Every day we are faced with various situations when, at some point, due to external influences or physical activity, the likelihood of injury arises. A bone fracture is one of the dangerous injuries that may require long-term treatment and a long period of rehabilitation for complete healing. A common diagnosis among traumatologists is a broken toe, since the bones and joints of the foot are most vulnerable to accidental impacts or unsuccessful jumps. By what external signs and characteristic symptoms can you recognize a broken toe?
Briefly about the anatomy of the foot
The foot is part of the human musculoskeletal system, the part of the lower limb most distant from the body, responsible for stable position, balance, and movement of the body in space.
The foot has a flexible, elastic and movable arched design, which allows you to distribute the load on the limb, adapt to unevenness, and achieve a smooth gait thanks to the powerful ligamentous apparatus. In interaction with other parts of the leg, it is responsible for moving the body.
Twenty-six bones structurally form the three sections of the foot: the tarsus, metatarsus, and phalanges (toes).
The first section includes seven bones arranged in two rows:
- posterior – calcaneus and talus,
- anterior - navicular, three wedge-shaped and cuboid.
All of them are connected by joints, which allows a person to bend, straighten and make circular movements with the foot.
The second section is the metatarsus, consisting of five short tubular bones, located between the tarsus and the fingers.
The third section is the phalanges - tubular bones (14 pieces), connected by muscles and joints to form the five toes.
At the same time, the thumb consists of two phalanges, and the rest - of three. All of them are significantly shorter compared to the fingers, and the middle phalanx of the little finger is often inseparable from the nail. The phalanges are connected to each other by joints.
Ligamentous apparatus
The entire joint system provides the necessary functionality of the foot.
- Tarometatarsal - Small, flat joints with limited mobility. They form the base of the foot, with the help of ligaments in the tarsus.
- Interphalangeal - Provides immobility of the phalangeal bones.
- Subtalar - Inactive, located in the hindfoot, providing the arch of the talus and calcaneus.
- Metatarsophalangeal - A ball-and-socket joint that allows the fingers to flex and extend.
- Talocaleonavicular - Connects three bones to the axis of rotation. The foot can be rotated outward and inward.
- Ankle - A large joint connecting three bones. Forms a block between the tibia and the talus. The joint is attached to cartilage and forms ligaments on the side.
- All rotational and flexion movements of the leg occur at the expense of the ankle. The entire load while walking or running falls on the ankle joint.
The foot performs 3 functions:
- Supportive
- the ability to prevent pressure from the supporting surface. If the function is impaired, the person experiences severe pain when running or jumping. When walking, the foot performs a pushing function - accelerating movement. - Cushioning
- smoothes out shocks when walking and running. It protects joints from damage. If the arch of the foot is low, then the function is reduced, diseases of the bones, joints, and sometimes internal organs develop. - Balancing
– provides full coverage of the support surface and maintains the position of the human body when moving.
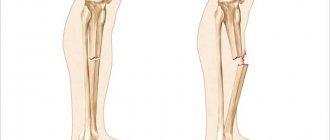
Classification of fractures and characteristic symptoms
- Toe fractures, depending on the cause of the injury, can be divided into two categories:
- Traumatic – mechanical damage to a relatively healthy bone (due to a bruise, twisting of the foot).
- Pathological - impaired bone strength and weakening due to diseases such as tuberculosis, malignant tumors, osteoporosis.
Based on type and condition, fractures are divided into:
- Open - the integrity of the soft tissues is broken by bone fragments, part of the bone is visible through the wound.
- Closed - the skin is not broken, the bone is not visible. This type of fracture avoids surgery and additional risk.
- With displacement - damaged bones can move to the side, pinching nearby nerves, muscles or blood vessels.
- No offset.
- Complete – with a bone fracture in one or more places.
- Incomplete - with the formation of a crack in the bone.
- Splintered - the appearance of fragments when the bone is crushed and they get into the wound.
Open fractures are most often accompanied by displacement of bones, which damages the skin, muscles and blood vessels. Complicated by bleeding.
Comminuted fractures most often occur when trauma is caused by a blunt object (stone, hammer, bat). When you fall and get hurt, there are usually no fragments.
Operative methods
The operation is necessary in the following cases:
- open fracture;
- comminuted fracture;
- closed with offset;
- osteomyelitis;
- incorrect fusion of fragments.
The following therapeutic methods are used:
Skeletal traction - Performed if closed reduction is not possible. Under local anesthesia, nylon threads are passed through the skin and bone fragments, which pull the fragments into the correct position. The ends of the threads form a ring that is held on a plaster hook. The patient remains in this state for 3 weeks, after which the threads are removed and the plaster is reapplied for another three weeks.
Open reduction - This is a full-fledged operation, during which bones and fragments are connected using screws and screws, plates, knitting needles, and wire. After the operation, the patient walks in a cast for another 4 weeks.
Closed one-stage reduction - Used for finger fractures without displacement of the nail phalanx. This is the setting of bones to their natural position, before injury. It is performed under anesthesia, as the procedure is painful. It is often possible to successfully set the bones only the third time. Traction devices are used for reposition. After the operation, the position and mobility of the bones are checked; if everything is in order, the foot is immobilized with a splint until complete recovery.
Removable bandage
A polymer bandage is used for fractures of the thumb, middle, finger or little finger. It keeps the finger stationary and does not interfere with everyday life. An adhesive bandage is especially indispensable for a fracture of the little toe, when there is no point in attaching a cast to the entire foot.
The bandage does not restrict a person’s movement and protects the phalanx from external influences.
Causes of toe fractures
There are many situations in which there is a danger of breaking your toes, both in everyday life and during the production process. Such cases include: an unsuccessful fall, a jump from a height, non-compliance with safety precautions at work and negligence when playing sports.
The main causes of foot injury:
- a strong blow or a heavy object falling on the foot;
- a situation where a person stumbles or stumbles;
- sports injury leading to forced hyperextension of the foot;
- hitting the front of the foot with a hard object (for example, furniture, a step on a staircase, a curb on the sidewalk).
How to identify a violation of bone integrity if there is no displacement
When determining a fracture, doctors can immediately differentiate it in accordance with the classification accepted in medicine:
- in the direction of the fracture - oblong or transverse;
- according to the type of fracture line - screw, oblique;
- according to the fault mechanism - direct and indirect.
Of course, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis only after an x-ray, but in order to suspect an injury, you can palpate the site of injury. First, the movements should be oblong, and then transverse and oblique.
When trying to listen to your feelings, you need to take into account that there may be several fractures, as well as the number of fragments. You can break a finger without them if you fall straight on your foot. Several fragments may occur as a result of a blunt and smooth object falling on the leg. The bone is broken into small fragments when an uneven object impacts the finger.
Signs of a toe fracture: phalanx or joint
Symptoms of a fracture are divided into absolute and probable.
Probable signs suggest the presence of a fracture, absolute signs prove and confirm a fracture.
| Possible signs of a fracture | Pain when feeling the injury site |
| Increase in volume of the finger due to swelling of soft tissues, redness | |
| Hematoma at the site of injury | |
| Sharp pain in the finger when moving | |
| Absolute signs of a fracture | Unnatural position of the finger, change in its appearance |
| Uncontrolled mobility of the injured finger | |
| Crunching of bone fragments when trying to press on a finger | |
| Bleeding and freely visible ends of the bone with an open fracture |
Symptoms and visual signs of bone loss
The presence of a fracture can be determined by a number of symptoms.
Damage without displacement
You can recognize a fracture by the nature of the pain. Pain sensations occur in the injured finger, the intensity of which does not subside, in some cases it can increase over several days. The pain persists not only during movement, but also at rest.
The skin in the damaged area turns red. In some cases, the skin may turn blue or black. Local temperature increases.
Due to severe discomfort, motor activity in the injured area is limited. It hurts to step on, to bear body weight, to bend and straighten. If you tap the tip of the nail, the pain will become more intense.
The severity of pain may vary. Since the bones in the fingers are small, violation of their integrity rarely leads to loss of consciousness or shock. In some cases, a person is able to walk and even play sports for several days.
Swelling appears within a few days. The swelling gradually increases in size.
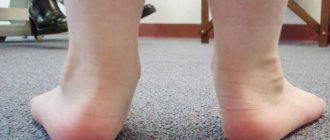
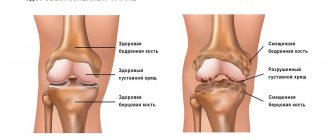
With offset
Deformation is often noted. The injured finger is in a forced position and can move. The feet become asymmetrical. Possible lengthening of the foot, shortening of the broken toe, and the appearance of bumps on the lateral surface.
Hematomas that occur near the injured finger help to recognize a fracture. Excessive mobility may occur in places where it has not previously been noted; normally it should not be present.
Diagnosis of foot injury
How to determine a broken toe? The diagnosis is made in a medical facility.
The traumatologist interviews the victim and conducts a visual examination to determine signs of a fracture. The doctor will definitely send the patient for an x-ray to confirm the diagnosis, see the location of the fracture and possible displacement of bone fragments.
Based on all the data obtained, the necessary treatment is prescribed.
Drug therapy
Three types of medications are used in the treatment of fractures:
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- chondroprotective.
They are taken orally and topically on the painful area.
The action of the drugs provides:
- stimulation of the processes of restoration of damaged tissues;
- improvement of salt metabolism in bones (calcium-phosphorus);
- replenishment of calcium deficiency;
- elimination of inflammation.
The patient is prescribed: Chondroitin, Teraflex, Calcemin, Vitamin D3, Calcium Gluconate, Nise, Nurofen, Dexalgin. For local impact on the inflamed area: Traumeel-gel, Nise-gel, Voltaren.
The gel is applied three times a day.
First aid
If a fracture is suspected, the injured toe and foot need to be fixed in one position. If possible, apply ice to the damaged area.
If there is an open wound, the injured limb is bandaged with a sterile bandage to avoid possible infections from entering the bloodstream. Then a splint is applied to the foot and secured with a bandage. This fixation of the foot will help to avoid further trauma to the bones and soft tissues of the damaged area of the toe.
Watch the video where a traumatologist gives recommendations on how to act immediately after an injury in order to alleviate the victim’s condition and avoid complications in the future:
Salt baths
A moderate concentration of saline solution will help cure a foot injury. To prepare it, dissolve 1 tbsp in a liter of hot water. a spoonful of salt, it is better to take sea salt for these purposes. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and has a beneficial effect on bone tissue.
The optimal water temperature is 37-38 degrees . A warm bath will warm the sore spot well and speed up recovery. After it, a positive effect occurs - the muscles relax, the sensitivity of the nerve endings decreases.
Take the salt bath for 10-15 minutes , after which you do not need to wash your feet. Pat them dry with a dry cloth and let your feet rest. To enhance the effect, decoctions of medicinal plants and fir branches are added to the water.
During the procedure, the limb must be freely located in the basin so that the person has the opportunity to move it.
Attention
! Salt baths are not used for open wounds, diabetes, hypertension and a tendency to blood clots.
Treatment methods for different types of fractures
Depending on the nature and location of the injury, different treatments are prescribed.
- Injury to the nail phalanx. Accumulations of blood are removed from under the nail, the fragments are fixed, and the injured phalanx is attached to the adjacent finger using a plaster. Complete removal of the nail is required when the hematoma under the nail is too large.
- Injury to the middle and main phalanges. If there is no displacement, the phalanges are immobilized with a plaster for two to four weeks to allow proper healing.
- Displaced fracture. The damaged finger is stretched along the axis. In case of multiple displacement, manual reposition of bone fragments is performed, and then a plaster “shoe” is applied for up to 3 weeks.
- For closed displaced fractures, as well as comminuted fractures. The bone fragments are returned to their place in a closed manner. This is a painstaking and complex job that requires care to prevent malunion of the bones and deformation of the finger in the future.
- Fracture of several fingers. Application of a plaster plate - splints.
- Damage to the big toe. Applying a plaster cast ranging in size from fingers to knee. In case of an intra-articular fracture, surgery is required to fix the joint with special knitting needles. The plaster is applied for 6-8 weeks.
- Open fracture. First, the bone is restored from fragments. Then antibacterial therapy is prescribed, which avoids secondary infections, and a tetanus vaccine is administered. If necessary, displacement and curvature are eliminated, and a splint is applied to ensure immobility until healing.
Rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation measures include massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy. Wearing a cast for a long time is not pleasant, but it is necessary for proper bone healing. If the bones do not heal properly, this will lead to improper distribution of body weight on the foot in the future and more problems when walking.
It is recommended to walk as little as possible during rehabilitation, wear comfortable, roomy shoes without high heels, and keep the affected leg elevated during rest, for example, place it on a pillow. To reduce severe swelling, you can apply cold compresses in the first 2-3 days, but do not overuse them.
You should eat rationally, eat enough vegetables and fruits, especially pay attention to foods rich in calcium: cheese, cottage cheese, etc. At the same time, limit or completely abandon strong coffee, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, as they remove calcium from body. It is also recommended to take multivitamins, C, D and B12.
Author of the article:
Kaplan Alexander Sergeevich |
Orthopedist Education: diploma in General Medicine received in 2009 at the Medical Academy named after. I. M. Sechenov. In 2012, she completed postgraduate studies in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics” at the City Clinical Hospital named after. Botkin at the Department of Traumatology, Orthopedics and Disaster Surgery. Our authors
What is the danger of a broken toe?
Often, after receiving an injury, the victim ignores mild pain and does not take the injury to medical institutions. This is fraught with complications and unpleasant consequences, such as:
- improper healing of the damaged bone;
- the formation of bone calluses, which slow down bone recovery and are a clear cosmetic defect;
- formation of a false joint;
- osteomyelitis - inflammation of the bone and bone marrow associated with infection during an open fracture. Pathogenic bacteria can enter the bloodstream, as well as the bone itself, during a comminuted fracture. To avoid infection, it is necessary to treat the wound with antiseptic solutions as quickly as possible and consult a doctor for further treatment;
- gangrene is the death of body tissue associated with oxygen starvation and impaired blood circulation at the fracture site. Without immediate intervention, gangrene can spread from the affected area to healthy tissue, increasing the risk of permanent limb loss.
A false joint can occur in the absence of timely reduction of a fracture with bone fragments. During the first two days after the fracture, the bone canals begin to close and the edges of the bones round and wear away. As a result, two separate bones are formed instead of one broken one. They are not connected to each other, which reduces the support function of the limb and interferes with full movement. The false joint is always in a state of inflammation due to the lack of cartilage between the ends of the formed bones, which reduces friction .
Physiotherapy
During the rehabilitation period, the following procedures are indicated:
- UHF . Used to warm tissues and enhance microcirculation. Improves metabolic and reparative processes, accelerates the formation of callus.
- Magnetotherapy . Sessions begin a few days after the injury, and the plaster cast and metal rods are not an obstacle to their implementation. The procedure enhances bone mineralization, improves calcium and phosphorus metabolism, and relieves swelling. The course consists of 10-15 sessions.
- Interference currents . Electrodes are applied to the affected area, which deliver rhythmic impulses of various frequencies (from 0 to 100 Hz). After exposure to electric current, blood circulation and tissue trophism improve, pain syndrome decreases, and lymph movement accelerates.
- Paraffin or ozokerite applications . The thermal procedure improves blood flow and accelerates bone tissue recovery. In addition, there are more than 70 nerve endings on the skin of the feet. Their irritation has a positive effect on the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
What to do to protect yourself from injury
- Shoes should be comfortable and match your foot size.
- Your diet should always include foods that contain calcium. Fermented milk products, potatoes, apples, beans, cabbage and other healthy foods will help maintain the necessary level of calcium for the normal functioning of the body.
- Take essential vitamins – C, D, B12 – in addition to proper nutrition.
- Do not neglect safety rules in places with an increased risk of injury - at work, sports grounds.
- Get regular medical checkups to help identify chronic conditions that can weaken your bones and cause unexpected injuries.
Life is filled with exciting activities and moments, you want to be everywhere and try as much as possible. The main thing is not to forget to monitor your health, because it is much easier to follow simple rules of personal safety than to undergo a long recovery from unpleasant injuries.
General recommendations
After removing the splint or splint, for the first time you should not put much weight on the sore leg, as this can lead to a new injury to the fragile foot. However, complete inaction is also not recommended. In the early recovery period, you will have to move with the support of a stick.
Make sure you have comfortable shoes without heels in advance. It should be worn not only at home, but also on the street. High heels lead to excessive stress on the toes, which can lead to the formation of large calluses and curvature of the toes.
Special orthopedic insoles are useful: they will give the foot a physiological position and improve blood circulation.
Basic safety measures that should be observed when carrying heavy objects, skating and roller skating will help you avoid a fracture.