- Causes
- Symptoms
- Kinds
- Degrees
- Differences between obesity in women and men
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications
- Prevention
- Price
Obesity is a disease that involves excessive deposition of fatty tissue, which is harmful to the human body.
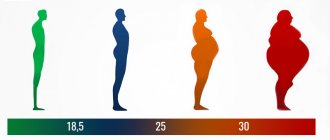
Like any other disease, it requires treatment. The diagnosis of obesity is made to an adult with a body mass index equal to or greater than 30. Body mass index is calculated as the ratio of body weight to the person's height in meters squared. With a body mass index of 25 to 29, body weight is simply considered overweight. Obesity occurs when there is an energy imbalance, which occurs when the body takes in more calories than it expends. For example, if a person leads a sedentary lifestyle and eats the same amount as an active person, this leads to fat deposition and weight gain. Obesity is often promoted by high levels of insulin, genetic predisposition, disorders in the functioning of internal organs (pancreas, intestines, liver) and the endocrine system.
Obesity is a dangerous condition that leads to an increased likelihood of concomitant diseases that disrupt a person’s normal functioning.
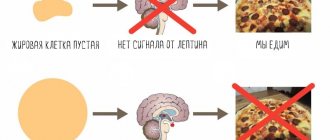
Causes of obesity
The main reason for obesity is that unspent energy remains in the body, which is deposited in adipose tissue. This condition can occur when a person takes in more calories than they expend. But this is aggravated if a person has a genetic predisposition or diseases that contribute to excess weight gain. The following factors contribute to obesity:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- increased insulin levels;
- lack of sleep;
- stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- endocrine diseases;
- hormonal contraceptives;
- psychotropic drugs;
- disruption of the hypothalamus;
- steroid hormones;
- Prader-Willi syndrome.
These factors can cause a person to become obese.
The function of fat deposition and weight gain when consuming large amounts of calories was acquired by the body in the process of evolution, in order to expend accumulated calories during times of lack of food. In modern society, the problem of hunger has generally been solved, so it is important to monitor your body weight and, at the first signs of obesity, consult a doctor for timely treatment.
Obesity symptoms
Obesity is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- excess weight;
- dyspnea;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- decreased performance;
- swelling;
- stretch marks on the skin;
- tachycardia;
- angina pectoris;
- high blood pressure;
- constipation;
- sweating;
- joint pain;
- pain in the spine.
If you have several symptoms with a body mass index equal to or greater than 30, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment of obesity.
Clinical manifestations of pathology
Since obesity most often affects vital organs such as the heart, liver, kidneys, blood vessels and lungs, symptoms include:
- shortness of breath with minimal physical activity;
- rapid fatigue and decreased performance;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- phlebeurysm;
- increased blood pressure;
- decreased sexual activity;
- disorders in the reproductive system (amenorrhea, infertility);
- development of sleep apnea;
- depression.
You can read more about the symptoms and indicators of abdominal obesity on the pages of our website Dobrobut.com.
Types of obesity
Types of obesity can be classified by:
- place of accumulation of adipose tissue;
- by the type of disease that causes it;
- for the reason that caused obesity.
Obesity based on the location of adipose tissue accumulation
- Visceral . In this case, fat is deposited around the internal organs. The most dangerous type of obesity, since fat negatively affects the functioning of the internal organs that surround it.
- Peripheral . Fat is deposited under the skin.
- Abdominal . In this type of obesity, fat is deposited in the abdomen, chest and shoulders, which forms an apple-shaped figure. Typically, this type of obesity develops in men. It happens both subcutaneously and can cover internal organs. It is a dangerous type of obesity, since in it fatty deposits put pressure on the abdominal cavity, disrupting the functioning of the heart, lungs, intestines and pancreas. Pressure on the heart and lungs causes hypertension and vascular disease. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus increases.
- Gynoid . In this type of obesity, fat is deposited in the lower abdomen, thighs and buttocks, creating a pear-shaped figure. In genoid obesity, fat is deposited under the skin. More common in women.
- Mixed . Fat is deposited evenly throughout the body. More common in children.
Obesity by disease type
- Cushingoid . The cause of obesity is Itsenko-Cushing's disease, in which the functioning of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal glands is disrupted, due to which hormones of the adrenal cortex are produced above normal. This leads to the formation of fat deposits in various parts of the body. Mostly fat accumulates on the stomach, chest, back, shoulders and face. This obesity, coupled with Cushing's disease, leads to osteoporosis, hypertension, diabetes and osteoporosis.
- Focal . The cause of this type of obesity is lipomatosis. The disease leads to the formation of many subcutaneous benign tumors from adipose tissue.
- Hypogenital . This type of obesity is caused by a lack of the hormone testosterone in men. Lack of testosterone production may be associated with disease of the testicles, pituitary gland, congenital pathologies and other reasons. With hypogenital obesity, fat accumulates mainly in the chest, abdomen and thighs. In addition to obesity, lack of testosterone leads to underdevelopment of primary and secondary sexual characteristics in men. In women, a lack of sex hormones can also lead to obesity.
- Spongy . The cause of this type of obesity is pathology of the veins and blood vessels against the background of heart failure. This leads to fluid retention in adipose tissue and weight gain.
- Brain . This type of obesity is caused by improper functioning of the pituitary gland due to injury, disruption of the nervous system, or poisoning. At the same time, less pituitary hormones are produced, which disrupts metabolism. This disease causes fat to be deposited on the thighs, abdomen and chest.
For the reason that caused obesity
- Stress . Causes eating disorders. In a state of depression or stress, a person tends to eat a lot, eating into a negative psychological state, thereby leading the body to obesity. With psychogenic overeating, fat is deposited mainly in the abdominal area.
- Metabolic syndrome . A condition in which the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats is disrupted, resulting in excess fat being deposited.
- Heredity . Some people may have a genetic tendency to accumulate excess weight and become obese. Mutations of certain genes make it so that a person with a tendency to obesity gains weight more actively than a person without a tendency to be overweight.
- Endocrine . Disorders associated with the production of hormones, leading to obesity. Conditions may include: hypothyroidism - dysfunction of the thyroid gland; hyperprolactinemia - increased production of the hormone prolactin; hypercortisolism - increased secretion of the hormone cortisol; hypogonadism - decreased sex hormones. All these conditions lead to excess weight gain.
- Cerebral . Obesity associated with brain damage by infections, autoimmune nature, neoplasms and injuries.
- Medication . The cause of drug-induced obesity is the use of medications - steroids, hormones, cytostatics and contraceptives.
Before treating obesity, doctors conduct diagnostics to identify the causes that caused obesity. An important task for weight loss is to eliminate the diseases that led to weight gain.
Obesity levels
Obesity is classified into 4 degrees:
- 1st degree . This type of obesity is diagnosed in patients with a Quetelet body mass index from 30 to 34.9 and if the weight exceeds the normal body weight by 15-29% according to the Brox formula. As a rule, patients with 1 degree of obesity have no health complaints. To treat grade 1 obesity, physical training is prescribed and the patient’s diet is adjusted. By reducing the intake of calories into the body and spending them during physical activity, the weight quickly returns to normal.
- 2nd degree . This type of obesity is diagnosed in patients with a body mass index according to Quetelet from 35 to 39.9 and if the weight exceeds the normal body weight by 30-49% according to the Brox formula. Some patients with degree 2 obesity have no health complaints, but some patients have diseases such as diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, arterial hypertension and others. To treat grade 2 obesity, lifestyle changes are prescribed: physical exercise, mental state stabilization, and regular health monitoring.
- 3rd degree . This type of obesity is diagnosed in patients with a Quetelet body mass index of 40 and if the weight exceeds the normal body weight by 50-99% according to the Brox formula. With degree 3 obesity, almost all patients experience health problems: irritability, fatigue, insomnia, erectile dysfunction, diabetes, infertility and other problems. To treat grade 3 obesity, you may need not only the help of a nutritionist and psychologist, but also an endocrinologist and a surgeon.
- 4th degree . This type of obesity is diagnosed in patients if their weight is 2-3 times higher than the normal body weight according to the Brox formula. Patients with stage 4 obesity have many health problems. Such obesity is often treated with surgical methods, including minimally invasive ones.
Metabolic syndrome and obesity
What is metabolic syndrome?
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of impaired carbohydrate metabolism, abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia and hypertension, and is associated with the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases.
In order for metabolic syndrome to be confirmed, a person must have at least 3 of these 5 syndromes:
1) Abdominal obesity. Doctors use the term "obesity" for people who have a "body mass index" of 30 or more. Waist size with abdominal obesity in men is more than 94 cm, in women – more than 80 cm.
2) Increased blood pressure. When measuring blood pressure, 2 numbers are determined. For example, your doctor might say that your blood pressure is "140 over 90 mmHg." The top number is the pressure inside the arteries when the heart contracts. The bottom number is the pressure inside the arteries when the heart relaxes. You have hypertension if:
- Top numbers 140 or higher
- Lower numbers 90 or higher
- Treatment with drugs for high blood pressure
3) High blood sugar. In order for all the cells in your body to function normally, glucose is needed. Sugar enters cells with the help of the hormone insulin. If there is not enough insulin, or if the body stops responding to insulin, glucose builds up in the blood. A disorder of sugar metabolism in the body is considered to be a fasting blood glucose level of more than 5.6 mmol/l, or treatment with glucose-lowering drugs.
4) High levels of triglycerides (lipid metabolism disorder). Triglycerides are fat-like substances in the blood. You have high triglyceride levels if they are higher than 1.7 mmol/L.
5) Low levels of HDL in the blood (high-density lipoproteins). High-density lipoproteins are "good cholesterol" because they reduce the risk of heart attacks and other health problems. You are considered to have low HDL levels if they are less than 1.0 mmol/L in men and less than 1.2 mmol/L in women.
Some doctors do not use the term "metabolic syndrome" for the collection of these syndromes. This is because the treatment for metabolic syndrome is no different from the treatment for each of the syndromes. Thus, there is no need to allocate a special name for this problem. The best and safest way to treat such a problem is to lose weight and eat less food. Losing weight will help reduce your waist size, your triglyceride levels, and your hypertension.
How is metabolic syndrome diagnosed?
As part of the examination, the doctor:
1) Measures blood pressure
2) Measures your height and weight to determine your BMI
3) Measure the widest part of your belly using a tape measure. This measurement is called “waist circumference”.
You also have a blood test to determine your blood sugar and lipid levels. Blood lipids include indicators such as triglycerides and cholesterol. People who have high triglyceride levels often have high cholesterol, too.
Can metabolic syndrome be prevented?
You can reduce your chances of acquiring metabolic syndrome if:
1) lose weight if you are overweight;
2) eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy products, and little meat or fatty foods;
3) walk a lot or do physical activity daily;
4) quit smoking if you smoke.
How is metabolic syndrome treated?
Treatment includes:
Diet. Healthy diets that will help you lose weight include:
- The Mediterranean diet is a diet high in fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains and olive oil. It may help reduce weight, blood pressure, lipid levels, and blood sugar levels.
- DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Prevent-Hypertension). This is a low salt and fat diet. It includes 4 to 5 servings of fruits and vegetables, and 2 to 3 servings of low-fat dairy products per day. This diet can reduce blood pressure, weight, lipids and blood sugar.
Exercises. It is recommended to exercise at least 30 minutes a day, 5 or more days a week. If you cannot exercise for 30 minutes at a time, try exercising for 10 minutes 3 or 4 times a day. Brisk walking is a good choice in such a situation.
Medicines. It is recommended to take medications to lower blood pressure, lipids and blood sugar.
If conservative methods of treating morbid obesity and other manifestations of metabolic syndrome are ineffective, patients may be indicated for surgical treatment aimed at reducing the volume of the stomach and reducing the absorption of food in the intestine. This is called bariatric surgery .
Diagnosis and treatment of morbid obesity and diseases associated with metabolic syndrome should occur in a specialized department with the participation of an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, nutritionist and bariatric surgeon.
Differences between obesity in women and men
Women are more likely than men to gain excess weight, since they are genetically programmed to accumulate energy to bear a child. In women, weight gain depends on the amount of estrogen and progesterone. Hormone levels can fluctuate for various reasons, for example, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, as a result of which body weight can change. In women, fat accumulates mainly under the skin. At the same time, in women, fat is deposited in the form of large fat cells of a soft structure, which causes a cosmetic problem - cellulite. Women gain weight faster due to the consumption of large quantities of carbohydrates in the form of various sweets.
Men are less likely to gain excess weight. The growth of adipose tissue in men is regulated by the hormone testosterone. Low levels of the male hormone lead to excess weight gain and obesity. Testosterone levels drop after age 30, making men more likely to become overweight. Male obesity is more promoted by the consumption of fatty animal products and alcohol. In men, fat is more often deposited in the abdominal area, both under the skin and around internal organs. The structure of fat in men is denser, and the skin is tougher, so cellulite does not form.
Obesity due to psychological reasons, due to disease or due to medication does not differ between men and women.
Abdominal obesity in men
The violation is not only externally unattractive, but also poses a serious threat to the body. Against the background of abdominal obesity, men may develop metabolic disorders, cardiovascular pathology, and diabetes. Abdominal obesity is a type of android obesity that occurs as a result of excess intra-abdominal fat.
Causes of abdominal obesity:
- poor nutrition and overeating;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- dysfunction of the hypothalamus;
- chronic fatigue, stress;
- decreased testosterone. Doctors say that the wider a man’s waist, the less male hormones he has in his body.
Predisposing factors include: impaired serotonin synthesis, malfunction of the digestive system, and genetics.
Diagnosis of obesity
Initially, obesity is determined by body mass index, as the ratio of body weight to a person’s height in meters squared. Using these calculations, the degree of obesity can be determined. Then the patient’s condition is studied in more detail and the causes of obesity are diagnosed in order to prescribe the correct treatment. For in-depth diagnosis of obesity and identification of causes, the following is carried out:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- body composition study;
- anthropometry;
- blood pressure measurement;
- blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- psychological analysis of the patient;
- other studies based on the patient's symptoms.
To compile a general picture of the disease, consultations with an endocrinologist, gynecologist, urologist, cardiologist, somnologist, psychologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist and other specialists may be required.
Based on the research data obtained, the nutritionist determines the patient’s condition, determines the causes of obesity and prescribes treatment aimed at eliminating the causes of obesity and weight loss.
Which doctor should I contact?
A gastroenterologist will be able to find out the causes of abdominal obesity and develop a treatment regimen. After a physical examination, the specialist will prescribe a number of additional studies and consultation with specialized doctors (endocrinologist, therapist and nutritionist).
Laboratory tests - general blood test and biochemistry.
Instrumental examination - gastroscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, computer diagnostics, magnetic resonance imaging and radiography.
After receiving the results, the doctor will write out a treatment regimen for abdominal obesity and monitor its implementation. Please note that the course of therapy is quite long - from 6 to 12 months.
Obesity treatment
To treat obesity, depending on the reasons that caused it, the doctor may prescribe:
- Diet;
- Physical activity;
- Drug treatment;
- Surgical treatment of obesity;
- Help from a psychologist.
The treatment regimen for obesity is determined by a nutritionist individually for each patient. A clinically significant result of obesity treatment is considered to be a decrease in body weight by 5–10% from the initial state, an improvement in the health and well-being of the patient.
Diet
The diet is prescribed by a nutritionist based on the degree of obesity and the patient’s health status.
In general, the diet consists of excluding from the diet:
- flour;
- sweet;
- cakes and pastries;
- fatty fish, meat and sausages;
- fatty dairy products;
- salted and pickled vegetables;
- sweet drinks;
- sweet fruits;
- fried foods.
Instead of excluded foods, the diet includes:
- whole grains;
- dietary varieties of bread;
- soups;
- cereals;
- green beans and peas;
- vegetables;
- fruits.
For each patient, a nutritionist individually creates a nutrition program for the most effective weight loss.
Physical activity
The following will help increase your daily calorie expenditure:
- physical education classes;
- aerobics;
- swimming;
- cardio exercises;
- walking 10,000 steps per day;
- other physical activity.
The doctor will prescribe a list of required daily physical activity individually based on the patient’s health condition.
Drug treatment
Treatment of obesity with drugs is carried out in order to eliminate the causes that caused obesity:
- In case of hormonal imbalance, medications are prescribed that bring hormone levels back to normal.
- For inflammatory diseases of the brain, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- For psychological problems, antidepressants are prescribed.
- In case of eating disorders, the doctor prescribes medications that reduce appetite.
- for other health problems that lead to obesity, medications are prescribed that can eliminate these problems.
Medicines in the treatment of obesity are not used as a primary means, but as part of an individual strategy aimed at losing weight for the patient, and are aimed at treating the diseases that caused obesity.
Surgical treatment of obesity
Among the surgical methods used against obesity are:
- Liposuction;
- Stomach reduction;
- Decreased absorption capacity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Liposuction
Surgical removal of subcutaneous fat for the purpose of body contouring. The operation gives a permanent effect. Liposuction is used when other methods of combating obesity and excess weight do not provide the desired results.
The operation is performed if there are no contraindications. Liposuction is preceded by consultation with various medical specialists. The operation is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia.
The surgeon injects a special solution into the fat layer, makes several incisions, into which thin tubes are inserted to suck out the fat, connected to a vacuum pump. Small areas of fat can be suctioned out with large plastic syringes.
After the operation, drains are installed in the incisions, the wounds are sutured and a tight bandage is installed. After surgery, the patient follows the doctor's postoperative recommendations for faster and more successful healing and recovery.
Stomach reduction
The stomach is reduced so that the patient eats less and gets full faster, thereby losing weight. This obesity treatment measure is used when other non-surgical treatments do not work.
The surgeon reduces the stomach in one of 3 ways:
- bypass - division of the stomach with isolation of a small part and insertion into the duodenal bulb to accelerate saturation and reduce appetite for sweet and fatty foods;
- banding - dividing the stomach into two parts using a special ring;
- introduction of an intragastric balloon , replacing the volume of the stomach, using endoscopic equipment, which allows reducing the volume of food consumed. If necessary, the cylinder can be removed.
Decreased absorption capacity of the gastrointestinal tract
Effective for the treatment of obesity of 3 and 4 degrees, when other treatment methods do not work. There are 2 main methods for reducing the absorption capacity of the gastrointestinal tract:
- biliopancreatic bypass - reduction of the volume of the stomach and reconstruction of the gastrointestinal tract with diversion of bile and pancreatic juice to the terminal ileum;
- small intestinal bypass is a complex operation that excludes the small intestine from digestion.
Help from a psychologist
Consultations with a psychologist to treat the patient’s mental problems leading to obesity - depression, anxiety, apathy and others. The psychologist gives his recommendations for adjusting the patient’s lifestyle and overeating. The psychologist's advice helps change life habits in order to increase activity, reduce food consumption and improve the patient's mental state.
How to treat obesity
Methods for getting rid of excess pounds depend on the cause of their occurrence and BMI. Diet and some physical activity are recommended for all patients. Drug therapy and surgical treatment are indicated for patients with high BMI.
Diet therapy
Diet changes are recommended for everyone, without exception, regardless of the cause of obesity. Since the disease is predominantly associated with excess calories, it is necessary to limit the amount of fat, salt, easily digestible carbohydrates, and liquids. It is also important to properly distribute your calorie intake throughout the day.
Breakfast should be the most high-calorie, since fat breakdown processes predominate in the first half of the day. Toward evening, fat cells accumulate mainly, so dinner should be as light as possible. The effectiveness of a hypocaloric diet is noted only with its constant adherence.
Physical exercise
To reduce body weight, in addition to proper nutrition, physical activity is necessary. You need to start with light exercises so as not to overload the body. Preference should be given to swimming, jogging, cycling or exercise bike, and aerobic exercise.
It is better to avoid heavy loads, especially with a high BMI, since such exercises can negatively affect the condition of the spine and joints. Physical activity must be adapted to the body’s capabilities, so a specialist should select a set of exercises. He will take into account physical characteristics, concomitant diseases and select the optimal load.
Drug therapy
Treatment with medications helps to obtain a short-term effect. If after a course of treatment a person does not change his lifestyle, the weight quickly returns. Drug therapy is usually indicated when a BMI is over 30 or when there is no effect of diet for more than 12 weeks.
Patients are prescribed medications to help reduce or control weight. They are aimed at reducing the feeling of hunger, accelerating satiety, which reduces the amount of food consumed. However, medications have side effects and can cause allergic reactions and addiction. There are groups of drugs that enhance metabolism in the body and block calories. If obesity is accompanied by pathologies of the endocrine glands, the endocrinologist prescribes hormonal therapy taking into account a blood test for hormones.
Prescribing drug therapy does not mean that you no longer need to adhere to a diet or an active lifestyle. They are always included in the comprehensive treatment of obesity in both women and men.
Surgery
If there is no result from conservative methods of treating obesity in women or complications arise due to excess weight, the issue of surgical intervention is decided. The problem of obesity is solved by bariatric surgery, which has 2 main goals: to reduce the amount of food consumed and to reduce the absorption of nutrients in the intestines. This is not a magical way to quickly lose weight, surgeons only push a person to a new lifestyle, so the result of the operation depends on the patient.
Do not confuse bariatrics with plastic surgery, the purpose of which is simply to remove accumulations of fatty tissue in certain areas using liposuction and abdominoplasty. Indications for bariatric surgery are: abdominal obesity, BMI more than 40 or above 35 if obesity in a woman has led to complications due to excess weight (diabetes mellitus, infertility, retinopathy, nephropathy, etc.).
All bariatric methods of treating women for excess weight produce results. During the first 1.5-2 years, they lose 60-70% of extra pounds if they follow all the doctor’s recommendations. To achieve weight loss, bariatric surgeons use the following operations:
- Banding is a popular method of treating obesity in women. It involves installing a silicone ring on the upper part of the stomach in order to reduce its volume and the amount of incoming food.
- Gastric ballooning is an endoscopic operation to install a silicone ball into the organ cavity. It occupies most of the stomach, preventing a person from eating much. In contact with the walls of the stomach, the ball irritates the receptors, suppressing the feeling of hunger.
- Gastric bypass. The essence of the operation is the resection of part of the stomach, the formation of a small pouch with a volume of up to 50 ml. It is then connected to part of the small intestine to allow food to bypass the duodenum. Weight is reduced by reducing the amount of food consumed, the degree of absorption of fats and carbohydrates.
- Sleeve (longitudinal) gastrectomy. Surgeons remove 80% of the organ, leaving a thin, long sleeve. Food stays in the stomach longer and satiation occurs quickly.
- Gastroplication is a modification of a previous operation. With this method, the stomach is not cut, but its walls are sewn together.
- Biliopancreatic bypass is the most complex method of treating obesity. During the operation, the size of the stomach and the length of the intestines are reduced. Weight loss occurs due to cutting back on food portions and reducing the absorption of nutrients - the breakdown of food begins near the large intestine.
After operations, metabolic processes improve, blood counts normalize, diabetes and other diseases that arise due to excess fat accumulation are stabilized. Many women are diagnosed with infertility due to obesity, and after treatment they manage to get pregnant.
Complications of obesity
Obesity can occur against the background of various diseases, but it can also lead to various diseases. Obesity without timely treatment can lead to complications such as:
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- cholecystitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- metabolic syndrome;
- joint diseases;
- depression;
- decreased reproductive function;
- cholelithiasis;
- other complications.
To avoid complications, you need to consult a doctor for help as soon as possible.
To treat obesity, you can contact our L-Med clinic by phone +7
.
Obesity prevention
In order to avoid obesity you need to:
- Monitor your weight and consult a doctor if your weight increases;
- move more;
- eat less animal fats;
- give preference to low-fat products;
- eat boiled or steamed food;
- eat less baked goods and sweets;
- reduce consumption or eliminate fried foods;
- eat more vegetables, fruits and legumes;
- eliminate hunger, eat small portions several times a day;
- do not overeat, leave the table with a slight feeling of fullness;
- half of the diet should be vegetables, a quarter - complex carbohydrates (cereals, bread), a quarter - proteins (meat, eggs and beans).
An active lifestyle and proper nutrition will help reduce the likelihood of obesity.
Cost of obesity treatment
In our clinic you can receive the following medical services:
- Liposuction (1 zone) — RUB 16,500.
- Endoscopic gastric banding for obesity - 70,000 rubles.
- Obesity surgical treatment program: bariatric surgery;
- domestic bandage - 140,000 rubles;
- imported bandage - 205,000 rubles;
- with gastric resection - 158,000 rubles.
- Appointment with a therapist—RUB 1,400.
- Appointment with an endocrinologist—RUB 1,400.
- Appointment with a cardiologist—RUB 1,400.
- Appointment with a neurologist - 1400 rubles.
- Various methods for diagnosing the disease.
You can sign up for obesity treatment at our L-Med clinic by calling +7 (4872) 302-902
or via the website.
All articles "