Catarrhal tonsillitis - almost everyone is familiar with this disease. This infectious disease in medicine is called acute tonsillitis. Catarrhal sore throat in adults is a sore throat in the usual sense. This disease proceeds according to the classical scheme, and is quite easy to treat, but only if it is not neglected and you consult a doctor in time, and do not try to prescribe therapy for yourself. Otherwise, even the mildest form of sore throat can lead to serious consequences.
The disease is a disease with a high degree of contagiousness, that is, it is very easy to become infected: just drink from the patient’s cup or use his towel. Moreover, the first symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis can occur several hours after contact with the patient. On average, the incubation period of the disease lasts from one to four days.
The peak of disease outbreaks occurs in autumn and winter. It is at this time that the body’s defenses decrease, the immune system weakens, and sometimes a slight hypothermia or a stressful situation in combination with the entry of a pathogen into the body is enough to trigger the inflammation mechanism.
Causes
The pathogen enters the body, covering the tissue of the palatine tonsils. Gradually, microbes spread through the bloodstream, causing the development of intoxication. Local immunity is immediately activated by producing a large number of leukocytes. Blood rushes to the tonsils, causing them to become red and swollen.
The main route of penetration of the pathogen is airborne. Children become infected through shared toys and close bodily contact. The infection begins to spread when the body is weakened and hypothermic. Adults become infected through droplets of saliva or household items.
Who is treating?
The treatment of catarrhal pharyngitis is most often carried out by an otolaryngologist. If it is impossible to visit him, you should contact a therapist or pediatrician. They will also be able to prescribe the necessary therapy to the patient. Most often, pharyngitis is treated by a general specialist when it is a symptom of a viral infection.
In cases where the disease is caused by an allergic reaction, you will need to involve an allergist to eliminate it. He will determine the irritant that causes the problem and select a way to correct the condition. If it is impossible to completely eliminate the effect of the irritant on the mucous membrane, then treatment is selected aimed at maintaining a satisfactory condition of the patient.
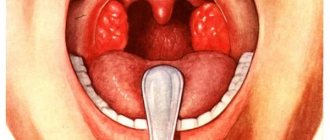
Symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis
The following symptoms are characteristic of catarrhal tonsillitis:
- Inflammation covers the tonsils on both sides. Unilateral pathology is a rare occurrence.
- The palatine arches and tonsils turn red.
- Mucous exudate is released.
- The lymph nodes located under the lower jaw become slightly enlarged.
- The throat is irritated and sore.
- Sore throat worsens when swallowing.
- The surface of the tongue dries and becomes covered with a white coating.
- Body temperature immediately rises (within 37-37.5°C).
- Over the course of several hours, malaise, fatigue, weakness increase, and chills appear.
Signs of the disease appear abruptly and develop rapidly. They are observed for 3-4 days, and then the disease also subsides suddenly, leaving a sore throat.
Diagnostics
A qualified specialist will quickly identify catarrhal sinusitis. The disease can be determined by the symptoms listed by the patient, x-rays, and examination of the nasal cavity. Using an X-ray examination, it is possible to determine not only the area of inflammation, but also the oversaturation of the paranasal sinus with exudate.
You can study the nature of the infection that provokes the development of catarrhal sinusitis using research:
- analysis of exudate and blood;
- CT;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses.
The results of these studies are informative and allow us to recognize the type of pathogenic bacteria that caused the disease. This helps to choose the optimal treatment method that will relieve the patient of the disease, even with severe symptoms.
Symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis in children
Most often, catarrhal tonsillitis occurs in children from six months to three years. Children tolerate the disease worse than adults. Sometimes parents mistake the symptoms of this disease for ARVI, and therefore do not attempt treatment in a timely manner.
In children under three years of age, the temperature rises to 38°C, less often above 39°C. In this case, medical attention is required. In addition, the child complains of dry mouth, weakness, headache and dizziness, and increased salivation. Sore throat is accompanied by meningism and convulsions.
The severity of symptoms is observed during the first three days.
Forms
When a pathogenic microorganism enters and penetrates the mucous membrane, bacteria begin to multiply there. When a high concentration of harmful microorganisms is reached, intoxication occurs, which is characterized by swelling and inflammation. Cell walls lose their permeability, and pressure in the blood vessels increases.
As the disease develops, exudate begins to come out in the form of serous fluid or mucus. When there is swelling, this fluid collects in the nasal passages, preventing normal breathing. This condition facilitates the penetration of a secondary infection, which provokes the formation and discharge of pus from the nose.
There are various forms of the disease, which depend on in which sinus the inflammation begins:
- Sinusitis. Occurs with inflammation in the maxillary sinus, characterized by nasal congestion, but not complete, but partial, which is explained by the connection with the maxillary canals. The process spreads to the two sinuses, making breathing difficult, which contributes to the development of laryngeal infections.
- Catarrhal sinuses affect the frontal sinuses. Develops as a result of infection entering the circulatory system. In addition to the swollen mucous membrane, there is pain throughout the day, in particular in the forehead area. In the evening the patient feels better. The main symptoms of this form of the disease are the production of tears and photophobia.
- Catarrhal ethmoiditis occurs when there is inflammation in the cavity, which is located between the frontal and maxillary bones. The patient complains of severe headache, which is not relieved by non-narcotic analgesics. The main danger is the possibility of inflammation in the brain, arteries and eye sockets. This form of the disease is considered the most severe and difficult to treat.
- Acute sphenoiditis is a rare form of the disease in which the sphenoid sinus becomes inflamed. The patient complains of pain in the back of the head, temporal region and eye sockets. The danger of the disease is the likelihood of inflammation spreading to the facial bones and brain.
Rarely, a patient may have several forms of this pathology at once. For example, inflammation of the sphenoid sinus and ethmoiditis occur simultaneously.
Treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis
- For the purpose of diagnosis, the ENT doctor performs a pharyngoscopy, examines the blood, and takes a swab from the throat for bacterial analysis. After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the necessary therapy. Typically, treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis comes down to taking the following medications:
- Antibiotics. Since this type of tonsillitis is caused by streptococcus, it is impossible to do without antibacterial drugs. Penicillin drugs and cephalosporins are effective. They suppress the growth and reproduction of pathogens, suppress the activity of pathogenic microflora. The course of treatment does not exceed 5-7 days. Usually tablets are prescribed, but in particularly severe cases intramuscular or intravenous injections are prescribed.
- An additional source of vitamins.
- Antihistamines to reduce swelling.
- Local drugs. Lozenges, lozenges, sprays and aerosols reduce inflammation, reduce swelling, and fight pain.
- Rinse. Rinsing with herbs, soda and salt, and antiseptics have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. During the first two days you need to gargle every hour.
The patient must take sick leave and stay in bed, which significantly shortens the duration of the illness. Precautions must be taken to avoid infecting anyone. To do this, you need to use only personal items, maintain hygiene, and stay in an isolated, ventilated room.
Important to remember! For children and adults, antibiotics are prescribed only after examination. For children under three years of age, all medications are prescribed in the form of drops, suspensions, solutions and syrup.
Features of treatment of the disease
Treatment is carried out, as a rule, at home, but strictly following all the instructions of the ENT doctor. For the first three days, the patient is prescribed bed rest. No physical activity. It is advisable that the patient does not have contact with other family members (especially children and pregnant women) and stays in a separate room. He must have his own dishes, linen and towels. The room must be ventilated at least twice a day. We should not forget about drinking plenty of fluids (water, compote, tea) and a gentle diet (porridge, purees, soups, broths - everything that will not injure a sore throat).
If the disease is bacterial in nature, treatment of sore throat with antibiotics is prescribed. These can be broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, for example, Amoxicillin or Azithromycin. If the causative agent of the disease is a virus, you need to take antiviral drugs such as Arbidol, Ingaverin, Interferon, etc.
Don't be surprised if your doctor prescribes antihistamines: they are needed to relieve swelling of the larynx and pharynx.
The set of measures for the treatment of sore throat includes gargling with Miramistin, Furacilin, and decoctions of chamomile and sage. You can irrigate the mucous membranes of the pharynx and tonsils with Hexoral, Tantum Verde, Inhalipt sprays. To relieve a sore throat, dissolve special tablets and lozenges, for example, Lizobakt. Such “local” therapy measures are especially important when treating pregnant women. All oral antiseptics, like other drugs, must be agreed upon with your ENT doctor!
In addition to self-treatment, procedures in an ENT doctor’s office are extremely useful and effective. You will be offered ultrasonic irrigation of the palatine tonsils and the back wall of the pharynx, irrigation of the pharynx and tonsils using an ENT machine, lubricating the palatine tonsils with iodine antiseptic, and will also undergo physiotherapeutic treatment - laser therapy sessions, ultraviolet irradiation (quartzing of the tonsils) and vibroacoustic therapy sessions.
Complications of catarrhal tonsillitis
It is extremely important to treat catarrhal sore throat under the supervision of an experienced ENT doctor, since improper independent treatment leads to negative consequences - the pathology penetrates deeper into the throat, covering all elements of the pharyngeal ring, including lacunae and follicles, flowing into a chronic purulent form. In addition, if inflammation penetrates beyond the palatine tonsils and attacks the nasopharyngeal tissues, then inflammation of the adenoids occurs.
In children, catarrhal tonsillitis is dangerous due to false croup. Due to inflammation of the larynx, the subglottic area of the larynx may swell, which can lead to airway stenosis. If there is no improvement in the condition within four days, the temperature persists, spots appear on the tonsils, the voice begins to wheeze, and swallowing causes unbearable pain, then you need to visit the doctor again to adjust the treatment plan.
If the treatment tactics are chosen correctly, the disease is easily treatable and the risk of complications is low.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, experienced ENT doctors prescribe treatment that is effective for both children and adults. Doctors will collect anamnesis, carefully examine the throat, conduct diagnostics, and only based on the tests will prescribe effective medications. The clinic also has the opportunity to conduct highly effective physiotherapeutic treatment methods to prevent the development of complications and quickly rehabilitate the patient after an illness.
When there is a risk of getting sick
Like any similar infection, the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The main cause of catarrhal sore throat is the causative bacteria: staphylococci, streptococci and rhinoviruses. In addition to these bacteria, our oral cavity is inhabited by many microorganisms that are in a passive state and do not cause harm if the person is healthy. They wait for the right moment, and as soon as the body’s defenses weaken under certain conditions, microorganisms begin to become active, and as a result, inflammation of the tonsils and pharynx occurs.
The inflammatory process covers the palatine tonsils, or tonsils, as they are commonly called. The tonsils are affected superficially; in the catarrhal form there is no purulent plaque and pus in the lacunae of the tonsils. Despite the fact that catarrhal tonsillitis is the simplest form of tonsillitis, in the absence of proper treatment, it can develop into another, more severe form of the disease.
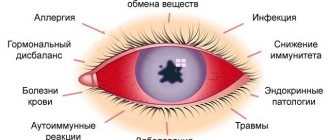
Factors that provoke the development of the disease include:
- weak immunity;
- the presence of a permanent source of infection in the body (for example, with chronic sinusitis or dental caries);
- unfavorable environmental conditions, gas pollution;
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- unbalanced diet, eating “on the run”;
- stress.
As doctors note, in order for pathogenic microorganisms to have a chance to survive and become more active, it is necessary that the body’s defenses weaken. In other words, for a healthy person, with a strong immune system, who eats well, avoids the negative influence of stressful situations, and does not abuse bad habits, the risk of getting sick is greatly reduced.
Complications of acute tonsillitis
You should not self-medicate, as complications often arise with inadequate therapy, incorrect dose selection, or without treatment. For example, the transition of an acute process to chronic tonsillitis, the development of such dangerous conditions as tonsillogenic abscesses (limited accumulation of pus in tissues) of various localizations (peritonsillar, retropharyngeal), phlegmon and mediastinitis - purulent melting of the tissue of the retrosternal space. This dangerous condition can be accompanied by the development of sepsis, symptoms of multiple organ failure and requires treatment in the intensive care unit. Delayed complications in the form of damage to organs and their systems may also occur. The favorite localization of group A B-hemolytic streptococcus is heart tissue. Accumulations of bacteria settle on the valves, destroying them. This can lead to the formation of heart defects, which in turn is dangerous for the development of heart failure. With frequent tonsillitis, the kidneys and joints are affected. In addition, the infection itself can serve as a trigger for the development of autoimmune diseases. Fortunately, with timely treatment and proper use of medications, complications are quite rare.
Up to contents