What is a microstroke
A microstroke differs from a regular stroke only in the extent of damage to brain cells. This is the same disruption of blood supply as a result of blockage of capillaries or small vessels. A microstroke can also occur with severe spasm of a bunch of small arteries and vessels. The main difference from a regular stroke is that after a mini-stroke a person recovers faster. Even a few minutes may pass, after which the patient will feel well and continue to carry out daily activities.
The main danger of a micro-stroke is that it can go unnoticed. Or, when the attack does not produce significant consequences, the patient decides not to waste time visiting the clinic and leaves the attack unattended, while at the first manifestations of the problem it is necessary to urgently seek advice from a specialist.
With a mini-stroke, brain tissue is affected that does not receive blood supply as a result of blockage of small arteries by a thrombus, blood clot, or due to spasm. Tissue necrosis affects a small area, which is why the patient does not show signs typical of an ischemic attack:
- difficulty lifting limbs;
- slurred speech;
- dizziness;
- severe headache.
If these signs appear, they disappear on their own after a short time. It may take no more than a day, and all body functions are restored again.
Prevention
To prevent a micro-stroke, you need to follow these fairly simple recommendations from specialists:
- Give up bad habits: alcohol, smoking, and especially drugs;
- Avoid stress and overexcitement, do not quarrel whenever possible and do not succumb to depression;
- Play sports with moderate physical activity;
- Get enough sleep;
- Avoid obesity, eat properly and in moderation;
- Periodically undergo examination and preventive treatment.
It is enough to follow these simple rules, and the likelihood of a micro-stroke can be minimized.
Symptoms of a microstroke
Due to the fact that the symptoms of a microstroke are short-term, sometimes it is not possible to accurately determine the cause of the ailment. The main signs of a microstroke are:
- increasing and persistent headache;
- sudden deterioration in condition without obvious reasons;
- dizziness, loss of coordination;
- numbness of the tips of the fingers and toes, especially predominantly on one side of the body;
- decreased visual acuity - cloudy picture, blurry shapes;
- goosebumps without obvious provoking factors;
- heavy sweating;
- manifestation of facial asymmetry.
If the patient himself can feel a headache and numbness of the limbs, then the asymmetry of facial expressions becomes noticeable at first only to the person next to him. It is this sign that should be considered indicative in the matter of making a diagnosis. At the first manifestations of asymmetry, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Most often, strokes and micro-strokes occur when changing body position. For example, after a person gets up from a sitting or lying position and walks. The position has changed, the blood flow has accelerated, the pressure has increased for a short time - these are provoking factors that can contribute to the removal of a fragment of a blood clot from the vessel wall and blockage of small capillaries or arteries.
General information
Cerebrovascular diseases , which include stroke and transient ischemic attack (ministroke), are an important medical and social problem. What is a microstroke? This is a short-term episode of neurological dysfunction caused by temporary cerebral ischemia, which does not lead to changes in this part of the brain and the development of stroke .
The arterial cerebral blood supply is formed from two vascular systems: vertebrobasilar and carotid. The carotid basin is formed by the external and internal carotid arteries, which arise from the common carotid artery, or rather from its carotid sinus. The internal carotid artery is a larger branch of the common carotid artery, which enters the skull, passing through the carotid canal and making several bends, which, in congenital pathology, can cause a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain. The internal carotid artery gives off five branches that supply blood to different parts of the brain and there are anastomoses (connections) between the branches.
The vertebrobasilar basin is formed by the basilar and two vertebral arteries, which enter the canal of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae (VI–II), and then make several bends along their course. Thus, even the anatomical bends and passage of the vertebral arteries in the bone canal of the cervical vertebrae are a predisposing factor to a decrease in blood supply to the brain under certain conditions, which will be discussed below.
The classic definition of transient ischemic attack indicates an interval of persistence of neurological symptoms of up to 24 hours. However, the 24-hour period is arbitrary, and the average duration of an episode can be 8-15 minutes, but most often the symptoms disappear within one 1 hour. Since 2002, the definition of this condition has been expanded and the main fact taken into account is the absence of pathological changes in brain tissue during the period of temporary ischemia .
A transient ischemic attack develops suddenly and has symptoms similar to those of a stroke , but they are reversible because transient ischemia does not cause changes in brain tissue. The highest incidence of micro-strokes is observed in people aged 65 to 80 years. However, cases are not uncommon in people of young working age from 29 to 45 years. In most cases, the causes of transient cerebrovascular accidents in young people are: increased blood pressure due to neurocirculatory dystonia or true uncontrolled arterial hypertension , as well as heart or blood diseases, which occurs even in children. Circulatory disorders can occur in any arterial area of the brain, but in the carotid area they occur 4-5 times more often than in the vertebrobasilar area.
Many patients do not attach importance to transient disorders and do not consult a doctor. In most cases, the diagnosis is established after the fact, when the doctor asks about other diseases. In the best case, the patient comes in, but the diagnosis is made from the patient’s words, since by the time of the examination the symptoms have already regressed. Nevertheless, TIA is an emergency condition that requires hospitalization of the patient, determination of the causes of cerebral ischemia and treatment according to the algorithm for acute cerebrovascular disorders. This is due to the fact that in some patients, attacks can be repeated during the day (2-3 attacks) and everyone after a TIA has a risk of developing stroke and myocardial infarction . Approximately one third of patients develop a stroke within a year after the first transient circulatory disorder.
Causes of microstroke
The causes of a microstroke can be various pathologies associated with the condition of the heart and blood vessels, diet, lifestyle and arterial hypertension. At risk are young people over 35 years of age who are overweight and suffer from nicotine addiction. Smoking is a habit due to which a person himself spoils the condition of his blood vessels, reducing their elasticity, narrowing the lumen and increasing pressure.
The main causes of microstroke identified by doctors:
- tendency to thrombosis;
- atherosclerosis;
- tachycardia;
- hypertension;
- arrhythmia;
- weather dependence;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
The lifestyle of a modern person often provokes the formation of factors that contribute to the occurrence of a micro-stroke. Nutrition has a great influence on health. Love for sausage products is a big step towards a micro-stroke. Also, dangerous foods include:
- frequent consumption of fried pies, pasties, sausages in dough;
- starting each day with fried eggs;
- abuse of chips, hamburgers, snacks;
- a large amount of vegetable oil used for preparing fried foods.
A sedentary lifestyle helps cholesterol from harmful foods to be released and deposited on the walls of blood vessels, reducing their permeability. When the morning does not start with exercise, and the evening ends on the couch instead of walking in the fresh air, adipose tissue builds up, increasing the load on the heart, resulting in an increase in blood pressure and heart rate.
Tests and diagnostics
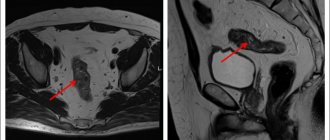
All patients with transient ischemic attack should be examined within 24 hours of the onset of neurological symptoms. Since there is no brain damage in a microstroke, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will not help diagnose this disease, but they are performed to rule out a stroke.
- Magnetic resonance imaging in a diffusion-weighted mode provides accurate and early diagnosis of ischemic brain damage. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging is based on the study of the diffusion of water molecules in normal and altered tissues.
- For diagnosing microstrokes, a more informative research method is duplex ultrasound examination of intracranial vessels and neck vessels. This allows us to identify the presence of occlusion and its degree. Ultrasound and Doppler studies are of less value in assessing vertebral arteries where occlusion cannot be corrected.
- If damage to the vertebral arteries is suspected, angiography - a contrast agent is injected into the artery and pictures of the head and neck are taken. CT angiography examines the condition of the arteries of the neck and large branches of cerebral vessels.
- In addition to CT angiography, perfusion computed tomography after intravenous administration of a contrast agent is performed to study cerebral blood flow at the capillary level.
- a cardioembolic microstroke is suspected, echocardiography is performed, which allows identifying cardiac pathology.
- For differential diagnosis with an epileptic attack, electroencephalography is performed.
- Clinical and biochemical blood test (coagulogram).
- Blood sugar test.
- Lipidogram.
Types of microstrokes
Microstrokes are divided into two types, based on the cause of their occurrence:
- Ischemic occurs when the blood supply to certain parts of the brain is stopped due to obstruction of blood vessels or arteries. It does not matter what blocked the blood flow - a blood clot, a blood clot or an overgrown atherosclerotic plaque.
- A hemorrhagic stroke is a microstroke that occurs as a result of a hemorrhage that occurs when a small vessel ruptures. In addition, thinning of the vascular wall is also a risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Both conditions are dangerous and require the help of qualified professionals.
Pathogenesis
The key point in the pathogenesis of this condition is reversible cerebral ischemia, which occurs when there is a mismatch between the needs of the brain and the currently existing blood supply. Local anemia of brain tissue develops when perfusion decreases below 18-22 ml of blood per 100 g/min.
A transient drop in blood flow, due to various reasons, causes the development of ischemia in the brain tissue and is accompanied by reversible focal symptoms. The main pathogenetic mechanisms for the development of transient disorders are: microembolism ; hypotonic and hypertensive crisis , pathological tortuosity of the main vessels of the brain, as well as disorders of the anticoagulation system of the blood.
The outcome of ischemic cerebral circulatory disorders is determined by the caliber of the artery, the rate of development of blockage, localization, and the development of collateral circulation. If cerebral perfusion is restored, regression of symptoms is observed and the episode of transient ischemic attack ends. In the event of a further drop in blood supply to 8-10 ml per 100 g/min, which causes irreversible changes in brain tissue, cerebral infarction ( ischemic stroke ) develops.
Treatment of microstroke in women
Treatment in this case is aimed at preventing the development of a full-fledged stroke with serious impairment of brain functions in the future.
To treat a microstroke, therapy is selected that restores blood circulation to the brain. In particular, doctors use vasodilators and medications that improve metabolic processes in blood vessels.
Also, during treatment, doctors adjust the treatment of related diseases. If the patient suffers from hypertension, then cardiologists are involved in the work and prescribe effective antihypertensive drugs. Together with them, a treatment plan is developed by a gynecologist and an endocrinologist, who render a verdict on the woman’s further use of hormonal contraceptives and, if necessary, select a remedy suitable for each specific patient.
Recovery
To restore impaired brain functions after an attack, doctors select nootropic drugs. Their goal is to make the affected areas of the brain work and protect those parts that are in close proximity to the focus of necrosis. Taking nootropics has a positive effect on the condition of people who have suffered from certain neurological diseases.
Psychotherapists are involved in the recovery process of a woman after a mini-stroke. Working with them restores a deteriorated psychological state and strengthens the body's resistance to stress factors and nervous overload.
Consequences
If you pay attention to alarming symptoms in time, then timely and high-quality treatment will allow you to avoid noticeable consequences, even if the woman suffered the disease on her legs.
If a full examination is not completed, there is a risk of deterioration in cognitive function and general psychological well-being. People who did not receive help in time experience deterioration in their memory and ability to concentrate. In addition, patients experience mood problems. Often, even calm and balanced women face outbreaks of causeless sadness, aggression or even depression.
One of the most dangerous consequences is a recurrence or development of a full-fledged stroke, which can seriously impair the quality of life.
Symptoms of a microstroke according to its concentration
A microstroke causes certain symptoms, depending on the area where it is located. In relation to this factor, there are:
- damage to the anterior cerebral artery - motor functions are primarily affected - speech, facial expressions, since partial paralysis of the tongue and facial area occurs;
- violation of the middle cerebral artery - the main difference is a change in movements on one side of the body; when a microstroke occurs, they are insignificantly expressed, spreading only to the face, and occasionally to the hands and fingers; susceptibility on the side opposite to the damaged lobe of the brain is noticeably reduced;
- violation of the posterior artery - visual function is affected; Hallucinations and blurred vision are possible.
These signs are weakly expressed. According to statistics, 60% of patients who have suffered a mini-stroke will soon develop an ischemic attack.
It is important to promptly prevent dangerous vascular accidents.
The main cause of microstroke is considered to be hypertensive pathology and atherosclerosis. It is these diseases that cannot be left to chance.