Stereotypes and differences from radiography
When undergoing an examination, it is important to pay attention to the direction issued by the attending physician. If it says that you need to undergo fluorography, you do not need to change the order yourself, relying on a classic X-ray to better show the condition of your lungs. Such ignoring of specialist advice will only lead to unreasonable radiation exposure to the body. In medicine, radiation dose limits (1 mSv/year) are established only for healthy people when conducting preventive studies (for example, when applying for a job). Limits on radiation doses required for diagnostic purposes (in sick people) are not established by law. It only states that the doctor should strive for a minimum level of radiation, but not at the expense of the quality of diagnosis. In general, a reasonable postulate, but how is it implemented in practice? But in practice in Russia the average “medical” radiation dose turns out to be several times higher than in the UK, USA and France. At the same time, in some of our regions the average “medical” radiation dose exceeded 3 mSv. Fluorography provides less information than radiography. But the World Health Organization does not recommend the use of traditional film fluorography, even in underdeveloped countries. The solution to the problem was the transition to digital fluorography, which, with high information content, reduces the radiation dose several times. Here are the approximate radiation doses (mSv) that a person receives when examining the chest using various methods:
- radiography (in two projections) – 0.25;
- fluorography (in one projection) – 0.6–1.6;
- fluoroscopy – 3.0;
- digital fluorography – 0.01–0.06;
- computed tomography – 3.5–5.0.
So, if nothing bothers you, and you are referred for an X-ray for prevention, then it is better to undergo digital fluorography or radiography (“image”) instead of conventional fluorography. You should definitely refuse to perform fluoroscopy (when the doctor looks at the patient behind a screen): not only does the patient receive a large dose, but his image will not remain, and the conclusion will be solely on the conscience of the doctor who conducted the study.
What can you see on fluorography?
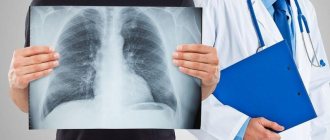
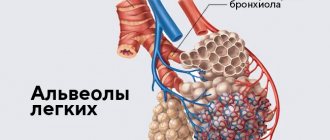
In a fluorographic image, the doctor sees a black and white image of the chest and internal organs. The organs of the chest absorb radiation differently, so the picture on the image is heterogeneous. The heart and bronchi appear as light spots; a white shadow from the heart is visible in the center of the fluorogram. Hollow structures (lungs) appear dark, while dense ribs and clavicles appear light. If the lungs are healthy, their tissue looks homogeneous.
What can a doctor detect?
- An increased heart size may indicate heart failure or cardiomyopathy.
- The accumulation of fluid (effusion, blood) is an important symptom that requires further diagnosis.
- Bone fractures.
- Tumors.
- Granulomas may indicate tuberculosis.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Other pathologies.
Chest fluorography should be distinguished from x-rays. The last diagnostic method is used according to the doctor’s indications.
Both fluorographic and x-ray examinations of the lungs are a simple, fast and effective diagnostic method that has been helping doctors prevent and diagnose diseases for several decades.
Classification of fluorography modes
A preventive examination of the lungs should be done once every 2 years, and for certain categories (for example, people with chronic diseases or members of other risk groups) - once a year or even 2 times a year.
Patients who are already registered at a tuberculosis dispensary are prescribed a test much more often: at the beginning of a course of therapy, the interval between procedures is about three to four months, depending on the intensity of treatment, the characteristics of the development of the disease, and the individual properties of the body.
With positive dynamics of treatment, the regimen changes. At first, monitoring is carried out approximately once every six months while maintenance therapy continues, and after complete recovery and deregistration, the patient needs to be examined on a general basis - annually.
Using a digital camera ensures that the image is quickly captured when the image is reconstructed using high-tech software. The result is displayed on a computer monitor, which you can:
- put on digital media;
- print on paper.
The examination results are stored in a database, which ensures their availability for the patient and doctor during the entire observation period. When you enter your last name along with your residential address, the program will display all previously recorded survey results. All that remains is to compare the updated and past information to track the dynamics.
How is it carried out?
The X-ray room has a moving camera with a large metal plate. For an accurate diagnosis during fluorography, you will be asked to stand in front of the plate, turn your shoulders forward, take a deep breath, hold your breath for the duration of the exposure and do not move. This will allow you to get a clear image without blur. The x-ray technician or radiologist will tell the patient how to stand up correctly and when to hold his breath.
Is it possible to perform fluorography in clothes?
You can undergo fluorography in a T-shirt or shirt, but do not forget to check your chest pocket. It is recommended to remove jewelry and metal objects from the chest - this may make it difficult to evaluate the image. For the same reason, women are recommended to undergo the study without a bra.
Fluorography of the chest is completely painless and is not felt at all. And after it is done, you do not need to follow any doctor’s recommendations.
Main indications
The main objective of the diagnostic method is to identify diseases of the lungs or bronchi. It is not for nothing that the technique is considered a preventive approach that prevents serious complications for diseases of the respiratory system.
As a rule, a local therapist or pulmonologist gives a referral for testing when a patient comes to them with characteristic symptoms:
- prolonged persistent cough;
- dyspnea;
- pain syndrome in the chest area.
When the above signs are detected, the chance of detecting a pulmonary or bronchial deviation increases significantly. Often the study allows you to establish:
- inflammatory process even at the initial stage of development;
- pneumothorax;
- neoplasms of malignant and benign nature;
- pleural damage;
- emphysema.
But most often, even during a preventive examination, tuberculosis is detected, so annual mandatory examinations are recommended, which help prevent the disease, which currently leads in a high percentage of deaths.
In addition to standard indications, there are two more categories for examination: family members living with pregnant women or newborns in order to minimize the risk of illness in infants and persons of military age.
The second category will include unscheduled fluorography if there is suspicion of:
- foreign body in the lungs;
- inflammation;
- tuberculosis;
- tumors of the mediastinal organs;
- diseases of the heart, large vessels.
Such precautions make it possible to recognize concomitant diseases such as fibrosis or sclerosis. Also, using a small image, it is possible to determine the localization:
- cysts;
- cavern;
- abscesses;
- infiltrates;
- accumulations of gases.
Despite the productivity of the technique, fluorography can hardly be called the main argument for diagnosing pulmonary pathologies. It is often necessary to use auxiliary tests, including sputum analysis, radiography, and MRI with contrast.
Photo interpretation
Deciphering an image requires special knowledge, so this is done exclusively by doctors with the appropriate education. X-rays are absorbed differently by tissues of different densities, which leaves dark and light silhouettes on the film. Soft structures have a dark tint, hard structures have a light tint. It is their interpretation that is carried out by these specialists.
Pregnancy and other contraindications
Contraindications to manipulation are pregnancy and childhood. It is believed that the minimum threshold is 15 years, since before this time it will be difficult for children to tolerate increased radiation exposure.
Among the relative contraindications, which are sometimes ignored when the benefit exceeds the possible harm, are:
- claustrophobia;
- dyspnea;
- general serious condition.
But sometimes even pregnancy, which is a contraindication for almost all types of diagnostics, does not become an obstacle to the procedure. It should be done only after preliminary consultation with your doctor. Control must be carried out by a specialist throughout the entire manipulation.
An important factor in the success of diagnosis and safety for the fetus is the appointment of an examination after 25 weeks. During this period, it had already formed its basic systems.
The reasons for “photographing” the respiratory system of pregnant women and women during the breastfeeding period should be as compelling as possible. Preventive X-ray examinations are not carried out for pregnant women and children under 15 years of age.
Is it possible to do fluorography for girls during menstruation?
Doctors remind us that it is important for every girl of reproductive age to know the answer to this question. On critical days, the procedure is performed if there are compelling reasons.
Diagnosis for preventive purposes in the period from 1 to 8 days of the menstrual cycle is not recommended by doctors. These precautions will prevent accidental exposure of the egg if it is fertilized.
X-ray
Allows you to explore the internal structures of the body. The photo is usually life-size. The method can be survey or targeted, when a specific area of our body is studied. As a result, even small pathological changes can be seen. It is used only to clarify or make a correct diagnosis. It is not used for prophylactic purposes.
Examination helps to detect tuberculosis, pleurisy, cancer, fractures and other conditions. The image will allow you to form a clear picture regarding the size and contours of organs, the presence of cavities and foci of inflammation.
What problems does fluorography show?
The image of a healthy person should not contain such pathological darkening and changes as:
- Strengthening the pulmonary pattern. It may indicate pneumonia, swelling of the bronchi, lungs and more.
- Ring shadows. Indicate open tuberculosis, lung abscess or cysts with fluid inside.
- Focal opacities in the lungs. This is a shadow of any shape measuring less than 12 mm. Such spots may indicate the onset of an oncological process or vascular problems. This may also indicate pathology of the respiratory organs. Then the patient is additionally sent for a computed tomography scan and sputum analysis.
- Segmental darkening. They have clearly defined boundaries and a triangle shape. If there is one such spot on the image, the doctor may suspect injury to the lung tissue, an endobronchial tumor, or a foreign body. Multiple segmental spots may indicate tuberculosis, pneumonia, metastases, the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity, as well as chronic or acute pneumonia.
- Lobar darkening. They have clear contours and a slightly convex or concave shape. They indicate the development of pneumonia, bronchial asthma, helminthic infestation or purulent tissue damage as a result of inflammation. Also, a lobar spot may be the result of a bone fracture, due to which a callus appears in the bone tissue. If the lobar spot has blurred edges, this may be an indicator of a staphylococcal infection, heart attack, or accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity.
- Calcifications. These are inclusions with a density resembling bone tissue. They are light in the photo. They are evidence that the patient was in contact with a patient with tuberculosis, but his own disease did not enter the active phase.
- Spikes. These are seals that are localized between the pleura (the film covering the lung itself and the inner surface of the chest wall) and the parenchyma (the main functional tissue of the lungs). They indicate a history of pleuropneumonia (an inflammatory disease in which damage to segments of the lung is accompanied by involvement of the pleura in inflammation).
- Small shadows in the form of a “snow storm”. Indicates the presence of tuberculosis or Pneumocystis pneumonia (caused by the yeast-like fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii).
- Strengthening the pulmonary pattern. In appearance, this pattern resembles the branches of a tree crown. It is formed by arteries and veins, as well as bronchi. Normally, the “twigs” look thin and barely noticeable. If pathologies are present, they become more obvious.
This is not a complete list of pathologies that fluorography helps to identify. Regular completion of this procedure will allow you to diagnose dangerous diseases in time and begin treatment in a timely manner before the disease takes on a chronic form.
Remember that you should not decipher the image yourself. Only a radiologist can interpret it correctly. He will describe all pathological changes, if any, after which a description of the results along with the image is transferred to the therapist or specialist who referred the patient to undergo fluorography. This specialist will decide on the course of further treatment.