In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the main follicle, which is called dominant, grows and matures. Ovulation is the rupture of the wall of the dominant follicle and the release of the egg. It enters the fallopian tube. Within 24 hours she can be fertilized. The dominant follicle in the 2nd phase of the cycle is transformed into the corpus luteum, the main function of which is the synthesis of progesterone.
The corpus luteum functions for 10–12 days. If conception does not occur, the egg dies, the corpus luteum regresses, resulting in menstruation.
Symptoms of ovulation
- Mucous discharge from the vagina;
- Increased sex drive;
- Mood changes;
- Heaviness in the chest;
- Increase in body temperature.
For most women, ovulation is completely asymptomatic, although some representatives of the fairer sex say that they may experience the onset of such days in advance. During ovulation, a woman may feel a pulling pain in the lower abdomen. They can be very pronounced. This disorder is called ovulatory syndrome. The discomfort lasts for several days. A woman's discharge may change and become more viscous. During ovulation, her sexual desire increases. The maturation of the egg varies from day to day as follows:
- On days 5–7 from the beginning of menstruation, the cell is 4–5 mm in diameter.
- On days 8–10, a cover of connective tissue appears. The dominant stands out among other formations.
- On days 11–13, the diameter of the dominant reaches 16–18 mm. The remaining follicles regress. When the follicle volume is more than 16 mm, an egg-bearing tubercle appears. After 3-4 days, the egg matures and leaves the follicular cavity. She is able to become fertilized only during her life. It does not exceed 48 hours.
- On days 14–16, the next ovulatory cycle begins. The diameter of the remaining follicular cell, called the Graafian vesicle at this stage, is 20–22 mm.
Studies during one cycle are considered non-indicative. The duration of the menstrual cycle directly depends on the rate of maturation of the egg in its first phase, before ovulation. The standard classic version is 14 days with a 28-day cycle.
After the release of the egg, the second phase of the cycle begins (luteal) and for the same woman it is constant - from 12 to 16 days, but most often 14. In a long cycle, the maturation period of the egg is longer than in the standard one, and ovulation occurs later. For example, if a woman has a cycle length of 32-35 days, then the egg is released not in the middle of the cycle, as many believe, but on the 18-21st cycle or two weeks before the start of the next period.
Errors in tests
There are cases when the diagnostics carried out do not show an accurate result, even on those days when, according to all signs, the day of ovulation has arrived. This happens due to a sharp increase in the level of luteinizing hormone; this can happen for various reasons that have nothing to do with a woman’s readiness for fertilization.
Among the main reasons for the increase in hormones are the following:
- Ovarian disease.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body.
- Impaired kidney function.
- Use of medications.
- Use of contraceptives.
- Eating disorder.
- Recent abortions.
- Transferring stressful situations.
If it is not possible to determine the exact result, experts recommend using the ultrasound observation method, which will help determine the appropriate time with greater accuracy.
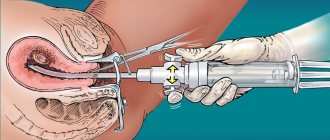
Ultrasound folliculometry
Several ultrasound procedures using a vaginal probe can calculate the day of ovulation or conception in a woman. A visit to the ultrasound room is carried out 3-4 times per cycle with an interval of every 2-3 days. If the cycle is irregular, you will have to visit the doctor 3-4 times, starting from the 7th day after the end of your period - every 2-3 days.
If the cycle is regular, it is worth conducting an ultrasound 2-3 days before the expected day. With a 30-day cycle, ultrasound monitoring begins on the 10-11th day of the cycle, i.e. approximately 4-5 days before the middle of the monthly cycle. Subsequent sessions of ultrasound monitoring of the egg are carried out every two days and last until the egg is released. The onset of the ovulatory period is confirmed by ultrasound diagnostics, when the day before the size of the follicle was 20-24 mm, and now the growth of the corpus luteum has begun. The procedure can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. During intravaginal examination, no preliminary preparation is required, the main thing is to empty the bladder. During an abdominal examination, a traditional examination is performed through the abdominal wall. In order for it to pass without difficulties, three days before monitoring it is necessary to exclude all foods that can cause flatulence or bloating, and on the day of the examination it is necessary not to eat and drink at least a liter of water.
Positive result: what next?
A positive test result indicates a surge in LH. This means that ovulation should occur in the next 24–48 hours. And this is the best time to get pregnant.
However, this is not always the case. Therefore, in order to conceive, it is recommended to have sex starting from the day you receive a positive result and for the next 3 days.
If you are unsure of the result, refer to the instructions for use (included in the test kit).
Additionally, the Flo app can provide valuable information to help you determine the best time in your cycle to conceive.
Ovulation tests
If you can track the follicle using ultrasound, then ovulation tests can be done at home. They work like this: 24–36 hours before the release of the egg from the ovary, the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine sharply increases. A day or two before, he seems to “push” the egg through the wall of the ovary.
Ovulation tests determine whether the amount of the hormone is increased. They also allow you to calculate days favorable for conception. 5-6 days before expected ovulation, tests are performed twice a day. Since we are interested in ovulation in a cycle of 30 days, we need to start taking measurements from about day 13. If ovulation is not observed, then the second stripe will be absent. But the day before or on the 15th day, the test line will be as bright as the control line. This sign indicates that the upcoming ovulatory period is coming, which should be expected in the next 24 hours. You need to immerse the strip in a container with fresh urine for a few seconds, then place it on a dry surface and after about five minutes read the result. testing is carried out in a similar way to tests to detect conception.
All about ovulation. Most Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it rare for a healthy woman to have several eggs mature at the same time?
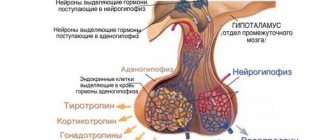
The maturation of eggs is a complex process that depends on the hormonal activity of the body. It is known that the maturation of most embryonic germ cells occurs in utero. Starting from adolescence, under the influence of pituitary hormones, cyclic changes occur in the ovaries. The fate of each follicle is under the control of endocrine systems, from which subsequent events occur - follicle growth, choice of a dominant (leading), egg maturation, ovulation and formation of the corpus luteum. As a rule, people mature 1 egg per cycle. The maturation of multiple eggs is rare for women. Most often, this can happen to couples who have had twins in their family. Also, the maturation of several eggs occurs in ART (assisted reproductive technology) programs. During the programs, several eggs are grown and fertilized.
2. How does a woman’s age affect ovulation? Is it normal to have a cycle without ovulation?
A woman’s age is an indisputable argument in assessing the functional state of a woman’s reproductive system. To date, the basic patterns of the processes of follicle growth, ovulation and development of the corpus luteum have been determined, and they are associated, in particular, with the hormonal regulation of the body. With age, the number of follicles in a woman’s ovary decreases and the quality of the eggs changes. The process of “aging of the ovaries” begins at the age of 30 and after 37 years the number of follicles from which eggs mature sharply decreases. Although within the limits of age, especially the older reproductive age, there are individual characteristics determined by human genetics. However, the age at which the ability to conceive is lost and the age at which the ovaries lose hormonal function, as a rule, do not coincide. At the age of 40 to 45 years, a woman loses the ability to conceive, since few cycles with ovulation occur, but she may continue to have menstrual cycles and hormonal activity of the ovaries for another 10 years.
Anovulatory cycles are considered a variant of the norm during the year when menstrual function develops in adolescents and when taking contraceptives. There may be no ovulation for a short time due to stress or illness. Anovulatory cycles are also possible in healthy women (1-2 times a year). The constant absence of ovulation during reproductive age is not the norm and requires consultation, examination, and treatment by a doctor, since it indicates a disease and the development of infertility in a woman.
3. What diseases interfere with egg maturation?
There are several groups of diseases that disrupt the maturation of the egg. Often several diseases are detected simultaneously that affect ovulation and lead to infertility in a woman.
1. The psychological state of the woman (chronic stress).
2. Mental illness.
3. Genetic diseases.
4. Benign and malignant tumors of various organs and systems.
5. Diseases of organs such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, mammary glands, ovaries, which can cause changes in hormonal status
6. Inflammatory diseases, especially of the reproductive organs.
7. Obesity and other metabolic disorders.
4. Measuring basal temperature - an indicative method? Can ovulation occur at temperatures below 37*. Can the temperature rise and ovulation not occur?
Measuring basal body temperature (BT) is a functional diagnostic test that allows you to assess the hormonal function of the body and indirectly determine the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle. Temperature is influenced by many factors in a woman’s physical and psychological state: sleep disturbance, illness, stress, sexual intercourse. In this regard, changing BT is not the main, but an auxiliary method for determining ovulation in a woman and the state of her hormonal levels. The measurement results are entered into a special chart. In the first half of the cycle it is below 37*, the day before ovulation the temperature drops, and during ovulation it rises by 0.3 - 0.6* and remains at this level until the end of the cycle, at least 12 days (within 37.0 - 37.4*). 2-3 days before the start of menstruation, BT begins to decrease, reaching approximately 37* at the beginning of menstruation. The difference between the first phase and the second phase must be at least 0.4 – 0.5*. An ideal schedule is quite rare. BT variants can be varied, with each feature indicating certain disorders. As a rule, the difference between the average BT value of phases 1 and 2 is less than 0.4* - the egg does not mature. More detailed advice on the results of BT and ovulation is given individually by the doctor in each specific situation. To establish ovulation, several parameters of a woman’s examination are analyzed at once: BT, ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus, blood hormones according to the phases of the menstrual cycle, as well as examination and questioning of the patient. Low temperature in both phases (for example, 36.0 – 36.5*) while maintaining a difference of at least 0.4* is also a normal individual phenomenon.
5. Can ovulation tests lie? Is a positive test always an indicator that ovulation has occurred?
Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovary, which is ready for fertilization and is controlled by hormones. When the follicle reaches a certain size and functional activity, it ruptures, through which the egg leaves the follicle. There is about 36-48 hours between the process of preparing for ovulation and ovulation itself. If fertilization of the egg has occurred, then by day 4 the embryo enters the uterus and implantation occurs. If fertilization does not occur, the egg dies.
On average, ovulation occurs on day 14 of the menstrual cycle (with a 28-day cycle). Deviation from the average is observed quite often and is not a pathology.
Urine ovulation tests are based on the determination of luteinizing hormone (LH) in it. Tests are either one-time or multiple-use. The tests are not completely accurate. Reasons for false negative ovulation results may include:
— different testing times;
- the amount of liquid drunk the day before testing;
- different sensitivity of the test;
— each woman’s body produces a different amount of LH;
- if you test once a day with an irregular cycle, it is possible to miss ovulation.
Unfortunately, ovulation tests do not show ovulation, but the LH level over time.
An increase in LH levels is characteristic of the ovulation phase, but can be elevated with hormonal dysfunction, postmenopause, exhausted ovarian syndrome, kidney disease, and when ovulation is stimulated after hCG injections.
Therefore, you should not rely only on tests for hormonal dysfunctions. It is necessary to additionally use ultrasound to determine the presence and timing of ovulation.
Obstetrician-gynecologist
City Family Planning Center Maternity Hospital No. 2 Zubareva A.V.
Basal temperature method
This method involves measuring the temperature in the rectum (rectally). It is measured immediately after sleep during the cycle. To do this, you need to use one thermometer. You need to knock it down the night before bedtime. Measurements are taken in the morning, immediately after waking up. Correctly measuring basal temperature will help determine whether a patient is ovulating normal, early or late. This is one of the easiest ways to determine favorable days for conception. This should be done after waking up in the morning, but you cannot get out of bed. I just woke up, and right after the thermometer. All results must be scrupulously noted on a special graph. At the end of the cycle, all points with measurement results are connected into a broken graph. During menstruation, measurements are not taken. On the first day of the cycle, the temperature reaches 36.9°C. A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2°C – 36.4°C. An increase in temperature to 37°C - 37.4°C indicates that ovulation is occurring. If the temperature rises after ovulation, the woman is likely pregnant.
Reliable ultrasound
Nowadays, an ultrasound examination performed by a competent specialist is the most accurate source of information about the occurrence of ovulation. An ultrasound procedure for tracking ovulation is called folliculometry. How is such research carried out?
With a 28-day menstrual cycle, from day 10, every 1 or 3 days, the woman undergoes an ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus. The doctor monitors the growth of the dominant follicle and the condition of the uterine mucosa, its thickening. In one of the procedures, a corpus luteum is detected at the site of the follicle, which means that ovulation occurred between the previous day and the present day. In other words, the doctor will please you with the news that the favorable time for conception has arrived.
Calendar method
This method of determining ovulation is suitable for those who have a regular menstrual cycle. It is 14 days before the start of a new cycle that full ovulation occurs. In order to determine the calendar of days for conception, it is necessary to analyze the last 3 months. The first day of the menstrual cycle is the first day of menstruation. It is 12–14 days before the start of a new cycle that full ovulation occurs. The cycle changes under the influence of various factors - health status, nervous tension, stress, physical activity, climate change when traveling, and so on.
Anovulatory cycles
The anovulatory cycle is the absence of ovulation and the accelerated growth of the corpus luteum. During an anovulatory cycle, women experience regular menstrual discharge, but the process of egg maturation does not occur completely.
An anovulatory cycle can be caused by the following reasons:
- Presence of disruptions in hormonal balance
- Pathology caused by genetic factors
- Ovarian disease
- Lack of timely sexual development
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle
- Menopause period
- Disturbances in the endocrine system
If an anovulatory period is present, the girl should undergo a special examination, based on the results of which the doctor will prescribe suitable treatment.
If you do not receive treatment in a timely manner, the anovulatory period can cause complications, which include infertility and uterine bleeding.
To prevent the development of anovulation, girls are recommended to:
- Maintain proper nutrition
- Avoid excessive physical activity
- Promptly treat all inflammatory processes of the genital organs
- Visit a gynecologist regularly for examination.
- You should also be careful about personal hygiene and avoid various types of hypothermia.
Why doesn't ovulation occur?
Ovulation may be absent for various reasons. They can be divided into 2 groups: physiological and pathological.
Do not worry about the lack of ovulation in the following cases:
- Pregnancy: during pregnancy and in the first months after childbirth, women do not ovulate;
- Breastfeeding: if you breastfeed your baby, including at night, ovulation does not occur;
- In young girls (12–14 years old), when the menstrual cycle has not yet been regulated;
- Menopause: when menstruation stops, ovulation also stops;
- Taking oral contraceptives: normally, in this case, ovulation should not occur either.
Ovulation - reasons for absence
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Inflammation of the genitals.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Dysfunction of the adrenal cortex.
- Tumors of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
- Systemic diseases.
- Stress.
- Early ovarian failure.
- Overweight or underweight woman.
- Starvation.
- Chronic lack of sleep.
- Mental and physical overload.
- Past infectious diseases of the nasopharynx.
- Radioactive exposure.
- Taking certain medications.
How to decipher test results?
During the test, the main attention should be paid to the color and the presence of flats.
When the required period of fertilization is determined, the test should display two stripes. In cases where the control line is not displayed during diagnostics, this means that the egg is only at the stage of maturation.
If the second line is weakly expressed, this means that the day of ovulation has not yet arrived. The appearance of a strip of the same color or darker than the control line means that the required period will occur within 24 hours.
When using digital indicators, the device screen displays the number of hours after which the egg will reach the desired state and will be completely ready for the further process of conception.
False Negatives
False negative results are the indication of unreliable readings during diagnostics. To obtain a more reliable result, it is necessary to use other methods to identify the required period.
There are some reasons that contribute to the display of unreliable results:
- The tests carried out had insufficient sensitivity.
- Incorrect time chosen for analysis.
- Failure to comply with the rules of use.
- Using medications that increase hormone levels.
- Incorrect type of reagent.
- The reagent has expired.
- Disruption in the menstrual cycle.
- Presence of diseases that cause unreliable results.
To obtain a reliable result, it is necessary not only to take into account the readings of the reagents, but also to pay attention to the basal temperature and the general well-being of the body. Very often, women feel the approach of the necessary moment and highlight the presence of certain changes in their body that are unique to each girl.
When should you plan to conceive?
Conceiving a child requires, first of all, the readiness of the whole body for this type of procedure; therefore, first of all, the girl must undergo an examination and make sure that she is healthy and ready to bear a child.
Most experts believe that when planning a child, the most suitable time for fertilization of an egg is the period after 15 hours. At this time, male sperm reach their peak activity.
During ovulation, which occurs once a month for most women, the egg can be fertilized within several days.
Couples wishing to conceive a child should know that the result of fertilization can be influenced not only by physiological characteristics, but also by external ones, these include:
- Quitting bad habits - bad habits, especially smoking, reduce the possible chances of fertilization
- Reduce the intake of medications - many of which negatively affect the maturation of a woman’s egg
- Maintain a balanced diet - poor nutrition most often leads to a lack of essential vitamins in the body, which should not be allowed when planning conception.
- Regular sex - having sexual intercourse is necessary not only on days when the hormone increases. Regular unprotected sex is the main stage of successful conception.
- Heredity - many couples do not have children due to the heredity of one of the partners.
- Constant physical activity negatively affects the increase in hormone levels, which leads to incomplete maturation of the cells in the ovary.
To identify the most suitable time for conception, girls can monitor their basal temperature; periods when the indicators will decrease are the most productive and are used to plan a future child.