Anomalies of the uterus and vagina are observed in 4.3-6.7% of all women of childbearing age. They cause infertility in every eighth case, and in 12.6-18.2% they cause recurrent miscarriage, placental abruption, abnormal fetal position and other complications.
One of the most common anomalies of the uterus is its infantility (also called hypoplasia) - a defect associated with the small size of the main reproductive organ. With a slight decrease in the size of the uterus, the anomaly does not manifest itself with any symptoms, but a significant degree of hypoplasia can be suspected even in adolescence - by the late appearance and extreme pain of menstruation.
Causes of uterine infantilism
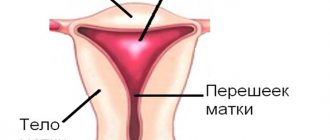
A girl’s uterus begins to form during the prenatal period – at the 5th week of its development. By the time of birth, it is fully formed, but still very small. Until the age of 9-10, it grows slowly, spending the first 3 years in the abdominal cavity, and then descending into the pelvis. From 10 to 13-14 years, her growth accelerates greatly, and by the time of puberty she should reach her normal size: 48±1 mm in length, neck length 26±1 mm (that is, a total length of 72-76 mm), 33 mm in thickness, 41 mm in width. If this does not happen, then one of the situations has occurred:
- The uterus either initially failed to develop: it was prevented either by intoxication that affected the mother’s body during the prenatal period, or a disorder occurred at the level of genes or chromosomes, due to which the organ will no longer be able to grow;
- The uterus began to develop, but the girl’s body (mainly her endocrine system) was adversely affected. This could happen as a result of:
- suffered severe influenza: the virus “likes” to affect the main endocrine organs - the hypothalamus and pituitary gland;
- frequent respiratory tract infections: ARVI, chronic tonsillitis;
- nicotine or drug intoxication;
- constant stress (they also affect the hypothalamus), including those caused by significant mental and physical stress at school;
- hypovitaminosis;
- tumors of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus;
- damage to the ovaries by mumps, measles, rubella viruses;
- insufficient nutrition of the girl, including as a result of her following a diet for weight loss;
- surgery on a girl's ovaries.
Why does pathology occur?
The main causes of acquired hypoplasia are hormonal disorders. The pituitary gland, ovaries and hypothalamus are involved in the production of sex hormones. Any malfunction in their work can lead to a stop or slowdown in the girl’s puberty.
All factors that can cause hormonal imbalances can be divided into 2 large groups:
External:
- surgical manipulation of the genitals in childhood or adolescence;
- disruption of the central nervous system as a result of injury or disease;
- heavy physical activity, such as professional sports;
- poor nutrition, diets during puberty;
- bad habits, teenage alcoholism is especially dangerous.
Internal:
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- malignant formations;
- congenital defects of the liver, heart;
- renal failure;
- autoimmune diseases;
- ovarian failure;
- unfavorable heredity.
Congenital pathology may also occur. In this case, this is due to the influence of unfavorable factors on the body of a pregnant woman. Sexual characteristics in the fetus begin to form a few weeks after conception. During this period, a woman may not yet know about pregnancy. Therefore, smoking, alcohol, taking medications or infectious diseases can become provoking negative factors that can cause disturbances in the process of formation of the fetus’s gender.
Severe emotional shocks can also harm the hormonal system and cause disruptions.
An underdeveloped uterus can become deformed over time. It develops a bend in the upper part, and the neck takes on the appearance of a cone.
Signs of an infantile uterus
If the teenage uterus does not manifest itself in any way, and a woman can only find out about this anomaly during pregnancy or even after childbirth, then more severe degrees of hypoplasia have their own symptoms:
- late onset of menstruation (after 16 years);
- painful periods;
- irregular periods;
- decreased libido;
- difficulty achieving orgasm;
- infertility or recurrent miscarriage.
Uterine hypoplasia is often combined with other gynecological pathologies: mainly endometriosis, frequent inflammation of the vagina and cervix. They can mask the manifestations of uterine hypoplasia.
Often, girls with uterine infantility have a characteristic appearance: they are short, thin, with very small breasts and a narrow pelvis. Upon examination, the gynecologist sees a small amount of pubic hair, underdeveloped labia and a small vagina.
Degrees of uterine hypoplasia
- Hypoplasia 1st degree
The fetal uterus has a length not exceeding 3 centimeters, almost entirely due to the cervix, since the uterine cavity itself is practically not formed.
- Hypoplasia 2nd degree
A child's uterus from 3 to 5 centimeters is characterized by a ratio of the length of the body of the uterus to the cervix in the proportion of 1:3.
- Hypoplasia 3rd degree
The teenage uterus measures from 5.5 to 7 centimeters.
Infantile uterus and pregnancy
With an embryonic type of uterus, pregnancy can occur only with the use of assisted reproductive technologies, but often it is necessary to resort to surrogacy with the woman’s egg.
The childhood type of hypoplasia makes pregnancy possible, but pregnancy is associated with the risks of premature birth, placental abruption, abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus, and premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
With the teenage type of anomaly in combination with preserved ovarian function, problems with conception and pregnancy usually do not arise. In the early postpartum period, uterine contractions need to be monitored.
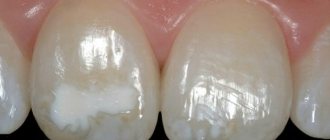
What is tooth enamel hypoplasia?
Literally, the term “hypoplasia” can be translated as “little enamel.” This formulation fully reflects the situation, since the disease is characterized by underdevelopment or absence of areas of enamel. The opposite of hypoplasia is enamel hyperplasia, when pathological growth of tooth tissue occurs, most often manifested in the form of enamel drops. Due to phonetic similarity, confusion often arises. Hypoplasia often develops on baby teeth, which, by default, have thinner and more vulnerable enamel, but the disease can also affect molars.
Attention!
The risk of hypoplasia of the enamel of permanent teeth increases many times if at the milk stage the pathology was not corrected in time and transferred to the rudiments of the molars. Enamel hypoplasia in adults occurs much less frequently and, as a rule, is a consequence of pathologies that developed in childhood.
Diagnostics and treatment in our clinic
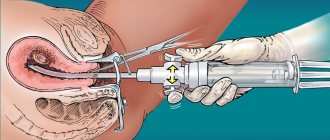
Having established a preliminary diagnosis of uterine hypoplasia and determined its degree by ultrasound, clinic specialists perform hysterosalpingography: this is how they find out the internal structure of the uterine cavity and determine the tortuosity of the fallopian tubes. After this, we need to create a hormonal profile of the woman.
Only on the basis of these studies will we be able to draw up a treatment plan for uterine hypoplasia. The main methods we use for this developmental anomaly are:
- physiotherapeutic methods: magnetic therapy, paraffin, ozokerite applications, endonasal galvanization, mud therapy and other methods;
- vitamin therapy;
- gynecological massage;
- Exercise therapy.
If the degree of uterine infantilism is high, and you want to get pregnant, we will select exactly the assisted reproductive technology that will solve your problem. This could be IVF or fertilization of your egg using the ICSI, PIXI, IMSI method, followed by the introduction of the embryo into a surrogate mother.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis is based on identification and assessment of external signs:
- small labia;
- lack of hair in the genital area;
- short vagina;
- the cervix is elongated...
The main way to determine the infantile uterus is an ultrasound of the uterus. This study helps to establish the degree of development of the pathology. Additionally, the gynecologist prescribes blood tests for hormones (estradiol, testosterone, LH, prolactin, FSH, progesterone, T3, T4, TSH).
Additional techniques are hysterosalpingoscopy, showing the degree of patency of the fallopian tubes, MRI.
Preventive measures and forecasts
When diagnosing the fertile type of uterine infantility, the possibility of conception is excluded. In this case, pregnancy is possible only with the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). If the generative function of the gonads is preserved, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is used using oocytes ready for insemination.
The course of pregnancy in patients with severe endometrial hypoplasia is associated with a high probability of spontaneous abortion and complicated delivery.
In women with miscarriage syndrome, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is performed as part of surrogacy. With minor changes in the structure of the reproductive organ and normal secretion of steroid hormones by the ovaries, the chances of conception and successful pregnancy increase by 45-50%.
Forms of enamel hypoplasia
Hypoplasia is divided into two types: systemic and local. They differ in both symptoms and etiology.
Systemic enamel hypoplasia
With systemic enamel hypoplasia in children, a large area of the dentition is affected. It is often called congenital and genetic, since it occurs immediately with the appearance of baby teeth. May cause changes in tooth shape, especially in the incisal area. The disease has several forms and varieties.
- Spotted.
Light spots appear on the enamel, but its structure is not damaged. - Erosive enamel hypoplasia.
A more severe form, in which round-shaped depressions appear on the surface of the enamel. - Furrowed.
Depressions in the form of large or small grooves, in some cases may resemble waves. - Mixed.
The simultaneous manifestation of two or more forms is observed.
Local enamel hypoplasia
Local enamel hypoplasia is localized, that is, it affects one or two teeth. Most often acquired and occurs against the background of inflammation and damage to the buds of the teeth. It appears in the form of spots of various shapes, pits and grooves. If left untreated, the disease affects the deeper tissues of the tooth and provokes the development of caries.
Aplasia or absence of enamel
The most severe form of the disease, which some experts distinguish separately. It can be either local or systemic (less commonly).
Treatment of enamel hypoplasia
Treatment of dental enamel hypoplasia in children is carried out in two directions. Firstly, it is necessary to eliminate or correct the main factor that provoked the development of the pathology. Of course, if the disease was inherited, it is difficult to do anything about it, but in most other cases it is necessary to minimize the influence of concomitant diseases and pathologies. The treatment method for manifestations of hypoplasia depends on the form and severity of the disease.
- Hypoplasia of the enamel of primary and molar teeth in the stained stage, when the enamel structure is not damaged, is treated conservatively. Remineralization, fluoridation, resurfacing and whitening are the main procedures that restore the aesthetics of a smile.
- Erosive and grooved hypoplasia affecting dentin is treated with filling with composite materials.
- Severe cases of hypoplasia, in particular aplasia, require orthopedic treatment. The most effective methods for treating enamel hypoplasia of permanent teeth are the installation of crowns and veneers.
Treatment of a small uterus
Underdevelopment of the genital organs in itself does not cause discomfort to a woman. This does not affect the quality of her life and sexual relationships. A woman may not be aware of her problem at all if there are no accompanying symptoms and she does not plan to have children in the near future. But when you try to get pregnant, the problem is revealed. Pregnancy either does not occur at all, or the woman cannot bear the baby. The patient goes to see a doctor. After this, instrumental research methods identify the problem and the need for treatment arises.
The main goal of therapy is to restore reproductive function with the goal of achieving pregnancy and ending with childbirth.
Features of treatment:
- With 2 - 3 degrees of the disease - with a positive effect.
- Comprehensive - hormonal, physiotherapeutic treatment and taking multivitamin preparations along with a good diet.
- Gynecological massage.
The prognosis for reproductive function depends on a number of factors: the woman’s age, changes in other organs of the reproductive system, and the level of sex hormones in the blood. In some cases, she can become pregnant naturally after conservative therapy, and carry the child to term with the support of doctors. If this is not possible, the woman is recommended IVF, and sometimes surrogacy.
Symptoms and signs
General symptoms of genital infantilism:
- developmental delay – primary and secondary sexual characteristics are poorly expressed;
- abnormalities of skeletal development - growth disorders, eunuchoid physique;
- appearance does not correspond to true age - a person looks younger than his age for a long time;
- there are no signs of sexuality - sexual desire, sexual behavior, need for a partner, etc.
Attention! In some cases, pathology can develop against the background of psychological infantilism - it is difficult for a person to establish contact with the opposite sex and engage in sexual intercourse. In this case, natural desires are suppressed, followed by involution of the reproductive structures.
Genital infantilism can be a manifestation of a general or partial form of the disease. In the first case, developmental delay extends to the entire human body and psyche. In the second, it only affects the reproductive system. Depending on gender, genital infantilism can be female or male, while in women it manifests itself much more often, while in men it has more pronounced external signs.
Signs of infantilism in girls/women:
- scanty painful menstruation;
- uterine hypoplasia of varying degrees;
- poor development of the mammary glands.
Signs of infantilism in boys/men
- micropenis (in adult men, the size of the penis is more than 2.5 times less than the average);
- absence of emissions and spontaneous erection.
Features of pathogenesis
Sexual infantilism can develop as an independent disease, but more often it is a symptom of more complex chronic pathologies (juvenile diabetes, hypothyroidism, pituitary dwarfism). Takes one of two possible forms:
- hypergonadotropic hypogonadism - the problem is disruption of the gonads while maintaining the normal functional activity of the gonadotropic function of the pituitary gland;
- hypogonadotropic hypogonadism - underdevelopment of the ovaries/testes occurs with weak secretory activity of the anterior pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of gonadotropic hormones.
Each of these two forms can be congenital or acquired, and the appearance of the patient and the method of treatment depend on the time of onset of the problem. The earlier stages of ontogenesis were affected, the more difficult it is to restore sexual function.
Underdevelopment of the endocrine system organs
Hypoplasia of any organ of the endocrine system, as well as hypoplasia of the central nervous system structures, is of systemic importance, since many body functions depend on the hormones they produce. Thus, underdevelopment of the adrenal glands provokes disruptions in the production of steroid hormones, without which normal metabolism and immunity are impossible. Hypoplasia of the thyroid gland in women and men is fraught with metabolic disorders. And underdevelopment of the pancreas, which produces insulin, can cause diabetes.