The appearance of a suspicious lump on the leg rarely goes unnoticed, because any attempt to walk without taking off shoes causes discomfort for the patient. But in most cases, seeing a doctor is postponed for months, or even years. It’s a pity, because going to the doctor in the early stages of arthrosis of the big toe allows you to “freeze” the disease and delay the appearance of irreversible foot deformities.
First, baths and applying onions in a sock are used, then, when the disease does not respond, ointments are used, and only then, exhausted by constant pain, the patient turns to an orthopedist or rheumatologist. What kind of diagnosis is this, how to treat arthrosis of the toe, how to recognize its first signs and what could be the consequences of postponing a visit to the doctor?
Why does the big toe on the left or right foot hurt?
There are more situations that lead to such pain than in the case of the hands.
For example, prolonged exposure to tight, uncomfortable, or simply unsuitable shoes can injure the foot and lead to unpleasant consequences. Among the most common causes of pain at rest and when walking in the big toe are:
- injuries - bruises, fractures;
- calluses and corns;
- papillomas;
- arthrosis and arthritis of various origins;
- systemic autoimmune diseases affecting the joints (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus) - with these diseases the pain is usually symmetrical;
- gout is a metabolic disease in which uric acid crystals are deposited in the joints;
- transverse (less often longitudinal) flatfoot;
- diabetes;
- valgus deformity of the first toe (colloquially “bunion”) is a disease in which the location and angle of inclination of the big toe changes, the joint becomes deformed, grows and hurts;
- ingrown nail.
There are, therefore, a lot of answers to the question of why the big toe hurts on the right or left foot. The doctor’s task is to find and eliminate the specific cause.
Arthrosis of the toe joints - what is it?
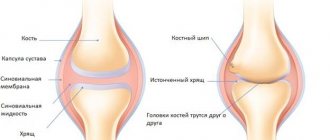
Osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal and metatarsal joints of the legs is a chronic degenerative disease that begins with the destruction of cartilage tissue and can disfigure the patient’s fingers and feet beyond recognition. Regardless of the causes of this condition, it leads to complete degeneration of cartilage and its replacement by bone growths - osteophytes.
Since the foot and toes - the load-bearing supports of the human body - are subject to enormous stress, arthrosis of the toes is extremely common. According to some estimates, it affects up to 10% of the human population over 60 years of age. It’s not surprising, because the foot doesn’t rest even when we sit!
Typically, the disease begins in the big toe or little toe and primarily affects the metatarsophalangeal joint. Osteoarthritis of the second or third finger is less common. In recent years, there has been a trend towards “rejuvenation” of the disease - arthrosis of the big toe is increasingly found in patients aged 30-35 years.
How to help a doctor identify a disease
Pain in the thumb is a symptom of many diseases. But depending on the specific disease, the condition of the leg will be different.
To more accurately describe your symptoms to your doctor, pay attention to the following properties of pain:
- pain during exercise or during rest;
- does it become easier if you take off your shoes;
- how long have you been sick?
- what is the nature of the pain - sharp, stabbing, or dull, aching;
- pain appears only on one leg or on both;
- are there similar sensations in the hands when loaded;
- the big toe just hurts or is additionally swollen;
- how the fingers adjacent to the patient feel;
- is there any pregnancy;
- Are you seeing an endocrinologist?
All these factors will help the doctor quickly and accurately establish a diagnosis and begin the correct treatment.
What happens during bunion removal surgery?
Surgery on a sore leg rarely lasts more than 1 hour, but the duration still depends on the degree of deformity. There are different options for surgical treatment of bunions, using both open and percutaneous surgical techniques. When using the closed method, artificial “fractures” called “osteotomies” are performed, which restore the normal position of the bones of the foot. With the open method, an incision about 5-7 cm long is made along the inner surface of the foot, which allows you to accurately determine the required angle at which to operate and the degree of displacement of the bone fragments. If the surgeon is experienced, the osteotomy can be performed in a closed manner. With such interventions, large scars are not left, and postoperative pain is usually less. But sometimes in such cases there may be incomplete correction of deformity and delayed consolidation of osteotomies. It is also possible to combine closed and open methods, for example, surgery on the 1st metatarsal bone is performed openly, and on the small rays and phalanges closed.
How to treat a sore big toe
Treatment depends on the causes of the disease.
The ingrown toenail is removed, then restrictions on the load on the leg, bandages and pain relief are required for several days. After this, a consultation with an orthopedist is necessary: sometimes this problem occurs due to incorrect position of the foot. If you don't straighten it, the nail will grow in again and again.
Calluses also need to be removed, and if they have already caused pain in the joint of the big toe, this should be done by a doctor - a dermatologist or podologist. It is necessary to understand what causes calluses. They can occur due to improperly selected shoes, flat feet, and warts may be hidden under them. In all these cases, treatment will be different. You can maintain the condition of your legs in a beauty salon if your doctor allows it.
Orthopedic treatment is required for flat feet, hallux valgus, and can alleviate the patient’s condition with arthrosis and arthritis. Diabetes mellitus, gout, and autoimmune diseases require a systematic approach, and joint pain is treated symptomatically.
Modern methods of eliminating diseased foot bones
In modern orthopedic operations, bone fragments are cut out and moved to eliminate the diseased bone and give the correct position to the big toe. The finger is fixed with medical screws or knitting needles until final fusion.
There is another treatment option - “closure” of the deformed joint. Orthopedic surgeons remove the cartilage completely and reattach the metatarsal bone to the first phalanx of the big toe in the correct position. As a result, the bone and pain disappear.
Considering what was described above, we can say that a surgical revolution has occurred in the treatment of diseased bones. The most important thing is that the attitude towards the problem and the very essence of treatment have changed. If in the past a deformity of the thumb was considered a defect of one joint and its bones, today an integrated approach is used in the fight against the bunion.
Nowadays, orthopedic surgeons, even taking into account the operation, can rehabilitate a patient in one day. The next day, people begin to walk on their own, albeit with more support on the heel and the outer edge of the foot, but without a cast or crutches. After two weeks, the sutures are removed, and after 1-1.5 months the patient returns to his usual lifestyle, but without pain in the foot.
We can say that modern operations have virtually no disadvantages. Unfortunately, they are not made everywhere. There is a shortage of highly qualified surgeons and special, high-quality, and therefore expensive, equipment. The situation is the same in other countries, but at a much higher cost for surgery on the leg bone.
Methods for diagnosing gout
Diagnosis of gout includes physical, laboratory and instrumental research methods. The diagnosis of gout is made when several signs characteristic of this disease coincide
Physical diagnosis
Physical diagnosis involves visual examination of the patient and palpation. The examination results are compared with the patient’s complaints and medical history.
Laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory diagnostics make it possible to establish that the cause of pathological changes in the joint is a violation of uric acid metabolism. The following analyzes play a decisive role in this:
- biochemical blood test (the level of uric acid in the blood plasma is important);
- analysis of synovial (intraarticular) fluid for the presence of urates in it. To do this, a puncture of the joint is done.
- 24-hour urine collection can be performed to assess glomerular filtration rate.
If there is a need to confirm that the detected tumors in the joint are tophi, a biopsy is performed with further examination of their contents.
Instrumental diagnostics
X-rays can reveal pathological changes in the joints. They occur in late stages, so the onset of the disease cannot be determined using x-ray methods. To identify tophi (they do not always protrude above the surface of the skin), computed tomography or MRI are used.
In the early stages, ultrasound can be used. Using ultrasound, fairly small deposits of salts are detected, so tophi are visible on ultrasound even at the stage of their formation. Also a characteristic sign of gout is a “double contour” - the appearance of an echogenic strip running parallel to the line of the articular cartilage. It occurs because salt crystals do not penetrate the structure of the cartilage, but simply cover it on top, creating a duplicate contour that is clearly visible during examination.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Treatment methods for gout
Treatment for gout is aimed at:
- in case of an acute attack - to relieve it;
- in the remission stage - to normalize uric acid metabolism. Of course, one should strive to eliminate the cause of the disease. However, if the cause of gout is fermentopathy, this is impossible. In this case, treatment will be symptomatic.
- for the treatment of concomitant diseases.
A complete cure for gout is impossible. However, with medical help, it is possible to reduce the frequency of attacks and achieve a significant increase in periods of remission.
Stiff finger: causes and risk factors
Articular cartilage destruction occurs between the first metatarsal and the proximal phalanx of the big toe. It is not known exactly why some people develop the disease and others do not. Possible causes of arthrosis of the big toe are hereditary factors, trauma, inflammation, excessive stress and deformation. Sometimes stiffness is a complication of gout.
The following factors may contribute to the onset and progression of arthrosis of the first toe:
- Inappropriate, tight shoes
- Foot deformity
- Flat valgus foot
- Improper or excessive weight bearing, such as gait disturbances or excess weight
- Bone fractures and soft tissue inflammation.
- Gout
How to prevent the disease
Basic preventive measures help prevent swelling in the toes. You just need to take care of your body and try to avoid the possibility of injury. The key to good foot health will be personal hygiene, which should be present in every person's life on an ongoing basis.
Particular attention should be paid to the choice of comfortable, high-quality shoes, which should be made from natural materials, and also have a not very high heel and a comfortable sole. In addition, you can use special orthopedic shoes or insoles. If fungal or other diseases are detected, treatment should be started immediately.
You should also monitor your diet so that it is complete and includes all the necessary microelements obtained from foods. It is necessary to reduce the amount of salt consumed, as it prevents excess water from leaving the body, which causes edema. It is also better to abstain from drinking alcohol or reduce it to a minimum.
Swelling of the fingers is easy to treat and is often completely eliminated, but only if treatment was provided in a timely manner. By following basic rules, you can prevent the formation of edema and also maintain your health.
What is a stiff finger
A stiff toe is arthrosis of the big toe.
As the articular cartilage deteriorates, the mobility of the finger gradually decreases. Long-term inflammation can result in complete immobility of the joint (ankylosis). Causes and risks
Symptoms and signs
Treatment
Insoles medi
Diagnosis of finger pain
CELT specialists recommend seeking medical help if you experience even a slight feeling of numbness in your fingers. Along with pain, this is a reason to visit a rheumatologist or neurologist in our Pain Clinic, conduct diagnostic tests and treatment.
In order to correctly make a diagnosis, in addition to a clinical examination and history taking, other diagnostic tests are carried out:
- radiography;
- manual muscle testing;
- ultrasonography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Which doctor treats gout?
For treatment of gout, you should consult a rheumatologist. The help of an orthopedic doctor may be required (for example, if surgery is necessary).
Treatment of an acute attack
First of all, the patient needs rest. The inflamed joint should be immobilized. It is recommended to apply cold. You need to drink plenty of alkaline fluids - up to 3 liters per day. It is important to follow a diet: foods high in purine bases should be excluded. Painkillers (NSAIDs) and glucocorticoids are used as prescribed by a doctor. Local treatment is carried out using ointments and gels that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
When the patient feels better, physical therapy is included in the treatment. Electrophoresis, UV irradiation, and UHF are used.
Treatment of gout in remission
Treatment in remission includes:
- lifestyle changes (primarily giving up alcohol);
- diet (exclude foods that contain a lot of purines - fish, mushrooms, legumes). The diet must be prescribed by a doctor;
- drug therapy (anti-gout drugs);
- local treatment - applications of medications, physiotherapy, massage, medicinal baths (in sanatoriums);
- surgical treatment: removal of tophi that are not amenable to conservative treatment, surgical restoration of affected joints.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating