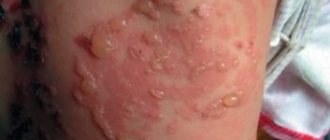
Carbuncle is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of several closely located sebaceous glands and hair follicles, caused by Staphylococcus aureus (St. aureus). It mainly affects the back of the neck, interscapular area, skin of the buttocks and face. On the extremities, carbuncles appear much less frequently.
Most often, a carbuncle is formed in patients with blood diseases, diabetes, obesity, and reduced immunity. Predisposing factors may also include oily skin type and poor personal hygiene.
Carbuncle - what is it?
Any carbuncle is an inflammation caused by an infection. Structurally, it is the result of the fusion of several boils, therefore, unlike the latter, it has a more severe manifestation.
On a note! According to statistics, pathology occurs 1.5 times more often in men than in women, and the main percentage of cases (up to 40%) occurs in the summer.
In its development, each carbuncle goes through 3 stages:
- infiltration – the formation and growth of dense nodules with the formation of a single inflamed infiltrate, which can reach a diameter of 10 cm or more;
- suppuration - maturation of the infiltrate with the formation of outlet openings emitting pus;
- necrosis and rejection - suppuration stops and the death of damaged tissue begins, followed by scarring.
A typical example of appearance is the carbuncle in the photo:
ICD-10 code
Carbuncle belongs to the group of infectious skin diseases with the code - L00-L08 .
It includes:
- carbuncle on the skin ( L02 );
- carbuncle in the facial area ( L02.0 );
- carbuncle of the neck ( L02.1 ) and body ( L02.0 );
- carbuncle of the buttocks ( L02.3 );
- carbuncle of arms and legs (L02.4);
- carbuncle of other ( L02.8 ) or unrefined localization ( L02.9 ).
Causes
The causative agent of the inflammatory process is usually Staphylococcus aureus, often accompanied by other bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Streptococcus). Their uncontrolled reproduction in the epidermis is caused by the following reasons:
- non-compliance with hygiene rules and unsanitary conditions at home;
- immunity disorders due to severe chronic diseases;
- metabolic pathologies – diabetes, obesity;
- anemia, vitamin deficiency, severe physical and emotional exhaustion;
- unfavorable environmental working and living conditions - frequent contact with petroleum products, exhaust gases, cement and asbestos dust;
- increased secretion of the sebaceous glands;
- skin microcracks, scratching insect bites.
Carbuncles prefer to appear in places with well-developed loose subcutaneous tissue - on the back of the neck, in the maxillofacial area, in the area between the shoulder blades, on the lower back, in the armpits, on the buttocks, and less often on the limbs.
Attention! The greatest danger is represented by purulent formations in the head area. The infection concentrated in them through the blood and lymph flow can easily penetrate the tissues of the brain and its membranes, causing severe damage to the nervous system. Self-medication of such carbuncles is strictly contraindicated!
Localization
The “favorite” places for the localization of carbuncles are the maxillofacial area and the back of the neck.
Pathology also develops:
- on the back, between the shoulder blades;
- on the buttock;
- under the arm;
- on the lower back.
More often, carbuncles appear in those places of the body where fatty tissue is more developed and has a looser structure.
Ulcers on the face, for example, in the lip area, on the chin or carbuncle of the nose, are the most dangerous.
Bacteria from this area, using the bloodstream and lymphatic vessels, can penetrate the veins inside the skull and thereby lead to inflammation in the brain and damage to the nerve trunks .
The formation of carbuncles on the chest and limbs is possible, although ulcers appear on the arm or leg quite rarely.
Carbunculosis in the groin in women can develop due to improper treatment of boils, as a complicated form of this pathology.
Therefore, ulcers on the labia should be treated in a timely manner by consulting an experienced doctor.
Purulent inflammation can also affect internal organs. Recently, doctors have noted an increase in cases of kidney carbuncle, a necrotic lesion in which an infiltrate forms in the cortex.
If you are interested in what is the proper treatment for seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, read our publication.
The causes, characteristic symptoms and treatment of herpes zoster are described in detail in this article.
Symptoms of carbunculosis
A skin carbuncle develops from a small nodule that quickly increases in size. External distinctive symptoms of pathology:
- local increase in temperature - the skin in the affected area is hot to the touch;
- pronounced swelling with a varnished, stretched surface;
- hyperemia with a dark (burgundy or blue) tint to the tissues;
- during suppuration, the skin of the infiltrate breaks through with the formation of small holes (“sieves”) oozing pus, which at a later stage merge into one large hole;
- unpleasant bursting pain during the growth of the tumor and sharp tugging pain - at the stage of suppuration; when moving or touching the carbuncle, irradiation to other parts of the body is possible.
The local focus of inflammation affects the entire body, dictating a general deterioration in well-being:
- increase in body temperature to 39-40 C;
- headache;
- intoxication of the body with nausea and vomiting;
- loss of appetite, loss of strength;
- increased heart rate.
With exhaustion, low body resistance, as well as in older people and in the absence of treatment, the process becomes more pronounced and leads to aggravation of symptoms with various complications - from fever to sepsis.
Kinds
- A traditional carbuncle forms on the face, body, limbs and torso and develops according to classical canons in several stages.
- Kidney carbuncle . Occurs as a complication after suffering pyelonephritis. Its manifestation is similar to inflammatory kidney diseases and is sometimes difficult to distinguish from them. Symptoms of the disease include fever, intoxication and pain in the lumbar region. Differential diagnosis using X-ray and ultrasound methods helps to identify pathology.
- Emphysematous carbuncle . It does not develop in humans; it affects cattle. When infected with a pathogenic microorganism, many swellings are found on the body of animals, they quickly weaken and die from cardiac and respiratory failure.
- Anthrax carbuncle . It is formed when a person is infected with the anthrax bacillus, has a severe course and is extremely contagious to others.
How to diagnose
The diagnosis of carbunculosis usually does not raise questions. The main approach used by the doctor is differential diagnosis, as well as laboratory tests to identify the pathogen.
In differential diagnosis, one should distinguish the signs of a carbuncle from the symptoms of a boil, abscess, phlegmon, anthrax, hidradenitis:
- A single boil forms only in the superficial layers of the skin, without covering the hypodermis and subcutaneous tissue. Pus does not come out through multiple openings, but through a single one. There is no pronounced effect on the entire body in the form of high temperature. The only similarity is that a carbuncle is essentially a union of several adjacent boils.
- Phlegmon is an inflammation spread throughout the tissue, without a separate center.
- An abscess can form not only in the dermis and tissue, but also in other tissues - muscle, bone, parenchymal.
- With hidradenitis, the inflammatory process does not involve the hair follicles, but the sweat glands, so the pathology manifests itself mainly in places of high concentration - in the groin, armpits, and chest.
- In carbunculosis with anthrax pathogens, there is no sensitivity at the site of the lesion, and the ulcer itself is devoid of purulent contents.
On a note! The most specific sign of a carbuncle is the dark color of the affected tissues (the origin of the name “carbuncle” is from the Latin carbunculus - ember), which allows us to draw a parallel only with the symptoms of anthrax. In all other above-mentioned cases, there is no characteristic tissue pigmentation.
In addition to an external examination with a patient interview, additional laboratory tests are carried out:
- general blood test - to assess the degree of inflammation;
- sugar test - to detect diabetes;
- blood test for sterility - to exclude the possibility of sepsis;
- bacteriological analysis of the contents of the carbuncle - to identify the causative agent of infection and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Benefits of contacting us
The opening of the carbuncle at the GMS surgery center is carried out using the “one-day surgery” technology. Within an hour after treatment, you will get rid of all discomfort, pain and can return to your usual activities. In more complex cases, hospitalization for a day is possible.
Autopsy of a carbuncle at GMS Hospital is:
- a team of experienced surgeons with many years of experience;
- safe anesthesia;
- 100% sterility;
- the use of gentle, minimally invasive surgical techniques;
- absence of surgical complications;
- short healing time.
The use of microsurgical technologies, including laser and radio wave surgery, makes it possible to minimize damage to health and perform surgery quickly, painlessly and with maximum therapeutic results. You can make an appointment with a surgeon by phone or using the online form.
Treatment methods for carbuncle
Depending on the stage of the inflammatory process, the general condition of the patient and the location of the carbuncle, conservative or surgical treatment is used.
Conservative treatment
Conservative methods using drug therapy and physiotherapy are relevant for small carbuncle sizes and in the early stages of the inflammatory process, until a purulent-necrotic core has formed. Also important is the absence of severe intoxication of the body and maximum removal of formations from the head and main lymph nodes. If these conditions are not met, conservative methods are used as an accompanying measure during surgery.
Attention! With carbunculosis, early diagnosis and timely treatment are of great importance. In such cases, there is a chance to avoid surgery, and the recovery itself is much easier and takes less time.
For carbuncle, the following are most often prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory (NSAID) compounds;
- painkillers;
- detoxifiers;
- drugs to regulate cardiac activity (if necessary) and antiplatelet agents to prevent thrombophlebitis.
After opening the abscesses, topical preparations are used:
- antiseptics for wound disinfection;
- antibacterial ointments;
- proteolytic and emollient compounds against scar formation.
For more active absorption of medications, physical therapy is prescribed. They have a disinfecting effect, increase blood circulation in the affected area, thereby reducing the size of necrotic areas and accelerating the healing process.
Physiotherapy techniques:
- UHF therapy;
- UFO therapy – ultraviolet irradiation of blood;
- magnetic therapy;
- ILBI – intravenous laser irradiation of blood.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the source of inflammation is the main treatment method for severe deep carbunculosis with the formation of necrotic areas and poor discharge of purulent contents. In addition, urgent removal of the carbuncle is indicated if there is a sharp deterioration in the patient’s general health.
The operation is performed in a hospital using local or general (if necessary) anesthesia. The procedure takes no more than half an hour and takes place in 3 stages:
- The infiltrate is excised, removing necrotic areas and pus.
- The wound is thoroughly washed with antiseptic solutions and drainage is installed to drain the purulent exudate.
- The cleaned wound is treated with antibacterial compounds and healing ointments.
The first days after surgery, antibiotics and antibacterial agents are prescribed. Other medications, as well as physical therapy, are prescribed depending on the patient's condition.
On a note! If a carbuncle of the neck or facial area is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed bed rest.
ethnoscience
Homemade recipes are good as an addition to therapy prescribed by a doctor, but not as independent treatment. They help reduce the toxicity of antibiotics, enhance the effect of disinfectants, increase the body's defenses and accelerate tissue regeneration.
Simple and effective recipes:
- Grind fresh plantain leaves into a paste and apply to the affected area; keep for 0.5-1 hour, then replace with a new compress; the herb effectively draws out pus, has an anti-inflammatory and detoxifying effect;
- ointment based on dry herbs of calendula, sweet clover, St. John's wort and fat (or baby cream); 1 tbsp. l. Grind herbs of your choice or mixtures thereof in a mortar to a powder and mix with 1 tbsp. l. fat and knead thoroughly; It is recommended to constantly lubricate the surface of the carbuncle with the resulting mixture until it is completely healed;
- rinsing and dressings with sea salt effectively draw out pus, relieve inflammation, and clean the wound; in this case, you can prepare either a hypertonic solution (with a teaspoon per glass of water) or a concentrated solution (more suitable for disinfection);
- aloe leaf - fresh or mixed with honey - apply as a bandage for half an hour 2-3 times a day;
- compresses with a decoction of celandine have a pronounced antibacterial effect - the name of the herb speaks for itself;
- internal intake of infusions of antibacterial herbs: St. John's wort, chamomile, sage, sweet clover, yarrow, wormwood, calendula, nettle, thyme.
It will not be superfluous to add natural antibiotics such as natural honey, turmeric, ginger, garlic, propolis, cranberries, onions, horseradish, and pomegranate to your daily diet.
Medicines
Photo: obaldela.ru
Outpatients are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics in tablets. During hospitalization, drugs are administered intramuscularly. General antibiotic therapy is supplemented by injecting the carbuncle with medications. Pain syndrome is eliminated with the help of analgesics. The choice of painkillers is made taking into account the severity of the symptom; it is possible to use NSAIDs, analgin, ketorol, and in severe cases, short-course narcotic analgesics.
The surface of the unformed carbuncle is treated with an alcohol solution, streptomycin or synthomycin emulsion. After opening the abscess, the above-mentioned proteolytic enzymes are used, then antibiotic ointments are used. To increase the body's defenses and accelerate wound healing, immunomodulators, ascorbic acid, and vitamins A and B are prescribed. In severe cases of the disease, plasma infusions are performed with the addition of anti-staphylococcal antibodies.
Complications of carbunculosis and its consequences
If a staphylococcal infection enters the blood and/or spreads to deeper tissues, covering adjacent organs, serious complications develop from individual systems and the entire body:
- lymphadenitis with damage to adjacent lymph nodes; in severe cases, the process develops into lymphangitis with the involvement of lymphatic vessels and can “spread” throughout the body’s lymphatic system;
- purulent meningitis - with cervicofacial localization of carbuncles, the infection with blood penetrates the blood-brain barrier, causing serious damage to the nervous system;
- extensive phlegmon - a purulent process forms diffuse purulent inflammation of the area adjacent to the carbuncle;
- phlegmons, adenophlegmons, abscesses with “spreading” of the infection and spreading to deeper layers of tissue;
- erysipelas of the skin - unlike phlegmon, does not penetrate into the deeper layers and occurs, as a rule, when affected by a streptococcal infection;
- vascular pathologies - infectious phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, as well as vascular bleeding with weakening of the vascular wall;
- osteomyelitis – when infection spreads to bone tissue;
- sepsis is a general blood infection with a high risk of death.
Complications are a typical phenomenon in the absence of timely treatment, with serious pathologies of the immune system and some chronic diseases, such as diabetes.
Folk remedies
Photo: fittedmagazine.com
You should not use local methods (lotions, compresses) on your own, because choosing treatment methods without taking into account the severity and stage of development of the abscess can cause severe complications. At home, it is recommended to use safer general remedies:
- Brewer's yeast . The high content of amino acids, vitamins B and D helps the body fight infection and eliminate toxins faster. Yeast is taken before meals 3 times a day in the amount of 1 teaspoon.
- Chicory . It has an immunostimulating effect, contains useful vitamins and minerals, and has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Pour 2 teaspoons of chicory root into a glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, then consume a third of a glass 3 times a day.
To increase immunity, rose hip tea, cranberry juice, infusion of ginger and lemon, infusion of sea buckthorn with lemon and honey, and a decoction of bay leaves are useful. Before using any folk recipe, you should consult your doctor to rule out contraindications.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Preventive measures
Particularly relevant when carbuncles appear repeatedly. In this case, it is imperative to take measures aimed at increasing the level of hygiene and strengthening the immune system.
Basic recommendations:
- Keep your body clean with water treatments - showers, wet wipes, baths; You can add infusions of medicinal herbs to the water - chamomile, calendula, sage, string, violet. Use only personal hygiene products!
- Enrich your diet with fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as mineral supplements and vitamins. This will help strengthen the immune system and increase the body's resistance to infections.
- Avoid prolonged overwork, stress, and nervous experiences. Alternate work with proper rest.
- Avoid tight “synthetics” in clothes. Fabrics should “breathe” allowing air to circulate freely.
- For insect bites and abrasions, treat the skin with antiseptics.
- Treat any infectious diseases, even common colds, in a timely manner. Do not be lazy to undergo therapy until complete recovery.
Remember, it is a neglectful attitude towards yourself and your health that causes diseases that in fact can be easily avoided.
Features of the rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after opening the infiltrate lasts 10-14 days. During this time, you should strictly adhere to all medical recommendations:
- for 5-7 days after the intervention, you need to change the dressings daily, using wound healing and antiseptic drugs prescribed by the doctor;
- avoid skin injury;
- eat rationally;
- maintain careful hygiene;
- lead an active, healthy life.
To prevent the spread of infection, a short course of massive antibiotic therapy is prescribed. To speed up healing, a course of physiotherapeutic procedures (UHF, UV irradiation) is carried out. For patients with a predisposition to purulent-inflammatory diseases of the skin and subcutaneous structures, consultation with an endocrinologist and immunologist is recommended. You can learn more about the operation at a consultation with a surgeon. You can make an appointment with a GMS Hospital specialist around the clock – on the website and by phone.