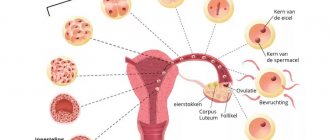
In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the main follicle, which is called dominant, grows and matures. Ovulation is the rupture of the wall of the dominant follicle and the release of the egg. It enters the fallopian tube. Within 24 hours she can be fertilized. The dominant follicle in the 2nd phase of the cycle is transformed into the corpus luteum, the main function of which is the synthesis of progesterone.
The corpus luteum functions for 10–12 days. If conception does not occur, the egg dies, the corpus luteum regresses, resulting in menstruation.
Symptoms of ovulation
- Mucous discharge from the vagina;
- Increased sex drive;
- Mood changes;
- Heaviness in the chest;
- Increase in body temperature.
For most women, ovulation is completely asymptomatic, although some representatives of the fairer sex say that they may experience the onset of such days in advance. During ovulation, a woman may feel a pulling pain in the lower abdomen. They can be very pronounced. This disorder is called ovulatory syndrome. The discomfort lasts for several days. A woman's discharge may change and become more viscous. During ovulation, her sexual desire increases. The maturation of the egg varies from day to day as follows:
- On days 5–7 from the beginning of menstruation, the cell is 4–5 mm in diameter.
- On days 8–10, a cover of connective tissue appears. The dominant stands out among other formations.
- On days 11–13, the diameter of the dominant reaches 16–18 mm. The remaining follicles regress. When the follicle volume is more than 16 mm, an egg-bearing tubercle appears. After 3-4 days, the egg matures and leaves the follicular cavity. She is able to become fertilized only during her life. It does not exceed 48 hours.
- On days 14–16, the next ovulatory cycle begins. The diameter of the remaining follicular cell, called the Graafian vesicle at this stage, is 20–22 mm.
Studies during one cycle are considered non-indicative. The duration of the menstrual cycle directly depends on the rate of maturation of the egg in its first phase, before ovulation. The standard classic version is 14 days with a 28-day cycle.
After the release of the egg, the second phase of the cycle begins (luteal) and for the same woman it is constant - from 12 to 16 days, but most often 14. In a long cycle, the maturation period of the egg is longer than in the standard one, and ovulation occurs later. For example, if a woman has a cycle length of 32-35 days, then the egg is released not in the middle of the cycle, as many believe, but on the 18-21st cycle or two weeks before the start of the next period.
A little physiology
During the first 1-2 years after the onset of menstruation, a regular menstrual cycle is established, and with it regular ovulations, which accompany the woman until perimenopause. The first day of the cycle is considered the first day of menstrual bleeding, the normal cycle is 21-35 days, the most common cycle is 28-30 days, the duration of bleeding is 3-5 days. With a regular 28-30 day cycle, ovulation occurs almost monthly; no more than 1-2 cycles a year go by without ovulation. The longer or shorter the menstrual cycle, the greater the likelihood of anovulatory cycles, in which the egg does not leave the ovary.
Let us consider in detail what happens in the female body during one cycle. In the first days of menstruation, the level of female hormones in the blood is the lowest. To raise it, a signal is sent from the higher nervous system to the pituitary gland to stimulate the ovaries and active production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) begins. Under its influence, several follicles grow in the ovaries, one of which will become dominant - leading, its size will be the largest, and a full-fledged egg will mature in it.
During its growth, the follicle is, on the one hand, a hormone-producing organ, and on the other, a nutrient medium for the growing egg and the future embryo. The level of estrogen produced by the growing follicle increases at first slowly, gradually, and then sharply. In response to this rapid increase in the concentration of estradiol in the pituitary gland, a preovulatory release of luteinizing hormone (LH) occurs, which provokes the rupture of the mature follicle and the release of the egg into the abdominal cavity. This process is called ovulation.
In the abdominal cavity, the egg is captured by the fimbriae of the fallopian tube, and subsequently fertilization occurs in the tube. And in place of the former dominant follicle, under the influence of the same LH, a new hormone-producing organ is formed, which is called the corpus luteum. Essentially these are the same cells, but different enzyme systems begin to work in them. The corpus luteum produces progesterone and partially estradiol within 13-14 days and prepares the uterus (mainly its inner mucous membrane) for implantation - the introduction of the fertilized egg into it. If pregnancy has occurred, a substance called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) begins to flow from the fetus into the mother’s blood. Early pregnancy diagnostic tests are based on determining the concentration of this substance in a woman’s blood or urine. This hormone causes the corpus luteum to work much longer than 13-14 days; in fact, it provides hormonal support for pregnancy during almost the entire first trimester. If pregnancy does not occur, then the corpus luteum undergoes reverse development, the level of hormones in the blood drops and rejection of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity begins - menstruation.
With a regular 28-day cycle, ovulation occurs on the 13-14th days of the cycle, and the probability of conception is highest on these days, they are about 33%. But if conception could only occur on one day per month, the chances of conception in each cycle would be very low. Fortunately, nature is much wiser, so the viability and fertilizing ability of sperm in the female body during the period of ovulation, that is, with a high concentration of estrogen, remains up to two, and according to some data - up to nine days, and the ability of the egg to conceive - up to 24- 36 hours. Accordingly, 2-3 days preceding ovulation and 1-2 days after ovulation become potentially “favorable”, that is, with a regular 28-30-day cycle, this is approximately the 10-17th day of the cycle. During this period, sexual intercourse is recommended at intervals of no more than once every 36 hours, because in less time the sperm concentration necessary for conception does not have time to accumulate in the sperm.
Ultrasound folliculometry
Several ultrasound procedures using a vaginal probe can calculate the day of ovulation or conception in a woman. A visit to the ultrasound room is carried out 3-4 times per cycle with an interval of every 2-3 days. If the cycle is irregular, you will have to visit the doctor 3-4 times, starting from the 7th day after the end of your period - every 2-3 days.
If the cycle is regular, it is worth conducting an ultrasound 2-3 days before the expected day. With a 30-day cycle, ultrasound monitoring begins on the 10-11th day of the cycle, i.e. approximately 4-5 days before the middle of the monthly cycle. Subsequent sessions of ultrasound monitoring of the egg are carried out every two days and last until the egg is released. The onset of the ovulatory period is confirmed by ultrasound diagnostics, when the day before the size of the follicle was 20-24 mm, and now the growth of the corpus luteum has begun. The procedure can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. During intravaginal examination, no preliminary preparation is required, the main thing is to empty the bladder. During an abdominal examination, a traditional examination is performed through the abdominal wall. In order for it to pass without difficulties, three days before monitoring it is necessary to exclude all foods that can cause flatulence or bloating, and on the day of the examination it is necessary not to eat and drink at least a liter of water.
Ovulation, conception and gender of the child
Research conducted at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (North Carolina) has shown that not only the actual conception of a child, but also its gender depends on the time of conception in relation to the time of ovulation .
The chance of conception is highest on the day of ovulation and is estimated at approximately 33%. A high probability is also noted on the day before ovulation - 31%, two days before it - 27%. Five days before ovulation the chance of conception is estimated to be 10%, four days before ovulation is 14% and three days before ovulation is 16%. Six days before ovulation and the day after ovulation, the likelihood of conception during sexual intercourse is very low.
If we consider that the average “life expectancy” of sperm is 2-3 days (in rare cases it reaches 5-7 days), and the female egg remains viable for about 12-24 hours, then the maximum duration of the “dangerous” period is 6- 9 days and the “dangerous” period correspond to the phase of slow increase (6-7 days) and rapid decline (1-2 days) before and after the day of ovulation , respectively. Ovulation , as noted above, divides the menstrual cycle into two phases: the follicle maturation phase, which with an average cycle duration is 10-16 days and the luteal phase (corpus luteum phase), which is stable, independent of the duration of the menstrual cycle and is 12- 16 days. The corpus luteum phase refers to the period of absolute infertility; it begins 1-2 days after ovulation and ends with the onset of a new menstruation.
Ovulation tests
If you can track the follicle using ultrasound, then ovulation tests can be done at home. They work like this: 24–36 hours before the release of the egg from the ovary, the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine sharply increases. A day or two before, he seems to “push” the egg through the wall of the ovary.
Ovulation tests determine whether the amount of the hormone is increased. They also allow you to calculate days favorable for conception. 5-6 days before expected ovulation, tests are performed twice a day. Since we are interested in ovulation in a cycle of 30 days, we need to start taking measurements from about day 13. If ovulation is not observed, then the second stripe will be absent. But the day before or on the 15th day, the test line will be as bright as the control line. This sign indicates that the upcoming ovulatory period is coming, which should be expected in the next 24 hours. You need to immerse the strip in a container with fresh urine for a few seconds, then place it on a dry surface and after about five minutes read the result. testing is carried out in a similar way to tests to detect conception.
Basal temperature method
This method involves measuring the temperature in the rectum (rectally). It is measured immediately after sleep during the cycle. To do this, you need to use one thermometer. You need to knock it down the night before bedtime. Measurements are taken in the morning, immediately after waking up. Correctly measuring basal temperature will help determine whether a patient is ovulating normal, early or late. This is one of the easiest ways to determine favorable days for conception. This should be done after waking up in the morning, but you cannot get out of bed. I just woke up, and right after the thermometer. All results must be scrupulously noted on a special graph. At the end of the cycle, all points with measurement results are connected into a broken graph. During menstruation, measurements are not taken. On the first day of the cycle, the temperature reaches 36.9°C. A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2°C – 36.4°C. An increase in temperature to 37°C - 37.4°C indicates that ovulation is occurring. If the temperature rises after ovulation, the woman is likely pregnant.
Ovulation and contraception
Some women experience peak sexual arousal around the days of ovulation . However, the use of a physiological method of contraception from pregnancy, based on sexual abstinence during ovulation , is especially difficult for young spouses, whose frequency of sexual intercourse reaches a fairly high level. In addition, with strong love excitement and nervous stress, additional ovulation can occur (especially with episodic, irregular intercourse) and then not one, but two eggs mature in one menstrual cycle. This should be kept in mind when choosing one or another method of contraception.
Calendar method
This method of determining ovulation is suitable for those who have a regular menstrual cycle. It is 14 days before the start of a new cycle that full ovulation occurs. In order to determine the calendar of days for conception, it is necessary to analyze the last 3 months. The first day of the menstrual cycle is the first day of menstruation. It is 12–14 days before the start of a new cycle that full ovulation occurs. The cycle changes under the influence of various factors - health status, nervous tension, stress, physical activity, climate change when traveling, and so on.
When does fertilization occur after ovulation?
After ovulation, the sperm has about a day to meet the egg and fertilize it.
If conception does not occur, the egg is destroyed in the fallopian tube within 24 hours, and after about 14 days the woman begins menstruation again - this is the release of an unfertilized egg.
If the meeting of the sperm and the egg was successful, the fertilized zygote descends into the uterus within 6–12 days, after which it is fixed there and pregnancy occurs. With the onset of pregnancy, the ovaries stop producing new eggs, so there is no fear that ovulation occurs during pregnancy - re-fertilization is impossible.
Why doesn't ovulation occur?
Ovulation may be absent for various reasons. They can be divided into 2 groups: physiological and pathological.
Do not worry about the lack of ovulation in the following cases:
- Pregnancy: during pregnancy and in the first months after childbirth, women do not ovulate;
- Breastfeeding: if you breastfeed your baby, including at night, ovulation does not occur;
- In young girls (12–14 years old), when the menstrual cycle has not yet been regulated;
- Menopause: when menstruation stops, ovulation also stops;
- Taking oral contraceptives: normally, in this case, ovulation should not occur either.
Ovulation - reasons for absence
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Inflammation of the genitals.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Dysfunction of the adrenal cortex.
- Tumors of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
- Systemic diseases.
- Stress.
- Early ovarian failure.
- Overweight or underweight woman.
- Starvation.
- Chronic lack of sleep.
- Mental and physical overload.
- Past infectious diseases of the nasopharynx.
- Radioactive exposure.
- Taking certain medications.
Expert opinion of a doctor
Barakhoeva Zarema Bekhanovna
Reproductologist, obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D.
Whether pregnancy occurs or not depends on the motility and viability of sperm. If sexual intercourse occurs too often, the relative number of sperm in the semen decreases. Therefore, a couple who is “striving” to conceive should abstain before ovulation to increase their chances. Using the calendar also helps prevent unwanted pregnancies. But this method should not be used by women who have hormonal problems and irregular cycles.