’t sing during menstruation and actively play sports.
15) The appearance of skin rashes before and during menstruation is not a pathology
During menstruation and PMS, fluctuations in the levels of the hormones estrogen and progesterone occur. There is a lot of progesterone, little estrogen - hence all the symptoms: chest pain, increased appetite.
Fluid retention during this period can lead to weight gain. The norm is no more than 2-3 kg. During menstruation, eat in small portions.
Due to hormonal changes and the excessive action of androgens, rashes may appear on the skin. This is not a pathology, but they can be prevented by prescribing combined oral contraceptives.
18) Permissible fluctuations in the menstrual cycle – /- 2 days
It happens that a girl’s period comes like clockwork, but this time there was a glitch. But foreign authors say that a delay of up to 20 days in patients with a regular cycle is a variant of the norm. There can be many reasons for this, the most common are stress, change in weather conditions, heavy physical activity.
But there may be other reasons - ovarian cysts, hormonal disorders, taking medications. My advice: if your period does not come on time, wait 7 days and contact your gynecologist. If, against the background of a delay, you have other complaints - vaginal discharge, abdominal pain - you need to contact a gynecologist as soon as possible.