Normal testosterone levels in men, women and children
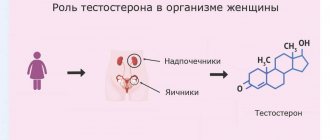
The study of testosterone levels is not limited to men, because women and children also produce small amounts of this substance in their bodies. The only difference is the place of production of the hormone: in men it is synthesized in the testes, in women ¾ in the adrenal cortex and a small part ¾ in the ovaries. In the female body, the function of the hormone is aimed at the development of secondary sexual characteristics, stable and healthy functioning of the reproductive system, as well as the synthesis of some protein components.
Children and adolescents need sufficient amounts of the substance due to active growth and development. Without the hormone in adolescence, the development of the musculoskeletal system, the growth of the bone skeleton and the development of the muscular system are impossible.
Testosterone circulates in the bloodstream both in free form and in a protein-bound state. Only 2% of the substance is the free fraction of the substance; the remaining amount is associated with albumins, globulins and other proteins of the human body.
The doctor usually prescribes a testosterone test in men, women or children to assess its total, total fraction. If the study revealed low testosterone, a more specific diagnosis will be needed - a test for bound testosterone.
The testosterone level in men is within certain limits depending on the age of the person being studied:
- in boys under 18 years of age, the concentration of the hormone in the blood ranges from 0.2 nmol/l to 37.67 nmol/l;
- in men aged 18-50 years ¾ from 5.76 nmol/l to 30.43 nmol/l;
- in men over 50 years old, ¾ in the range of 5.41–19.54 nmol/l.
- Female testosterone levels are considered normal if they are within the following values:
- in girls under 18 years of age, the concentration of the hormone in the blood ranges from 0 to 4.73 nmol/l;
- in women over 18 years of age ¾ from 0.31 to 3.78 nmol/l;
- in pregnant women, the concentration of the hormone increases 3-4 times compared to the age norm;
- during the postmenopausal period ¾ 0.42–4.51 nmol/l.
however, normal values are sometimes subject to individual fluctuations. Therefore, the interpretation of the test should be handled solely by your doctor.
TESTOSTERONE LEVEL DEPENDS ON:
- age of a man: after 25-30 years, hormone production begins to decrease by about 1% per year.
- level of physical activity.
- health conditions (the situation is worsened by various chronic diseases, obesity, diabetes, etc.)
- psychological health - the same notorious stress will negatively affect the production of testosterone.
In addition, the analysis time will also affect the indicators. So, in the morning hours from 4 to 8 am, the maximum concentration of the hormone is observed, in the evening – the minimum. So, when testosterone fluctuates towards a deficiency or excess, a man’s condition worsens. This can happen gradually. So that a man may not even understand what is happening to him and look for the cause anywhere, except in the state of his own hormones.
When do hormone levels increase?
In women, a slight increase in hormone levels can be observed when taking COCs (combined oral contraceptives), as well as during pregnancy. In both men and women, increased testosterone is a consequence of taking anticonvulsants (for example, therapy for epilepsy), as well as during treatment for hyperthyroidism.
An increase in testosterone is a clear signal that allows one to suspect the development of the following conditions in a patient:
- development of adrenogenital syndrome in women;
- the risk of tumor formation in the ovaries in women and testicles in men;
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease ¾ endocrine pathology, in which there is excessive synthesis of ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) at the level of the brain, which leads to increased activity of the adrenal cortex, where, in particular, testosterone is produced;
- Reifenstein syndrome (male pseudohermaphroditism);
- tumor process in the pituitary gland;
- excessive physical activity of patients;
- in some professional athletes taking steroid drugs.
Increased testosterone ¾ is an important symptom that cannot be ignored. When testosterone increases, the doctor, as a rule, conducts additional diagnostics to find out the reasons for the change in the level of the hormone in the patient’s body.
Testosterone hormone in women - where does the danger lie?
Femininity does not mean that women should have no testosterone at all.
Everyone knows that excess testosterone in women causes masculinity, infertility, excess hair growth, as well as increased excitability and aggression. But low testosterone in women and men leads to decreased libido, physical weakness, hair loss, excess body weight, osteoporosis, atrophic changes in the skin, decreased mood, and even depression. Therefore, both high and low testosterone pose a danger to women’s health.
Having learned from your doctor about testosterone, how to increase its level, you can use simple methods that are available to everyone and approved by modern medicine.
When does a decrease in hormone levels occur?
In men over 50 years of age, reproductive function begins to decline physiologically, which is accompanied by a decrease in testosterone levels. However, doctors often talk a lot about how to increase testosterone in men in natural ways, so you should not worry about a decrease in the level of the hormone if this is the age norm.
Cause for concern arises when low testosterone appears in a man aged 18-50 years, and the patient's hormone level differs significantly from the testosterone norm for men in this age group.
A decrease in the level of the substance often indicates the development of the following pathological conditions:
- diseases of the pituitary gland ¾ functional or organic lesions of the pituitary gland, which lead to disruption of the synthesis of gonadotropic hormones, which affects the production of testosterone in the gonads;
- pathology of the hypothalamus, which controls the function of the pituitary gland;
- pathology of the adrenal glands: insufficiency of adrenal cortex function, other diseases;
- active use of certain medications, glucocorticosteroid substances;
- hypogonadism (insufficient function of the gonads);
- chronic prostatitis ¾ inflammation of the prostate gland;
- male obesity, female alcoholism;
- malnutrition ¾ insufficient amount of protein in the diet, increased level of “fast” carbohydrates that are easily digested;
- certain dietary rules ¾ vegetarianism, long-term fasting;
- liver cirrhosis, renal failure;
- endocrine disorders that cause an imbalance in the ratio of male and female sex hormones in the human body.
A decrease in hormones in a woman by ¾ is not a very dangerous and formidable sign. As a rule, hormone levels naturally decrease during menopause. However, in this case, it may be necessary to increase testosterone in a natural way, because a lack of the hormone in the body often leads to osteoporosis, increased bone fragility, and affects the psycho-emotional sphere. For example, a woman may experience long periods of depression, insomnia, and even suicidal thoughts.
The level of the hormone in the body is determined using a special blood test. A diagnostic study allows you to detect the problem and begin drug treatment of the patient’s pathology.
Diseases that cause testosterone deficiency
It is known that some diseases (acute and chronic), as well as medications taken in combination with age-related changes, can provoke testosterone deficiency. Such diseases include:
- coronary heart disease;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- obesity;
- arterial hypertension;
- bronchial asthma;
- obstructive pulmonary disease in chronic form;
- diabetes.
In particular, a decrease in testosterone levels causes chronic alcoholism.
What to do with high and low testosterone levels?
High testosterone or low testosterone ¾ are manifestations of some physiological and pathological processes occurring in the human body. Often, a doctor prescribes a blood test for testosterone if he already suspects the formation of any pathology.
For example, the following conditions are considered indications for research:
- doctor's suspicion of female or male infertility;
- tumor process in the adrenal glands or gonads;
- the patient has a certain degree of obesity;
- formation of osteoporosis;
- skin manifestations ¾ acne, which may indicate a significant increase in testosterone levels, oily seborrhea;
- baldness.
In addition, a doctor prescribes a testosterone test in men if he suspects erectile dysfunction or decreased function of the gonads (hypogonadism). Low testosterone is often found in men who experience decreased libido. It is also necessary to check testosterone levels if you suspect the development of chronic prostatitis or osteoporosis. An enlarged mammary gland, as well as insufficient hair on the face and chest, also become a suspicious symptom. Disruption of the process of puberty in boys during adolescence, excessive sweating are also indications for checking testosterone levels.
Women are recommended to undergo diagnostics if they have the following manifestations or suspect the formation of such diseases:
- unstable menstrual cycle, cycle disorders;
- the appearance of uterine bleeding;
- disturbances in the course of pregnancy ¾ miscarriage;
- the formation of multiple cysts in the ovaries (polycystic ovary syndrome);
- endometriosis.
Thanks to the testosterone test, the doctor will be able to detect the pathology that has arisen in the patient’s body. Diagnosis of testosterone levels is one of the most effective methods for assessing the risk of formation of a tumor process and disorders in the reproductive system of men and women. So, after receiving the results of the study, the doctor selects the treatment tactics necessary for the patient with individual dosages of drugs, and after some time, using repeated analysis, monitors the dynamics of treatment.
Sometimes the doctor recommends changing your diet and adding testosterone-boosting foods to your daily meals. At the appointment, the doctor will talk about how to increase testosterone in men in natural ways if the analysis revealed a decrease in the concentration of the hormone. Therefore, the question of how to do this is not too pressing in modern medicine: effective and affordable treatment methods ensure rapid restoration of the patient’s body functions. Naturally, during therapy and after treatment it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
How does testosterone deficiency manifest?
The effects of testosterone on the body are described above, respectively, deficiency can manifest itself in various symptoms, the most common are:
- depression
- decrease in concentration
- fatigue
- decreased muscle mass and strength
- decreased sexual desire
- erectile dysfunction - problems with developing and maintaining an erection
- infertility caused by a decrease in sperm count
- osteoporosis (cause of brittle bones)
- tides
- reduction in size and soft consistency of the testicles
- anemia (low red blood cell count)
- reduction in prostate size
Preparing for diagnosis. How is the analysis carried out?
At the first stage, the patient receives a referral for research. The document is issued to the person by a gynecologist, endocrinologist, andrologist, reproductologist ¾ doctor to whom the patient turned for advice. However, diagnosis requires careful preparation. This is necessary to increase the accuracy of the study.
For example, it is prohibited to donate blood for testosterone if during the day before the test you performed ultrasound diagnostics, fluorographic examination, or underwent physiotherapeutic procedures. Rectal examination during the day can also distort the results of a blood test.
The patient is obliged to warn the doctor about taking hormonal drugs (for example, if a woman takes combined oral contraceptives as a method of contraception), as well as gel-based substances and ointments. The doctor will decide on the need to temporarily stop taking medications if this does not threaten the patient’s condition. It is allowed to donate blood for testosterone 2 weeks after stopping taking hormonal medications.
24 hours before diagnosis, any physical activity or drinking alcohol is prohibited. In addition, you need to stop smoking and change your diet slightly: do not eat fatty or fried foods the day before the diagnosis. Blood sampling for testosterone levels is carried out in the morning (before 11 am) on an empty stomach. During this period, the amount of the hormone in the blood reaches its maximum value.
In addition, to avoid distortion of the results during the diagnosis (for example, increased testosterone or low testosterone when receiving diagnostic results), it is necessary to stop drinking coffee, stimulating drinks, and also avoid stress and nervous tension 1 hour before the procedure.
Attention! The patient should warn the doctor if his diet differs from the normal diet. For example, followers of vegetarianism or people who exclude certain foods from their diet need to tell their doctor about this in order to correctly interpret the diagnostic result.
Preparing for a blood test for testosterone in women has its own characteristics and depends on the menstrual cycle. It is believed that the collection of biological material should be carried out on days 6-7 of the menstrual cycle. The patient's blood serum is used as diagnostic material. The research method is called enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Diagnosis of hypogonadism
The diagnosis of hypogonadism in men is established on the basis of anamnesis, clinical picture, confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies. Recent guidelines recommend that the diagnosis of hypogonadism should be made only in men with symptoms, external manifestations, and clearly reduced serum testosterone levels [2]. However, an analysis of the level of morning total testosterone in serum is recommended as an initial diagnostic test for hypogonadism.
Figure 2-3. Different types of hypogonadism
To calculate the level of free testosterone, you can use the online calculator www.issam.ch/freetesto.htm.
Table 2. Testosterone standards
If necessary, determine the levels of SSSH, FSH, LH, prolactin. High risk factors for developing hypogonadism:
- space-occupying formations of the hypothalamic-pituitary region;
- surgical interventions and/or radiation in the area of the sella turcica;
- long-term use of glucocorticoids, ketoconazole, opioids;
- diabetes mellitus, infertility, osteopenia and osteoporosis.
General population screening is not practical [3].
To identify a group at risk of hypogonadism, specialized questionnaires can be used.
Progress of the study
The patient is recommended to come to the laboratory 30 minutes before blood sampling in order to adapt to external conditions and normalize breathing. In a laboratory setting, blood is taken from a patient’s vein.
A standard set of materials is used: a disposable syringe or a special system. As a rule, the patient does not experience discomfort because a small amount of blood is needed for diagnosis. After 1-2 days, the laboratory provides diagnostic results on a special form. The interpretation of the results of the analysis is carried out exclusively by a doctor who knows the characteristics of the patient’s body.
The level of the hormone can be influenced by many different factors, ranging from stressful situations and nervous tension, to a specific diet and the presence of bad habits. Chronic diseases, episodes of decreased immune defense, use of steroid substances - these conditions can cause changes in the amount of testosterone in the human body.
In addition, testosterone levels often depend on the time of year.
For example, in the fall there is an increase in the hormone in the human body. Therefore, independent interpretation of research results in most cases turns out to be incorrect. So, the analysis should only be deciphered by your attending physician.
Treatment options for men with a similar situation?
There are many treatment options and regimens for patients with low testosterone levels. Testosterone replacement therapy can be given as a gel applied to the skin, intramuscular injection, long-acting granules, patches or tablets. The most common option is skin gel therapy, which is used in approximately 70% of patients. Men simply rub the gel onto their shoulders or stomach after showering. Approximately 20% of patients use testosterone injections and 10% of men use testosterone patches. a small percentage of patients (about 3%) use testosterone in the form of tablets or implantable testosterone pellets.
How to maintain hormone levels?
An increase in hormone levels, depending on the reasons, is often corrected with medication. The doctor prescribes a specific treatment regimen and then monitors the effectiveness of the treatment. However, there are situations when testosterone levels are low, and a man thinks about how to increase it in natural ways. This is a simple process if it does not concern organic pathology, and the decrease is explained only by functional reasons. Many doctors talk about how to increase testosterone, highlighting several main ways to solve the problem:
- Proper and rational nutrition. Doctors insist on eating foods rich in zinc, vitamins, microelements and other beneficial substances.
- Rational physical activity. During active sports, testosterone is actively released, which allows you to increase the level of the hormone in a natural way.
- Getting rid of excess weight, eliminating factors that contribute to excess weight gain (decreased physical activity, consumption of fatty, fried, overly processed foods).
- Competently designing a working day that corresponds to your biological clock. Rational distribution of work and rest time will help the body clearly and correctly adjust the hormonal balance.
- Refusal of nutritional supplements and products that stimulate the production of estrogen - the female sex hormone, which is found in small quantities in the male body. With the active production of estrogen, the intensity of testosterone synthesis in a man decreases.
These five ingredients will help increase testosterone naturally. Special attention must be paid to proper diet, because nutrients, vitamins, and minerals supplied with food become the basis for metabolic processes in a man’s body. Therefore, it is very important for a man to follow the principles of a healthy diet.
Classification
Depending on the level of damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system, the following are distinguished:
- hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (primary) in men. Testosterone production by the testicles is reduced or absent. Here we can distinguish congenital forms (Klinefelter syndrome - Fig. 1, anorchidism) and acquired forms (trauma, radiation, chemotherapy, other toxic lesions of the testicles, late initiation of treatment for cryptorchidism);
- hypogonadotropic (secondary) hypogonadism in men. Pituitary hormones that stimulate testosterone secretion are reduced or absent. This group also includes congenital forms (Kalman syndrome, isolated LH deficiency, other rare congenital diseases accompanied by hypogonadism), and acquired forms (tumors of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, their surgical treatment or radiation therapy, hemorrhages in them, etc.);
- normogonadotropic hypogonadism. This condition is characterized by low testosterone production with normal levels of gonadotropins. It is based on mixed disorders in the reproductive system, expressed not only in primary damage to the testicles, but also in hidden insufficiency of hypothalamic-pituitary regulation. Typical examples are hypogonadism in obese men, hypogonadism with hyperprolactinemia (Fig. 2) and hypothyroidism, age-related hypogonadism (Fig. 3), iatrogenic hypogonadism;
- hypogonadism due to target organ resistance (feminization as a result of tissue receptor resistance to androgens; 5α-reductase deficiency; deficiency of estrogens, which in physiological concentrations are modulators of the normal effects of testosterone).
Figure 1. Example of patients with Klinefelter's sign
Based on the time of occurrence, prepubertal and postpubertal hypogonadism can be distinguished.
The effect of testosterone on weight in women
What is testosterone and how does it work?
Testosterone? But this is a male hormone, isn’t it? Not really, it’s not only masculine. Before menopause, women's ovaries also produce testosterone, and in general our body produces even more testosterone than estrogen, if we compare them in the same units. As menopause approaches, as the body's production of hormones decreases, women lose on average more than 50% of their normal testosterone. Testosterone belongs to a group of hormones called androgens, from the Greek "andros", which means "masculine". All androgens are synthesized from cholesterol in women by the ovaries, in men by the testes, and also, although to a lesser extent, by the adrenal glands of both men and women. Androgens are created from chemical "building blocks" (or "precursor" molecules) in the body's fat tissue, muscles, liver, skin and brain. Therefore, overweight women have high androgen levels, which can subsequently have a negative impact on weight. However, in the ovaries and adrenal glands, these “precursor” molecules are modified, therefore, it turns out that the ovaries and adrenal glands are both directly and indirectly responsible for the production of testosterone in a woman’s body.
Women need testosterone: after all, it is a hormone that activates sex receptors in the brains of men and women and stimulates normal sexual desire. Does this hormone play an important role in regulating the ratio of fat and muscle mass in the body? This interesting hormone has many positive effects on a woman's body, especially when it comes to reducing body fat and building muscle mass. That's why testosterone is called an anabolic hormone - it stimulates the growth of muscle and bone tissue and uses fat to do this, converting it into energy. Remember, muscle is the best fat-burning machine, so if you're gaining weight as you age, one way to stop it is to improve your muscle structure. Which means checking your hormone levels!
There is a myth created by sellers of hormonal creams, which do not require a prescription, that by using these creams you can give the body “building blocks”, it will create testosterone and estrogen, the basis of which will be progesterone. It is not true! This process requires enzymes and reactions that occur only in the functioning ovaries of a woman and the testicles of a man. If you are menopausal, have had a hysterectomy or fallopian tube ligation, or have been exposed to other factors that lead to the loss of these functions, then you do not have the system that converts progesterone into testosterone and estradiol. It turns out that a lot of progesterone accumulates in your body, which cannot be converted into testosterone.
The cessation of testosterone production by the ovaries does not simply occur with menopause, although this is what most of us know. Even before menopause, women's adrenal glands reduce androgen production by 50%, and testosterone produced by the ovaries gradually stops entering the body. One of the reasons for the decrease in the active form of testosterone after menopause is that the “block” molecule decreases by 50% when the ovaries stop producing hormones. Thus, you lose the "blocks" normally produced by the ovaries, as well as the ovarian enzymes that carry out the entire process. Many doctors do not realize that a decrease in estrogen production entails a decrease in testosterone , since the "blocks" and enzymes found in the ovaries cease to exist.
These changes mean that you begin to lose muscle mass and become inexorably fatter in the years before your period stops, not to mention that your sex drive and ability to get aroused are significantly reduced! Now women live another 30-40 years after the production of ovarian hormones has ceased, i.e. they have to live for a long time without these hormones, which are very necessary for metabolism. Has anyone ever heard of a man who would like to live with only half his normal amount of testosterone?
If you had a hysterectomy to remove your ovaries before your body reached menopausal hormone levels, the changes are even more dire. The concentration of testosterone in the blood drops significantly within 24-48 hours after surgery. Since there are no more ovaries to produce testosterone or to more efficiently convert DHEA into testosterone, there is a sharp shortage of this strength-giving hormone. This is a huge shock to the body and another reason why women gain excess weight after a hysterectomy.
Even if the ovaries are left in place, and you did not have a hysterectomy until you were thirty, 60-70% of women experience a decline in hormone levels to menopausal levels 3-4 years after surgery. This is a scary statistic, especially if you had surgery at age 34 and you think (or have been told) that your ovaries will continue to function normally until you are 50! It is believed that this rapid hormonal decline after hysterectomy occurs due to decreased blood flow to the ovaries as a result of cutting and pinching the uterine artery during surgery.
In addition, if you have just started estrogen therapy, the amount of free, biologically active testosterone decreases even more because estrogen increases the release of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) , which binds most testosterone . This is one of the reasons that after a hysterectomy, women lose muscle mass, gain weight, and lose sex drive and strength. They think that this is a consequence of surgery, but, as a rule, the main reason for this is not surgery at all. In order to replenish the hormone levels you had before surgery, optimally formulated supplements containing both estradiol and testosterone are required.
Doctors tend to think that testosterone is not important for women, and many are still unsure whether to prescribe this hormone, so the use of testosterone therapy in treating women is a relatively new issue. The amount of active androgens in the female body is, of course, much lower than in the male body, but they are very important for maintaining a number of vital functions in women. Fortunately, women today are aware of the importance of androgens such as testosterone and DHEA, and are asking doctors to provide them with more information on how to measure them and remove what has accumulated in the body.
How does testosterone affect your weight?
Testosterone was initially associated with sexual desire (libido) in men and women; however, it also has a number of other effects on all body systems, including fat content in areas where it is deposited. Changes in hormonal balance during menopause can occur in various forms, but two of them are the most important because they affect testosterone production: a decrease in estradiol and an increase in estrone in relation to the available amount of testosterone . The consequence of this is that the effect of testosterone is very pronounced: you feel the “male” effect of this hormone in the distribution of fat, muscle mass, facial hair growth, effects on the voice, sexual desire and activity level.
A decrease in estradiol levels in adulthood causes a decrease in SHBG. Because this transporter protein binds sex hormones, their decrease means that more androgens are now in the blood in free or biologically active form. As you reach your forties and your testosterone and DHEA levels decline, most of it remains in the active (free) form, but less estradiol exerts its “feminine” effects: so your body goes from “pear-shaped” (feminine) the type changes to “apple-shaped” (male), i.e. more fat is deposited around the waist, more hair appears on the face, and hair falls out on the head. And it doesn't mean you don't have the willpower to lose belly fat; It's just that the hormone ratio is not in your favor.
When estradiol stops being produced, the dominance of androgens produced by the adrenal glands causes even greater negative metabolic changes in the woman’s body: an increase in blood pressure, cholesterol levels in general, a decrease in HDL (“good”) cholesterol and an increase in LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, insulin and cortisol. All of these changes contribute to an increased risk of heart disease, hypertension and diabetes in women over 35 years of age.
At first, doctors believed that it was testosterone negatively affected cholesterol levels. Recent research has revealed, however, that testosterone helps control the normal functioning of mechanisms such as the dilation of blood vessels when blood pressure decreases, but only if it enters the body along with the required level of estradiol. If this condition is not met, testosterone and DHEA stimulate the formation of blood clots, narrowing the walls of blood vessels (atherosclerosis). If androgens enter the body with estrogen, then they have the exact opposite effect on the walls of blood vessels and prevent the formation of cholesterol blood clots.
Throughout a woman's life, testosterone plays an important role in maintaining muscle mass, that remarkable fat-burning mechanism. Decreased testosterone levels mean a reduced ability to build muscle, even if you exercise several times a week. Testosterone is important for bone formation and the prevention of osteoporosis, even more so than estrogen, which is protective because women lose it as they age. Moreover, testosterone helps maintain proper energy levels. A decrease in this hormone is one of the undiagnosed causes of “chronic fatigue.” Women underwent numerous comprehensive medical examinations and spent hundreds or even thousands of dollars on tests and treatments to identify the causes and cure chronic fatigue syndrome, but never had a blood test done to measure their testosterone levels.
Effects of testosterone on muscle tissue
During menopause, when women lose both estradiol and testosterone, they lose muscle and bone tissue faster than men because testosterone levels drop more sharply and by a significant amount. Testosterone in men disappears more slowly over many years, so they lose muscle and bone tissue later in life and gradually. Women's loss of testosterone affects the formation of fat in the breast area, because this hormone is responsible for the formation of new muscles and maintains their health and normal functioning. Losing muscle tissue slows down your metabolism. You're getting fatter. As you age, you need the right levels of testosterone in your body to maintain your metabolic rate and healthy muscles! However, there must be a balance between it and estradiol, otherwise you will start gaining pounds on your belly!
Effect of testosterone on the brain
There are some pretty good reasons why I want to talk about this in relation to weight management in adulthood. Testosterone not only activates sex receptors in the brains of men and women, it also has an antidepressant effect and can affect mood swings, increasing feelings of satisfaction with life. Testosterone improves the ability to perform cognitive tasks. It is involved in the secretion of brain chemicals that are essential for maintaining a healthy weight! For some women, depression is not depression at all, but simply a lack of testosterone in the body. But if testosterone levels become too high (due to excessive secretion of the body or due to excessive use of supplements containing it), women experience sleep disturbances, they experience too many dreams and even nightmares, some of which contain aggression and violence, and sometimes even unpleasant ones. , but strong sexual desires. Excess testosterone compared to estradiol causes an increase in appetite and fat deposits around the waist. Excessive use of testosterone, for example when building muscle, in men and women causes abnormal behavioral reactions, such as excessive irritability, mood swings and short temper, aggressiveness. When the body has elevated levels of other androgenic steroids, such as DHEA and "andro" (androstenedione), the same abnormalities occur. Without a doubt, the answer lies in hormonal balance.
So how do these types of brain activities affect you if you're trying to lose weight? Think about the time your therapist prescribed you a tricyclic antidepressant to help you regain your strength and normalize your mood, thinking that depression was to blame for your overeating. It turns out that testosterone is your natural antidepressant hormone. It has a significant activating effect on the brain, mainly by increasing the level of norepinephrine in the brain. This is the same process as with tricyclic antidepressants such as desipramine (norpramin) and imipramine (tofranil). But the problem with using these drugs is that they increase appetite and body fat. Has anyone checked their testosterone levels before prescribing an antidepressant? It seems that in our reliance on medications, we have forgotten about the calming effect of natural hormones - testosterone and estradiol! And this is in addition to their ability to burn fat!
The latest developments have revealed the following: in order for testosterone to act in a given direction, it is necessary to have an optimal level of estradiol (estrogen). Testosterone receptors in the brain seem to be produced by the presence of estradiol. Without enough estrogen to start the engine, even the testosterone our bodies produce cannot function properly in the brain centers. Therefore, the presence of estradiol is important - because it determines the successful action of testosterone.
The effect of testosterone on sleep
Sleep disturbances can promote excess weight gain because normal cortisol production is disrupted and insulin release is increased. Excessive testosterone , especially with reduced estradiol, can further increase sleep disorders, because testosterone is a very important stimulant hormone. If you give a man or woman testosterone before bed, the hormone will prevent you from falling asleep - sleep will be interrupted, and you will have disturbing dreams in which violence or aggression is present. Afterwards, you wake up feeling like you've been fighting someone all night. The brain-boosting effect of testosterone disrupts stage 4 sleep, especially in women. At this stage, muscle tissue is built up and restored and growth hormone is released, which affects muscle formation. If phase 4 is not smooth, your muscles will not recover, despite all the testosterone in your body. For both sexes, it is best to take testosterone in the morning to ensure that you have the energy you need for the day without disrupting your sleep.
What should you do if you suspect you have too much testosterone in your body?
High levels of androgens in a woman’s body can lead to serious illnesses and an increase in fat deposits in the waist area. It is very important to properly measure your levels of these hormones if you suspect you have too much of them in your body. What should you pay attention to? For fat deposits in the chest area, excessive body hair growth, baldness, acne - all of these require checking the levels of testosterone, dehydrotestosterone, DHEA, DHEA-S. If their content is too high, further examination is necessary to determine the reasons. You may have polycystic ovarian syndrome or an androgen-producing tumor of the ovaries or adrenal glands.
We remind you that you can undergo all hormonal examinations in any treatment room at the OLIMP KDL. You must also remember that some tests are taken strictly at a certain period of the menstrual cycle.