Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
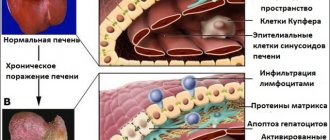
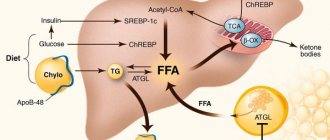
Fatty hepatosis or fatty liver is a disease in which a change in the structure and function of hepatocytes (liver parenchyma cells) occurs with the accumulation of fats in them. The cells increase in size and stop working properly, which affects the general condition of the organ.
Causes
The accumulation of fatty molecules in liver cells is due to either their excessive intake or impaired excretion. Risk factors for this process may include:
- Overweight;
- Impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Taking medications (corticosteroids, oral hormonal contraceptives, NSAIDs, antibiotics, cytostatics);
- Dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis;
- Disorders of the thyroid gland;
- Adrenal gland disorders;
- Hypertension, coronary heart disease;
- An unbalanced diet with an excess of fats, fried foods, simple carbohydrates;
- Lack of physical activity.
Separately, fatty hepatosis is distinguished as part of the general mechanism of development of alcoholic liver disease. In this case, ethanol consumption is a key factor in the disruption of the structure of hepatocytes and the development of dystrophic changes.
Symptoms
The main danger of the disease is that it does not manifest itself for a long time.
There are no specific symptoms of liver damage, which is why the person is not even aware of the slowly progressing changes. Fatty hepatosis can develop for years without any manifestations, and the clinic appears only when complications develop, when treatment becomes difficult, and changes in the liver become irreversible. Nonspecific symptoms of fatty hepatosis, which can appear with significant structural changes in hepatocytes:
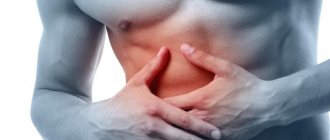
- Discomfort or periodic nagging pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Nausea, vomiting, stool disorders;
- Slight yellowness of the mucous membranes (visible on the whites of the eyes) and skin;
- General condition of asthenia, weakness.
With diffuse liver damage, periodic attacks of low blood pressure and fainting may develop. A person may also have symptoms specific to the underlying disease. For example, heart pain due to coronary heart disease. Or thirst, weight loss, polyuria, characteristic of diabetes.
Complications
Many people underestimate the danger of fatty liver disease because the disease is not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms.
However, as the disease progresses, more and more hepatocytes change their structure and cease to function normally, which ultimately results in a number of complications. Fatty liver degeneration is dangerous due to the following consequences:
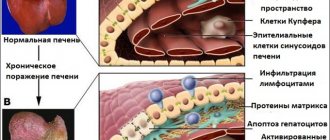
- Fibrosis is the proliferation of connective tissue when liver cells are damaged. It has been proven that this condition is treatable, but only if it is started in a timely manner.
- Hepatitis is a non-infectious inflammation of the liver, which can be either acute or chronic. The acute process most often occurs in people who drink alcohol in large quantities.
- Cirrhosis is a chronic disease that is accompanied by irreversible changes in the liver with a progressive reduction in functioning hepatocytes. The functioning of the liver gradually deteriorates, leading to life-threatening complications.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant degeneration of liver cells (cancer).
That is why treatment should be started as early as possible, until the process of changes is completely reversible. Complex therapy allows you to successfully restore liver function. If you start treatment at the stage of serious disorders and complications, then at best you can achieve a decrease in the rate of their progression, but not full restoration of the organ.
Diagnostics
Fatty liver disease is often found in people who are overweight or have insulin resistance (diabetes).
Diagnostics for liver dystrophy are also carried out for people who have systematically consumed or are consuming alcohol. In rare cases, pathology is detected due to a patient’s complaint about liver function. The diagnostic complex, in addition to standard questioning and examination, includes:
- General blood analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Coagulogram;
- Blood glucose level;
- Glucose tolerance test;
- Lipidogram;
- Ultrasound examination of the liver;
- Computed tomography of the abdominal organs (with or without contrast) or magnetic resonance imaging;
- Liver biopsy;
- Elastography.
The research results make it possible not only to confirm dystrophic changes in the liver, but also to assess their severity and identify the most likely causes. Diagnosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist or a more specialized specialist - a hepatologist. Only after confirming the diagnosis and identifying the exact causes of the disease, a treatment plan is developed.
Prohibited foods on the menu
In case of liver hepatosis, the following foods and drinks should be excluded from the daily menu:
- coffee, black tea, soda, alcohol;
- flour, incl. pasta;
- dairy products with a high fat content: cottage cheese, milk, cheese, sour cream, etc.);
- fresh bread, pancakes, crackers;
- radish, onion, garlic, sorrel, rhubarb, spinach, cauliflower, turnip, hot pepper;
- fatty fish and meats: catfish, salmon, pork, lamb, etc.;
- black or red caviar;
- strawberries, plums, grapes;
- raw eggs;
- spicy seasonings;
- fried, fatty, smoked;
- offal: liver, brains, etc.;
- legumes;
- lard or bacon;
- canned food;
- sausage, crab sticks;
- mushrooms in any form;
- pickled vegetables and fruits;
- cold drink;
- nuts, ginger, lemon, pumpkin seeds;
- fish, meat or chicken broths;
- confectionery products: sweets, cakes;
- sauces: mayonnaise, mustard, ketchup.
Prohibited Products
Diet features
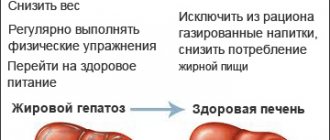
General recommendations for diet for fatty hepatosis:
- Refusal of alcoholic beverages;
- Limiting fatty, fried, smoked, sweet foods;
- Food at least 3 times a day;
- Increase fluid intake per day;
- Baked, boiled, steamed food;
- Increase in the diet of vegetables and seafood;
- A sufficient amount of calories in the diet (moderate deficit if necessary to lose weight);
- Limiting salt in the diet to 6-8 g per day;
- Limiting spices and spicy foods.
Following a healthy diet early in the course of the disease can be a key component of treatment.
Recipes for hepatosis
To make your daily menu varied and tasty, you can come up with various recipes yourself, taking into account permitted foods and diet restrictions. Do not forget about medical recommendations for creating a daily diet.
Vegetable soup
To prepare you will need 300 g potatoes, 150 g zucchini, 100 g carrots and 40 ml vegetable oil. We start by preparing the vegetables. So, the zucchini needs to be washed, chopped into pieces and simmered in oil until softened. Add washed, peeled and chopped carrots to it. Wash the potatoes, peel them, cut them into cubes and cook them separately, after which we combine them with the rest of the vegetables.
Now add a little salt and do not remove from heat for 5 minutes. In consultation with your doctor, you can add low-fat sour cream before serving.
In addition, you can add chicken meatballs to the soup. To prepare them, just grind the meat with a meat grinder, salt it and form into balls.
Stuffed cabbage rolls
The recipe includes lean meat 100 g, cabbage 130 g and rice 150 g. First you need to prepare the minced meat. To do this, you need to grind the chicken through a meat grinder and add salt. To easily separate the leaves, immerse the head of cabbage in boiling water for a couple of minutes, then “strip” the cabbage in layers.
Pour boiling water over the cereal and leave for a quarter of an hour. After the time has passed, pour it into the meat, after draining the water. Add butter and wrap the minced meat in each sheet like an “envelope”. Place the cabbage rolls in a pan, cover completely with water and cook until tender. For dressing use low-fat sour cream and a little herbs.
Casseroles
We present several casserole recipes:
- For cooking you will need 80 g beef, 80 g vermicelli, protein and butter. First you need to prepare the meat. To do this, boil it, cool and grind it with a meat grinder. Grind the egg with butter and mix with minced meat, then combine with boiled vermicelli. Next, keep it steamed until done;
- The recipe includes fresh cabbage 150 g, vegetable oil, semolina - 35 g, protein and milk 35 ml. Mix the last three ingredients and wait for the cereal to swell (about a quarter of an hour). Now you need to finely chop the cabbage and combine it with the resulting mixture. Grease the baking dish with oil and put it in the oven together with the prepared mass;
- we need a couple of large zucchini, 3 eggs, sour cream, 60 g of cheese, 100 g of minced chicken. First, grind the meat in a meat grinder and salt it. Now wash, peel and cut the vegetables into rings, beat the eggs, and grate the cheese. Place zucchini, tomato slices and some herbs in a baking dish in layers. This is followed by minced meat and cheese. Place vegetables on top again. Pour in sour cream and egg. The dish simmers in the oven for 40 minutes at 200 degrees.
Light meals
Dairy lovers will love this dish. It's called "curd pudding". To prepare it you will need the main ingredient 120 g, milk 60 ml, butter, semolina 10 g, protein and sugar 10 g.
Preparation begins by grinding the cottage cheese through a sieve. You can also beat it with a blender. Next, mix with milk, cereal and protein. Grease the baking dish with oil and place it in the oven with the resulting mixture. If desired, you can add raisins or dried apricots to the dish.
Another delicious dish is omelette with vegetables. The recipe includes 40 g each of cabbage, zucchini, carrots, as well as 2 egg whites, a little parsley and 60 ml of milk. The technological process begins with the preparation of vegetables. They need to be finely chopped and stewed.
Now add milk to the whipped whites and combine with vegetables. Cover with herbs and decorate with a spoonful of sour cream. Bake in the oven for 10 minutes.
Dietary nutrition is one of the most important parts of the treatment of hepatosis. A person who continues to abuse fatty foods will not be able to get rid of the disease only through medication. He needs to radically change his lifestyle, namely, give up alcohol, not take hepatotoxic medications, reduce heavy physical activity and control his psycho-emotional state, avoiding stress in every possible way.
Drug therapy
The prescription of drugs for fatty hepatosis largely depends on the cause of the disease. Treatment regimens may include:
- Hepatoprotectors;
- Vitamin complexes;
- Ursodeoxycholic acid preparations;
- Antihyperglycemic drugs for impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus;
- Lipid-lowering drugs;
- Antioxidants.
The prognosis for fatty liver disease is quite favorable, provided that you follow the diet and doctor’s prescriptions. Ignoring the problem can result in unpleasant complications, so it is better not to delay visiting the doctor.
treatment
First of all, it should be noted that since fibrosis is a problem that accompanies various liver diseases, as a rule, the most important task is to treat the underlying disease that caused fibrosis. However, general recommendations can be made that will be valid regardless of the cause of fibrosis. Such recommendations include lifestyle changes, namely, nutritional correction and a sufficient level of physical activity. Correction of the diet is made taking into account the patient’s age and gender, the body’s daily energy expenditure, the severity of the underlying disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies.